Do Ulcerative Colitis Causes And Crohns Disease Causes Overlap
In Crohns disease, areas of your digestive tract become irritated and inflamed. This can lead to symptoms like cramping, diarrhea, and unintentional weight loss, which heavily overlap with those of ulcerative colitis. While ulcerative colitis only affects your colon, Crohns disease can impact any part of your digestive tract. The most commonly affected areas are the last part of your small intestine, called the ileum, and the first part of your colon.
Much like ulcerative colitis, the exact causes of Crohns disease remain unclear. Similar factors are believed to play a role, including a dysfunctional immune response and genetics.
According to the NIDDK, the risk factors for Crohns disease include family history, smoking cigarettes, and being between the ages of 20 and 29. Its also possible that eating a high-fat diet or using medications like NSAIDs, antibiotics, or birth control pills may also slightly increase the risk of Crohns disease.
Infectious Colitis: Causes Symptoms And Treatment Tips
The term infectious colitis sounds awful, and it can be. Infectious colitis is inflammation of the main part of the large intestine and can lead to sudden lower abdominal pain. In some cases, the pain can be severe.
While inflammation is a common medical term and may not seem all that serious, the reality is that when left untreated, it can lead to complications and has the potential to be deadly.
Complementary And Alternative Medicine
Probiotics may modestly reduce disease activity in active disease, but do not increase remission rates.34 However, Lactobacillus GG and Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 have been shown to be as effective as 5-ASA for maintenance therapy.16,17 Acupuncture has shown a small symptomatic benefit in active disease.35 Wheatgrass has also shown some effectiveness in reducing symptoms of active disease.36
Also Check: Is Peppermint Tea Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Whats The Outlook For C Diff Infection In Ulcerative Colitis
Since C. diff infections can cause serious complications for people with ulcerative colitis, the outlook can be challenging. While not common, C. diff infections do cause more deaths among people with IBD than those without, especially if they need surgery. They also tend to have to stay longer in the hospital and need more surgeries. But with vigilance and treatment, most people start to feel better within 3 days of starting treatment.
If you have ulcerative colitis and have any symptoms of C. diff infection, call your doctor or health care team right away so you can start treatment as soon as possible.
Show Sources
Diagnosing And Treating Infectious Colitis
A history of bloody diarrhea with urgency, especially several hours after a meal, is usually a quick diagnosis of infectious colitis. In many cases, some investigation is required. A stool culture can detect bacteria, something called an O& P test can detect parasites in stool, and blood tests can determine if a person has elevated white cells in the body, which is an indication of inflammation. While a simple blood test cant confirm infection of the colon, doctors do know that a special type of white blood cell, called eosinophil, as well as IgE antibodies, are high in parasitic infection.
Infectious colitis treatment often focuses on antimicrobial drugs, which are directed at the toxin, which is causing the symptoms. Antimicrobial medications include antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals. Painkillers, as well as drugs to lower a high fever, may also be suggested in cases where the infection is severe. Addressing dehydration with a lot of fluids is important, but generally, those who suffer from infectious colitis are told to pay close attention to both fluid intake and salt due to the risk of loss during illness. There are some cases where iron supplements may be needed due to the fact that there has been severe or prolonged bleeding.
Also Check: Do Ulcers Hurt All The Time
European Approval For Abbvie’s Upadacitinib For Ulcerative Colitis
The European Commission has approved AbbVie Inc’s ABBV Rinvoq for active ulcerative colitis in patients who did respond to previous treatments.
The approval is based on the results of three Phase 3 studies: two for induction and one for maintenance, wherein Rinvoq achieved the primary endpoint of clinical remission and all secondary endpoints, including clinical response and mucosal healing.
Britain Approves Global Blood Therapeutics’ Sickle Cell Treatment
U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency has approved Global Blood Therapeutics Inc’s GBT Oxbryta for hemolytic anemia due to sickle cell disease in patients 12 and above.
The approval comes for Oxbryta as monotherapy or in combination with hydroxycarbamide .
Voxelotor is the first medicine authorized in Great Britain to directly inhibit sickle hemoglobin polymerization, the molecular basis of sickling, and the destruction of red blood cells in SCD.
Don’t Miss: Bone Broth For Stomach Ulcer
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Ulcerative Colitis Risk Factors
Most people with UC dont have a family history of the condition. However, about 12 percent of people with UC do have a family member with IBD, according to research from 2014.
