Foam Dressings For Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
@article, author=, journal=, year=, volume=, pages=}
- The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
- The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
- The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
- View 1 excerpt, cites background
- Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology
The Management Of A Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcer Using Activheal Phmb Foam
Diabetic foot infection may lead to serious complications so prevention and effective management of wound infection is a high priority for clinicians. Antimicrobial-impregnated wound dressings may reduce the risk of infection and even treat mild infections. Polyhexamethylene Biguanide has recently been added to wound care products as an alternative to silver or honey. This case study evaluates the effectiveness of the Activheal® PHMB foam dressing in the management of an infected plantar neuropathic foot ulcer.
The International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot has reported that as many as 50% of people with diabetes will have significant peripheral neuropathy and at-risk feet. Nerve dysfunction in people with diabetes can affect three different types of nerves in the lower legs and feet, namely the sensory nerves, motor nerves and autonomic nerves. Sensory neuropathy is a major risk factor for developing diabetic foot ulcers approximately 4560% of diabetic foot ulcers are due to sensory neuropathy . The loss of protective sensation can increase the risk of trauma or injury to the foot .
This case study will explore the management of a neuropathic diabetic plantar foot ulcer using ActivHeal PHMB foam.
Are you a healthcare professional? This website is for healthcare professionals only. To continue, please confirm that you are a healthcare professional below.
Treating An Infected Ulcer
An ulcer sometimes produces a large amount of discharge and becomes more painful. There may also be redness around the ulcer.
These symptoms and feeling unwell are signs of infection.
If your ulcer becomes infected, it should be cleaned and dressed as usual.
You should also elevate your leg most of the time. Youll be prescribed a 7-day course of antibiotics.
The aim of antibiotic treatment is to clear the infection. But antibiotics do not heal ulcers and should only be used in short courses to treat infected ulcers.
Read Also: How To Treat An Ulcer After Gastric Bypass
You May Like: Blood Clots In Stool With Ulcerative Colitis
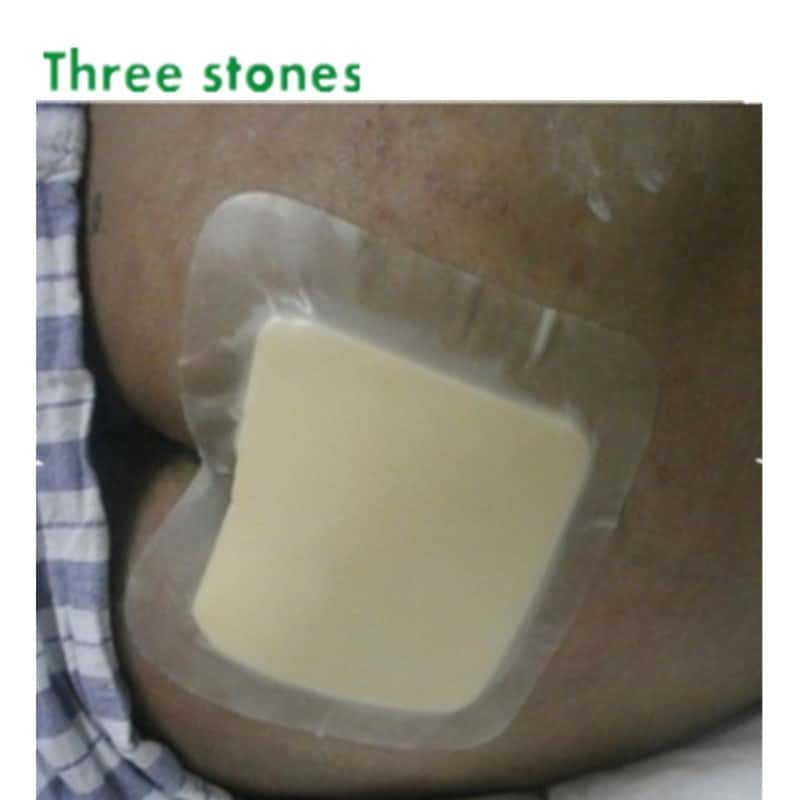
What Is A Foam Dressing
Foam dressings are absorbent, non-adherent padded wound dressings that absorb moisture and provide a barrier from environmental contaminants while protecting intact skin from damage related to pressure and friction.
Foam dressings are made up of fibers with small open cells that form an absorbent, sponge-like material. These open cells draw up drainage and debris from the wound bed, promoting a moist healing environment for natural healing.
Foam dressings are non-adherent and provide thermal insulation while acting as a protective cushion over the healing wound bed. These dressings allow water vapor across the surface of the wound, but block fluids, bacteria, and other contaminants from entering.
