Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis
Similar to other inflammatory diseases, the exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but research suggests that genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors are involved. Foreign substances in the environment may directly cause inflammation, or they may trigger the body’s defenses to produce inflammation that does not subside.Once the immune system in a child with ulcerative colitis is switched on,” it may not know how to properly “switch off.” As a result, the inflammation damages the tissues causing the symptoms of ulcerative colitis.
Guidelines And Conflicts Of Interest
All members of the expert panel complied with the IDSA policy on conflicts of interest, which requires disclosure of any financial, intellectual, or other interest that might be construed as constituting an actual, potential, or apparent conflict. To provide thorough transparency, IDSA requires full disclosure of all relationships, regardless of relevancy to the guideline topic . Evaluation of such relationships as potential conflicts of interest is determined by a review process that includes assessment by the SPGC chair, the SPGC liaison to the development panel, and the BOD liaison to the SPGC, and, if necessary, the COI Task Force of the Board. This assessment of disclosed relationships for possible COI is based on the relative weight of the financial relationship and the relevance of the relationship . See Acknowledgments section for disclosures reported to IDSA.
Clinical Practice Guidelines For Clostridium Difficile Infection In Adults And Children: 2017 Update By The Infectious Diseases Society Of America And Society For Healthcare Epidemiology Of America
Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 66, Issue 7, 1 April 2018, Pages e1e48, : 15 February 2018
L Clifford McDonald, Dale N Gerding, Stuart Johnson, Johan S Bakken, Karen C Carroll, Susan E Coffin, Erik R Dubberke, Kevin W Garey, Carolyn V Gould, Ciaran Kelly, Vivian Loo, Julia Shaklee Sammons, Thomas J Sandora, Mark H Wilcox
For full document, including tables and references, please visit the Oxford University Press website.
To view the 2021 focused update, please visit the Oxford University Press website.
Don’t Miss: Acute Exacerbation Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed In A Child
Your child’s healthcare provider will ask about your child’s health history. He or she will also give your child an exam.
Your child will have blood tests. These tests can tell if your child has anemia. They can also tell if your child has a high white blood cell count. This can be a sign of inflammation. Your childs healthcare provider may also do other tests.
Further Information On Cme
- Participation in the CME certification program is possible only over the Internet: cme.aerzteblatt.de. This unit can be accessed until 16 August 2021. Submissions by letter, e-mail or fax cannot be considered.
- All new CME units will be accessible for 12 months. The results can be downloaded starting four weeks after the beginning of each CME unit. Please be aware of the submission deadlines, which can be found at cme.aerzteblatt.de.
- This article has been certified by the North Rhine Academy for Continuing Medical Education. Participants in the CME program can manage their CME points with their 15-digit uniform CME number , which is found on the CME card . The EFN must be stated during registration on www.aerzteblatt.de or else entered in Meine Daten, and the participant must agree to communication of the results.
CME credit for this unit can be obtained via cme.aerzteblatt.de until 16 August 2021.
Only one answer is possible per question. Please select the answer that is most appropriate.
Question 1
Participation is possible only via the Internet: cme.aerzteblatt.de
Also Check: Clinical Manifestations Of Ulcerative Colitis
What Is Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis
What are the symptoms of pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Diarrhea, sometimes with blood, pus, or mucus
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Feeling the need to go urgently
- Intestinal bleeding
What treatments are available for pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Anti-inflammatory medications that reduce immune system activity or the inflammatory processes
- Corticosteroids
- Biologic therapies
- Acetaminophen to help relieve mild pain
Where can I find more information about pediatric ulcerative colitis?
Getting Started With Humira Dosing
Recommended dosing by weight for pediatric UC patients
If your child weighs 44 lbs to 87 lbs
Starting dose
20 mg every week or40 mg every other week
If your child weighs 88 lbs or more
Starting dose
Day 15
80 mg
*Can be given as a single dose in one day or split over 2 consecutive days
Maintenance dose
40 mg every week or80 mg every other week
Pediatric patients who turn 18 years of age and are well-controlled on their HUMIRA regimen should continue their prescribed dose.