UC can develop in a person of any race, but its more common in white people. If youre of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, you have a greater chance of developing the condition than most other groups.
Young people with IBD may also be dealing with acne at the same time. Some older studies have suggested a possible link between the use of the cystic acne medication isotretinoin and UC. However, newer research has yet to find a definitive causal relationship.
Theres no solid evidence indicating that your diet affects whether you develop UC. You may find that certain foods and drinks aggravate your symptoms when you have a flare-up, though.
Practices that may help include:
- drinking small amounts of water throughout the day
- eating smaller meals throughout the day
- limiting your intake of high fiber foods
- avoiding fatty foods
- lowering your intake of milk if youre lactose intolerant
Also, ask a doctor if you should take a multivitamin.
You May Like: How Do You Heal An Ulcer
When Should Someone Contact A Doctor About Colitis
Diarrhea is a common sign of colitis. It is usually self-limited and resolves on its own with supportive care, including rest and a short course of a clear-fluid diet. However, seek medical care if diarrhea persists for more than two to three weeks, if there is blood in the stool, fever, or the person has signs of dehydration.
- Blood in the stool is never normal and should always be evaluated. Common causes of blood in the stool include hemorrhoids however, other serious causes of bleeding need to be investigated. Colitis is not the only cause of rectal bleeding. Other causes include diverticular disease of the colon , colon polyps, anal fissures, and cancer.
- Chronic diarrhea may lead to dehydration and changes in the electrolyte balance in the body. If it is severe enough, the dehydration may require treatment with IV fluids or oral rehydration therapy. The symptoms of dehydration may include
- lightheadedness , especially when changing from a sitting or lying position to a standing position
- weakness
Leaving Abbvie Web Site
You are leaving the RINVOQ site and connecting to a site that is not under the control of AbbVie. AbbVie is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. AbbVie is providing these links to you only as a convenience and the inclusion of any link does not imply the endorsement of the linked site by AbbVie. You should also be aware that the linked site may be governed by its own set of terms and conditions and privacy policy for which AbbVie has no responsibility. Conversely, the presence of this link does not imply the linked site’s endorsement of RINVOQ.com or AbbVie.
Do you wish to leave this site?
Also Check: How Do You Get Ulcers On Your Legs
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis
Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. Colitis causes symptoms such as abdominal pain and cramping, bloating, and diarrhea.
An inflamed colon can be caused by several conditions. UC is one possible cause. Other possible causes of colitis include:
- infection
- Crohns disease
- an allergic reaction
To diagnose the cause of colitis, a doctor will order a series of tests. These tests will help them understand what other symptoms youre experience and rule out conditions based on what youre not experiencing.
Treatment for colitis will depend on the underlying cause and other symptoms you have.
What Blood Tests And/or Stool Samples Diagnose Colitis
- A complete blood count measures hemoglobin and hematocrit, looking for anemia. If the red blood cell count is elevated, it may be due to dehydration, where total body water is decreased and the blood becomes concentrated.
- The CBC also measures the white blood cell count, which may be elevated as the body responds to infection. However, an elevated white blood cell count does not necessarily equal infection, since elevation may be due to the body’s reaction to any stress or inflammation.
- Electrolytes may be measured looking for changes in the sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate levels in the blood that help determine the severity of dehydration and loss of fluid.
- Kidney function may be checked by measuring the BUN and creatinine levels this may be an important clue as well to the severity of dehydration.
- Urinalysis may reveal dehydration if the specific gravity is elevated or if there are ketones present.
- Blood tests for markers of inflammation may also be measured, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein . These are nonspecific tests that may help guide decision-making.
- Stool samples may be collected for culture, searching for bacterial and parasitic infections as the cause of colitis. The stool may also be tested for blood.
Recommended Reading: Can Stomach Ulcers Be Cancerous
The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is also an inflammatory bowel disease . The 2 diseases affect the digestive tract differently:
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the large bowel , and inflammation is only in the surface layers of the bowel lining. It causes ulcers to form in the lining of the bowel.
- Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus , but usually just the last section of the small bowel and/or the colon. Inflammation can extend into the entire thickness of the bowel wall.
Is Ulcerative Colitis Curable
Currently, theres no nonsurgical cure for UC. Treatments for the inflammatory disease aim to extend periods of remission and make flare-ups less severe.
