How Does Crohn’s Disease Affect The Intestines
Early stages of Crohn’s disease
In the early stages, Crohn’s disease causes small, scattered, shallow, crater-like ulcerations on the inner surface of the bowel.
- These erosions are called aphthous ulcers.
- With time, the erosions become deeper and larger, ultimately becoming true ulcers , and causing scarring and stiffness of the bowel.
- As the disease progresses, the bowel becomes increasingly narrowed, and ultimately can become obstructed.
- Deep ulcers can cause puncture holes or perforations in the wall of the bowel, and bacteria from within the bowel can spread to infect adjacent organs and the surrounding abdominal cavity.
Obstructions in the intestines
When Crohn’s disease narrows the small intestine to the point of obstruction, the flow of the contents through the intestine ceases.
- Sometimes, the obstruction can be caused suddenly by poorly digestible fruit or vegetable matter that plug the already-narrowed segment of the intestine.
- When the intestine is obstructed, food, fluid and gas from the stomach and the small intestine cannot pass into the colon. The symptoms of small intestinal obstruction then appear, including severe abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distention.
- Obstruction of the small intestine is much more likely since the small intestine is much narrower than the colon.
Ulcers in the colon and small intestine
Dietary changes and supplementation that may help control Crohn’s disease
What Is The Treatment For Ibd
Your doctor will discuss with you a treatment plan that may include any of the following:
Diet awareness is also a necessary step to take in treating and living with IBD. What you eat does not cause IBD, however it can cause symptoms when the disease is active.
Your doctor will only consider surgery if any of the following occurs:
- A large amount of bleeding
- Long-lasting and serious illness
Complications Caused By Nutritional Deficiencies
Some of the complications of malnutrition include:
- Dehydration diarrhoea causes your body to lose fluid, which can lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia reduced iron in the diet combined with losing blood from the bowel can lead to anaemia .
- Weight loss reduced appetite and poor absorption of food nutrients can cause weight loss.
- Reduced growth inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can impair a childs growth and physical development.
Recommended Reading: Is Olive Oil Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Is Surgery Ever Used To Treat Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Surgical treatment for IBD depends upon the disease. Ulcerative colitis, for instance, can be cured with surgery, because the disease is limited to the colon. Once the colon is removed, the disease doesn’t come back. However, surgery will not cure Crohn’s disease, although some surgeries may be used. Excessive surgery in people with Crohn’s disease can actually lead to more problems.
There are several surgical options available for people with ulcerative colitis. Which one is right for you depends on several factors:
- The extent of your disease
- Your overall health
The first option is called a proctocolectomy. It involves the removal of the entire colon and rectum. The surgeon then makes an opening on the abdomen called an ileostomy that goes into part of the small intestine. This opening provides a new path for feces to be emptied into a pouch that’s attached to the skin with an adhesive.
Even though surgery will not cure Crohn’s disease, about 50% of people with Crohn’s require surgery at some point. If you have Crohn’s disease and need surgery, your doctor will discuss your options with you. Be sure you ask questions and understand the goal or goals of the surgery, the pros and cons, and what could happen if you don’t have the surgery.
Show Sources
Chinese Medicine Aetiology And Pathology
Crohn’s disease is not mentioned directly in Chinese medicine, but according to the pathology and symptoms described by Western medicine, it can be characterized as Fu Tong, abdominal pain, Bian Xue, haemafaecia, and Xie Xie, diarrhoea.
When a patient has a Yin-deficient constitution, if Cold-Dampness, Damp-Heat, and/or Heat-Toxin invade the body, vital Qi cannot resist the invaders. These exogenous factors can stagnate in the Small Intestine, causing Blood stasis, and destroy blood vessels, thereby causing Crohn’s disease.
While the Small Intestine is digesting, the Spleen absorbs the pure Essence and then distributes it to the Lung and the entire body. Liver Qi assists the general Qi activities of ascending, descending, exiting and entering in the whole body including the Small Intestine. The Lung has an internal channel that connects to the Large Intestine. Qi moving downward from the Lung assists the Large Intestine in descending smoothly and transporting normally. Therefore, any factor such as external or internal pathogens, emotional disorder, poor diet and/or congenital variables may negatively affect the intestinal function of transportation, leading to Qi stagnation, Damp-Heat stasis and/or Blood stasis causing the illness. Qi stagnation, Blood stasis and Heat are the most critical pathogens in the process of the illness.