Your doctor will follow up with you on a regular basis. For more information, refer to the Patient Instructions for Use and the Medication Guide located inside your HUMIRA carton and within the Full Prescribing Information.
Your child should continue taking HUMIRA as directed by your doctor. Remember, HUMIRA is a treatment, not a cure. Your doctor can tell you if and when your child should stop taking HUMIRA. If your child experiences any adverse reactions or discomfort when taking HUMIRA, discuss them with their doctor right away.
Common side effects of HUMIRA include administration site reactions , upper respiratory infections , headaches,rash, and nausea. These are not all of the possible side effects with HUMIRA. Tell your doctor if your child has any side effect that bothers them or that does not go away.
Read about the Important Safety Information for HUMIRA.
Don’t Miss: Diet For Crohn’s Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
New Aga Guideline: Management Of Ulcerative Colitis
Check out the new AGA clinical guideline in Gastroenterology with recommendations for the management of adult outpatients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis as well as adult hospitalized patients with acute severe UC. The guideline focuses on immunomodulators, biologics and small molecules to bring on and maintain remission for patients with moderate to severe UC and to decrease the risk of colectomy.
Here are five of the most noteworthy recommendations. For all 15 recommendations, review the full guideline.
Response To Corticosteroids And 5
As for any chronic condition, the optimal management for pediatric UC is to use the lowest dose of the safest therapy that is effective for maintaining full remission. For a child with UC, sustained corticosteroid-free remission on maintenance therapy with 5-ASAs is the ideal outcome. Prior studies have demonstrated that corticosteroid-free clinical remission with this strategy ranges between 38 and 40% .
Historically, 5-ASA therapy with or without corticosteroids during induction of remission was the most common first-line strategy for the majority of mildly to moderately active UC prior to resorting to alternative salvage therapy. Predictors of responses to a combination of corticosteroids and 5-ASA regimens were evaluated in a multicenter retrospective cohort study . Interestingly, corticosteroid-free clinical remission 3 months after diagnosis, as evidenced by a PUCAI < 10, was the strongest predictor for 1-year sustained corticosteroid-free clinical remission on 5-ASA. No baseline variables, including PUCAI, endoscopic evaluation, or laboratory serum markers, predicted corticosteroid-free remission or colectomy. However, baseline PUCAI did predict subsequent acute severe colitis and need for salvage therapy.
Table 2. Predicted probability of week 52 outcomes for select patient scenarios based on the PROTECT study predictive models.
Read Also: How Long Does Prednisone Take To Work For Ulcerative Colitis
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is not clear. It is probably a combination of genetics, the immune system, and something in the environment that causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Diet and stress may make symptoms worse, but probably don’t cause ulcerative colitis.
Ulcerative colitis tends to run in families. But not everyone with ulcerative colitis has a family history of ulcerative colitis or IBD. Ulcerative colitis can happen at any age, but is usually diagnosed in teens and young adults.
Remission At Week 52 In Week 8 Pms Remitters1*
~84% of patients in the study were bio-naive1,§
Study design intro: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 52-week trial in 93 pediatric patients from 5 to 17 years of age with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis who had an inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy. Co-primary endpoints: clinical remission per PMS at Week 8, and clinical remission per FMS at Week 52 in patients who achieved clinical response per PMS at Week 8. Only the every week maintenance dose is depicted. See Study Details and Additional Results for additional data.1
At Week 8, patients who demonstrated clinical response per PMS were randomized equally to receive double-blind maintenance treatment at a dose of 0.6 mg/kg every week or every other week.1
*Clinical remission per full Mayo score defined as a Mayo score 2 and no individual subscore > 1.1Clinical remission per partial Mayo score defined as a partial Mayo score 2 and no individual subscore > 1 no endoscopic component.1Modified intent-to-treat population, non-responder imputation .§Bio-naïve refers to patients who were anti-TNF naïve.
