Incorporating Uc Clinical Guidelines Into Practice
Multiple international and national clinical practice guidelines are available to guide clinicians in various aspects of UC management.11,14–16 In the United States, guidelines for UC management have been updated recently by both the ACG16 and the AGA.11 Although both guidelines were developed using GRADE methodology, they differ in several key areas. Published in 2019, the ACG guidelines cover a broad scope of UC management, addressing diagnosis, treatment, and overall management of adults across varying severities of UC, including hospitalized patients.16 In contrast, the AGA published 2 guidelines, one in 2019 and the other in 2020, focusing on the medical management of mild-to-moderate17 and moderate-to-severe UC,11 respectively. Whereas the ACG guidelines include recommendations for the use of conventional therapies ,16 the AGA restricts recommendations for moderate-to-severe UC to the use of immunosuppressive agents, biologics, and small molecules for the induction and maintenance of remission.11 Furthermore, the AGA bases its recommendations for these therapies on a technical review of the evidence that included a network meta-analysis to inform the comparative efficacy of different pharmacologic therapies.11,18
William J. Sandborn, MD
Prognosis For Ulcerative Colitis
Usually, ulcerative colitis is chronic with repeated exacerbations and remissions. In about 10% of patients, an initial attack becomes fulminant with massive hemorrhage, perforation, or sepsis and toxemia. Complete recovery after a single attack occurs in another 10%.
Patients with localized ulcerative proctitis have the best prognosis. Severe systemic manifestations, toxic complications, and malignant degeneration are unlikely, and late extension of the disease occurs in only about 20 to 30%. Surgery is rarely required, and life expectancy is normal. The symptoms, however, may prove stubborn and refractory. Moreover, because extensive ulcerative colitis may begin in the rectum and spread proximally, proctitis should not be considered localized until it has been observed for ⥠6 months. Localized disease that later extends is often more severe and more refractory to therapy.
Pathophysiology Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis usually begins in the rectum. It may remain localized to the rectum or extend proximally, sometimes involving the entire colon. Rarely, it involves most of the large bowel at once.
The inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis affects the mucosa and submucosa, and there is a sharp border between normal and affected tissue. Only in severe disease is the muscularis involved. Early in the disease, the mucous membrane is erythematous, finely granular, and friable, with loss of the normal vascular pattern and often with scattered hemorrhagic areas. Large mucosal ulcers with copious purulent exudate characterize severe disease. Islands of relatively normal or hyperplastic inflammatory mucosa project above areas of ulcerated mucosa. Fistulas and abscesses do not occur.
Read Also: Hindgut Ulcers In Horses Treatment
Treatment Modalities Administered For Lcv In Patients With Uc
Most patients were treated with corticosteroids . Among thee corticosteroids, prednisone or prednisolone were administered in more than 2/3 of patients . Aminosalicylates and steroid-sparing immunosuppressants were administered in nine , and eight patients, respectively. Biologic agents were given in five cases . Due to the inability to control UC disease course, colectomy was performed in two patients .
Ulcerative Colitis Causes And Risk Factors
Ulcerative colitis happens when your immune system makes a mistake. Normally, it attacks invaders in your body, like the common cold. But when you have UC, your immune system thinks food, good gut bacteria, and the cells that line your colon are the intruders. White blood cells that usually protect you attack the lining of your colon instead. They cause the inflammation and ulcers.
Doctors arenât sure why people get the condition. Your genes may play a role the disease sometimes runs in families. Other things in the world around you may make a difference, too.
Things that can affect your risk of getting ulcerative colitis include:
- Age. Itâs most likely if youâre between 15 and 30 years old or older than 60.
- Ethnicity. The risk is highest in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
- Family history. Your risk could be up to 30% higher if you have a close relative with the condition.
Food and stress donât cause it, but they can trigger a flare of symptoms.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Biologics Side Effects
Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
UC increases your risk of developing colon cancer. The longer you have the disease, the higher your risk of this cancer.
Because of this increased risk, your doctor will perform a colonoscopy and check for cancer when you receive your diagnosis.
Repeat screenings are recommended thereafter, according to the American Cancer Society. Regular screenings help lower your risk of colon cancer. Follow-up screenings can detect precancerous cells early.