For people with severe UC, curative surgery is a treatment option. Removing the entire large intestine will end the symptoms of UC.
This procedure requires your doctor to create a pouch on the outside of your body where waste can empty. This pouch can become inflamed and cause side effects.
For that reason, some people choose to have only a partial colectomy. In this surgery, your doctor only removes the parts of the colon that are affected by UC.
While these surgeries can help ease or end symptoms of UC, they can have adverse effects and possible long-term complications. Read more about these issues to determine if surgery is an option for you.
You May Like: Stage Iv Sacral Decubitus Ulcer
Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Colitis
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two types of inflammatory bowel disease that cause colitis. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are considered autoimmune diseases .
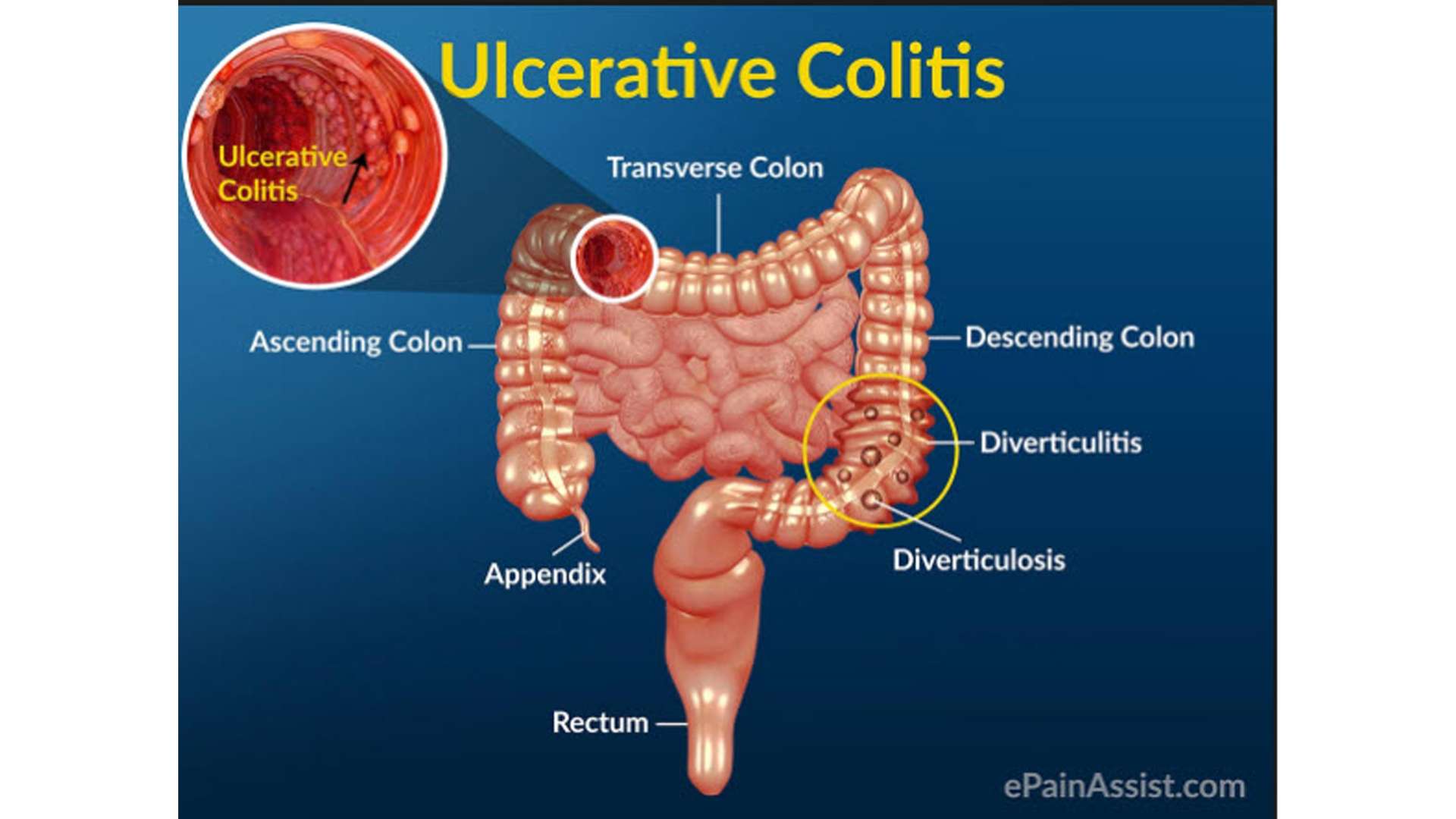
- Ulcerative colitis always begins in the rectum and may spread to the rest of the colon, spreading from the rectum to the sigmoid, descending, transverse, and finally the ascending colon and cecum in that order. Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, and symptoms include abdominal pain, and bloody, diarrheal bowel movements.