You May Like: How Do You Know Have Diabetes
What You Need To Know
-
The cornerstone of treatment for venous leg ulcers is compression therapy, but dressings can aid with symptom control and optimise the local wound environment, promoting healing
-
There is no evidence to support the superiority of one dressing type over another when applied under appropriate multilayer compression bandaging
-
When selecting a dressing, look at the wound bed, edge and surrounding skin and decide on the goal of the dressing: for example, if there are signs of localised infection consider an antimicrobial dressing, if there is heavy exudate consider an absorbent dressing
A 65 year old man presents with a two month history of a wound in the gaiter area of his left leg. He has a history of a left leg deep vein thrombosis after a long flight but is otherwise fit and well. He had been self-managing with dressings bought over the counter, but the wound has gradually increased in size. The wound is not painful but is weeping serous fluid, causing irritation of the surrounding skin. Examination shows a 4×3×0.1cm wound above the left medial malleolus. There is haemosiderin deposition, venous flare, and moderate oedema in the limb. The ankle-brachial pressure index is normal at 1.0. He is diagnosed with a venous leg ulcer, which is managed with dressings and compression bandaging.
About 1% of the adult population in Westernised countries are affected by venous ulcers on the leg or foot.2 The prevalence increases with age to 1.7% in
Recommended Reading: L Glutamine Ulcerative Colitis Dosage
Description Of The Condition
Diabetes, a condition which leads to high blood glucose concentrations, is common and affects around 2.8 million people in the UK . This number is set to increase over the next 25 years as the incidence of diabetes increases rapidly . Global projections suggest that the worldwide prevalence of diabetes is expected to rise to 4.4% by 2030, meaning that approximately 366 million people will be affected .
Peripheral arterial disease and neuropathy can occur separately or in combination . The overarching term ‘diabetic neuropathy’ refers to a number of neuropathic syndromes. Chronic distal sensorimotor symmetrical neuropathy is the most common, affecting around 28% of people with diabetes. It can lead to ulceration through the following route .
- Sympathetic autonomic neuropathy leads to decreased sweating causing anhidrotic skin, which is prone to cracks and fissures causing a break in the dermal barrier .
- Motor neuropathy causes wasting of the small, intrinsic muscles of the foot by deenervation. As the muscles waste they cause retraction of the toes and lead to a subsequent deformity. The abnormal foot shape can promote ulcer development due to an increase in plantar pressures .
- Sensory neuropathy results in impaired sensation, making the patient unaware of potentially dangerous foreign bodies and injuries.
Description Of The Intervention
Broadly, the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers includes pressure relief by resting the foot or wearing special footwear or shoe inserts the removal of dead cellular material from the surface of the wound infection control and the use of wound dressings. Other general strategies in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers include: patient education optimisation of blood glucose control correction of arterial insufficiency and surgical interventions .
Dressings are widely used in wound care, both to protect the wound and to promote healing. Classification of a dressing normally depends on the key material used. Several attributes of an ideal wound dressing have been described , including:
- the ability of the dressing to absorb and contain exudate without leakage or strikethrough
- lack of particulate contaminants left in the wound by the dressing
- thermal insulation
- permeability to water and bacteria
- avoidance of wound trauma on dressing removal
- frequency with which the dressing needs to be changed
- provision of pain relief and
Basic wound contact dressings
Lowadherence dressings and wound contact materials: usually cotton pads which are placed directly in contact with the wound. They can be either nonmedicated or medicated . Examples are paraffin gauze dressing, BP 1993 and Xeroform dressing a nonadherent petrolatum blend with 3% bismuth tribromophenate on fine mesh gauze.
Advanced wound dressings
Antimicrobial dressings
Specialist dressings
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of An Ulcer In The Esophagus
Activheal Foam Adhesive Is An Absorbent Foam Dressing Ideal For Moderate To High Exuding Wounds
FEATURESEXCELLENT ABSORPTION OF EXUDATE // VERSATILE // PROMOTES HEALING THROUGH A MOIST WOUND ENVIRONMENT // REDUCES THE RISK OF MACERATION // WATERPROOF // BACTERIAL BARRIER // SOFT AND COMFORTABLE //
ActivHeal® Foam Adhesive is a two layer dressing indicated for moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Each layer of the ActivHeal® Foam Adhesive contributes to the performance of the dressing.
The dressing comprises of a polyurethane absorbent foam pad and a polyurethane membrane. The core of the dressing is a layer of absorbent polyurethane foam which absorbs wound exudate vertically into the dressing. The absorbent pad retains the exudate within the dressing preventing the exudate from re-entering the wound and preventing maceration to the peri wound and surrounding skin. The polyurethane membrane provides an effective barrier function and is waterproof whilst allowing the transpiration of exudate which aids the total fluid handling capacity of the dressing.
