Allergic Colitis In Infants
Allergic colitis is a condition that can occur in infants, usually within the first months after birth. The condition can cause symptoms in infants including:
- possible flecks of blood in a babys stool
Doctors dont know exactly what causes allergic colitis. One of the most popular theories is that infants with allergic colitis have an allergic or hypersensitive reaction to certain components in breast milk. A 2020 review of studies indicated that a protein allergy, either through breast milk, cows milk, or formula, could contribute.
Eosinophilic colitis is a type of allergic colitis that can also show up in infants with these symptoms. Its causes are similarly unknown , but its likely also related to a protein allergy.
Doctors will often recommend an elimination diet for the birthing parent, which involves slowly cutting out certain foods known to contribute to allergic colitis. Examples include cows milk, eggs, and wheat. If the baby stops having symptoms of allergic colitis, these foods were likely causing the problem.
In severe cases, monoclonal antibodies, such as those used to inflammatory bowel disease , may also be another treatment option.
Getting The Right Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about the type and timing of your symptoms. Theyâll probably feel your belly to see if itâs tender. Let them know about any medications that you take and if anyone in your family has ever had IBD or other digestive issues.
Everything you tell your doctor gives them clues about other tests you might need, such as:
Stool samples and bloodwork. Your poop and blood can reveal signs of infection or inflammation. Blood tests can also show low levels of iron. Thatâs called anemia. It can happen when colitis causes a lot of bleeding in your colon.
Imaging. Your doctor may take pictures inside your colon or rectum. They might use a special liquid called barium for some tests. Thatâs a substance thatâll coat your colon to help it show up better on X-rays.
You may also need:
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans
- Computed tomography scans
Endoscopic tests. An endoscope is a camera attached to a thin, bendy tube. Your doctor can use it to look at your lower colon and rectum or entire colon .
Tissue biopsy. Your doctor may remove some tissue during a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. A lab technician will use a microscope to check for signs of inflammation or other abnormal cells.
Severe Or Fulminant Colitis
Severe or fulminant colitis. Patients need to be hospitalized immediately with subsequent bowel rest, nutrition, and IV steroids. Typical starting choices are hydrocortisone 100 mg IV q8h, prednisolone 30 mg IV q12h, or methylprednisolone 16â20 mg IV q8h. The last two are preferred due to less sodium retention and potassium wasting. 24-hour continuous infusion is preferred than the stated dosing. If the patient has not had any corticosteroids within the last 30 days, IV ACTH 120 units/day as continuous infusion is superior than the IV steroids mentioned above. In either case, if symptoms persist after 2â3 days, Mesalazine or hydrocortisone enemas daily or bid can be given. The use of antibiotics in those with severe colitis is not clear. However, there are those patients who have sub-optimal response to corticosteroids and continue to run a low grade fever with bandemia. Typically they can be treated with IV ciprofloxacin and metronidazole. However, in those with fulminant colitis or megacolon, with high fever, leukocytosis with high bandemia, and peritoneal signs, broad spectrum antibiotics should be given . Abdominal x-ray should also be ordered. If intestinal dilation is seen, patients should be decompressed with NG tube and or rectal tube.
Don’t Miss: When To Go To The Hospital For Ulcerative Colitis
How Do Doctors Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis
To assist with diagnosing the cause of your symptoms, your doctor may take a full personal and family medical history and carry out a physical examination, according to . They may then order tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Tests that your doctor may order to assist with diagnosing ulcerative colitis include:
- Blood tests: checking for anemia, infection, and other digestive conditions
- Stool sample: checking for signs of inflammation and to rule out other possible conditions
- Endoscopy of the large intestine: looking inside your intestines using an endoscope
- Endoscopy of the large intestines can include a colonoscopy and a flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Your doctor can provide more information about the diagnostic tests they order. Make sure to ask them any questions you have before your tests.
Learn more about how doctors diagnose UC. You can also find out about what to expect after a UC diagnosis.
Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
X-rays of the abdomen taken after barium is given by enema do not require any special preparation . These x-rays usually can show a blockage or paralysis… read more ) may indicate the severity and extent of the disease but are not done when the disease is active, such as during a flare-up, because of the risk of causing a perforation. Other x-rays of the abdomen may also be taken.
Don’t Miss: Do Probiotics Help Stomach Ulcers
Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
A small number of people with colitis can develop inflammation in other parts of the body, such as the liver, skin, joints and eyes.
Regular monitoring by a gastroenterologist, as well as colonoscopies, may help prevent complications from developing. But medications, including steroids and drugs designed to prevent inflammation and occasionally surgery may be needed.
Osteoporosis can develop as a side effect of long-term corticosteroid use.
Cases of marked inflammation caused by UC can also lead to:
- nutritional deficiencies
- heavy bleeding due to deep ulcers
- perforation of the bowel
- problems with the bile ducts, affecting the liver
- fulminant colitis and toxic megacolon, conditions that cause the bowel to stop working
In the long-term, UC is associated with an increased risk of developing bowel cancer. After 10 years the risk of bowel cancer is 1 in 50, and after 20 years it increases to 1 in 12. This risk can be decreased by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising and avoiding alcohol and smoking.
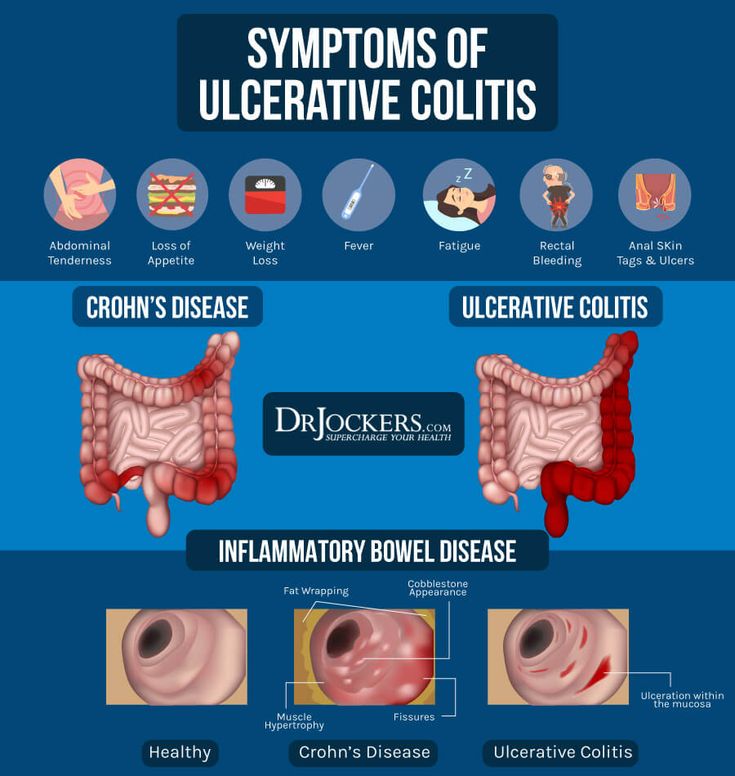
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease Vs Irritable Bowel
Other gut diseases can have some of the same symptoms.
- Ulcerative colitis affects only your large intestine and its lining.
- Crohnâs disease causes inflammation, but it affects other places in your digestive tract.
- Irritable bowel syndrome has some of the same symptoms as UC, but it doesnât cause inflammation or ulcers. Instead, itâs a problem with the muscles in your intestines.
You May Like: Diet For Stomach Ulcer Patient
Is Ulcerative Colitis Curable
Currently, theres no nonsurgical cure for UC. Treatments for the inflammatory disease aim to extend periods of remission and make flare-ups less severe.
For people with severe UC, curative surgery is a treatment option. Removing the entire large intestine will end the symptoms of UC.
This procedure requires your doctor to create a pouch on the outside of your body where waste can empty. This pouch can become inflamed and cause side effects.
For that reason, some people choose to have only a partial colectomy. In this surgery, your doctor only removes the parts of the colon that are affected by UC.
