What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What type of IBD do I have?
- Whats the best treatment for me?
- What foods or drinks should I avoid?
- What lifestyle changes should I make?
- Am I at risk for other problems?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most people with inflammatory bowel disease enjoy active lives. Still, symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis can be life-disrupting. Some people go into remission after taking medications. Some people need surgery to deal with severe symptom flare-ups. Your healthcare provider can suggest dietary and lifestyle changes to manage IBD.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/03/2021.
References
Diagnosing Ibs Vs Ibd In Children
Because children with IBS and IBD can have similar symptoms, your child’s doctor will need a thorough medical history of your child’s symptoms. To determine a diagnosis, your doctor will conduct a physical examination, sometimes including a rectal exam. Your doctor may request blood work and/or stool tests. In many cases, these tests are sufficient to differentiate IBS from IBD.
Based on the findings, your doctor may add additional testing, such as upper and lower endoscopy, a CT scan or MRI scans of the intestines and colon. An upper endoscopy and colonoscopy are required to confirm the diagnosis of IBD before offering treatment.
“Occasionally, it is possible to have both conditions simultaneously,” says Dr. Gurram. “One of the theories for this is that the inflammatory process has led the bowel to be hypersensitive to even small stimuli, like certain eating food. So, we have to carefully evaluate if their IBD is not well controlled or if they have IBS on top of IBD.”
Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Colitis
Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are the two types of inflammatory bowel disease that cause colitis. Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are considered autoimmune diseases .
- Ulcerative colitis always begins in the rectum and may spread to the rest of the rest of the colon, spreading from the rectum to the sigmoid, descending, transverse, and finally the ascending colon and cecum in that order. Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, and symptoms include abdominal pain, and bloody, diarrheal bowel movements.
- Crohns disease may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract , including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. In Crohns disease, there may be skip lesions, that is, abnormal segments of the GI tract interspersed with normal segments.
Both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis may have other organ systems involved in addition to the gastrointestinal tract.
Either collagen or lymphocytes infiltrate into the layers of the wall of the colon, presumably as a result of inflammation. This is an uncommon illness and maybe an autoimmune disease. Diarrhea often is watery, and no blood is present in the stool.
Recommended Reading: Fish Oil And Ulcerative Colitis
Does Ulcerative Colitis Make You Immunocompromised
Ulcerative colitis doesnt make you immunocompromised. Some of the medicines that treat it may change the way your immune system responds. This change is different for each medication. Some of these changes may increase the risk of certain infections or other issues. A discussion with your health care team before starting a medication is the best way to understand these risks and ways to prevent them.
Q What Are The Causes Of Ibs And Ibd

Researchers are still working to understand the exact causes. Some people develop IBS after a GI infection. Other potential causes include diet, environmental or psychological factors, such as stress, and frequent use of antibiotics.
With IBD, stress may worsen the condition and studies suggested that your genes, immune system and environmental factors may also play a role. Those with IBD are known to have an overactive immune system, which causes inflammation in the GI tract.
Don’t Miss: Foods To Avoid If You Think You Have An Ulcer
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is another type of IBD. Its also an autoimmune disorder. Unlike Crohns disease, ulcerative colitis only involves the colon, or large intestines. It only affects the inner lining of the colon, instead of the whole wall thickness.
What are symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis include:
-
Bloody or mucousy diarrhea
These complications may need surgery to treat them.
Microscopic Colitis And Ibs
Microscopic colitis is a disease in which a person experiences chronic, watery diarrhea. The disease differs from IBS in that signs of infection can be seen when intestinal cells are examined under a microscope.
- Abdominal pain and/or cramps
Symptoms unique to microscopic colitis include:
- Nausea
Infectious colitis is an illness that is caused by an infectious agent, such as:
- Campylobacter
The symptoms of infectious colitis are quite different from those of IBS, and include:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Fever
You May Like: Is Ulcerative Colitis Considered An Autoimmune Disease
Ibs Vs Ibd: What’s The Difference
Both IBS and IBD are chronic GI conditions, but they affect the digestive tract in vastly different ways.