Indicated for moderate to heavily exudating wounds. The dressing offers a pressure sensitive acrylic adhesive border ensuring the dressing remains in place allowing the patient to continue everyday activities confidently. The dressing conforms to the contours of the body which reduces the risk of rucking or catching on clothing and bedding.
Foam Dressings For Venous Leg Ulcers
Venous leg ulcers are a common and recurring type of chronic wound. Compression therapy is used to treat venous leg ulcers. Dressings that aim to protect the wound and provide a moist environment to aid ulcer healing are applied beneath compression devices. Foam dressings are one of several types of dressing available. We evaluated the evidence from 12 randomised controlled trials that either compared different types of foam dressings, or compared foam dressings with other types of wound dressings. We found no evidence to suggest that polyurethane foam dressings are significantly better or worse than hydrocellular foam dressings in venous leg ulcer healing. Similarly, we found no evidence to suggest that foam dressings are significantly better or worse than other types of dressings , for the healing of venous leg ulcers. We found insufficient evidence to draw any conclusions regarding: adverse events, quality of life, costs, pain, or dressing performance. Overall, the current evidence is of low or unclear methodological quality. This limits the making of any specific recommendations regarding the use of foam dressings. Further, good quality evidence is required before definitive conclusions can be made regarding the role of foam dressings in the management of venous leg ulcers.
You May Like: Best Way To Heal Stomach Ulcers
You May Like: Best Fruits For Ulcerative Colitis
Process Outcomes Evaluation And Reporting
During the EBP realization, the information about cost-efficiency, time of healing, and the overall patient outcomes should be collected. The evaluation will be carried out based on the objective patient data and nursesâ self-reports regarding the compliance with the specifically designed care protocols. The information will be collected on a daily basis and, by the end of week 11, evaluated by the nurse epidemiologist and the project leader. A comprehensive report on the project outcomes will be submitted to the hospital management and discussed at the collective meeting of the involved stakeholders.
Selection Of Appropriate Wound Dressing For Various Wounds
- 1School of Nursing, Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 2Orthopaedic Medical Center, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 3Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China
There are many factors involved in wound healing, and the healing process is not static. The therapeutic effect of modern wound dressings in the clinical management of wounds is documented. However, there are few reports regarding the reasonable selection of dressings for certain types of wounds in the clinic. In this article, we retrospect the history of wound dressing development and the classification of modern wound dressings. In addition, the pros and cons of mainstream modern wound dressings for the healing of different wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, burns and scalds, and chronic leg ulcers, as well as the physiological mechanisms involved in wound healing are summarized. This article provides a clinical guideline for selecting suitable wound dressings according to the types of wounds.
Read Also: Stage 4 Sacral Decubitus Ulcer
Silver Colloid Dressings Score Over Conventional Dressings In Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Rajkumar Sharma, Niraj Gupta, Vipan Kumar, Sanjay Pal, Vishal Kaundal, Vikrant Sharma
Abstract
Background: Topical silver treatments and silver dressings are increasingly used for the local treatment of contaminated or infected wounds however, there is a lack of clarity regarding the evidence for their effectiveness. To compare the outcome of silver colloidal based dressing in comparison to conventional dressing in management of diabetic foot ulcers.
Methods: This was a single institution prospective randomized controlled trial. Patients with Wagner grade 1and 2 diabetic foot ulcer were enrolled in this study. Patients were assessed on day one and then at two weeks interval for twelve weeks for ulcer size by planimetry.
Results: Out of 25 patients, 13 were randomized to silver colloid group and 12 in conventional dressing group. Age and sex distribution was comparable among two groups. Total 29 ulcers were present in silver colloidal and conventional dressing group. Mean wound area in silver colloidal dressing group and conventional dressing group on admission was 36.8 and 20.46 cm2 respectively. After 12 weeks of dressing mean wound area in silver colloidal dressing group and conventional dressing group decreased by 31.52 and 14.04 and after 12-week complete healing was seen in 11 patients in silver colloidal dressing group and 5 patients in conventional dressing group.
Keywords
Mertz PM. Cutaneous biofilms: friend or foe. Wounds. 2003 15:129-32.
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment

The first step in treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is to remove necrotic wound tissue from the wound. It is essential that the method of debridement utilized does not damage nerves, tendons, and blood vessels. Since many people with diabetes dont feel pain from the wound site, health care practitioners cant rely on the patient to let them know when sensitive areas are being examined. The debridement will:
- Reduce pressure on the ulcer.