While these surgeries can help ease or end symptoms of UC, they can have adverse effects and possible long-term complications. Read more about these issues to determine if surgery is an option for you.
Living With Ulcerative Colitis
With careful management, most people with UC are able to enjoy life, including work, travel, recreation, sex and having children.
To keep healthy, consider:
- eating a nutritious diet to help with healing and reduce fatigue
- keeping a food diary to check if there are any foods that make your symptoms worse during a flare-up
- asking your doctor about supplements if you think you may be malnourished
- exercising regularly to lift your mood and help relieve stress
- learning some relaxation techniques to help manage stress
Don’t Miss: Foods To Treat Ulcerative Colitis
Role Of Bacteria In Ulcerative Colitis
The presence of E coli in patients with UC has been investigated, and it has been reported thatE coli could be detected only in a small proportion of tissue samples., Studies on mucosal adhesion of pathogenic bacteria in UC are controversial. A significantly enhanced adhesion of isolates of E coli from stool specimens and rectal biopsies from UC patients to buccal epithelial cells was found in comparison with patients with infectious diarrhoea or normal controls. The adhesive properties were similar to those of pathogenic intestinal E coli, suggesting that virulent E colistrains might participate in the pathogenesis of UC.,Another study reported adherence of only the DAEC and EaggECE coli subtypes to rectal mucosa, however, no differences in adhesion could be found between UC patients and controls. Adherence of a different strain has also been described. Using a hybridisation in situ technique, a significantly higher number of bacteria was found within the mucus layer and not adherent to the surface of the epithelium in UC patients compared with controls, independently from the degree of inflammation. It is most likely that the bacteria belong to a variety of species, when considering the broad specificity of the probe used in this study.
To summarise, there is incomplete information and continuing controversy about the role, adherent properties, and subtypes ofE coli which might be important in the pathogenesis of UC.
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis Different
A key difference is what triggers colitis. For instance, IBD is usually an autoimmune issue. Thatâs when your immune system attacks healthy tissue in your body. Other kinds of colitis can be the result of outside factors, such as germs or medical treatments.
People with UC or other kinds of IBD may also have inflammatory symptoms alongside bowel problems, including:
But those arenât the only distinctions. Hereâs a breakdown by colitis type:
Ulcerative colitis . This type of IBD causes sores and constant inflammation in the inner lining of your large intestine. UC often starts in the rectum and extends through the left side of your colon. But some people have colitis throughout most or all of their colon. Thatâs called extensive colitis or pancolitis.
Crohnâs colitis. This is a feature of Crohnâs disease, another type of IBD. Crohnâs can impact any part of your gastrointestinal tract â thatâs your mouth to your . Unlike UC, you may have healthy tissue in between spots of inflammation. Crohnâs disease can also affect many layers of your GI tract.
Microscopic colitis. This is another type of IBD. Itâs not related to ulcerative colitis or Crohnâs disease, but itâs associated with other autoimmune diseases. Like the name suggests, your doctor has to use a microscope to see any evidence of this kind of colitis.
There are two main forms:
Some experts think collagenous and lymphocytic colitis may be different phases of the same condition.
Read Also: Best Ulcerative Colitis Diet Book
Can I Get Surgery For My Ulcerative Colitis
Surgery is an option if medications arent working or you have complications, such as bleeding or abnormal growths. You might develop precancerous lesions, or growths that can turn into colorectal cancer. A doctor can remove these lesions with surgery or during a colonoscopy.
Research shows that about 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery sometime during their life. About 20% of children with ulcerative colitis will need surgery during their childhood years.
There are two kinds of surgery for ulcerative colitis:
Proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch
The proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch is the most common procedure for ulcerative colitis. This procedure typically requires more than one surgery, and there are several ways to do it. First, your surgeon does a proctocolectomy a procedure that removes your colon and rectum. Then the surgeon forms an ileoanal pouch to create a new rectum. While your body and newly made pouch is healing, your surgeon may perform a temporary ileostomy at the same time. This creates an opening in your lower belly. Your small intestines attach to the stoma, which looks like a small piece of pink skin on your belly.