Also Check: Hospital Acquired Pressure Ulcers Lawsuit
How Can I Help My Child Live With Ulcerative Colitis
Children with this condition need long-term care. Your child may have times when symptoms go away . This can sometimes last for months or years. But symptoms usually come back.
Your child should learn what foods trigger his or her symptoms and avoid these foods. You and your childs healthcare provider should make sure your child gets enough nutrients to grow and develop well. Support groups can help you and your child. Work with your childs healthcare provider to create a care plan for your child.
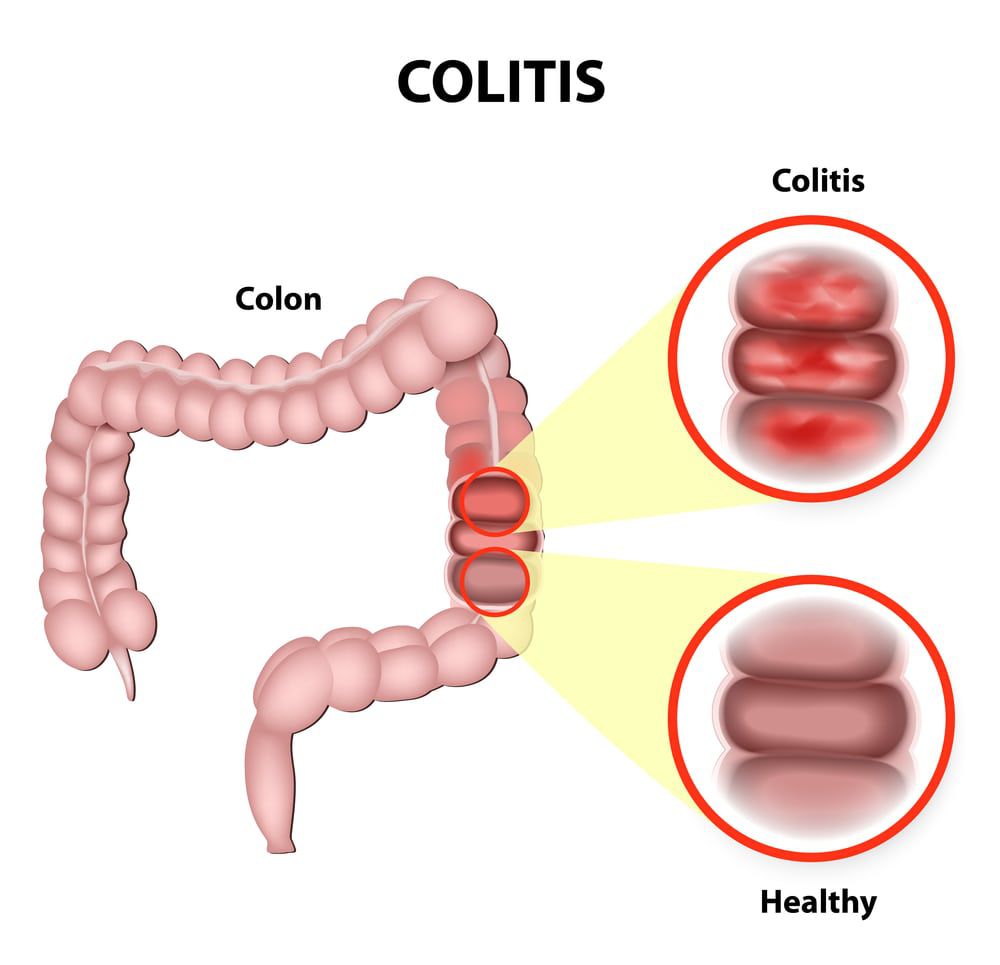
Ulcerative Colitis In Children: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Inflammatory bowel diseases, which are chronic inflammatory conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract, include ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease . While Crohns disease can affect any area of the GI tract, ulcerative colitis involves only the colon, also known as the large intestine. Inflammation associated with UC begins in the rectum and can involve the entire colon.
