Caring For The Patient Undergoing Stoma And Ilealanal Pouch Formation
The Advanced IBD Nurse is well placed to support the patient in the peri-operative period by being a source of education and referring to appropriate members of the MDT, particularly the stoma nurse. Psychologists, sexual therapists and country-specific patient organizations can help with information provision and psychological support .
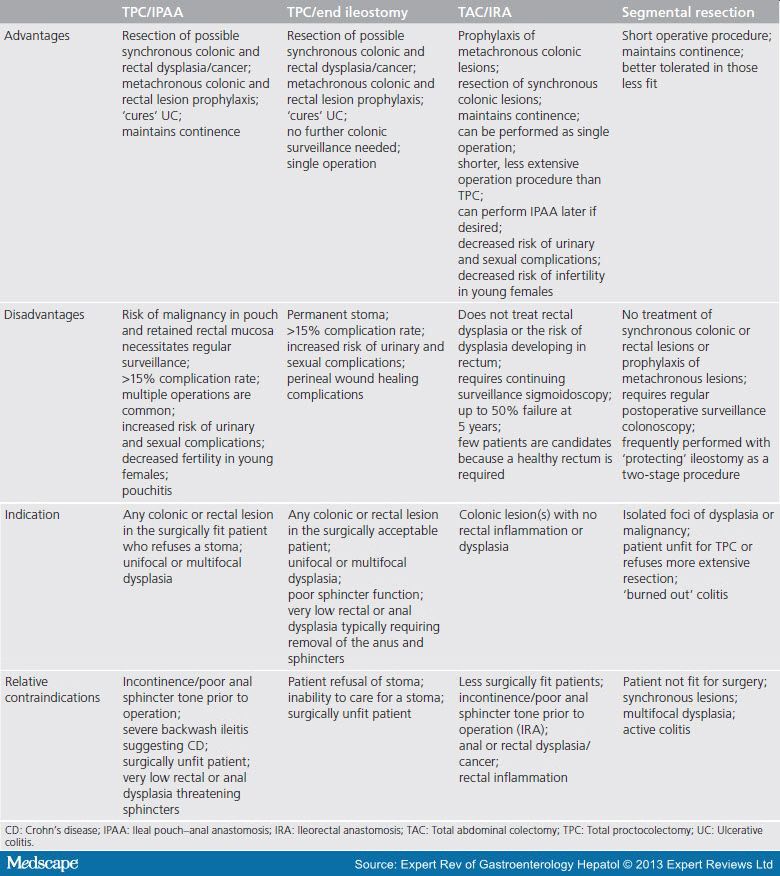
Many patients are understandably distressed at the thought of undergoing either planned or emergency surgery, and the Advanced IBD Nurse plays a key role in coordinating health-care professionals. Patients may undergo a colonic resection without stoma formation, or require further surgery to include restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouchanal anastomosis . The main indication for IPAA is in patients with medically refractory UC,372,373 or dysplasia or cancer developed from underlying UC.
For any complex surgical procedure, the patient is best managed within an MDT including the Stoma Care Nurse. In the event of stoma formation, the Stoma Care Nurse provides essential support and education for the patient and their family prior to surgery, during the hospital stay and following discharge.374
Stoma and IPAA surgery provide numerous benefits, including long-term symptom relief,372,375 although recent evidence suggests that while outcomes are often better than anticipated, some patients require a long time to decide about stoma surgery and find benefit from pre-operative contact with another patient with IBD living well with a stoma.29
Nursing Interventions For Diarrhea
1. Encourage a liquid diet.Diarrhea normally requires bowel rest and the healthcare provider may order an NPO diet, but more likely a clear or full liquid diet.
2. Educate on diet changes to prevent diarrhea.A bland diet with low fiber is needed to bulk the stools. This includes soft foods without added sugar or spices such as white rice, white toast, crackers, and eggs. Raw, fresh foods and caffeine are not recommended.
3. Review medications.Medications may need to be changed if diarrhea is an intolerable side effect. Review how a patient is taking their medications. If they are taking laxatives or stool softeners, educate on the appropriate use and to discontinue if diarrhea develops.
4. Administer antidiarrheals as appropriate.Once the cause of diarrhea has been determined and it is not contraindicated, administer antidiarrheals to stop diarrhea. These should not be given if the patient has a parasitic infection as the infectious process needs to be eliminated.
