Geriatric Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
There are some differences in how ulcerative colitis appears in new cases diagnosed at age 60 and beyond compared to those cases diagnosed in the first few decades of life.
Younger people who are diagnosed with ulcerative colitis usually experience more small bowel and upper gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea. Older people diagnosed with ulcerative colitis often like anemia and weight loss. Another consistent sign of UC is chronic inflammation of the colon.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Ulcerative colitis is a systemic disorder with no cure. The disorder has numerous extraintestinal involvement in addition to the colon. Thus, it is best managed by an interprofessional team. All patients with the disorder need lifelong monitoring. Because of the risk of colorectal cancer, surveillance colonoscopy should occur every 1-2 years. Further, since patients are often treated with biological agents, they need to undergo screening for melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer.
The pharmacists should assist the team by educating the patient on the importance of medication compliance to avoid relapse. The nurse should encourage regular vaccinations, hand washing, and cancer screening. A dietary consult should be obtained to educate the patient on foods to eat and what not to eat, especially if they have a stoma. In addition, a stoma nurse should be involved in the teaching of stoma care.
An infectious disease nurse should monitor the patient in the outpatient setting to ensure that they are not immunocompromised. Social workers should be involved to ensure that the patient has ample support and finances so that the treatments are not missed. Patients with risk factors for osteoporosis need screening for bone mineral density periodically. Patients should be encouraged to undergo annual vaccination against influenza and pneumococcus. Finally, many patients with ulcerative colitis develop depression and anxiety and should be referred to a mental health counselor.
Outcomes
How Do I Know I Have Sacroiliitis
Pain is the main symptom of sacroiliitis. You’ll feel it in your lower back, buttock, hip, or thigh. Sometimes the pain might spread down your leg and even to your feet.
Back pain can also be a sign of an injury. The difference is that sacroiliitis pain typically lasts for more than 3 months. It’s worse when you first wake up in the morning, and it improves when you move.
If you have lower back pain that’s not getting better, see a rheumatologist. Thatâs a specialist who diagnoses and treats arthritis. The doctor will do a physical examination and press on parts of your lower back, hips, or legs to find the painful areas.
Another way to diagnose sacroiliitis is with imaging tests like X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging , or computed tomography . These scans will show if you have any problems in your sacroiliac joint.
Signs of sacroiliitis could show up on an X-ray even before you have any symptoms. Or the doctor might find sacroiliitis accidentally on a CT to check your IBD.
Recommended Reading: How Do They Test For Ulcers
Effects Of Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Every person responds differently to IBD. The severity of symptoms will vary from time to time and from person to person. IBD is not a progressive disease . Rather, flare-ups can range from mild to severe and back to mild again. Some people will experience periods of relief from symptoms in between flare-ups.We cannot predict how long a person will stay free from symptoms, or when their next flare-up will occur. Some flare-ups settle down quite quickly with treatment. Other times, it may take months for a persons symptoms to respond to treatment.IBD interferes with a persons normal body functions. Signs and symptoms can include:
- pain in the abdomen
- delayed or impaired growth in children.
