Psychological Stress And Gastrointestinal Motility And Water And Ion Secretion
As in humans, acute stress in the form of restraint stress, loud noise, inescapable foot shock, or water avoidance all increase colonic motility and defecation in the rodent. The mechanisms for these changes involve CRF and its receptors .
Similar alterations in ion and water transport to those seen in humans are also well described in animals in response to psychological stress. Increases in gastrointestinal water and chloride ion secretion occur in response to restraint stress in the rat. It is now recognised that, as with changes in intestinal permeability, this secretory response is related to both cholinergic nerves and mast cells as it was increased in cholinesterase deficient Wistar-Kyoto rats, blocked by pretreatment with atropine, and absent in mast cell deficient rats. Restraint stress also increased colonic mucus secretion in ex vivo colonic segments and in vivo, as measured by histological goblet cell depletion. This effect could also be reproduced by peripheral CRF administration and inhibited by mast cell stabilisers.
The Link Between Ulcerative Colitis And Stress
Stress can exacerbate colitis symptoms such as cramping and diarrhea. Heres how to find relief from uncomfortable flare-ups.
Stress does more than make your palms sweat and your brow furrow. For people with ulcerative colitis , it may bring on a painful flare.
Stress is well known for exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease symptoms, says Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of medicine at NYUs Grossman School of Medicine and a gastroenterologist at NYU Langone Healths Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center in New York City. My patients always tell me that their symptoms feel worse when theyre stressed.
Acute Psychological Stress And Gastrointestinal Immune And Inflammatory Function
Both of the two small studies which have examined the role of acute daily stress in IBD suggest a positive association between disease relapse and exacerbation .
There have been few examinations of the effects of experimental stress on gastrointestinal inflammation in humans. One study did find that physical stress, induced by immersion of the hand in iced water, increased the luminal jejunal concentration of the mast cell mediators tryptase and histamine in healthy volunteers and even more so in those with food allergies. We have found that acute psychological stress in the form of a dichotomous listening test increases the production of reactive oxygen metabolites by rectal mucosal biopsies in patients with quiescent UC .
There is also limited anecdotal evidence that artificially induced alterations in neural function can affect gastrointestinal inflammation. One reported example is of a man whose previously refractory UC went into complete remission following a Brown-Sequard paralysis at the level of C5. Kemler described a patient who suffered recurrent flares of his UC in association with spinal cord stimulation given for post-traumatic pain in his arm. Neuromodulatory drugs such as lidocaine, which decreases neuronal release of SP, clonidine, and nicotine have been claimed for many years to have benefit in UC in clinical trials and remain potential therapeutic agents in IBD.
Recommended Reading: What To Avoid Eating With Ulcerative Colitis
How Often Do I Need A Colonoscopy
Especially when you have symptoms or are just starting or changing medications, your doctor may want to periodically look at the inside of the rectum and colon to make sure the treatments are working and the lining is healing. How often this is needed is different for each person.
Ulcerative colitis also increases your chance of developing colon cancer. To look for early cancer signs, your healthcare provider may have you come in for a colonoscopy every one to three years.
Manage Your Stress To Ease Ulcerative Colitis
Stress doesn’t cause ulcerative colitis , but if it spirals out of control, it can make your symptoms worse.
So make it a priority to notice and manage the things that get to you. Take a good look at how you respond. Then use these simple tips to tap into relaxation and relief.
You May Like: What Over The Counter Medicine For Ulcers
How To Manage Pain And Fatigue
Pain and fatigue are common symptoms of ulcerative colitis. They can each cause distress, and a range of strategies and treatments can help.
A doctors first approach is to reduce these symptoms by managing the underlying condition. They may also prescribe acetaminophen to ease the pain. Unlike nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , acetaminophen is with an increased risk of ulcerative colitis flare-ups. It may also be worth noting that a 2018 systemic review did not find conclusive evidence that NSAIDs increased the risk of flare-ups.
Doctors sometimes prescribe anticonvulsants to ease nerve pain, though there is very limited evidence that these drugs can address the pain when it relates to bowel symptoms.
Doctors also prescribe antidepressants to people with irritable bowel syndrome as an adjuvant analgesic, a drug not only intended to relieve pain but used for that purpose.