IBS does not cause any visible changes or inflammation in the digestive tract. While the cause of IBS is unclear, it is believed to result from both psychological factors and gastrointestinal dysfunction, which lead to bowel hypersensitivity. This hypersensitivity presents as pain, diarrhea and/or constipation.
IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, causes areas of inflammation in the digestive tract. This inflammation can be seen during an endoscopic evaluation by your doctor. Without proper treatment, IBD can progress and lead to various complications that may need surgery.
“If we don’t treat these areas of inflammation, your child has an increased risk of surgery, hospitalization or a great need for medications,” explains Dr. Gurram.
Allergic Colitis In Infants
Allergic colitis is a condition that can occur in infants, usually within the first months after birth. The condition can cause symptoms in infants including:
- reflux
- fussiness
- possible flecks of blood in a babys stool
Doctors dont know exactly what causes allergic colitis. One of the most popular theories is that infants with allergic colitis have an allergic or hypersensitive reaction to certain components in breast milk. A 2020 review of studies indicated that a protein allergy, either through breast milk, cows milk, or formula, could contribute.
Eosinophilic colitis is a type of allergic colitis that can also show up in infants with these symptoms. Its causes are similarly unknown , but its likely also related to a protein allergy.
Doctors will often recommend an elimination diet for the birthing parent, which involves slowly cutting out certain foods known to contribute to allergic colitis. Examples include cows milk, eggs, and wheat. If the baby stops having symptoms of allergic colitis, these foods were likely causing the problem.
In severe cases, monoclonal antibodies, such as those used to inflammatory bowel disease , may also be another treatment option.
Recommended Reading: What Causes A Bleeding Ulcer In Stomach
Specialized Diets To Manage Crohns And Ulcerative Colitis
In some cases, following a strict and specific diet protocol can do wonders for managing and reversing the massive inflammation seen in these inflammatory bowel conditions. In particular, two specific diets that have been found to be especially effective components of treatment are:
The Specific Carbohydrate Diet
This diet restricts specific carbohydrates that encourage the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the gut. These harmful bacteria and their byproducts trigger and amplify inflammation in your gut. The SCD diet eliminates carbohydrates that contain two or more linked sugar molecules such as:
- Potatoes
- All grains including wheat, rice, corn, millet, quinoa, etc.
- Any processed meats or meats containing additives
- Dairy
- Most legumes
- Processed sugar, artificial sweeteners and sugar alcohols
- All processed foods
Eliminating complex carbs can yield impressive and significant results in many Crohns and ulcerative colitis patients.
The Elemental Diet
This diet allows your digestive tract to take a break without sacrificing your nutritional intake by consuming nutritionally complete liquids that are pre-digested. These premade formulas contain all of the carbs, fat, proteins, and nutrients your body needs in a super digestible form that doesnt require your digestive tract to break them down essentially allowing your gut to focus entirely on healing and repairing inflammation.
Q What Are The Symptoms Of Ibs And Ibd
Both are digestive conditions and affect the esophagus, stomach and intestines. IBS is a chronic syndrome made up of a group of symptoms. IBD, on the other hand, refers to inflammation or chronic swelling of the intestines.
IBS symptoms include chronic abdominal pain and changes in bowel habitsdiarrhea and constipation, or alternating between both. Symptoms can vary person to person and can often change over time, making it difficult to manage.
IBS does not develop into IBD or cause permanent harm in your intestines, such as intestinal bleeding, other intestinal diseases or cancer. But it can significantly affect your quality of life. Some have reported they would be willing to give up their essential pleasurescaffeine, use of cell phone and the internet and even sex to be free of IBS symptoms.