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
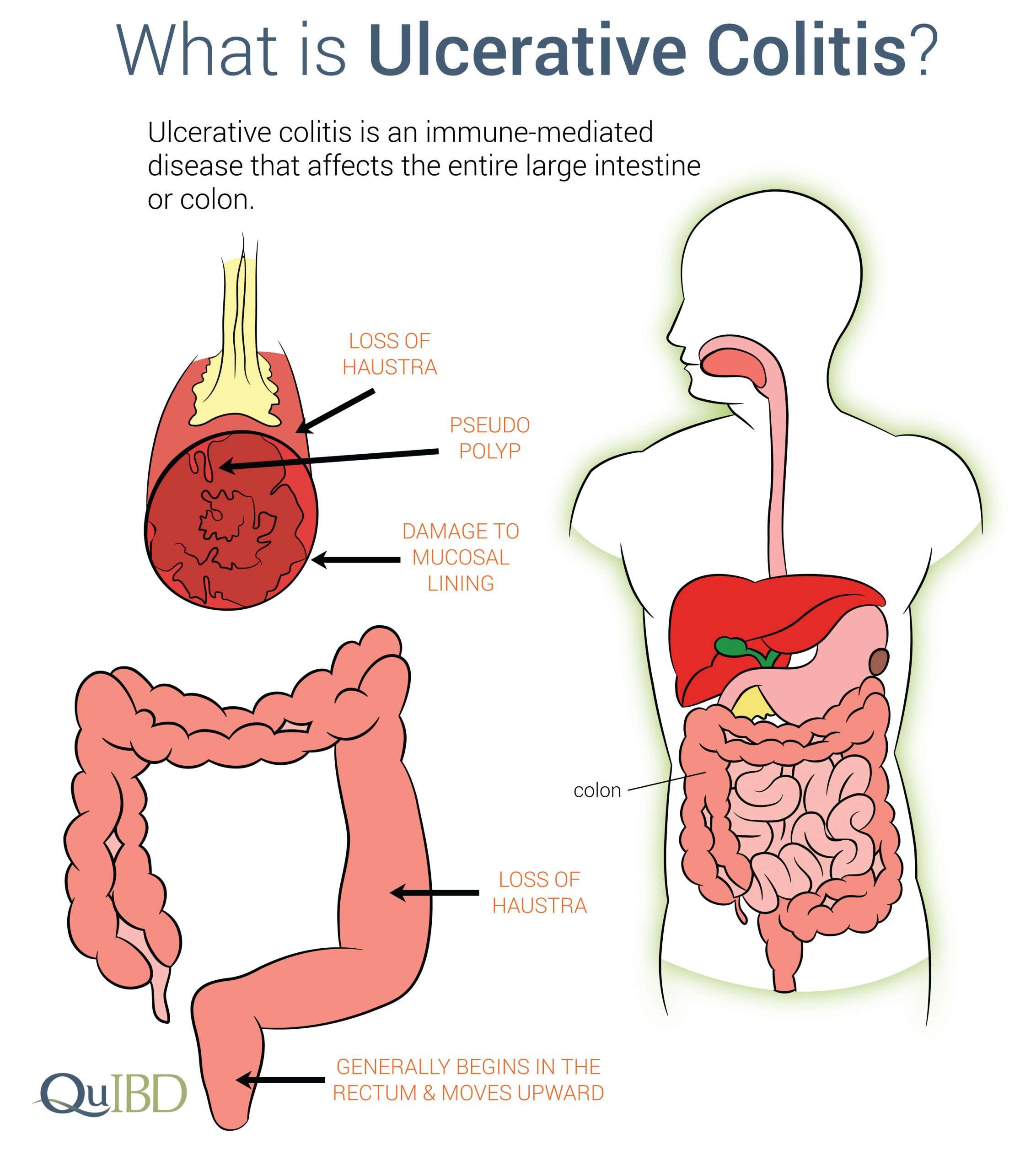
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Don’t Miss: Ulcerative Colitis Shortness Of Breath
What Else Should I Know About Ulcerative Colitis
Poor appetite, diarrhea, and poor digestion of nutrients can make it hard for teens with ulcerative colitis to get the calories and nutrients the body needs. Be sure to eat a variety of foods, get plenty of fluids, and avoid foods that make your symptoms worse. Some teens may need supplements, like calcium or vitamin D. Someone who isn’t growing well may need other nutrition support.
Perforation Of The Colon
Chronic inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis can weaken the wall of the colon until a hole, or perforation, develops. Once the colon has been perforated, the contents of the intestine can spill into the abdomen and cause a serious infection called peritonitis.
This is a potentially life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical treatment.
Also Check: What To Put On Leg Ulcers
Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis
Current therapies to treat patients with ulcerative colitis include aminosalicylates , steroids, immune suppressants, and biologic therapy . For some of these drugs, treatments are available in pill form, suppositories, enemas, injections under the skin, and intravenous infusions. Although medical treatment can be effective in controlling the symptoms of ulcerative colitis, patients must take medications continuously to prevent the symptoms from returning.
Although some patients require a ileostomy after colectomy, another surgical procedure can be performed in many patients later to reverse the ostomy called a restorative proctocolectomy or J pouch. This procedure allows patients to have bowel movements without an ostomy.
There have been many advances in surgery for ulcerative colitis. The most significant are development of restorative proctocolectomy and use of minimally invasive surgery .
What Should You Eat When You Have Ulcerative Colitis
When it comes to food, theres no known dietary cause of ulcerative colitis, but different foods may aggravate or help limit symptoms of the disease.
Youre more likely to need to change your diet during periods of active disease , when eating soft, bland foods can help limit symptoms like cramping and diarrhea.
During flares, you may also want to avoid or limit high-fiber and high-fat foods, as well as caffeine, alcohol, dairy products, and spicy foods.
If youre losing nutrients and water in your diet due to diarrhea, you may need to focus on increasing your fluid intake and getting enough calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals from foods or supplements.
Learn More About Diet and Ulcerative Colitis
Don’t Miss: Can Stomach Ulcers Cause Blood In Your Stool
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
Researchers think the cause of ulcerative colitis is complex and involves many factors. They think its probably the result of an overactive immune response. The immune systems job is to protect the body from germs and other dangerous substances. But, sometimes your immune system mistakenly attacks your body, which causes inflammation and tissue damage.
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Stage 4 Sacral Ulcer
Severity Of Ulcerative Colitis
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis tend to come and go throughout a persons life. In fact, the Crohns & Colitis Foundation estimates that during the year:
- 48 percent are in remission
- 30 percent face mild disease
- 20 percent face moderate disease
- 1 percent to 2 percent have severe disease
Also, 70 percent of those with active UC will go through another episode the following year. Thirty percent of those in remission in a given year will live through a flare in the next year. This means that the longer a person with UC stays in remission, the less likely they will have flares.6
What Are The Risk Factors Of Ulcerative Colitis
The cause of ulcerative colitis is unclear, but its thought that a combination of genetics and environmental factors are at play. Up to 20 percent of people with ulcerative colitis have a parent, sibling or child with the disease.
Ulcerative colitis is more common for people living in urban, industrialized areas compared to undeveloped countries, which indicates that highly refined diets may play a role. Although all ethnic groups are affected, the problem is most common among Caucasians and people of Eastern European Jewish descent.
Lastly, there appears to be a connection to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Its not that these medications cause the disease but, because they inflame the bowel, they can worsen symptoms. This category of medication includes ibuprofen , naproxen sodium and diclofenac sodium .
Read Also: How Do You Heal An Ulcer
Ulcerative Colitis Causes And Risk Factors
Ulcerative colitis happens when your immune system makes a mistake. Normally, it attacks invaders in your body, like the common cold. But when you have UC, your immune system thinks food, good gut bacteria, and the cells that line your colon are the intruders. White blood cells that usually protect you attack the lining of your colon instead. They cause the inflammation and ulcers.
Doctors arenât sure why people get the condition. Your genes may play a role the disease sometimes runs in families. Other things in the world around you may make a difference, too.
Things that can affect your risk of getting ulcerative colitis include:
- Age. Itâs most likely if youâre between 15 and 30 years old or older than 60.
- Ethnicity. The risk is highest in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
- Family history. Your risk could be up to 30% higher if you have a close relative with the condition.
Food and stress donât cause it, but they can trigger a flare of symptoms.
What’s The Link With Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis causes swelling and sores in the lining of the large intestine. But it also can affect other parts of your body, like your joints, skin, lungs, or eyes.
Doctors call these extraintestinal symptoms, meaning they happen outside of your intestines. Sacroiliitis and other types of joint damage are the most common extraintestinal signs of IBD.
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Ulcerative Colitis
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis causes irritation and ulcers in the large intestine . It belongs to a group of conditions called inflammatory bowel disease . It often causes diarrhea with blood, cramping and urgency. Sometimes these symptoms can wake a person up at night to go to the bathroom as well.
The inflammation in ulcerative colitis usually starts in the rectum, which is close to the anus . The inflammation can spread and affect a portion of, or the entire colon. When the inflammation occurs in the rectum and lower part of the colon it is called ulcerative proctitis. If the entire colon is affected it is called pancolitis. If only the left side of the colon is affected it is called limited or distal colitis.
The severity of UC depends on the amount of inflammation and the location. Everyone is a little different. You could have severe inflammation in the rectum or very mild inflammation in the entire colon .
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may notice a pattern of flare-ups , when symptoms are worse. During times of remission, you might have little to no symptoms. The goal with therapy is to remain in remission as long as possible .
Does Ulcerative Colitis Make You Immunocompromised
Ulcerative colitis doesnt make you immunocompromised. Some of the medicines that treat it may change the way your immune system responds. This change is different for each medication. Some of these changes may increase the risk of certain infections or other issues. A discussion with your health care team before starting a medication is the best way to understand these risks and ways to prevent them.
Don’t Miss: Best Way To Treat Ulcers In Horses
How Can I Find Support After An Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosis
When taking care of your physical well-being, dont forget that ulcerative colitis can take a toll on your emotional and mental well-being too. If it turns out your symptoms are ulcerative colitis, you can find a support group, or ask your doctor if they can connect you with a therapist or G.I. psychologist. Dr. Riehl, for example, works with patients on aspects of body image and even connects them with other patients who have experienced colectomy or ostomy . We talk openly about the impact that it can have on them from an intimacy perspective to how it impacts their self-identity, she says.
Since ulcerative colitis often starts at an age when people are thinking about their first job or starting a family, it can be particularly tough. One of the reasons that I and several of my colleagues went into this field is precisely because of thatso that we can hopefully make a difference in peoples lives early, and have them be able to lead productive and complete lives by putting their disease in remission, Dr. Sinha says.
What To Expect After Your Surgery
Most people do very well after their surgery and are able to return to work and their normal daily activities after they recover.
-
You should expect an adjustment period of up to one year to get used to the changes in your body after your proctocolectomy.
-
You will likely be on liquid or soft food diet for the first few days after surgery. Your doctor will then have you slowly introduce bland solid foods. You should chew your food thoroughly and avoid any foods that may cause gas, diarrhea or anal irritation. Its also important to drink plenty of water. We recommend six to eight glasses a day.
-
Some patients may still feel as if they need to have a bowel movement after their surgery, just as people who have lost a limb sometimes still feel as if the limb is still there. This called phantomrectum and it completely normal. It does not require any treatment and often subsides over time.
-
Your doctor may recommend a physical activity restriction for a minimum of six weeks, depending on what type of surgery you had.
-
Talk to your doctor about resuming normal sexual activity after your surgery. Some people find their sex life improves some time after surgery due to improvements in pain, inflammation, and other ulcerative colitis symptoms.
You May Like: Foam Dressings For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
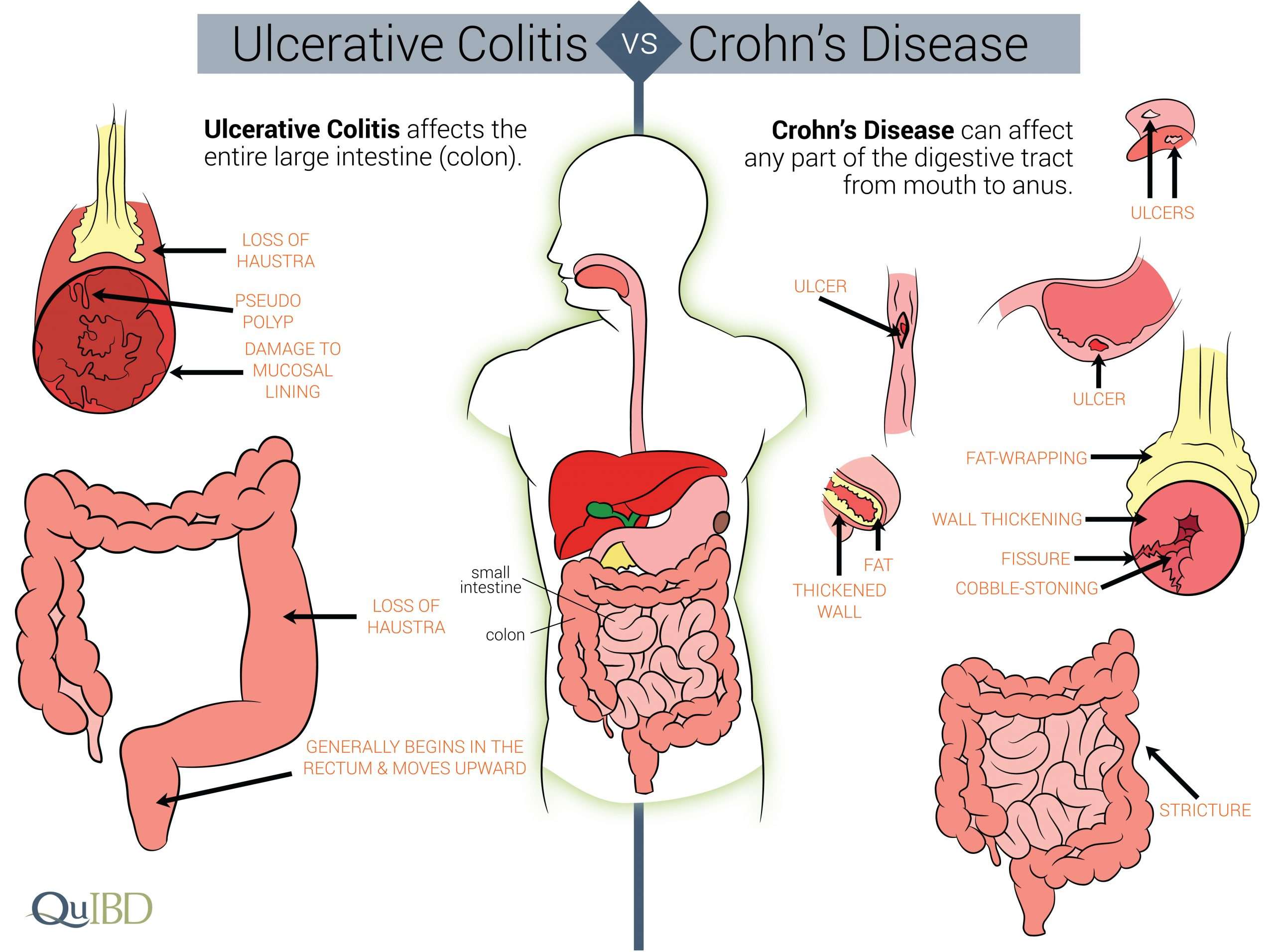
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease
The list of symptoms for ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are very similar, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding. The biggest difference can be found in the location of the active inflammation. Since Crohns can appear anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, you might see things like inflammation of the small bowel that you wouldnt see with ulcerative colitis. Another difference is that Crohns doesnt stop at the intestine lining. It can actually affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall.6
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medicine, such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. But more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital.
If medicines are not effective at controlling your symptoms or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
During surgery, your small intestine will either be diverted out of an opening in your abdomen or be used to create an internal pouch that’s connected to your anus called an ileoanal pouch.
Recommended Reading: Can I Take Tylenol With An Ulcer
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease Similar
- Both diseases often develop in teenagers and young adults although the disease can occur at any age
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease affect men and women equally
- The symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are very similar
-
The causes of both UC and Crohn’s disease are not known and both diseases have similar types of contributing factors such as environmental, genetic and an inappropriate response by the body’s immune system
Things No One Tells You About Life With Ulcerative Colitis
People who have never experienced ulcerative colitis may think it means getting the occasional bad stomachache or having a fussy gastrointestinal system. But as anyone with ulcerative colitis knows, the effects of this inflammatory bowel diseasein which sections of the large intestine develop inflammation and ulcerscan be severe and disrupt many aspects of your life. After a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis, it can be incredibly hard to navigate the reality of your new normal. Knowing the following seven facts about life with ulcerative colitis might help make the whole experience a little bit easier.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Gum Ulcers
Fatigue From Ulcerative Colitis Can Be Brutal
Exhaustion from ulcerative colitis can be so severe its hard to get through day-to-day life. For Sam, fatigue was one of the first signs that something was wrong. I’m usually a pretty energetic person, she says. I like running every day, things like that. And I just couldn’t do it anymore.
After developing ulcerative colitis, you might have to be more careful than youre used to about how you use your energy. Some days I’m just hit with a truck of fatigue, Skomski says. So I always give myself an out. If I have plans with friends or we’re going out of town, Ill tell the other people, I might not feel good and we might have to reschedule.
Sam has had to have similarly frank conversations about the fact that her energy can take a major dip sometimes. I’ve had to teach everyone around me that it doesn’t mean I’m mad at them, it doesn’t mean I’m not happy, she says. It’s just that I have a very concrete amount of energy that day.