5. Correct electrolyte imbalances.Dehydration is common with diarrhea. Administer IV fluids if dehydration is severe. Replace electrolytes such as potassium if required.
6. Children may need oral rehydration.Children experiencing diarrhea may need oral rehydration solutions such as Pedialyte. These can also be concocted through a mixture of water, sugar, and salt to replace lost fluids.
Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel Disease 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements related to altered absorption of nutrients secondary to Inflammatory bowel disease, as evidenced by diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to achieve a weight within his/her normal BMI range, demonstrating healthy eating patterns and choices.
Recommended Reading: Enema Medication For Ulcerative Colitis
Nursing Management Of Patients With Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease specialist nurse, Endoscopy Unit, University Hospital Aintree, Liverpool
Ulcerative colitis is a relapsing chronic disease that has an unpredictable course. A relapse in the condition requires timely intervention and expert monitoring. A severe flare-up will often necessitate admission to hospital. This article provides an overview of the medical management of severe ulcerative colitis and the nursing interventions required.
Nursing Standard.24, 17, 48-58. doi: 10.7748/ns.24.17.48.s59
Keywords :
Better Access To Care Reduced Waiting Times And Cost Benefits Arising From An Ibd Nursing Service

Patients describe the IBD Nurse as a constant and reliable source of contact, providing immediate advice.285,393,395,410 Prompt access is the most frequently cited benefit of an IBD nursing service from the patient perspective. Increased access to the IBD team, via telephone ALs managed by Advanced IBD Nurses, has also been demonstrated to significantly reduce costs associated with unscheduled primary and secondary health-care visits.259,285,410 High levels of patient contact episodes are recorded via helpline services across Europe.285,411 Where a monetary tariff can be attached, ALs generate income for the IBD service.285,288,412 Studies demonstrate that outpatient visits and hospital admissions can be avoided through counselling by phone or email with the IBD Nurse.73,259,288 AL services enable Advanced IBD Nurses to conduct rescue work408 and facilitate faster access to procedures and other relevant departments.259,288
Recommended Reading: What Does And Ulcer Feel Like
Nursing Assessment For Diarrhea
1. Assess onset and pattern of diarrhea.Note when symptoms started, recent foods eaten, any recent travel, or change in medications. Length of time of diarrhea can dictate between acute or chronic diarrhea and determine treatment.
2. Assess characteristics and number of stools.Either through observation or patient verbalization, gather an understanding of the number of loose stools per day, the color, and any blood or mucus in the stool.
3. Obtain a stool culture.A stool culture will help determine treatment if a specific organism can be identified.
4. Assess for abdominal pain and related symptoms.Assess the type and location of abdominal pain as well as related symptoms of nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and faintness or dizziness from dehydration.
5. Assess bowel sounds.Diarrhea normally results in hyperactive bowel sounds.
6. Monitor electrolyte imbalances.Severe or prolonged diarrhea can result in dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Obtain these results through blood work.
7. Assess gastrointestinal history.Assess for a history of colitis, Clostridium Difficile, autoimmune diseases, or recent GI surgery that may be causing diarrhea.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Inflammatory Bowel Disease NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Inflammatory bowel disease is an umbrella term to describe two inflammatory disorders of the digestive tract: ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease. IBD is a long-term condition characterized by diarrhea, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weight loss.
You May Like: What Is Best Medicine For Ulcer
Don’t Miss: Plant Based Diet Ulcerative Colitis
What Can Happen If I Have Diarrhea
Acute diarrhea is uncomfortable but rarely dangerous in healthy adults and children. However, diarrheal stools may contain viruses and bacteria that spread infections. For example, the bacterium Escherichia coli causes about 9% of all foodborne infections in the United States. If there is severe diarrhea with vomiting, dehydration can occur. This occurs when there is excessive water loss from your body due to diarrhea and/or vomiting. Severe dehydration may be life-threatening.
- Avoid eating contaminated food- If food poisoning is suspected to be a cause of your diarrhea, contact a local health department or call your doctor for instructions.
- Maintain hygiene -Keep hands clean by washing with soap and warm water for 20 seconds.
Follow these steps to prevent dehydration:
1. Drink plenty of water and other liquids. Water is important because your body loses water when you have diarrhea. Fluids that contain electrolytes are also helpful.
2. Avoid coffee and tea while you have diarrhea because they may worsen the problem by irritating the bowel wall, causing pain and inflammation, and increasing fluid loss.