Other complications of UC include:
- thickening of the intestinal wall
- intestinal bleeding
Does Ulcerative Colitis Make You Immunocompromised
Ulcerative colitis doesnt make you immunocompromised. Some of the medicines that treat it may change the way your immune system responds. This change is different for each medication. Some of these changes may increase the risk of certain infections or other issues. A discussion with your health care team before starting a medication is the best way to understand these risks and ways to prevent them.
Also Check: Is Burping A Sign Of An Ulcer
Demographic Characteristics And Co
The median age of patients described in this review was 18 years , with no predominance regarding sex . Half of the patients were pediatric cases . The majority of patients had no co-morbidities . In one patient, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension were reported, while in another case, only diabetes mellitus was noted.
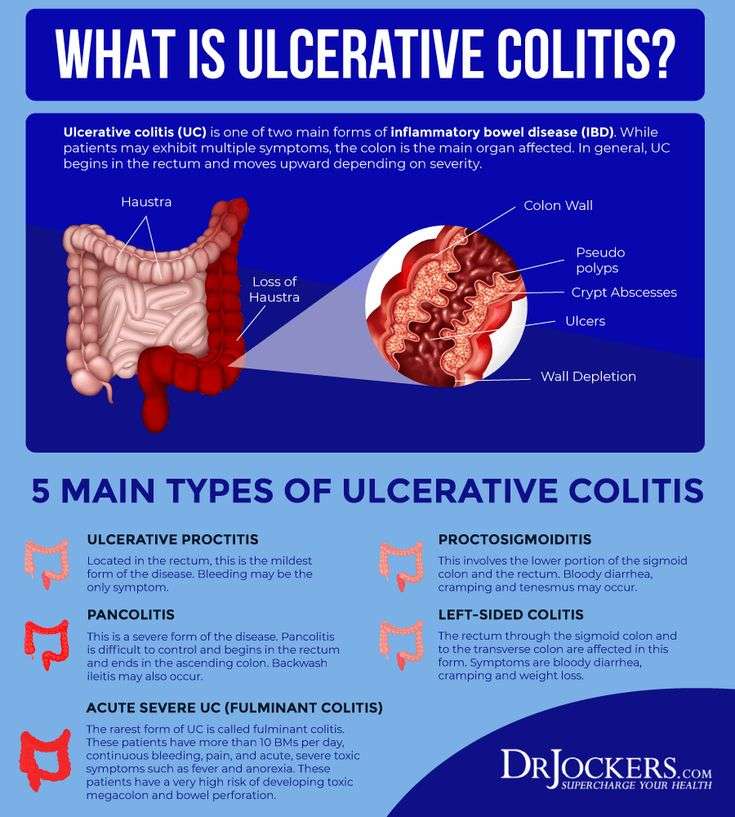
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
UC can be categorized according to the parts of the GI tract that it affects.
- Ulcerative proctitis. In ulcerative proctitis, only the rectum is inflamed. Its considered a mild form of UC.
- Left-sided colitis. Left-sided colitis causes inflammation in the area between the splenic flexure and the last section of the colon. The last section of the colon, known as the distal colon, includes the descending colon and sigmoid colon. Left-sided colitis is also known as distal ulcerative colitis.
- Proctosigmoiditis. Proctosigmoiditis is a form of left-sided colitis. It causes inflammation in the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Different tests can help a doctor diagnose UC. UC mimics other bowel diseases such as Crohns disease. A doctor will order multiple tests to rule out other conditions.
Tests to diagnose UC often include:
Read Also: How To Ease Stomach Ulcer Pain
What Is The Outlook
With modern medical and surgical treatment, there is just a slight increase in the risk of death in the first two years after diagnosis, compared with the general population. After this there is little difference in life expectancy from that of the general population. However, a severe flare-up of ulcerative colitis is still a potentially life-threatening illness and needs expert medical attention.
As mentioned, if you do not take medication to prevent flare-ups, about half of people with ulcerative colitis have a relapse on average once a year. This is much reduced by taking regular medication. However, even in those who take regular medication, some people have frequent flare-ups and about a quarter of people with ulcerative colitis eventually have an operation to remove their colon.
A year from diagnosis, about 9 in 10 people with ulcerative colitis are fully capable of work. So, this means that, in the majority of cases, with the help of treatment, the disease is manageable enough to maintain a near-normal life. However, the condition can cause significant employment problems for a minority.