Nearly 25 percent of patients with IBD are diagnosed as children and about one-third of children with IBD have ulcerative colitis. Over the past several decades, IBD has become increasingly common.
Recommended Reading: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Bladder Problems
When To Speak With Your Childs Doctor
Children can be especially challenging to diagnose. Reach out to your childs doctor if you notice continued abdominal pain, diarrhea, unexplained weight loss, unexplained rashes, or notice any blood in their stool.
Early detection is key to preventing complications, so keep an open dialogue with your child about symptoms and speak with their doctor to rule out other conditions.
Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
While the clinical signs of ulcerative colitis can vary from child to child, some symptoms may be more common than others, including bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms related to inflammation in the colon may include: abdominal pain, urgent or uncontrollable bowel movements, poor appetite, weight loss, and fatigue. Some children may experience less common symptoms, including skin rashes, joint pain, fatigue or fevers.Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition, meaning children may have periods of no symptoms alternating with periods of active symptoms . Mild symptoms may present at first, while in other children, the onset of symptoms is more severe.
Recommended Reading: Cost Of Biologics For Ulcerative Colitis
Tips For Creating A Comfortable Treatment Environment
Here are some tips that may help both you and your child feel more at ease during treatment:
- Develop a routine by administering at the same time on the day your child is due for treatment
- Choose a quiet and calm place to administer treatment
- Describe to your child where the administration process will take place and how long it will last
- Try to get your child to focus on something enjoyable, such as a TV show or an upcoming event
- Project a positive and confident attitude
If you need help with administering treatment, HUMIRA Complete connects you with your own Nurse Ambassador who is available throughout your child’s treatment with HUMIRA.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis In A Child
Symptoms can happen a bit differently in each child. They can include:
-
Loss of body fluids and nutrients
-
Anemia caused by severe bleeding
Some children also have the following symptoms:
Many of these symptoms may be caused by other health problems. Make sure your child sees their healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Read Also: How Can You Tell If You Have An Ulcer
Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis
The treatment for ulcerative colitis is complex and may be different for every child, but the main goals are the same: to relieve symptoms, prevent flares, and achieve mucosal healing and remission. There is no one size fits all treatment for ulcerative colitis, and children respond to therapy differently. Using a combination of medication, nutritional therapy, and in more severe cases, surgery, we aim to promote each childs quality of life without limiting his or her goals or dreams. Primary treatment for ulcerative colitis includes medications. Those most often used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis are 5-aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, antibiotics, and medications that alter the immune system, called immunomodulators or biologics.
Active Uc Of Any Extent Not Responding To Aminosalicylates
In mild-to-moderate UC of any extent, aminosalicylates such as mesalamine are the preferred initial treatment . In patients with disease activity limited to the rectum, topical therapy alone might suffice, but combination therapy is more effective and is also recommended for left-sided and extensive UC . Table 2 gives an overview on current treatment options.
Table 2.
Medical therapy for UC
Fig. 1.
Active ulcerative colitis of any extent not responding to 5-aminosalicylates . MMX, multimatrix AZA, azathioprine 6-MP, 6-mercaptopurine.
Except in case of isolated proctitis, where topical corticosteroids alone may be considered, treatment with oral corticosteroids should be initiated in patients who do not respond adequately to 5-ASA . In case of isolated proctitis, topical corticosteroids alone might be considered. The introduction of corticosteroids should be a shared decision-making process that includes patients preference of therapy and tolerance to 5-ASA. It is, however, recommended to start corticosteroids in patients with sustained rectal bleeding for 2 weeks, persistent abdominal symptoms after 6 weeks of adequate therapy with 5-ASA or if symptoms deteriorate . In selected cases, a prolonged therapy with up to 16 weeks might still be able to achieve remission.