Bret A. Lashner MD, Aaron Brzezinski MD, in, 2010
Recommended Reading: Can Ulcers Make You Throw Up
Crohn’s Disease Endoscopic Index Of Severity
The Crohn’s Disease Endoscopic Index of Severity scores have been developed for the assessment of the severity of lesions in CD with endoscopy . The CDEIS is a validated scoring system in which six endoscopic variables are assessed in the rectum, sigmoid and left colon, transverse colon, right colon, and ileum, respectively. For the five segments, the percentage of ulcerated colonic surface and the percentage of surface affected by any CD lesion are indicated on a 10 cm visual analog scale.40 The CDEIS scores range from 0 to 44 with higher scores indicating more severe disease.
Table 1.6. Crohn’s Disease Endoscopic Index of Severity
| Items |
|---|
J. Nowak, in, 2014
What Are The Symptoms Of Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
The most frequent symptoms of Crohns disease are chronic diarrhoea , even at night, associated with abdominal pain and cramps, sometimes with blood loss mixed with stools, and with a fever occurring in the evening, or with joint pain.
The patient often has a significant weight loss.
Ulcerative colitis is manifested by diarrhoea mixed with blood, even at night, associated with abdominal pain and cramps.
There is often defecatory urgency, with difficulty in holding the urge, and evacuation of small volume or even just mucus and blood.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Mouth Ulcers On Gums
Intestinal Infections Can Mimic Cd
Yersinia enterocolitica infection occurs mainly in the TI and causes mucosal ulceration, neutrophil invasion, and thickening of the ileal wall. Distal ileal and cecal involvement predominates, and patients present with symptoms of small-bowel obstruction and a tender abdominal mass. The diagnosis is made most directly by colonoscopy with biopsy and culture. Endoscopic features of Yersinia include aphthoid lesions of the cecum and TI with round or oval elevations with ulcerations. The ulcers are mostly uniform in size and shape, in contrast to CD . Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex infection occurs in advanced stages of HIV infection and in other immunocompromized states it usually manifests as a systemic infection with diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, fever, and malabsorption. Diagnosis is established by culture of mucosal biopsies. Disseminated histoplasmosis can also involve the ileocecal area. TI can be affected in other intestinal infections caused by Salmonella spp., cytomegalovirus. Ileitis was described in infection with Clostridium difficile , typical pseudomembranes were seen on ileal mucosa.
Complications Of Crohn’s Disease
Several complications of Crohn’s disease have already been mentioned, including nutritional deficiencies, loss of weight, anemia, growth retardation, and delayed puberty. Two more serious complications also mentioned previously are strictures or narrowing of the intestine due to scarring and the formation of fistulas. Massive intestinal bleeding and perforation are unusual.
Don’t Miss: Best Ointment For Leg Ulcers
Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Refers To Immune
These diseases affect patients of both sexes and are particularly prevalent between adolescence and 45 years of age.
The data also indicate an increase in incidence in recent decades.
Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are two complex diseases that significantly impair the patients quality of life and for which it is essential that the patient is followed by a reference centre, both in the diagnosis phase and in the management of the disease.
Actions For This Page
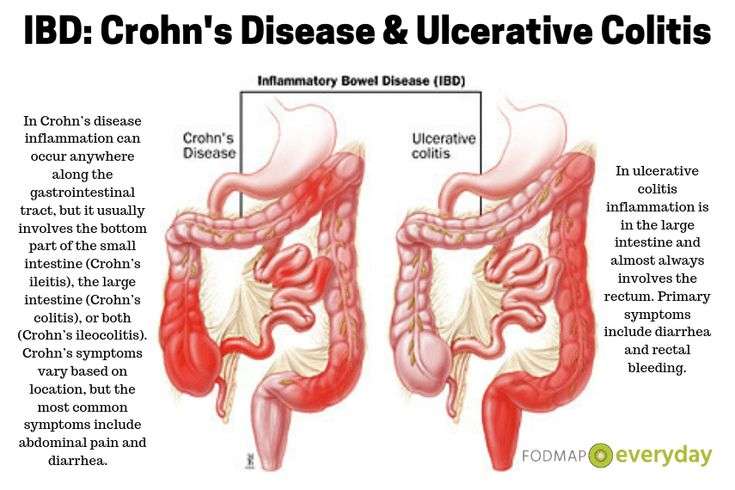
- Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease .
- Ulcerative colitis is located only in a persons large bowel .
- Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD.
- Medications help manage the symptoms of IBD.
- People with IBD can lead useful and productive lives.
- Some dietary changes can help you manage symptoms of IBD and allow medications to work better.
- Always talk with your doctor, healthcare specialist or dietitian before changing your diet. Arrange an emergency plan of action with your doctor, including after-hours phone numbers.