Common forms of IBD include Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Both cause chronic inflammation in the GI tract. These conditions can cause rectal bleeding and diarrhea, bloating, abdominal cramping, pain, reduced appetite, unintended weight loss and fatigue.
Also Check: Crohn’s Disease And Mouth Ulcers
What Kind Of Doctor Diagnoses And Treats Colitis
Most often colitis is treated by a primary health care provider or internal-medicine specialist, especially when the colitis is first diagnosed and the cause is uncertain. Once the cause is found, that health care provider may be the only person needed to continue care. Should there be a need for further investigation and diagnostic testing, specialists may be consulted, such as a gastroenterologist. If an infection is the cause of colitis, an infectious-disease specialist may be consulted. In some cases, other specialists may be involved in treatment, such as surgeons and interventional radiologists.
Patient history
Treatments For Ibs And Ibd

Treatment is very different for IBS and IBD. If you have IBD, you will take medications that lower the inflammation in the GI tract such as anti-inflammatory medications, biologic agents, and immunomodulators which can reduce the damage IBD is causing.
Treatment of IBS is different. You and your providers will focus on treating the specific symptoms you are having. Changes to your diet and exercise habits are a good first step.
Heres a few examples of some foods to avoid when you have IBS:
-
Apples
If diarrhea is one of your main IBS symptoms, you might take medications that reduce the diarrhea, such as rifamixin and eluxadoline . If you are more often constipated, you might take medications that help keep the GI tract moving, such as lubiprostone , linaclotide , or plecanatide .
You might also need treatment of stress, anxiety, or depression with medications or therapy if you and your provider think this is playing a role in your IBS.
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Psychological Therapies In Uc
In addition to antidepressants, psychological therapies have also been shown to be beneficial in IBS. These include cognitive behavioral therapy and gut-directed hypnotherapy, and both are recommended by national guidelines for the management of IBS., However, evidence for their use as an effective treatment for UC, particularly in those with IBS-type symptoms, is lacking. A Cochrane review investigated the efficacy of psychotherapy, patient education, and relaxation techniques for IBD. Outcomes assessed included health-related quality of life, coping, emotional status, and disease activity. In total, 21 studies were included, but there was no clear benefit identified for any of the psychological interventions in adults with UC for any of the outcomes of interest.
Another systematic review of 16 studies of psychological interventions, including stress management, psychodynamically informed therapy, CBT, and hypnosis assessed their effects on anxiety and depression, quality of life, and IBD activity. CBT and psychodynamically informed therapy were beneficial for anxiety and depression, but they appeared to have no effect on disease activity, whereas hypnotherapy, used in two studies, demonstrated a beneficial effect on disease activity, but not anxiety, depression, or quality of life.
Does Ibs Get Worse With Age
IBS is long-term disorder of the gut and is an inevitable part of aging. It comes and goes over time. The sensitivity of the gut nerves may elevate with age and the symptoms overlap is possible. Different signs and symptoms related to IBS may show up with age. However, there are some ways like exercise, avoidance of foods that irritate the digestive system etc. that help to help reduce the overall risk of IBS and aid in reducing the symptoms.
You May Like: Sand Beds For Pressure Ulcers
Keep Up With Your Checkups
If you have either condition, youâll need to keep up with your checkups, even if your symptoms start to ease up.
You may also need to get colonoscopies more often and start them at a younger age. A colonoscopy can check for cancer or polyps that need to come out. Experts recommend that you start these tests within 8 to 10 years of developing UC or Crohnâs symptoms, and then typically every 1 to 3 years after that. Your doctor will tell you a schedule that is best for you.