- Crohn’s disease may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract , including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. In Crohn’s disease, there may be “skip lesions,” that is, abnormal segments of the GI tract interspersed with normal segments.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may have other organ systems involved in addition to the gastrointestinal tract.
Either collagen or lymphocytes infiltrate into the layers of the wall of the colon, presumably as a result of inflammation. This is an uncommon illness and maybe an autoimmune disease. Diarrhea often is watery, and no blood is present in the stool.
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
UC may affect the mouth. About 8% of individuals with UC develop oral manifestations. The two most common oral manifestations are aphthous stomatitis and angular cheilitis. Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by ulcers in the mouth, which are benign, noncontagious and often recurrent. Angular chelitis is characterized by redness at the corners of the mouth, which may include painful sores or breaks in the skin. Very rarely, benign pustules may occur in the mouth .
UC may affect the eyes. Inflammation may occur in the interior portion of the eye, leading to uveitis and iritis. Uveitis can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light . Untreated, uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss. Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye or the overlying connective tissue , causing conditions called scleritis and episcleritis. Uveitis and iritis are more commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, whereas episcleritis is more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease.
Recommended Reading: Best Dressing For Venous Stasis Ulcer
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis
Anyone at any age, including young children, can get ulcerative colitis. Your chance of getting it is slightly higher if you:
- Have a close relative with inflammatory bowel disease .
- Are between 15 and 30 years old, or older than 60.
- Are Jewish.
- Use frequent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen .
Pathogenicity Of Different Species
Aeromonas species was the most common pathogen in 62.5% patients with an initial UC diagnosis and 47.8% of patients with chronic IC . C. difficile was the most common pathogen in 44.4% of UC patients with flare-ups and the second most common pathogen in chronic IC patients. However, there was no statistically significant difference in pathogens between UC and chronic IC.
Recommended Reading: Can Lemon Water Help Ulcerative Colitis
What Causes Infectious Colitis
Infectious colitis is not to be confused with other types of colitis, such as ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease, but its causes are normally due to infections from bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungus. The term colitis refers to the main symptom, which is diarrhea.
Infectious colitis is often linked with food poisoning, which is an infection of the stomach and rectum. The most common cause of a food poisoning type of infectious colitis is contaminated water, and it comes from a parasite called entamoeba histolytica. You can also experience sudden diarrhea after consuming food contaminated with bacteria. E-coli, salmonella, shigella, yersinia, or campylobacter are all bacterial intestinal infections.
In recent years, you have likely heard the term C. difficile, or C. diff. Over the last few years, some hospitals and nursing homes have experienced C. diff outbreaks. While the bacterium clostridium difficile is present in our colon and is part of our normal intestinal flora, when it is destroyed by antibiotics, it can overgrow, releasing toxins that lead to inflammation in the colon.
There are also situations where the cause of the infectious colitis is viral or fungal. Viral colitis is rare but can occur in people with low immunityfor instance, in those who are going through chemotherapy or fighting AIDS. Fungal colitis is much like a virusit happens mostly in cases where a person has a compromised immune system.
