What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
However, there are cases where the diagnosis of one form of IBD over the other is very difficult. At times, a final diagnosis is possible only after an event during the course of the disease or its treatment makes the form of IBD readily apparent.
Patients with IBD may be very confused as to the differences between these diseases. As with any chronic condition, education is an important tool to become an active participant in ones own treatment plan.
If your diagnosis isnt firm, dont panic. In some people, it can take time to determine if the IBD is more like Crohns disease or more like ulcerative colitis. In about 5-20% of cases, people are diagnosed as having indeterminate colitis .
IBD is becoming increasingly treatable and there are now many medications in the arsenal that are helping people with all forms get greater control over their disease. The main differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are described below.
-
Smoking can worsen condition
What Types Of Surgery Can Treat Ulcerative Colitis
There are different procedures. All are major surgery on your digestive system. Talk with your doctor about which one they recommend for you.
Hemicolectomy. This is an operation that removes part of your colon. There are two types, depending on where your problem area is:
- Right hemicolectomy: Removes the right, or ascending, part of your colon. The surgeon may also take out some other areas, like your appendix and part or all of your middle large intestine. Theyâll connect whatâs left of your colon to your small intestine.
- Left hemicolectomy: Removes the left, or descending, part of your colon. The surgeon will attach the right and middle parts to your rectum. This is the last place your bowel movements pass through on their way out.
Colectomy. This is surgery to remove the entire colon.
Proctocolectomy. This procedure removes both the colon and rectum.
Proctocolectomy is considered the standard treatment when surgery for ulcerative colitis is needed.
If the entire colon is removed, the surgeon may create an opening, or stoma, in the abdominal wall. The tip of the lower small intestine is brought through the stoma. An external bag, or pouch, is attached to the stoma. This is called a permanent ileostomy. Stools pass through this opening and collect in the pouch. The pouch must be worn at all times.
Ulcerative Colitis Complications Vs Crohns Disease Complications
When it comes to potential complications due to ulcerative colitis or Crohns disease, there are some that these two diseases share, and others that are more likely to occur in one versus the other, according to a 2017 study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology.6
- Colon cancer: People with ulcerative colitis, we well as people who have Crohns disease that affects most of their colon, do have a slightly increased risk of developing colon cancer.Screenings will typically be recommended 810 years after an IBD diagnosis, and your doctor will let you know how frequently youll need screening.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Inflammation can cause scarring of the bile ducts . This can lead to liver damage.
- Blood clots: Both people with ulcerative colitis and Crohns have a greater risk of blood clots, though it isnt entirely clear why. It may be due to genetic predispositions coupled with severe inflammation in the GI tract, according to Cedars Sinai.
- Medication side effects: The medications used to treat both conditions can potentially increase the risk for certain cancers, like lymphoma, when used long-term. Consistent corticosteroid use is also associated with things like high blood pressure and osteoporosis.
Don’t Miss: Stage Iv Sacral Decubitus Ulcer
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohn’s Disease: What’s The Difference
Shadi Hamdeh, MD, is a board-certified gastroenterologist and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Kansas Medical Center.
The two primary forms of inflammatory bowel disease Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitisare often lumped together. Both include symptoms of abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, and an urgent need to defecate. However, some of their characteristics are very different.
This article discusses the similarities and differences between ulcerative colitis versus Crohn’s disease, including symptoms and treatments of both.
Vitamin And Mineral Supplements For Ibd
A person with IBD who eats a healthy, varied diet does not usually need to take vitamin supplements. But if they have a dietary deficiency, they may need tablets or occasional vitamin B12 injections. For example, a person on a low-fibre diet may need extra vitamin C and folic acid because they dont eat enough fruit and vegetables.A person with Crohns disease who experiences steatorrhoea may need calcium and magnesium supplements. Most children with IBD should take supplements to help them grow and develop normally.