Show Sources
Subjects And Sample Collection
UC and IBS patients were recruited via the Gastroenterology Clinics at the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital . Healthy controls were recruited through the Institute of Food Research Human Nutrition Unit . A total of 13 UC patients , 11 IBS patients and 22 controls with no gastrointestinal symptoms , were recruited over a period of 13 months between June 07 – July 08. The median ages were 45 years for UC group, 45 years for the IBS group, and 45 years for controls. All patients were anonymous and in remission when samples were collected. All UC patients had a disease activity score in the moderate to severe range when recruited. Participants in the study provided written consent prior to the completion of a health questionnaire. Infectious diseases and structural abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract were excluded in all subjects. Each patient had a diagnosis of IBS or UC made by their clinician. Volunteers enrolled in the study had not taken probiotics or prebiotics in any form in the previous two weeks, and had not received any antibiotics within 4 weeks before providing their samples. Our study was approved by the Institute of Food Research Human Research Governance Committee , East Norfolk & Waveney Research Governance Committee and the Suffolk Research Ethics Committee , project ref .
You May Like: How To Treat Ulcer Pain
Ibs Vs More Serious Causes Of Intestinal Symptoms
Even though IBS can significantly impair your quality of life, it is usually not considered a serious illness, and it doesn’t lead to life-threatening complications.
However, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms that could point to a more serious condition, including:
- Severe pain
- New, long-lasting constipation or diarrhea
- Shortness of breath
- Change in quality of stool
- Weight loss
- Mouth ulcers
Extraction Of Total Dna From Stool Samples
Bacterial DNA was extracted from 0.2 g aliquots of frozen faecal sample using QIAamp Stool Mini Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purity and concentration of the extracted DNA were measured using a spectrophotometer at 260 and 280 nm . The integrity of genomic DNA was also visualized following electrophoresis using a 1% agarose gel.
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Leg Ulcers
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease Similar
- Both diseases often develop in teenagers and young adults although the disease can occur at any age
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohnâs disease affect men and women equally
- The symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohnâs disease are very similar
-