After you heal, waste from your small intestines comes out through the stoma and into an attached bag called an ostomy bag. The small bag lies flat on the outside of your body, below your beltline. Youll need to wear the bag at all times to collect waste. Youll have to change the bag frequently throughout the day.
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis
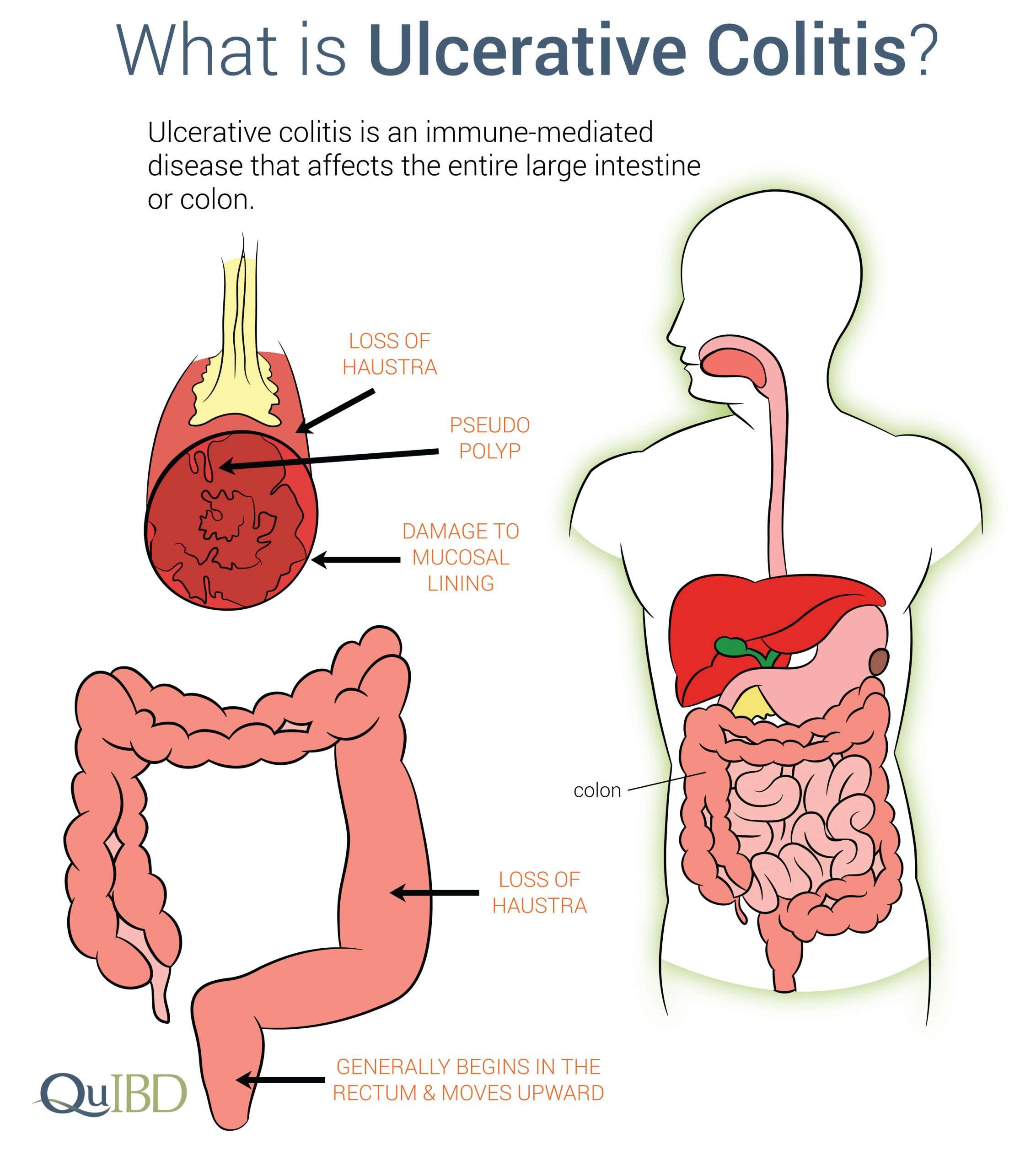
Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. Colitis causes symptoms such as abdominal pain and cramping, bloating, and diarrhea.