Meanwhile, fatigue affects
To support and enhance mental wellbeing while dealing with ulcerative colitis, a person might try:
- eating healthy, nourishing food that does not cause digestive upset
- limiting the consumption of alcohol and caffeine
- exercising regularly
- trying to get plenty of sleep each night
- practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or yoga
- using supplements, if a doctor recommends it
The following techniques may also help reduce anxiety and depression:
Having social support can also help. People may benefit from:
Traveling With Ulcerative Colitis
Doing some research and planning ahead of time can help make trips go more smoothly. Here are a few tips:
Talk to your healthcare team about your travel plans. They may be able to offer advice and information about any necessary precautions or immunizations.
Take along your healthcare teams contact information and copies of insurance cards.
Remember to bring enough medicationpreferably in its original packaging. And make sure the sizes of liquids can go through security.
If you have an ostomy bag, make sure you tell TSA personnel before you go through security. Check out the TSAs page for people with medical conditions.
Research your destination. Know as much as possible about where youre going so you know what to expect. Aside from activities, places to stay, and where to eat, you might want to find out about nearby restrooms, when pharmacies are open, and if water is safe to drink.
Your diet when you travel should be as close as possible to your diet at home. Bring along dry, packable foods and follow the same precautions when eating out as you would when not traveling.
Use helpful resources that are availablelike a Restroom Request Card, which can let you discreetly communicate your condition and gain access to restricted bathroomsto be prepared in case you have sudden symptoms away from home.
Recommended Reading: Can I Donate Blood If I Have Ulcerative Colitis
When To Seek Medical Advice
You should see your GP as soon as possible if you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis and you havent been diagnosed with the condition.
They can arrange blood or stool sample tests to help determine what may be causing your symptoms. If necessary, they can refer you to hospital for further tests.
Read more about diagnosing ulcerative colitis.
If youve been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and think you may be having a severe flare-up, contact your GP or care team for advice. You may need to be admitted to hospital.
If you cant contact your GP or care team, call NHS 24 111 service or contact your local out-of-hours service.
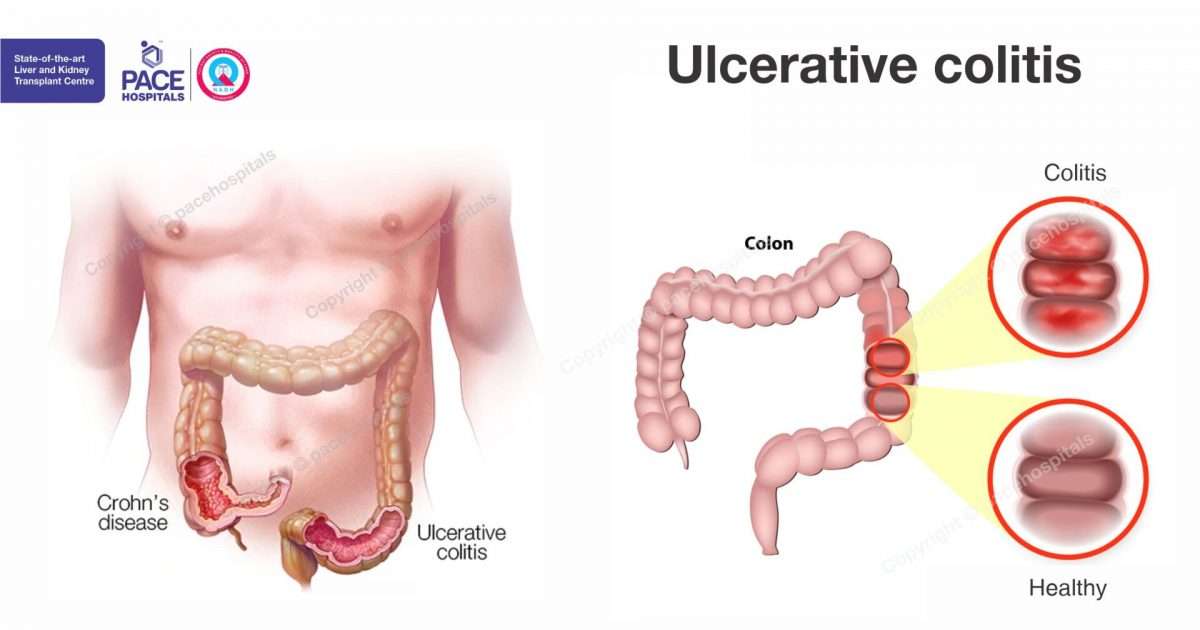
The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is also an inflammatory bowel disease . The 2 diseases affect the digestive tract differently:
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the large bowel , and inflammation is only in the surface layers of the bowel lining. It causes ulcers to form in the lining of the bowel.
- Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus , but usually just the last section of the small bowel and/or the colon. Inflammation can extend into the entire thickness of the bowel wall.
Recommended Reading: Foods To Eat To Heal Stomach Ulcers
The Relationship Between Stress & Colitis
The systemic effects of psychological stress on the immune and inflammatory systems are complex, and experts believe that both chronic and acute stress is associated with colitis, in terms of encouraging the inflammation that leads to colitis flare-ups. The duration and intensity of the colitis reaction most likely relate directly to the duration and intensity of the stressor. For example, adverse life events or difficult situations, such as being a caregiver or going through a marital separation are more likely to trigger more severe colitis symptoms than a bad day at work or an argument with your best friend.
Stress may not directly cause the condition of ulcerative colitis, but it can aggravate symptoms of the condition and increase the risk, frequency, and severity of flare-ups. And severe, chronic psychological stress may lead to increased bowel inflammation. Also, colitis patients who also suffer from chronic anxiety are at a higher risk for requiring surgeries, reduced medication adherence, lower quality of life, and higher perceived level of stress. In other words, left unchecked, your stress and anxiety may lead to additional and increased stress and anxiety.
Breaking the GI Stress Cycle can be as simple as focusing on taking deep, diaphragmatic breaths and muscle relaxation can begin to slow the sympathetic arousal mechanisms.
Stress May Be A Trigger Of Bowel Disease Symptoms
By Amy Norton, Reuters Health
4 Min Read
NEW YORK – People with inflammatory bowel disease commonly believe that stress can trigger their symptoms, and a new study suggests they may be right.
Canadian researchers found that among 552 bowel-disease patients they followed for a year, the risk of a symptom flare-up increased when patients were feeling particularly stressed.
The findings, reported in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, lend support to what many people with inflammatory bowel disease have believed to be true.
IBD refers to a group of conditions marked by chronic inflammation in the intestines, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea. The major forms are Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis.
The precise cause of the conditions is unclear, but they are thought to involve an immune system overreaction that injures the bodys own intestinal tissue. While stress does not cause IBD, it is one of the environmental factors suspected of triggering symptom flare-ups in some people.
Studies show that many people with IBD feel that stress worsens their symptoms, but there has been relatively little scientific evidence of that.
This is among the first evidence to show that the perception of stress had a direct association with disease course, Dr. Charles N. Bernstein, the lead researcher on the new study, told Reuters Health in an email.
Read Also: Skin Graft Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Still Feeling Stressed Out
Recognize when you need help and ask for it. When people offer to pitch in, take them up on it.
If your symptoms bother you, call your doctor. They can check to see if your treatment plan is on track or if it needs changes.
Join a support group for people with UC. Talk about what you’re going through with others who understand your situation. The Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America can help you find one in your area, or you can ask your doctor.
If you can’t shake your worries or if you feel depressed or anxious, talk to your doctor or a counselor. Even a few sessions can help you know what changes to make and whether you might benefit from medicine, so you feel more like yourself again.