Get the following premium features for free after ordering a custom nursing assignment from us:
Causes Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is idiopathic which means it has no known cause. It was suspected before that diet and stress are the causes behind this condition.
However, studies now suggest that they are only aggravating factors. It is believed that IBD is caused by a defective immune response and genetic predisposition.
Although the exact cause of IBD is unknown, there are known risk factors that predispose an individual to this condition.
- Age Most IBD cases are diagnosed in people before they turn 30 years old. However, some cases can still develop after the age of 50-60 years.
- Race and ethnicity people of Hispanic and non-Hispanic White descent are at higher risk.
- Family history having a close relative with IBD is a risk for developing the disease.
- Cigarette smoking cigarette smoking is known to prevent ulcerative colitis. However, its known benefit far outweighs the harm that it can cause the persons overall health.
- Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications the use of NSAIDs is known to increase the risk of IBD and worsen the symptoms of those who already have the disease.
You May Like: What Foods To Eat If You Have An Ulcer
Ibd In Elderly Patients
The Advanced IBD Nurse is in a position to assess the health risks or frailty of elderly patients with IBD regarding medication , medical history, co-morbidities, bone density, incontinence, cognitive deficit, and depression .
Care of the elderly patient with IBD is extensively covered in the ECCO topical review.378 A key characteristic of the health status of the elderly is its large heterogeneity in terms of the effects of ageing on individuals quality of life, functional limitation, and the type of diseases and conditions affecting them.
Until recently, little data existed about IBD in the older person. Possible explanations for this include higher rates of exclusion from clinical trials and less endoscopic procedures being performed within this population.379
When making management decisions for care of the elderly with IBD, the Advanced IBD Nurse needs to assess the patients frailty and acknowledge the difference between the chronological and biological age.382 Validated measures of frailty may be used.383
4.6.1. Health risks in the elderly with IBD
The Advanced Ibd Nurse Caring For Complex Patients
The Advanced IBD Nurse plays a key role in the IBD MDT when caring for complex patients, and will be able to assess the patients care needs and refer them on, if needed .
Advanced IBD Nurses have a pivotal role within the IBD MDT because they can provide direct care as well as holistic support266,267 and make a significant contribution to patient experience, including facilitating complex decision-making regarding patient care. The Advanced IBD Nurse develops the role of providing social, physical and psychological support in addition to providing education and promoting understanding for the patient and their family when IBD becomes complex. Further, the Advanced IBD Nurse plays a key liaison role, acting as the patients advocate at IBD MDT meetings and ensuring there is focus on managing IBD in the context of the patients life, rather than just in terms of disease activity.88
The changing demands of IBD in terms of complex treatment algorithms, place the Advanced IBD Nurse at the centre of care to ensure that the patients needs are met through ongoing delivery of high-quality evidence-based care.
Don’t Miss: Why Is Ulcerative Colitis Worse At Night
Active Left Sided Disease And Extensive Disease
Doses of oral mesalazine > 3 g a day are associated with greater clinical improvement than lower doses. Combined topical and oral treatment can help induce remission in left sided colitis and extensive colitis., Oral corticosteroids are indicated in mild disease that fails to respond to topical treatment and in moderate disease .
Delays in treatment may increase the risk of colectomy. Patients should be treated promptly with an optimal dose of corticosteroids .
You Are Reading A Preview
Activate your 30 day free trial to continue reading.
Image result for ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
Image result for ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
Also Check: Foods To Avoid During Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Scheduled And Emergency Uc Surgery
Most UC surgery can be arranged at time thatâs convenient for you. Try scheduling it while your symptoms are calm to cut the chances of complications.
The risks are higher when you have emergency surgery. You may need it if you get toxic megacolon â a life-threatening condition when your colon rapidly swells and gas and bacteria build up inside. Get medical help right away if you have fever, belly pain, constipation, or swelling.
Recommended Reading: Best Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
What Is Happening To The Large Intestine With Ulcerative Colitis
There is massive inflammation in the large intestine . The inflammation causes the cells of the lining to die which causes ulcers to form and they bleed and produce pus.
Due to the massive amount of inflammation, the large intestine cannot function normally. Therefore, it cant absorb water. Normally, when GI contents enter into the large intestine from the small intestine the contents is watery. The large intestine will absorb that water as it travels through the different areas of the colon. The stool will then start to have a solid form. However, due to the inflammation with ulcerative colitis it cant, so the patient has diarrhea. The diarrhea will be bloody because as the contents passes over the ulcers it will mix with the blood/pus/mucous.