Also Check: Which Is Worse Ulcerative Colitis Or Crohn Disease
How Are They Similar
Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are similar in a few ways. For starters, theyre both types of IBD and both cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. They also share many similar symptoms which is why you shouldnt try to self-diagnose. Its important that you see your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Both diseases commonly affect teens and young adults, however, they can also develop at any age. The disease also affects men and women equally, says UCLA Health. The source also notes, both diseases have similar types of contributing factors such as environmental, genetic and an inappropriate response by the bodys immune system.
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
There are multiple contributing risk factors that can lead to ulcerative colitis and Crohns. Evidence does suggest that both are associated with an inappropriate immune response, which can arise from many different environmental factors, gut microbiome imbalance, as well as genetics .
The body creates temporary inflammation as part of a normal immune system response to threats and foreigners that may cause harm. An inappropriate immune response occurs when the immune system attacks something that is probably not harmful or overreacts to a possible pathogen. This creates unnecessary or excessive inflammation that can become chronic inflammation.
For example, in addition to toxins and infections, the immune system may attack food particles, beneficial gut bacteria, and, in the case of ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, the lining of the digestive tract [1
What might be causing the inflammation of the digestive tract and an inappropriate immune response?
Some of the contributing factors in IBD are:
You May Like: Peptic Ulcer Food To Eat
You May Like: What Does A Stomach Ulcer Feel Like Symptoms
What Procedures And Tests Diagnose Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Doctors diagnose ulcerative colitis by endoscopy . During this procedure, the doctor can see and take pictures of the patients abnormal gut mucosa , and the presence of continuous disease . Other blood tests and imaging tests like CT scans or MRI are used, but these tests are not definitive.
Doctors use the same procedures and tests to diagnose Crohns disease. However, they also use small bowel studies, colonoscopy, and upper GI endoscopy to identify the abnormal gut mucosa that usually occurs in multiple areas anywhere in the intestinal tract. These areas are not continuous but are separated by normal areas of the intestinal mucosa that distinguish them from ulcerative colitis lesions.
As with Crohns disease, nutrition is important if you have ulcerative colitis because symptoms of diarrhea and bleeding can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and loss of nutrients. It may be necessary to take nutritional supplements if your symptoms do not allow you to eat a nutritionally balanced diet. Talk to your healthcare professional about what supplements to take.
Daily Life For People With Ibd
People with IBD lead useful and productive lives, even though they need to take medications. When they are not experiencing a flare-up of their disease, they feel quite well and are often free of symptoms.People with IBD can marry, enjoy sexual activity and have children. They can hold down jobs, care for families and enjoy sport and recreational activities.Even though there is currently no cure for IBD, medical therapy has improved the health and quality of life of most people with Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Research underway today may lead to further improvements in medical and surgical treatment, and even a cure.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Prevent Pressure Ulcers
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease Different
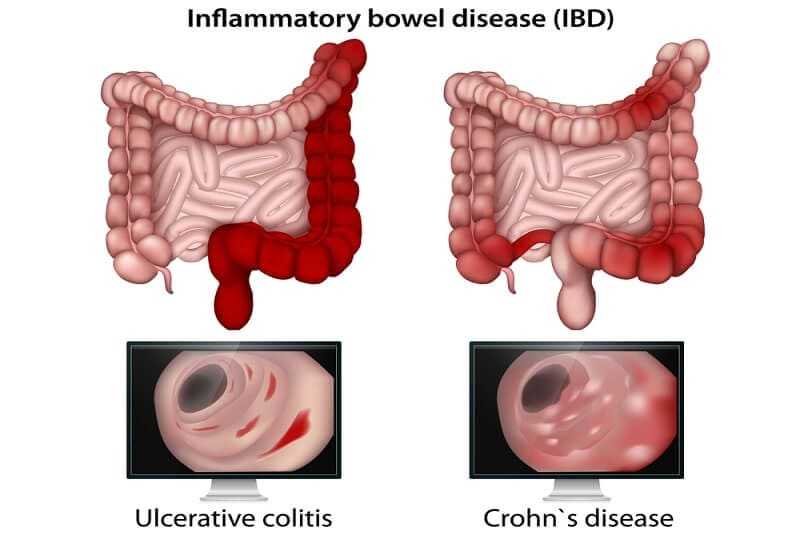
Ulcerative colitis symptoms reside in the large intestine only and often vary from person to person, depending largely on the part of the colon thats affected and the severity of the inflammation. It affects everyone differently, and symptoms range in severity. UC is a progressive disease and will change over time in your body.