Show Sources
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
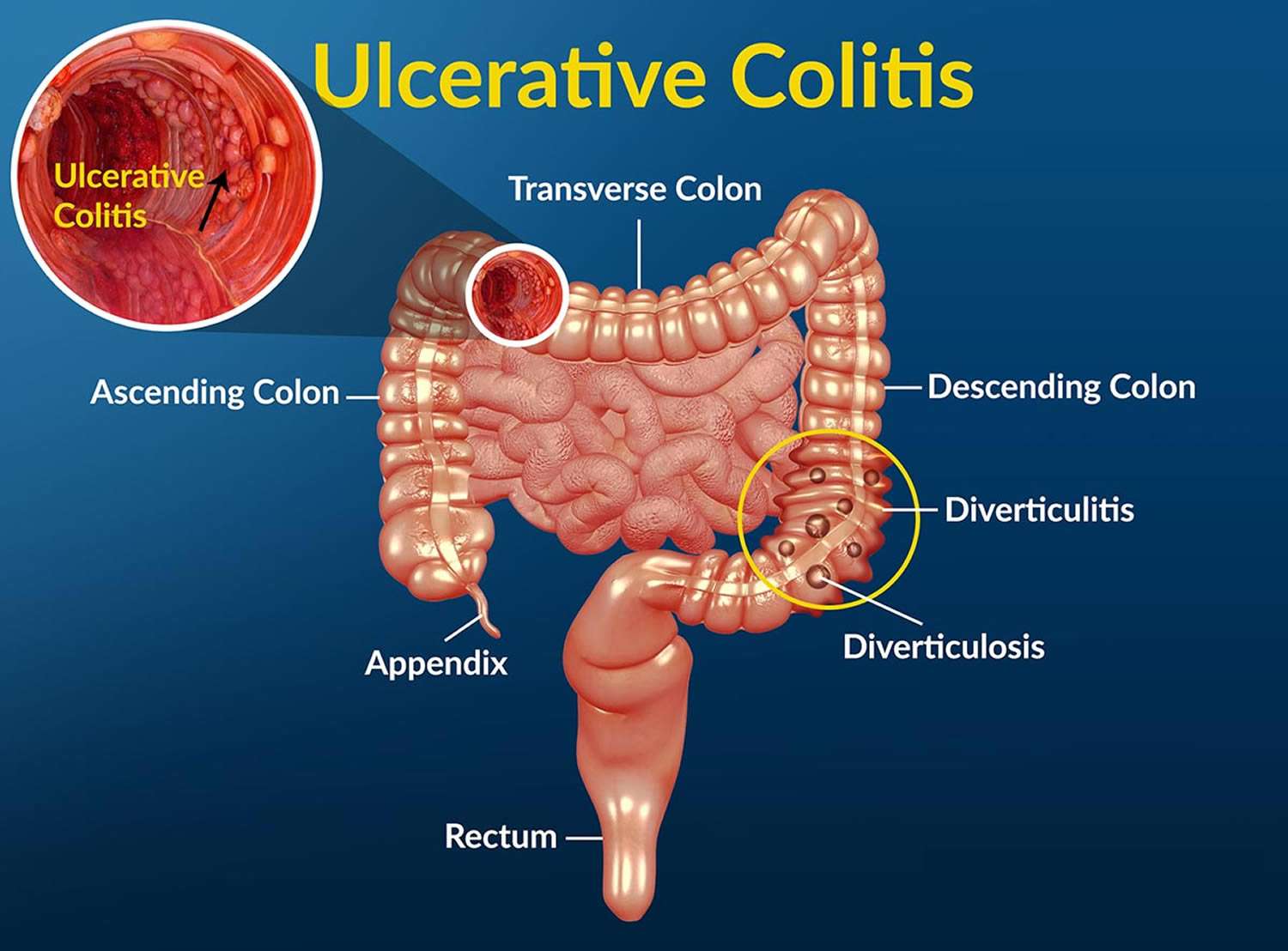
Ulcerative colitis is classified according to its location. Types of ulcerative colitis include:
- Proctosigmoiditis: affects the rectum and lower portion of the colon
- Left-sided colitis: affects the left side of the colon beginning at the rectum
- Pancolitis: affects the entire large intestine
- Ulcerative proctitis: inflammation is confined to the rectum and rectal bleeding may be the only sign of the disease. This form tends to be the mildest.
- Acute severe ulcerative colitis: rare form that affects the entire colon and causes severe pain, profuse diarrhea, bleeding, fever, and inability to eat.
Read Also: What Does An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Feel Like
What Is The Best Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Theres no single diet that works best for ulcerative colitis. If the disease damages the lining of the colon, your body might not absorb enough nutrients from food. Your healthcare provider may recommend supplemental nutrition or vitamins. Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan.
Overactive Immune System And Ulcerative Colitis
The immune system protects the intestinal epithelial cells from pathogens, dietary antigens and toxins. These factors trigger and activate the immune response creating inflammation as a protective mechanism.
Ulcerative colitis is currently thought to be an autoimmune, or immune-mediated condition. Autoimmune conditions occur when the immune response is overactive and targets healthy tissue. With ulcerative colitis, the immune system has an abnormal immune reaction which targets the large intestine and causes inflammation .
Foods, toxins, and pathogens may cause this overactive immune response. Food sensitivities are one of the primary culprits. When a person has an overactive immune response to certain foods, exposure to these causes the immune system to react to the foods as a threat and produce antibodies to the food.