You May Like: What Is An Ulcer Diet
Recommended Reading: Can You Treat Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Risk Factors For Ulcerative Colitis
The exact causes of ulcerative colitis are not understood, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disease. This means the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks harmless bacteria in the colon, thereby inflaming healthy tissue.
Why this happens is unclear, but medical experts suspect a combination of genetics and environmental factors are at play. The disease can occur in all ethnic groups, but whites and people of Eastern European Jewish descent are at highest risk. Oher risk factors include:
- Family history: Having a family member with ulcerative colitis increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Environment: Ulcerative colitis is more common in urban, industrialized areas than it is in undeveloped countries. This suggests that a high-fat and refined-food diet may play a role. It is also more common in northern climates.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications: Medications including ibuprofen , naproxen sodium , diclofenac sodium and others dont cause ulcerative colitis, but they can inflame the bowel and worsen symptoms.
Ulcerative Colitis In Children

Gastroenterologists at Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital at NYU Langone provide specialized care for children with ulcerative colitis. This is a type of inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, in which a chronic or recurring inflammation affects the intestines. Though symptoms of this conditionsuch as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigueare similar to those of Crohns disease, ulcerative colitis can require different types of treatment.
Specialists at the Pediatric Gastroenterology Program create a personalized treatment plan to address your childs needs, with the goal of relieving symptoms and achieving and maintaining remission. Our team includes gastroenterologists, surgeons, nutritionists, and child life experts who support your child and family throughout treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Is Acute Ulcerative Colitis
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis From Prevalence To Outcome
Hasan M Isa1 , Afaf M Mohamed2, Halima E Al-Jowder3 and Khadija A Matrook4
1Consultant, Pediatric Department, Salmaniya Medical Complex, Arabian Gulf University, Bahrain
2Consultant, Shaikh Jaber Health Centre, Bahrain
3Chief Resident, Pediatric Department, Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain
4Intern, Pediatric Department, Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain
*Corresponding author: Hasan M Isa, MBBCh, CABP, Consultant, Pediatric Department, Arabian Gulf University, Manama, Bahrain, Tel: +973-66364449, Office: +973-17284547, Fax: +973-17279738, E-mail:
Received: April 14, 2017 | Accepted: June 28, 2017 | Published: June 30, 2017
Citation: Isa HM, Mohamed AM, Al-Jowder HE, Matrook KA Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis from Prevalence to Outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol Treat 3:046. doi.org/10.23937/2469-584X/1510046
Copyright:© 2017 Isa HM, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
New Guidelines For Treating Patients With Ulcerative Colitis
David Rubin, MD
New guidelines on diagnosing and managing ulcerative colitis are aimed at helping patients experience sustained periods of remission from the debilitating inflammatory disease while relying less on traditionally used steroids.
These novel recommendations will help doctors better prevent and care for patients with ulcerative colitis by shifting us from managing flare-ups to better monitoring and preventing them in the first place, said gastroenterologist David Rubin, MD, chief of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition and co-director of the Digestive Diseases Center at the University of Chicago Medicine.
Rubin led the team of experts that established the guidelines, published in the March issue of The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Ulcerative colitis , a chronic disease affecting roughly 1 million Americans, is characterized by periods of inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine. Symptoms include bloody stool, diarrhea, abdominal pain and urgency to go to the bathroom, as well as joint pain.
Rubin says the new management guidelines are geared towards relieving symptoms, preventing harmful secondary effects that may be brought on by treatment, and helping patients into remission. The guidelines place added importance on reducing inflammation and ulcers in the innermost lining of the colon and rectum, which physicians refer to as mucosal healing.
You May Like: How Can I Get Rid Of Mouth Ulcers
Don’t Miss: What Foods To Eat When You Have An Ulcer