Ongoing inflammation of the GI tract happens with both Crohns and UC, but there are a few key distinctions, such as:
- With Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis includes continuous inflammation of the colon.
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the innermost lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls.
In approximately 10% of cases, an inflammatory bowel disease will exhibit features of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. We typically refer to these as indeterminate colitis.
Again, symptoms for both conditions can vary greatly from person to person, so its important to have an honest conversation with a doctor who specializes in this area, such as the ones at Alabama Colon & Rectal Institute.
Can You Drink Alcohol With Crohns Disease
- Drinking alcohol is not recommended for most people with Crohns disease.
- Alcohol may irritate the lining of the intestinal wall, causing or worsening symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
- It also may contribute to malabsorption, further complicating nutritional deficiencies.
- Alcohol interacts with many medications, causing side effects that may be serious.
- Alcohol disrupts sleep cycles and can leave you feeling tired, and irritable the next day. However, if alcohol is well tolerated and not causing any complications, it can be consumed in moderation.
- Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration very easily.
- Dehydration makes you feel weak, tired, light-headed, or just blah.
- Alcohol can cause headaches, abdominal pain, and other symptoms. It also can place dangerous strain on your kidneys.
- Dehydration can be avoided by making a special effort to take in plenty of nonalcoholic fluids.
- You should take at least 8 full glasses of fluid every day.
- Try to stick to water, diluted fruit juice, sports drinks, decaffeinated beverages, and fruit and vegetable drinks.
- Avoid caffeinated beverages and sodas.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Mouth Sores Pictures
Can Medications Raise Your Risk For Developing Ulcerative Colitis
Taking several courses of antibiotics, especially broad-spectrum ones that act on different types of bacteria, may raise your risk for both UC and Crohns. This might be because antibiotics can affect the delicate balance of bacteria in your gut, known as the microbiome.
Some research has suggested that taking birth control pills could raise your risk for UC by 30% if youre genetically prone to the condition. But we need more studies on this.
If you have UC, your doctor might warn you that taking aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen could make your symptoms worse. But these medications arent thought to raise your risk for UC.
One thing that might lower your risk of developing UC? Having your appendix removed before age 20 because of an inflammation . Its not clear why this happens. But scientists theorize that your appendix may have an impact on your immune system.
Getting The Right Diagnosis
Since the differences between the two conditions mostly revolve around where in the digestive system inflammation happens, the best way for a doctor to give you the right diagnosis is to take a look inside.
You might get tests such as:
X-rays that can show places where your intestine is blocked or unusually narrow.
Contrast X-rays, for which you’ll swallow a thick, chalky, barium liquid so doctors can see how it moves through your system.
CT scans and MRIs to rule out other conditions that might cause symptoms similar to an inflammatory bowel disease.
Endoscopy, in which a doctor uses a tiny camera on a thin tube to see inside your digestive system. Specific types of endoscopy can:
- Examine lower part of your large intestines. Your doctor will call this test “sigmoidoscopy.”
- Look at your entire large intestine. This is a colonoscopy.
- Check the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This is an EGD .
- Additional testing to look at your small intestine using a pill-sized camera. This is often called pill, or capsule, endoscopy.
- See the bile ducts in the liver and the pancreatic duct. This test is called ERCP .
Scientists are working to make several blood tests better at helping to diagnose ulcerative colitis and Crohnâs. They check on levels of certain antibodies found in the blood. Two of these are:
You May Like: Signs You Might Have An Ulcer
Diagnostic Tests And Tools: Getting The Right Diagnosis
The ultimate diagnosis and testing method for ulcerative colitis is colonoscopy, which is done using a thin tube with a light and camera at the end, allowing your doctor to examine the colon or/and take a tissue sample for biopsy.