- Stimulate wound healing.
- Allow the healthy underlying tissue to be examined.
- Help the wound to drain.
- Optimize the effectiveness of the wound dressing.
Recommended Reading: How Dangerous Is Ulcerative Colitis
Define The Scope Of The Ebp
VLU is a common chronic condition affecting nearly 2.5 million individuals annually, characterized by an extended healing trajectory and a high risk of recurrence. According to the statistics, only 58 percent of patients heal, and 4 percent undergo amputation . Thus, the condition poses great clinical and economic challenges and requires an effective approach to its treatment.
Nowadays, practitioners may choose various methods for the healing of VLUs. Foam dressing is one of them, but it is not utilized so often compared to other products . Currently, there is not enough evidence on the efficacy of foam dressings in the treatment of the condition. Thus, the EBP research in this area is of great importance as it may contribute to the expansion of the existing knowledge base.
Reviews For Medvance Silicone Bordered Silicone Foam Dressing 48
John V. Mccall March 10, 2021
Hamid Copeland
Carly Cashman March 10, 2021
Healing of small area of skin breakdown after trauma in an awkward spot by the ankle. This dressing applies easily and adheres to an irregular surface. It stays put for up to three days without wrinkling at the edges.
Iram Holden
BB December 3, 2020
PERFECT!!
I used these for my incision on my upper thigh that would not heal. My skin is so sensitive to tape and these stayed in place. I changed every 24 hrs, took off to shower. Perfect size pad, adhesive section is not too much or too little, and super absorbent as my incision would leak through thinner bandages that were the same size. Definitely recommend!
Recommended Reading: Purpose Of Insulin In The Body
Don’t Miss: How To Detect A Bleeding Ulcer
Data Collection And Analysis
Two review authors independently performed study selection, Risk of bias assessment and data extraction. We conducted this NMA using frequentist metaregression methods for the efficacy outcome the probability of complete healing. We assumed that treatment effects were similar within dressings classes . We present estimates of effect with their 95% confidence intervals for individual treatments focusing on comparisons with widely used dressing classes, and we report ranking probabilities for each intervention . We assessed the certainty of the body of evidence using GRADE for each network comparison and for the network as whole.
Curavance Foam Ag Bordered Dressings
CuraVance Foam Ag Dressings are indicated for the management ofmoderate to heavily exuding, acute and chronic wounds including: diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, pressure ulcers, graft and donor sites, trauma wounds, second-degree burns, and post-operative wounds and skin abrasions.
The semipermeable polyurethane film outer layer acts as a liquidand microbial barrier to prevent contamination, while delivering balanced oxygen and moisture vapor transfer for a moist wound healing environment.
Non-adherent foam absorbs and retains exudate and ensures atraumatic dressing removal to deliver optimal patient outcomes.
Laboratory testing has demonstrated that CuraVance Foam Ag Dressingsprovide broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against the most commonpathogens associated with wound infections for up to 7 days.
CuraVance Foam Ag Dressings are available withand without adhesive border.
- Absorbent foam absorbs excess wound fluid to maintain the optimal moist wound healing environment.
- Non-adherent foam reduces pain and trauma during dressing changes.
- Broad spectrum antibacterial activity protects against the most common pathogens associated with wound infection.
- High MVTR semi-permeable PU film provides low coefficient of friction and extends wear time
- Transparent film serves as a physical barrier to prevent fluid and microbial contamination
Don’t Miss: What Foods To Eat When You Have An Ulcer
Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Treatment And Prevention
Estimates are that by 2030 there will be 550 million individuals with diabetes in the world. Because almost a quarter of all people with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer at some point, health care workers need to know the best practices for diabetic foot ulcer prevention and treatment.
Determining which diabetic foot ulcer type is important to determine an effective treatment. Here are the different types of these wounds:
- Neuropathic ulcers arise when the nerve damage from diabetic neuropathy causes the individual with diabetes to not feel pain from an injury, which often leads to the ulcer progressing substantially before the person is even aware of it. Foot and toe deformities, corns, calluses and areas repetitive stress are likely places of injury. Footwear can not only hide these issues, but can exacerbate the injury if the shoe is ill-fitting.
- Ischemic ulcers or arterial ulcers as they are sometimes called may occur due to lack of blood flow to the extremity. When an ulcer occurs as the result of an injury to the extremity, the lack of blood flow makes these ulcers difficult to heal.
- Neuroischemic ulcers occur in individuals with both neuropathy and poor arterial blood flow and are the most difficult to heal.
- Infected wounds occur in about half of patients with a diabetic foot ulcer and require particularly close care.