Don’t Miss: Foam Dressings For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Living With Ibd And Psoriasis
Managing IBD and psoriasis can be challenging. MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam members have discussed their experiences managing psoriasis on top of Crohns or UC.
I have ulcerative colitis, and Humira helped that and my psoriatic arthritis, but it did nothing for my scalp psoriasis, a member wrote.
Another member discussed her condition. Im on Stelara for psoriasis and my colitis, and methotrexate and prednisone for psoriatic arthritis, and its helping the other two. But the past couple of weeks since my latest shot, my colitis has flared and my psoriasis is starting to peek through, they wrote. So needless to say, Im frustrated because I know autoimmune disease is all about management.
One member wrote, I believe it took me roughly four or five months before I actually reached clinical remission, they said. At about two to three months, I recall feeling no more joint pain, my psoriasis was beginning to clear, and minimal cramping with no blood or mucus in my stools. Like you mentioned, everyone is different.
Overview Of Crohn’s Disease
Crohns disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract. Understanding Crohns disease can help you and your loved ones navigate the uncertainty that comes with a new diagnosis.
Calling all Crohns patients! Have you or a loved one been recently diagnosed? Or were you diagnosed with Crohns disease years ago but still dont fully understand your disease? Check out our latest video chat to learn more.
Video Length00:32:16
Video Chat: Crohn’s Disease 101
Crohns disease belongs to a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel diseases, or IBD. It is named after Dr. Burrill B. Crohn, who first described the disease in 1932 along with his colleagues, Dr. Leon Ginzburg and Dr. Gordon D. Oppenheimer.
Video Length00:07:09
Crohn’s 101 – Overview This introductory video provides information on potential causes, symptoms, treatment and overall management of Crohns disease.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should I Eat With Ulcerative Colitis
What Is Crohn’s Disease
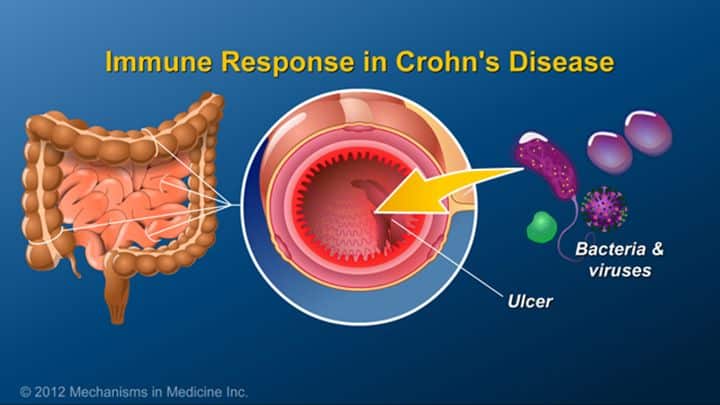
Crohn’s disease is a type of chronic bowel inflammation. It usually affects the small intestine and less commonly the colon, but it can involve the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. The chronic inflammation that is the basis of Crohn’s disease causes ulceration, swelling, and scarring of the parts of the intestine that it involves. It eventually requires surgery for most people. Other names for Crohn’s disease include granulomatous enteritis, regional enteritis, ileitis, and granulomatous colitis when it involves the colon.
What Causes Inflammatory Bowel Disease
IBD is a disease with an unknown cause. Some agent or a combination of agents — bacteria, viruses, antigens — triggers the body’s immune system to produce an inflammatory reaction in the intestinal tract. Recent studies show some combination of hereditary, genetic, and/or environmental factors may cause the development of IBD. It could also be that the body’s own tissue causes an autoimmune response. Whatever causes it, the reaction continues without control and damages the intestinal wall, leading to diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Evidence to suggest a genetic basis for IBD is strong, including:
- Family history: As many as 20% of people with IBD have a family history of it.
- Race and ethnicity: IBD is more common in white people. It’s also more common in Jews, especially Ashkenazi Jews.
In 2006, the first gene associated with Crohn’s disease, the NOD2 gene, was identified. Since then, researchers have uncovered more than 200 related genomic regions for IBD.
Finding a genetic link would help scientists understand the changes that lead to IBD and help them improve treatments. A genetic link could also lead to a test for IBD.
You May Like: How To Reduce Ulcerative Colitis Flare
Treat To Target In Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The approach we use is the so-called treat to target approach, i.e. a treatment aimed at improving symptoms, improving test results and restoring the integrity of the intestinal mucosa.