The causes of both UC and Crohnâs disease are not known and both diseases have similar types of contributing factors such as environmental, genetic and an inappropriate response by the bodyâs immune system
Can Ibs Turn Into Crohns Disease
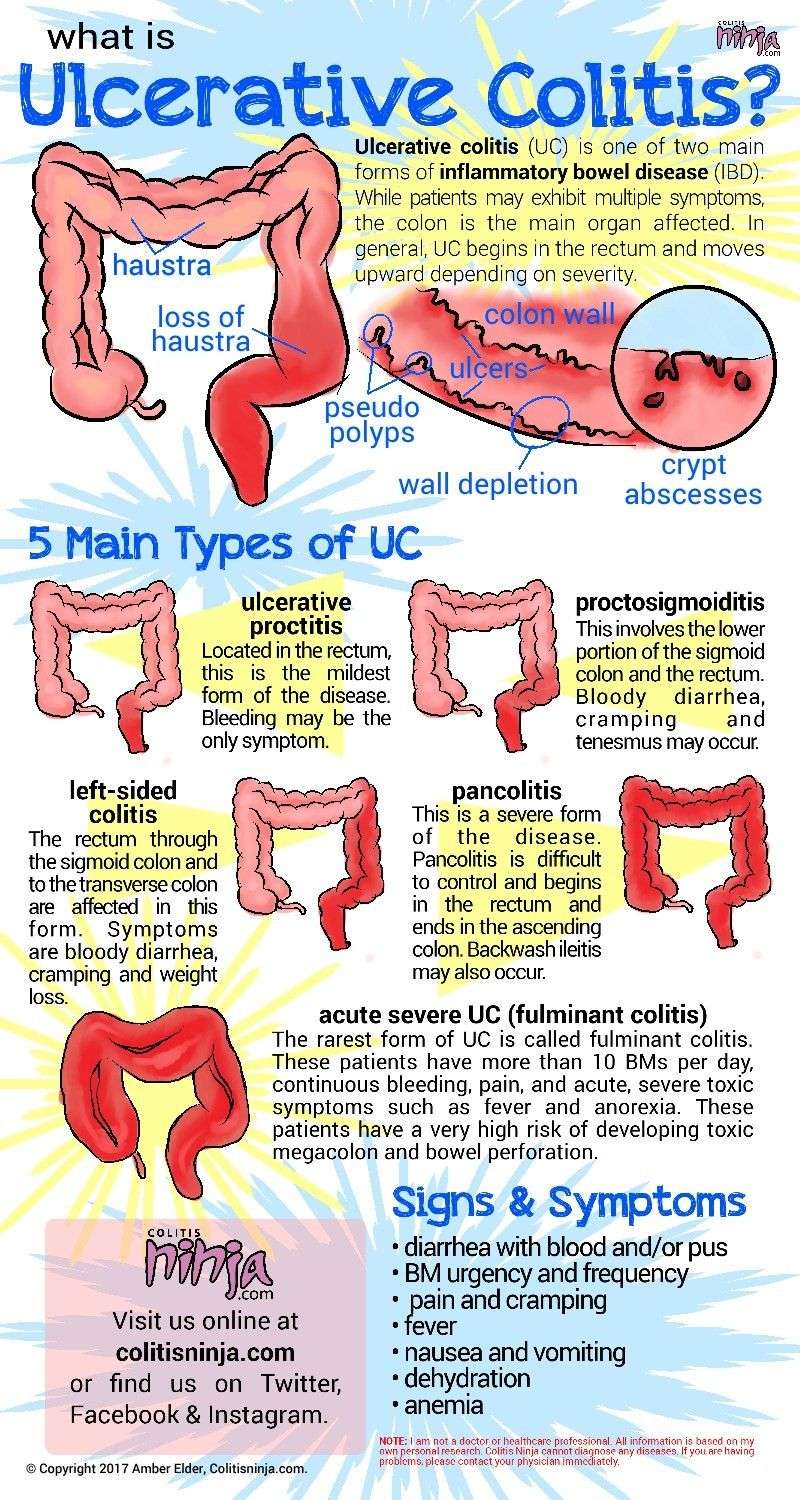
There is no medical evidence that irritable bowel syndrome progresses to any other sickness or disease like Crohns disease or even results in any aggravating medical conditions outside of the regular symptoms. Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a syndrome and a functional disorder that changes the way the bowel functions. It is not a progressive disease.
Recommended Reading: Does Turmeric Help Ulcerative Colitis
Ibd Vs Ibs: Understanding Different Gastrointestinal Conditions
Contents
Although there are many distinctions between the two, one key differentiator is that IBD involves swelling of the intestines, whereas IBS does not. These conditions require very different treatments, and as such, an accurate diagnosis is vital to ensure proper management.âRead on to learn more about IBD and how it differs from IBS.â
Stress Anxiety And Depression And The Braingut Axis A Bidirectional Relationship
Several of the studies in the aforementioned meta-analysis also demonstrated a negative impact of the presence of IBS-type symptoms on both mood and quality of life in patients with IBD. Stress, anxiety, and depression are common in both IBS and IBD. However, the effect of psychological comorbidity on the natural history of these conditions remains controversial. Prior understanding of the cause of these conditions led health care professionals to assume that IBS was a centrally mediated process but that UC was a condition restricted to the colon and rectum. Evidence now exists to suggest that the relationship between stress and flare-ups of disease activity in the two conditions may be more complex and that the presence of psychological comorbidity is associated with greater symptom severity and more flare-ups of disease activity in both.
The perception of visceral pain is thought to involve the spinothalamic, spinoreticular, and spinomesencephalic tracts. Interestingly, the central coordinating center for each of these pathways involves the limbic system, which also serves to mediate emotional responses this supports the theory that psychological as well as physiological pathology contributes to the development of functional GI symptoms in IBS and UC. It follows that psychological health, stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms and visceral hypersensitivity are interrelated and, therefore, that mood may influence the generation and perception of symptoms.
Read Also: Oats For Horses With Ulcers