Treatment for ulcerative colitis is an evolving field. Various new medicines are under investigation. These may change the treatment options over the next ten years or so and improve the outlook .
Is Ulcerative Colitis Curable
Currently, theres no nonsurgical cure for UC. Treatments for the inflammatory disease aim to extend periods of remission and make flare-ups less severe.
For people with severe UC, curative surgery is a treatment option. Removing the entire large intestine will end the symptoms of UC.
This procedure requires your doctor to create a pouch on the outside of your body where waste can empty. This pouch can become inflamed and cause side effects.
For that reason, some people choose to have only a partial colectomy. In this surgery, your doctor only removes the parts of the colon that are affected by UC.
While these surgeries can help ease or end symptoms of UC, they can have adverse effects and possible long-term complications. Read more about these issues to determine if surgery is an option for you.
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis And Bowel Obstruction
Do I Have An Increased Risk Of Cancer If I Suffer From Ulcerative Colitis
Unfortunately, yes. People with ulcerative colitis have a slightly elevated risk of developing colon cancer, and this risk increases with time:
- 2% risk after 10 years
- 8% risk after 20 years
- 18% risk after 30 years
Your risk also increases if:
- You have severe ulcerative colitis affecting large portions of the colon.
- Symptoms start at a younger age.
- You have a family history of colorectal cancer.
- You have developed swelling in the biliary tree called the primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Your doctor may suggest regular colon screenings via a colonoscopy. This is the only way to detect colon cancer in the early stages when it is still treatable. During a colonoscopy, a scope attached with a camera is inserted into the anus and moved upward, allowing your doctor to look for any suspicious masses in the colon or rectum.
Most doctors typically recommend colonoscopies every 1-3 years, starting 8 years after ulcerative colitis starts. If your doctor suspects that you may be at higher risk, they may recommend that you be checked on a more frequent basis.
Outlook For People With Ulcerative Colitis

If you have UC, a doctor will need to monitor your condition, and youll need to carefully follow your treatment plan throughout your life.
The only true cure for UC is removal of the entire colon and rectum. Your doctor will usually begin with medical therapy unless you have a severe complication that requires surgery. Some people will eventually require surgery, but most do well with nonsurgical therapy and care.
You May Like: Ulcerative Colitis And Colon Cancer Statistics
Indexed Through The National Library Of Medicine Pubmed Central And Embase
Disclaimer
This supplement is supported by an educational grant from Pfizer Inc. Support of this supplement does not imply the supporters agreement with the views expressed herein. Every effort has been made to ensure that drug usage and other information are presented accurately however, the ultimate responsibility rests with the prescribing physician. Gastro-Hep Communications, Inc., the supporter, and the participants shall not be held responsible for errors or for any consequences arising from the use of information contained herein. Readers are strongly urged to consult any relevant primary literature. No claims or endorsements are made for any drug or compound at present under clinical investigation.
Positioning Therapies In Uc
With the availability of several classes of biologics and targeted therapies with demonstrated efficacy in UC, positioning different agents in the treatment course of patients can be challenging.57 Although clinical practice guidelines effectively synthesize the evidence regarding efficacy and safety of these therapies, they offer limited guidance on choosing the optimal first- and second-line therapies for individual patients. Commenting on this, Dr Sandborn noted that All the tightening of the guideline process and adding other stakeholders doesnt solve the underlying problem, which is a lack of data to help distinguish what is similarly effective and what drugs you should use in what order. Such decisions require consideration of the advantages and limitations of each therapy in the context of patients values, preferences, and clinical circumstances. Beyond efficacy, key factors that may inform clinical decision-making include the rapidity of action, safety, safety in pregnancy, route of administration, effect on extraintestinal manifestations , and cost/access .58,59
Read Also: What Is An Ulcer In Your Mouth
What Should I Ask My Doctor On Behalf Of My Child Or Teenager
Ask your healthcare provider the following questions in addition to the ones listed above:
- What vitamins should my child take?
- Will my other children have pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child at risk for other conditions?
- Can you recommend a psychiatrist or therapist to help my child with emotional issues related to pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child growing at a normal rate?
- What can I do to help my child cope at school?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
When you have ulcerative colitis, its essential to work closely with your healthcare team.