Food sensitivities are very common and affect 45-75% of individuals. Gluten, dairy, corn, soy, nuts, eggs, and nightshades are common food sensitivities. If you are sensitive, repeated exposure to these foods inflames the gut lining causing intestinal permeability and digestive problems. For more information on food sensitivities and how to test for food sensitivities, read this article.
You May Like: Best Probiotic Brand For Ulcerative Colitis
Colon Cancer And Other Ulcerative Colitis Complications
The most serious complication of ulcerative colitis can be colon cancer. This is more likely to occur in people who have had UC for eight or more years and in people who have inflammation through the whole colon.
People with UC should talk with their health care provider about scheduling recurring cancer screenings. People with ulcerative colitis may need colonoscopies every one to three years if they have UC in more than a third of their colon or have had the condition for eight years or more.
Another life-threatening but rare complication is toxic megacolon. It involves the widening of the colon and an overwhelming bacterial infection resulting in sepsis. Sepsis is the bodys extreme reaction to an infection. It can lead to tissue damage, organ failure and death according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Other complications of ulcerative colitis:
- Rectal bleeding leading to anemia
- Dehydration and malabsorption if the colon is unable to absorb fluids and nutrients
- Bone changes such as osteoporosis or osteopenia
- Inflammation to other parts of the body such as the joints, eyes, skin or liver
Stress Can Trigger A Flare
Both Crohns disease and colitis are inflammatory diseases and can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms including:
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Blood in your stool
Inflammation in your GI tract causes these symptoms, and many people experience inflammation in cycles. This means you might have a handle on your symptoms and then suddenly something triggers a flare-up.
A flare-up is a reappearance of your symptoms. There are many things that can trigger a flare-up including missing your medication or taking the wrong dose, eating foods that irritate your GI tract, or even drinking carbonated beverages.
Many studies also show that stress can trigger a flare-up. Stress doesnt have to be a big event like moving to a new house. Everyday stressors can trigger a flare-up.
But why does an everyday stressor affect your gut health? The brain and digestive system are connected. This brain-gut connection allows your stomach to prepare for a meal by releasing stomach acids when you start thinkingabout food.
But the brain-gut connection goes both ways, which means mental stress can affect your gut health. This explains why you might feel butterflies in your stomach if youre nervous.
This, unfortunately, also explains how psychological stress can impact your digestive health and trigger a flare-up in your symptoms.
You May Like: In Order To Prevent Pressure Ulcers
Medications For Ulcerative Colitis
No medicine can cure UC. The goal of medication is to make a patients ulcerative colitis manageable. People with UC may have to take medicines indefinitely to control their condition.
Medications for treating ulcerative colitis:
- Aminosalicylates
- These medications may be used in people with mild or moderate symptoms and most people can tolerate them. They contain an active ingredient called 5-aminosalisylic acid, or 5-ASA, which helps control inflammation. Drugs in this class include balsalazide, mesalamine, olsalazine and sulfasalazine.
- Corticosteroids
- More commonly known simply as steroids, these medicines reduce the immune systems response. They are used if aminosalicylates dont seem to work. Drugs in this class include prednisone, methylprednisone, hydrocortisone and budesonide. These drugs shouldnt be used long-term.
- Immunomodulators
- These drugs reduce immune system activity as well, but may take as long as three months to work. Immunomodulators include Azasan or Imuran and Purinethol or Purixan .
- Biologics or TNF therapy
- This group includes Humira , Simponi and Remicade , medications that decrease inflammation by targeting a protein made by the immune system called tumor necrosis factor, or TNF. Side effects of these medications include higher risks for tuberculosis, fungal infections, skin cancer and psoriasis.
Doctors may also recommend antibiotics to prevent infection and other medications to treat diarrhea.
Psychological Stress And Pain Processing
Acute psychological stress has been shown to decrease thresholds for the perception of pain. Dichotomous listening tests decreased the threshold for the perception of pain in response to rectal distension in both patients with IBS and healthy volunteers. Although this experiment has not been repeated with patients with IBD, if stress does lower pain thresholds in these patients it may, in part, explain how acute stress can worsen IBD symptomatology.
The central release of SP from afferent neurones has been shown to be important in mediating stress induced gastrointestinal hyperalgesia. Central administration of an SP antagonist prevented restraint stress induced hypersensitivity to rectal distension in the guinea pig. However, the SP antagonist had no effect on rectal sensitivity in animals which had not been sensitised with restraint stress.
Also Check: How Does Ulcerative Colitis Affect The Body