If the doctor, during a colonoscopy, notices a continuous inflammation starting from the rectum, that could be a sign of ulcerative colitis. Otherwise, you might have Crohns disease if the inflammation is in other parts of your GI tract.
To ascertain whether or not you have Crohns, your GI specialist or gastroenterologist can use magnetic resonance imaging or CT scan if your small intestine is affected. They may also perform an endoscopy if the upper parts of your GI tract, like the esophagus, are involved in determining the site of inflammation. Other diagnosis methods for Crohns disease include capsule endoscopy.
Keep Up With Your Checkups
If you have either condition, you’ll need to keep up with your checkups, even if your symptoms start to ease up.
You may also need to get colonoscopies more often and start them at a younger age. A colonoscopy can check for cancer or polyps that need to come out. Experts recommend that you start these tests within 8 to 10 years of developing UC or Crohnâs symptoms, and then typically every 1 to 3 years after that. Your doctor will tell you a schedule that is best for you.
Show Sources
You May Like: Low Fiber Foods For Ulcerative Colitis
Crohns Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Danielle Gaffen, MS, RDN, LD
Home | Blog | Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Crohns Disease vs. Ulcerative Colitis
Co-written by Luis Tejeda
Have you ever wondered the difference between Crohns disease vs. ulcerative colitis? Many of my clients ask me what the difference is between the two conditions. While both share similar symptoms and are both types of inflammatory bowel disease , they are not the same illness and affect different areas of the GI tract. This blog will compare the key differences between Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis .
Recommended Reading: Best Diet For Gerd And Ulcers
What Supplements Should You Take For Crohn’s Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn’s disease nutritional diet deficiencies
- Your need for vitamin and mineral supplements depends on several factors, your diet, which parts of your digestive tract are affected, and whether you have had surgery on your small intestine.
- The most common vitamin deficiencies are
- vitamins D and B-12.
Ulcerative colitis nutritional deficiencies
As with Crohn’s disease, nutrition is important if you have ulcerative colitis because symptoms of diarrhea and bleeding can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and loss of nutrients. It may be necessary to take nutritional supplements if your symptoms do not allow you to eat a nutritionally balanced diet. Talk to your healthcare professional about what supplements to take.
Recommended Reading: Best Over The Counter Probiotic For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease: An Overview
Both ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease cause inflammation along the digestive tract. However, Crohns disease tends to affect different parts of the track compared to ulcerative colitis. In most cases, Crohns disease affects the ileum. This is the last part of the small and large intestine. In as many as 45% of cases, the condition affects both the small and large intestines.
Ulcerative colitis only affects the large intestine and the rectum is always involved. This condition occurs in the inner layer of the colon, or mucosa, in a continuous segment of the gut. Crohns disease can involve all four layers of the gut wall and often appears in patches.
Inflammatory bowel disease currently affects all ethnic groups. However, Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are more prevalent in Caucasians. Specifically, people of Northern European, Anglo-Saxon, or Ashkenazi Jewish descent develop the condition. Hispanics and Asians are likely to have pancolitis, a form of ulcerative colitis that affects the entire colon.
The prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases is on the rise. In the 1990s, two million people developed a condition. Currently, three million people worldwide live with Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis.
Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotic use during childhood may increase the risk of both conditions.
Hispanic Ethnicity Is Associated With Milder Disease Severity In Crohns Disease But Not Ulcerative Colitis
2019, Current Trends in Gastroenterology and Hepatology
to the 2013 U.S. Census Bureau, are increasingly being identified with IBD . Therefore, it is important to recognize epidemiologic differences in order to optimize treatment for these patients. Similar to what was seen in AAs, studies identifying phenotypic variations, treatment preferences, and disease outcomes in Hispanics have been conflicting . One group found that Hispanics were diagnosed at a significantly older age than Caucasians and had a lower number of bowel resections per patient. Additionally, UC was found to be more common than CD in Hispanic IBD patients . On the other hand, another group found that prolonged steroid exposure was more common among Hispanics with UC, and these patients had more UC-related surgeries and hospitalizations, although these differences were not significant in multivariate analysis .
You May Like: Cost Of Biologics For Ulcerative Colitis