This approach is customised during follow-up, if necessary by modifying the course of treatment.
In some cases, drug therapy is not sufficient and surgery is necessary.
It is essential to be followed up in a referral centre, as the management of the patient requires regularity and constancy and includes visits, blood tests and other instrumental examinations, in order to keep the disease under control and avoid or limit intestinal damage and the risk of subsequent disability.
Diet Recommendations For Ulcerative Colitis Flare
- Follow a low residue diet to relieve abdominal pain and diarrhea.
- Avoid foods that may increase stool output such as fresh fruits and vegetables, prunes and caffeinated beverages.
- Try incorporating more omega-3 fatty acids in your diet. These fats may have an anti-inflammatory effect. They are found in fish, including salmon, mackerel, herring and sardines.
- Patients often find that smaller, more frequent meals are better tolerated. This eating pattern can help increase the amount of nutrition you receive in a day.
- Consider taking nutritional supplements if appetite is poor and solid foods are not tolerated well .
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Loss Of Appetite
How Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated
Treatment for IBD involves a combination of self-care and medical treatment.
Self-care
Although no specific diet has been shown to prevent or treat IBD, dietary changes may be helpful in managing your symptoms. It’s important to talk with your doctor about ways to modify your diet while making sure you get the nutrients you need. For instance, depending on your symptoms, the doctor may suggest that you reduce the amount of fiber or dairy products that you consume. Also, small, frequent meals may be better tolerated. In general, there is no need to avoid certain foods unless they cause or worsen your symptoms.
One dietary intervention your doctor may recommend is a low-residue diet, a very restricted diet that reduces the amount of fiber and other undigested material that pass through your colon. Doing so can help relieve symptoms of diarrhea and abdominal pain. If you do go on a low-residue diet, be sure you understand how long you should stay on the dietà because a low-residue diet doesn’t provide all the nutrients you need. Your doctor may recommend that you take vitamin supplements.
Participating in a support group puts you in contact with others who know exactly the effect IBD has on your day-to-day lifeà because they are going through the same things you are. They can offer support and tips on how to deal with symptoms and the effect they have on you.
Medical treatment
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
The differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are:
- In Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is continuous inflammation of the colon
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls
Read Also: Ozanimod Mechanism Of Action Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms Of Crohn’s Disease
The most common symptoms of Crohn’s disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea. Other signs of inflammation are often present, including fever and abdominal tenderness. Because symptoms can be worsened by eating, the intake of food is reduced, and this leads to loss of weight, and, less commonly, nutritional deficiencies. Slow, continuous loss of blood into the intestine that may not even be recognizable in the stool can lead to iron deficiency anemia.
Are Nutritional Needs Different For People With Ibd What Are The Specific Nutritional Needs For People With Crohn’s Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Nutritional needs are specific to the individual and differ with disease state, body size and age. A nutritionist can help you estimate your individual needs. Calorie and protein needs are similar for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. In both diseases, needs increase during inflammation and immediately after to restore losses. The following are general statements about nutritional needs that may apply to you.
Don’t Miss: Marshmallow Root For Ulcerative Colitis
Do Any Medications Have Nutritional Side Effects
Moderate to severe flares of IBD are often treated with corticosteroids , cholestyramine and 5-ASA compounds . These medications have nutritional side effects that should be addressed. If you use any of these medications, talk to your doctor or registered dietitian for treatment advice.
- Prednisone causes decreased absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the small intestine. It also causes increased losses of calcium, zinc, potassium and vitamin C. With continual use of high doses of prednisone, the result may be bone loss and development of bone disease. People on prednisone may need up to 1200 milligrams a day. Protein needs also are increased for people taking prednisone because it increases protein breakdown in the body.
- Cholestyramine decreases absorption of fat-soluble vitamins , as well as folate, vitamin B-12, calcium and iron.
- Sulfasalazine interferes with folate absorption. People taking this drug also should take a 1 milligram folate supplement each day.
No Pouch For Crohn’s Disease
Because Crohn’s disease can attack the small intestine as well as the colon, the pouch is not used for Crohn’s disease. When surgeons tried the pouch for Crohn’s disease, the complication rate was very high. In most cases, the Crohn’s disease attacked the pouch and it could no longer be used.
For those with Crohn’s disease, if the colon is very diseased but the rectum is not, then the colon can be removed except for the rectum, and the small intestine can be connected directly to the rectum. In many cases, if the Crohn’s disease involving the rectum is not severe, it can be controlled with Rowasa enemas or Rowasa suppositories.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Prednisolone Take To Work For Ulcerative Colitis