Furthermore, the patient will have frequent bowel movements because of the inflammation causing the rectum to want to empty.
Patients will have bouts of flare-ups and remission . The ulcerative sites will heal but the lining will be damaged. So, from the continuous cycle of healing and ulcer formation, polyps will form along with scar tissue which leads to bowel narrowing and shortening.
Overtime, due to severe cases, the large intestine will start to lose its unique form. It wont have those small pouches present. The haustra help with food churning throughout the large intestine. Instead, the large intestine will start to appear smooth.like a lead pipe which is called the lead pipe sign and is seen on a barium enema.
Recommended Reading: Ulcerative Colitis How To Treat
The Advanced Ibd Nurses Role In The Planned Review Care And Follow
The Advanced IBD Nurse can conduct regular patient reviews face to face, via telephone or electronically in order to monitor treatments, and arrange appropriate investigations as required, in accordance with local policy or guidance . The limitations of remote contact must be considered and skilled judgement used in knowing when further assessment is required .
Patients with IBD require long-term outpatient follow-up and surveillance. Disease activity often fluctuates over time, requiring maintenance therapy and acute interventions for disease flares. Complex disease management requires a specialized MDT approach that enhances the level of continuous care and improves outcomes. In this dedicated team, a key role for the Advanced IBD Nurse is increasingly being recognized.259 Advanced IBD Nurses are consistent team members who work with patients over a period of time. This continuity is one of the advantages, over other groups of health-care professionals, of Advanced IBD Nurses involvement in follow-up.260,261
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
Complications of ulcerative colitis can include:
Bleeding. This can lead to anemia.
Osteoporosis. Patients bones might become weak because of the diet or if they take a lot of corticosteroids.
Dehydration. A patient might need to get fluids through a vein if the large intestine cant absorb enough.
Inflammation. This can affect the joints, skin, or eyes.
Fulminant colitis. If UC attack is severe, the colon might burst, or infection could spread through the body. The intestines stop moving waste, and the belly swells.
Megacolon. Fulminant colitis can cause the large intestine to swell or burst. This is a dangerous complication, and a patient will probably need surgery.
Liver disease. The bile ducts or liver could become inflamed or could get scar tissue.
Colon cancer. Ulcerative colitis puts a patient at higher risk of getting colon cancer, especially if the whole large intestine is affected or if UC persists for a long time.
Read Also: Evidence Based Practice Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
A doctor will use tests to tell if a patient has UC instead of another gut disease.
Blood tests can show if a patient has anemia or inflammation.
Stool samples can help the doctor rule out an infection or parasite in the colon. They can also show if theres blood in the stool.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy lets the doctor look at the lower part of the colon. Theyll put a bendable tube into the lower colon through the bottom. The tube has a small light and camera on the end. A doctor might also use a small tool to take a piece of the lining of the lower colon. This is called a biopsy. A doctor in a lab will look at the sample under a microscope.
Colonoscopy is the same process as flexible sigmoidoscopy, only the doctor will look at the whole colon, not just the lower part.
X-rays are less common for diagnosing the disease, but a doctor may want a patient to have one in special cases.
Ibd In Population Genetics
Detection of natural selection in the human genome is also possible via detected IBD segments. Selection will usually tend to increase the number of IBD segments among individuals in a population. By scanning for regions with excess IBD sharing, regions in the human genome that have been under strong, very recent selection can be identified.
In addition to that, IBD segments can be useful for measuring and identifying other influences on population structure. Gusev et al. showed that IBD segments can be used with additional modeling to estimate demographic history including bottlenecks and admixture. Using similar models Palamara et al. and Carmi et al. reconstructed the demographic historyof Ashkenazi Jewish and Kenyan Maasai individuals. Botigué et al. investigated differences in African ancestry among European populations. Ralph and Coop used IBD detection to quantify the common ancestry of different European populations and Gravel et al. similarly tried to draw conclusions of the genetic history of populations in the Americas. Ringbauer et al. utilized geographic structure of IBD segments to estimate dispersal within Eastern Europe during the last centuries. Using the 1000 Genomes data Hochreiter found differences in IBD sharing between African, Asian and European populations as well as IBD segments that are shared with ancient genomes like the Neanderthal or Denisova.
Read Also: What To Avoid Eating If You Have An Ulcer
Don’t Miss: Clinical Manifestations Of Ulcerative Colitis