Take your medications as prescribed, even when you dont have symptoms. Skipping medications youre supposed to take can lead to flareups and make the disease harder to control. Your best shot at managing ulcerative colitis is to follow your treatment plan and talk to your healthcare provider regularly.
What Are The Treatment Options For A Flare
When you first develop ulcerative colitis it is usual to take medication for a few weeks until symptoms clear. A course of medication is then usually taken each time symptoms flare up. The medicine advised may depend on the severity of the symptoms and the main site of the inflammation in the colon and the rectum .
Topical treatments applied locally by an enema or suppository are widely used for treating ulcerative colitis, particularly aminosalicylate and steroid medicines – see below. They are a treatment option if ulcerative colitis affects only the lower part of the bowel .
Medication options include the following:
Read Also: Where Are Stomach Ulcers Located
How Does Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Affect My Childs Mental/emotional Health
Like many conditions, ulcerative colitis can have a negative psychological effect, especially on children. They can experience physical, emotional, social and family problems. Because of the medications and/or general stress from the situation, your child may experience:
- Mood swings.
- Worry about appearance and physical stamina.
- Vulnerability because their body doesnt function normally.
- Poor concentration.
- Misunderstandings with friends and family.
Children need mutual support from all family members. Its helpful for the entire family to learn about the disease and try to be empathetic. Seek out a psychiatrist and therapist to help your child manage such challenges of their ulcerative colitis.
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis And What Causes It
Colitis can develop at any age, but usually first appears in people aged 15 to 30.
Experts are not sure why UC or Crohn’s disease occurs in some people. It may be due to a combination of genetic, environmental and infectious factors that cause a fault in the immune system leading to inflammation of the bowel.
Read Also: Can Stomach Ulcers Cause Bloating
Inflammation Of The Rectum
Symptoms may be different if a flare-up only affects the rectum and not the colon. You may have fresh bleeding from the rectum and you may form normal stools rather than have diarrhoea. You may even become constipated further up in the unaffected higher part of the colon but with a frequent feeling of wanting to go to the toilet.
What About Network Meta

Principles of network meta-analysis.9
After the quality of the evidence is assessed, recommendations are developed and graded to differentiate those based on strong evidence from those based on weak evidence.5 This information is intended to provide the user with an estimate of the groups confidence that following the recommendation will produce the desired health outcome.7 As with levels of evidence, many classification schemes have been developed for grading recommendations. The GRADE approach is commonly used to grade the strength of recommendations and has been adopted as the standard by many guideline developers and organizations, including the AGA and the ACG.4,11,12 The GRADE approach typically scores the strength of recommendations as either strong or weak, also known as conditional or discretionary.2,6 While the GRADE approach acknowledges that expertise is required to interpret any form of evidence, it considers that opinion is an interpretation ofrather than a form ofevidence.6
Once recommendations are developed and graded, the guidelines are then made available for public policy evaluation. This step is critical, Dr Feagan pointed out, because there is no point in having guidelines if they cant be implemented. Lastly, the guidelines are submitted for peer review and published.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test For Ulcers
Treatment By Disease Severity And Location
Mild-moderate distal colitis
- Oral aminosalicylates, topical mesalamine, or topical steroids
- Combination of oral and topical aminosalicylates is better than either alone
For refractory cases, oral steroids or IV infliximab can be used
Mild-moderate extensive colitis
- Oral sulfasalazine 4-6 g/day or alternative aminosalicylate 4.8 g/day
- Oral steroids for patients refractory to above therapy + topical therapy
- 6-MP or azathioprine for patients refractory to oral steroids, but not so severe as to require IV therapy
- Infliximab in patients who are steroid refractory/dependant on adequate doses of 6-MP/thiopurine or who are intolerant to these medications
Severe colitis
- Infliximab if urgent hospitalization is not needed
- If patient is toxic, should be admitted to the hospital for IV steroids
- Failure to improve in 3-5 days is indication for colectomy or IV cyclosporine
Indications for Surgery
- Absolute: Hemorrhage, perforation, documented or strongly suspected cancer
Also, surgery is recommended for severe colitis refractory to medical therapy
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medicine, such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. But more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital.
If medicines are not effective at controlling your symptoms or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
During surgery, your small intestine will either be diverted out of an opening in your abdomen or be used to create an internal pouch that’s connected to your anus called an ileoanal pouch.
Also Check: Difference Between Colon Cancer And Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms