Microscopic Colitis Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
People with celiac disease have an increased incidence of microscopic colitis and inflammatory bowel disease . Microscopic colitis is an inflammation of the colon, or large intestine. Crohns disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract.
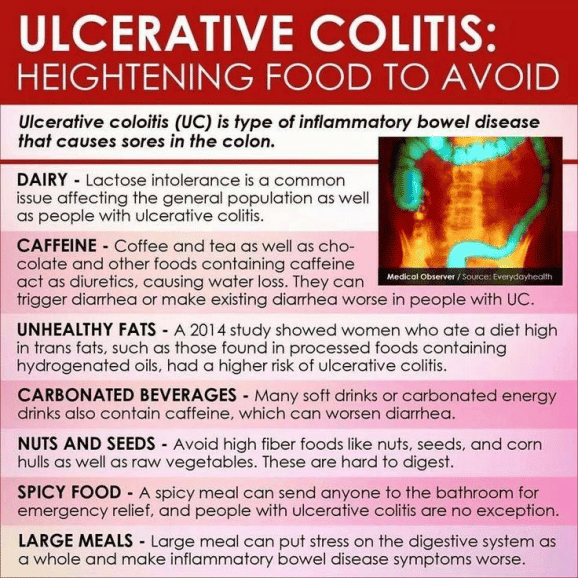
Ulcerative colitis is type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes sores in the colon. A colonoscopy is required to diagnose these.
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic type of inflammatory bowel disease , like Crohns disease and microscopic colitis that affects the colon .
Recent studies estimate that IBD affects 2 million people worldwide .
Ulcerative colitis causes inflammation and sores in the inner lining of the colon. Inflammation often begins in the rectum, but it can spread throughout the large intestine.
Summary: Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and sores in the colon.
Eating When You Are In Remission
While theres no cure for UC, you may experience periods of remission. During this time, youll be symptom-free and your UC wont interfere with your daily life.
Theres no definitive way to avoid flare-ups forever, but you can prolong your remission periods by maintaining a diverse and nutrient-rich diet that does not include trigger foods.
To stay symptom-free, it may be helpful to follow one of the diets that other individuals with UC find successful, as well as introduce new foods slowly and stay hydrated.
However, its important to consult with your doctor or dietician before making any changes to your diet.
Some foods that may help keep you feeling good and hydrated during remission
Recommended Reading: High Dose Remicade For Ulcerative Colitis
What Should I Eat
Its not always easy knowing what foods best fuel your body, especially when you have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Your diet and nutrition are a major part of life with inflammatory bowel disease , yet there is no single diet that works for everyone.
Nutrition affects not just your IBD symptoms, but also your overall health and well-being. Without proper nutrients, the symptoms of your Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis can cause serious complications, including nutrient deficiencies, weight loss, and malnutrition.
We have several tips for a healthy diet thats well-balanced and nutrient rich. These tips are for educational purposes only. You should work with your doctor or a dietitian specializing in IBD to help you develop a personalized meal plan.
Watch our with Emily Haller, registered dietitian at Michigan Medicine! Tune in to hear Emily review diet facts, debunk myths, speak about restrictions, and highlight ongoing research.
Girls With Guts Retreat Registration

The Girls With Guts organizations annual retreats are an opportunity for adult women with UC to create friendships and learn about different ways to improve their lives emotionally, mentally, and physically. These events can be life-altering for a lovely lady living with UC. The retreat usually goes from a Friday through Monday and allows the attendees to connect, learn, and share their stories with each other. Registration ranges in price but hasnt gone above $300 in years past.
Also Check: Can Ulcers Cause Blood In Urine
Foods That May Fight Uc
Some research shows that certain nutrients may help fight the irritation and swelling in your gut caused by UC. Scientists have studied how linoleic acid affects people with the condition. Although everyone needs this “good” fat, donât overdo it, since there is some evidence it may play a role in inflammation if you get too much.
Other studies show that an omega-3 fatty acid called EPA may fight inflammation. This is another âgoodâ fat that blocks certain chemicals in your body called leukotrienes. Fish oil is a good source of EPA. In some studies, folks with UC saw some benefits when they took high doses. Many people, though, didn’t like the fishy taste. There is also some evidence that adding fish oil to aminosalicylates may be helpful, but this isnât proven. DHA is another omega-3 found in fish oil that can fight inflammation and is used by some people with UC.
Some research also shows that yogurt with gut-healthy bacteria, called probiotics, eases inflammation. Scientists are still studying how they may help people with UC and similar conditions. Some people also believe that a diet low in FODMAPs — a type of highly-fermentable carbs found in meats, fruits, dairy, and lots of other foods — may help ease UC symptoms. But the evidence is unclear if it does. And without close monitoring, any diet that restricts certain foods may lead to poor nutrition and other problems.
Show Sources
An Ulcerative Colitis Diet: Summarizing The Evidence
Despite many reports online that certain diets or supplements can cure ulcerative colitis, the only known cure is total removal of the colon and rectum.
Those with digestive symptoms during remission may find relief from a low FODMAP diet to identify trigger foods.
A semi-vegetarian diet has also shown promise in maintaining remission in Crohns disease and may be helpful for ulcerative colitis, but we cannot make firm conclusions.
Even without following elimination diets, certain patterns have been shown to reduce symptoms:
- A diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables provides fiber and antioxidants, which are linked to lower disease risk. Reducing intake of high-fiber fruits and vegetables may increase comfort during flares.
- Limiting dietary fat, especially fatty meats, may be beneficial.
- Certain probiotics are helpful in bringing about and maintaining remission. Ask your doctor for a recommendation.
- A few herbal supplements show promise but lack sufficient scientific evidence to support their use.
- Avoid foods that irritate the gut during flares, including fatty foods, caffeine and alcohol.
A registered dietitian can help you identify foods that trigger your symptoms and design a well-balanced meal plan.
You May Like: Ulcer In Colon Found In Colonoscopy
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Studies were included in the qualitative synthesis when: there was an RCT design there was a comparison of at least one treatment using a FODMAP elimination diet to a non-FODMAP elimination scheme, sham or usual diet, or placebo the study included patients with IBD in remission where an FGD was diagnosed without any restrictions concerning the age of participants or the intervention duration published at any date until April 2020.
Exclusion criteria were: studies without an RCT design studies performed on animals or on patients with other diseases as well as IBD studies which included IBD patients who were not in remission or did not have FGD studies using interventions other than a LFD studies comparing a FODMAP elimination diet to other FODMAP elimination schemes studies lacking a comparator or using a one group cross-over design.
Low Fodmap Diet For Colitis
It can be embarrassing to talk about your bowel movements. And so many people suffer from loose stools now and then, that you may not see it as a great health issue. However, if you start to see blood or pus in your stool during bowel movements, then it could be something more serious. As of 2015, about 1 in 100 adults suffer from inflammatory bowel disease , which can be either Crohns disease or colitis. Colitis is an inflammatory disease of the large intestine that can worsen over time if left untreated. Therefore, lets talk about what colitis is, how it can be treated, and if the low FODMAP diet could help.
What is colitis?
Colitis, also known as ulcerative colitis , is a condition where the large intestine becomes chronically inflamed. The most common symptom of colitis is bloody diarrhea or loose stools with pus in it. Other signs and symptoms of colitis include:
- Urgent need to have bowel movements
- Anemia, or a low level of red blood cells in the blood
Early stages of colitis may only have mild to moderate symptoms. Bu as the disease progresses, symptoms may become more severe such as frequent bloody stools, fever, and severe abdominal cramping. These more severe symptoms are only seen in about 1 in 10 of people in the early stages of colitis.
Colitis treatment
The low FODMAP diet and colitis
Take home message
-written by Staci Gulbin, MS, MEd, RD at LighttrackNutrition.com
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis Joint Pain Treatment
Overview Of Uc And Causes
UC is a chronic condition of the gastrointestinal tract . It is a form of inflammatory bowel disease , causing inflammation, irritation, and sores, referred to as ulcers, in the innermost lining of the large intestine and rectum.
While the cause of UC is unknown, experts believe that changes in the gut microbiota and abnormal immune responses in the gut may UC. Genes also play a role since having first degree-relatives is the highest risk factor for IBD.
Environmental factors can IBD risk at an individual level, such as diet. They may also be factors that modify the risk to entire populations, such as air pollution or UV light exposure.
While diet does not directly cause UC, certain foods can trigger or worsen UC symptoms.
For more research-backed information about the microbiome and how it affects your health, please visit our dedicated hub.
What Types Of Diets Should I Consider
Both experts agree that everyones ulcerative colitis symptoms, triggers, and treatments are different, but there are certain eating styles that may be worth considering.
Talk with a health professional about whether one of these diets could be beneficial for you.
FODMAP is an acronym for types of carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine, specifically:
Some health care providers may counsel their patients to try a FODMAP elimination diet during an UC flare, followed by reintroduction of FODMAP foods once in remission.
What does that mean for actually eating food? Well, you may want to try swapping high-FODMAPs like cauliflower, mushrooms, dried fruit, cows milk, and legumes for low-FODAMPs like eggplant, carrots, grapes, potatoes, eggs, quinoa, and tofu.
The Mediterranean diet is widely considered to be one of the worlds healthiest eating patterns for people with and without chronic conditions.
Characterized by a high consumption of fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fatshello, olive oil and fish the Mediterranean diet has been linked with increased diversity of the gut microbiome9. Good news for people with IBD, since diversity in the gut bacteria could help to ease symptoms.
While you may have heard of the paleo diet, the autoimmune protocol diet , which is considered to be similar to the paleo diet, may have some benefits for people with IBD.
Also Check: Push Score For Pressure Ulcers
Research In The Pipeline
Table 5 details all ongoing RCTs registered in Clinicaltrials.gov, examining the efficacy of the LFD on patients with IBD. Three trials in total, implemented in Mexico , Iran , and Denmark , have results pending to be published. All trials have both subjective and objective outcomes, with intervention duration ranging between 4 and 10 weeks.
Characteristics Of The Trials
Out of 4862 records in total, four RCTs fulfilled the protocolâs criteria . Table 1 details the characteristics of the included trials. The Halmos et al. trial originated in Australia , the Cox et al. RCT was conducted in the UK , the Bodini and associates trial was Italian-based , and the Pedersen et al. RCT was implemented in Denmark . The trial of Pedersen et al. had open-label masking, and the Bodini and Cox RCTs were single-blind. The trial of Halmos et al. reported only participant blinding in the manuscript text , while referencing a previous study performed using double-blind masking , although the principle diagnoses of participants between the two studies failed to match. Only the Halmos et al. RCT adopted a cross-over design and the remaining trials compared parallel interventions .
PRISMA flowchart of the randomized controlled trials selection process. CENTRAL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials IBD, inflammatory bowel disease IBS, irritable bowel syndrome FODMAP, Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Monosaccharides, and Polyols PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses RCT, randomized controlled trial.
You May Like: Things Not To Eat With A Stomach Ulcer
Eating When You Are In A Flare
There are certain foods you may want to avoid when you are in an IBD flare, and others that may help you get the right amount of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals without making your symptoms worse.
Your healthcare team may put you on an elimination diet, in which you avoid certain foods in order to identify which trigger symptoms. This process will help you identify common foods to avoid during a flare. Elimination diets should only be done under the supervision of your healthcare team and a dietitian so they can make sure you are still receiving the necessary nutrients.
Some foods may trigger cramping, bloating, and/or diarrhea. Many trigger foods should also be avoided if you have been diagnosed with a stricture, a narrowing of the intestine caused by inflammation or scar tissue, or have had a recent surgery. Certain foods can be easier to digest and can provide you with the necessary nutrients your body needs.
Best Gifts For People Living With Ibd
You may wonder what would be a good gift for someone with inflammatory bowel disease . Anything that would help them live more comfortably, or maybe ease a symptom such as pain or fatigue, would be welcome in most cases. Either that or a fun distraction that can be enjoyed by someone who might be housebound or does not have a lot of energy is also a good idea. Here are some gift ideas for people who have IBD.
Read Also: Infusion Medication For Ulcerative Colitis
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If Your Horse Has Ulcers
Back Up: What Is Ulcerative Colitis Exactly
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes ulcers and sores in the lower quarter to third of your digestive tract. Typically, these ulcers are found in your rectum or in the inner lining of your lower intestine . This can cause bloody diarrhea, the most common symptom of ulcerative colitis, but you might also experience things like abdominal cramping, constipation, and a general sense of fatigue. Weight loss and a loss of appetite can also crop up, per the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Diana Whitehead, M.D., director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center at the Greater Baltimore Medical Center, explains that though ulcerative colitis has a strong genetic component, symptoms are often set off by a triggering event that activates inflammation in the lower intestine. Basically, your immune system is not doing what it should do, which is to protect you, but its gone kind of into overdrive, Dr. Whitehead says. In other words, even though the exact causes of ulcerative colitis arent fully understood, experts consider it to be an autoimmune condition thats set off by this overreaction in the gut.
What Foods Should I Avoid
Certain foods can exacerbate UC flares, but everyone has different trigger foods. For some, it might be a juicy burger and for others, it could be their morning latte.
In general, inflammatory foods, like fast food, processed food, alcohol, and sugary drinks contribute to the development of flares, says Dr. Singh. Freuman adds that saturated fat, specifically, can be an issue for certain people. Foods that contain significant amounts of saturated fat include:
- Whole-milk dairy, such as cheese, cream, butter, and full-fat yogurt
Lactose is the sugar present in milk and dairy products, and lactase is the enzyme people need to break down those sugars during digestion. If someone is lactose-intolerant, it means they dont produce enough lactase to break down the sugars, which can cause cramps, bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
To complicate matters, UC is sometimes coupled with lactose intolerance. But lactose intolerant dairy lovers, take heart: Its often possible to still consume dairy with lower lactose content, like cottage cheese and yogurt. Because these products contain live cultures that produce their own lactase, your body doesnt have to do all the work to break down lactose5.
Thats a win-win, since dairy foods provide important nutrients, like calcium and vitamin D, to your diet. In fact, avoiding them completely is not recommended unless 100% necessary.
Recommended Reading: Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer Pictures
What To Eat In Remission
When in remission, a person will not have symptoms. While there is not always a way to avoid them from returning, a person may prolong the state of remission.
A person will benefit the best from a diverse and nutrient-rich food source. Foods to consider include:
- high fiber foods, unless the personâs doctor says otherwise
- healthy fats such as nuts, seed butter, and olive oil
Effects On Gut Microbiota
Table 4 details all changes in fecal bacteria abundance following the LFD intervention compared with the control diet. No differences were noted in the total species abundance or the total Bifidobacteria sp. in either trial where this was studied . Cox et al. showed no differences in the gene count, phyla distribution, α and β-diversity, nor in targeted Bifidobacteria including animalis, bifidum, breve, and pseudocatenulatum species. On the other hand, a reduction in the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium adolescentis, dentium, and longum was recorded in the LFD group compared with the controls . The Halmos and Cox RCTs were unable to reach a unanimous finding concerning the total Faecalibacterium prausnitzii abundance post LFD intervention. Finally, Halmos and associates suggested a reduction in the absolute and relative fecal content of Clostridium cluster XIVa, Akkermansia muciniphila, and the relative abundance of Ruminococcus torques following the LFD, and a lack of significant difference concerning Roseburia, Lactobacilli sp., Ruminococcus gnavus, and Clostridium cluster IV.
You May Like: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Positive Ana
Grains To Eat And Skip
Love bread, pasta, cereal, and crackers? Sorry. Foods made with wheat, barley, and rye are off-limits on a low FODMAP diet. What can you have instead? Try quinoa, rice, millet, and cornmeal. You can also enjoy many gluten-free breads and pastas. Just check the label for any high-FODMAP ingredients like onion or honey.