An inflamed colon can be caused by several conditions. UC is one possible cause. Other possible causes of colitis include:
- Crohns disease
- an allergic reaction
To diagnose the cause of colitis, a doctor will order a series of tests. These tests will help them understand what other symptoms youre experience and rule out conditions based on what youre not experiencing.
Treatment for colitis will depend on the underlying cause and other symptoms you have.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
The differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are:
- In Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is continuous inflammation of the colon
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls
Ulcerative Colitis In Children
According to one study of IBD in the United States, 1 in 1,299 children between ages 2 and 17 years old were affected by the condition in 2016. Crohns disease was twice as common as UC, and boys were more likely to have IBD than girls.
For children with IBD, a diagnosis is more likely after 10 years old.
UC symptoms in children are similar to symptoms in older individuals. Children may experience bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and fatigue.
In addition, they may experience issues compounded by the condition, such as:
- anemia due to blood loss
- malnutrition from poor eating
- unexplained weight loss
UC can have a significant effect on a childs life, especially if the condition isnt treated and managed properly. Treatments for children are more limited because of possible complications. For example, medicated enemas are rarely used as a treatment method in children.
However, children with UC may be prescribed medications that reduce inflammation and prevent immune system attacks on the colon. For some children, surgery may be necessary to manage symptoms.
If your child has been diagnosed with UC, its important that you work closely with their doctor to find treatments and lifestyle changes that can help. Check out these tips for parents and children dealing with UC.
You May Like: What To Do For Mouth Ulcers
When To Seek Medical Advice
You should see your GP as soon as possible if you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis and you haven’t been diagnosed with the condition.
They can arrange blood or stool sample tests to help determine what may be causing your symptoms. If necessary, they can refer you to hospital for further tests.
Read more about diagnosing ulcerative colitis.
If you’ve been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and think you may be having a severe flare-up, contact your GP or care team for advice. You may need to be admitted to hospital.
If you can’t contact your GP or care team, call NHS 24 111 service or contact your local out-of-hours service.
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
UC and Crohns disease are the most common forms of IBD. Both conditions are thought to be the result of an overactive immune system.
They also share many symptoms, including:
However, UC and Crohns disease do have distinct differences. Understanding the key differences between them can help you obtain a proper diagnosis.
Location
These two conditions affect different portions of the GI tract.
Response to treatment
Similar medications are prescribed to treat both conditions. Surgery is also a treatment option. Its a last resort for both conditions, but it can be a cure for UC, whereas its only a temporary therapy for Crohns.
Read Also: List Of Foods Good For Ulcers
Prognosis For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is usually chronic, with repeated flare-ups and remissions . In about 10% of people, an initial attack progresses rapidly and results in serious complications. Another 10% of people recover completely after a single attack. The remaining people have some degree of recurring disease.
People who have disease only in their rectum have the best prognosis. Severe complications are unlikely. However, in about 20 to 30% of people, the disease eventually spreads to the large intestine . In people who have proctitis that has not spread, surgery is rarely required, cancer rates are not increased, and life expectancy is normal.
What Happens During Ulcerative Colitis
The cause of ulcerative colitis, which is called pathophysiology, is not well understood. It’s thought that it may be connected to something causing the bacteria and other microbes that normally live in the colon to be out of balance, leading to an immune response and inflammation.
However, there is research underway that has started to uncover some of the reasons why people might develop the disease, including the following.
You May Like: Turn Clock For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Medications For Ulcerative Colitis
Your doctor may prescribe medication to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of relapse when you are in remission, according to .
Medications for UC include:
- aminosalicylates to reduce inflammation in mild to moderate UC
- corticosteroidsto treat moderate to severe UC, particularly if you do not respond to aminosalicylates
- immunosuppressantsfor moderate to severe UC
- biologics to reduce inflammation in cases of moderate to severe UC
Find out more about treatment options for UC. You can also learn about finding the right treatment for UC.