Ulcerative Colitis In Children
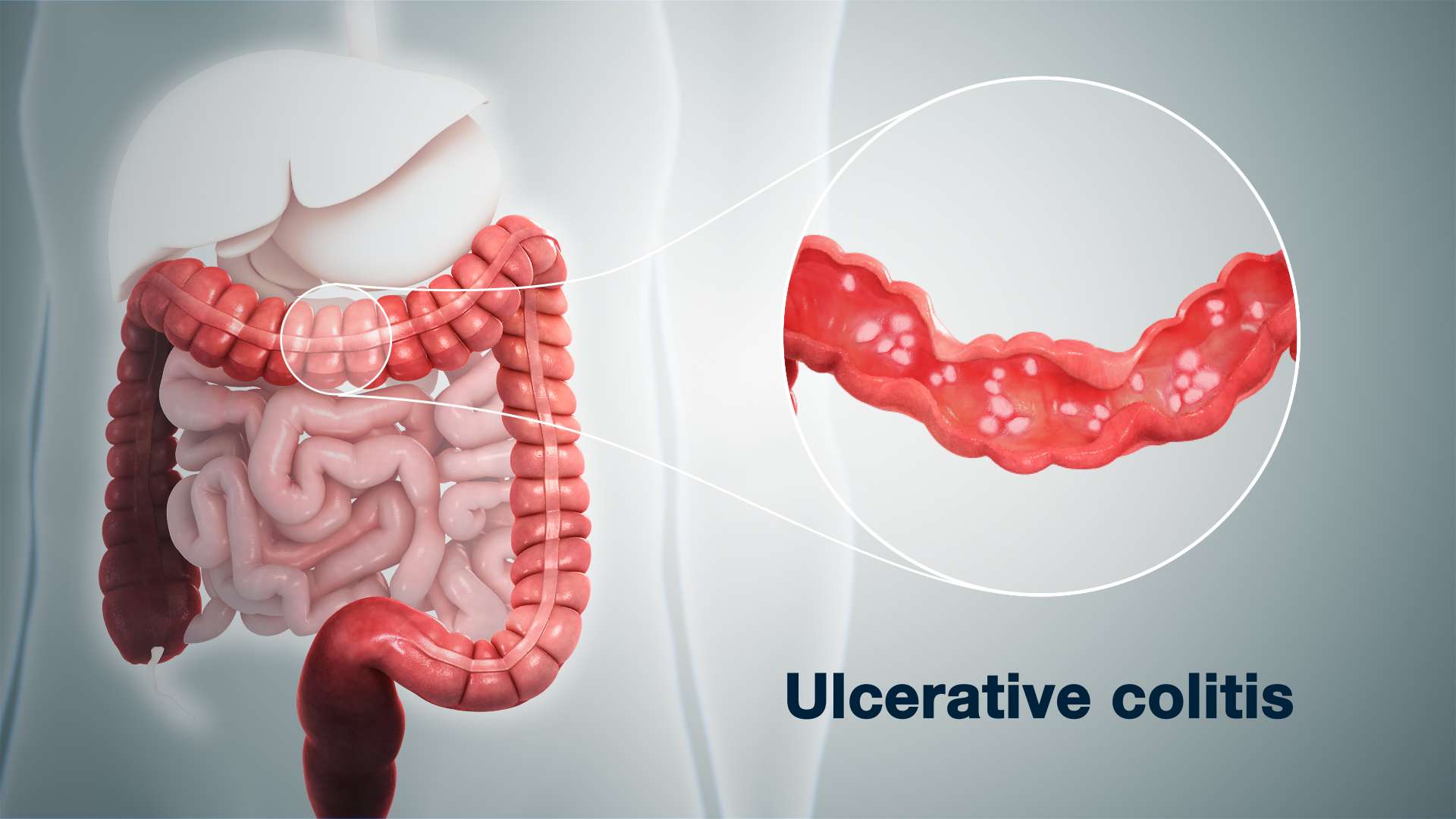
According to one study of IBD in the United States, 1 in 1,299 children between ages 2 and 17 years old were affected by the condition in 2016. Crohns disease was twice as common as UC, and boys were more likely to have IBD than girls.
For children with IBD, a diagnosis is more likely after 10 years old.
UC symptoms in children are similar to symptoms in older individuals. Children may experience bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and fatigue.
In addition, they may experience issues compounded by the condition, such as:
- anemia due to blood loss
- malnutrition from poor eating
- unexplained weight loss
UC can have a significant effect on a childs life, especially if the condition isnt treated and managed properly. Treatments for children are more limited because of possible complications. For example, medicated enemas are rarely used as a treatment method in children.
However, children with UC may be prescribed medications that reduce inflammation and prevent immune system attacks on the colon. For some children, surgery may be necessary to manage symptoms.
If your child has been diagnosed with UC, its important that you work closely with their doctor to find treatments and lifestyle changes that can help. Check out these tips for parents and children dealing with UC.
Also Check: What Do Diabetic Ulcers On The Feet Look Like