Causes And Risk Factors Of Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is still unknown, but there are a few suspected conditions that may aggravate it.
Diet and stress are two risk factors that can make Ulcerative colitis worse, but not necessarily cause it.
Some research studies are focused on the nature of ulcerative colitis being an autoimmune condition.
The immune system is the bodys way to protect itself by attacking foreign bodies like viruses and bacteria.
This process sometimes fails due to certain factors, making the body attack its own cells. Cells in the digestive tract may be mistakenly attacked, causing ulcerative colitis.
Another cause thought to explain ulcerative colitis is heredity. It is noted that family history is apparent in some, but not all, people with ulcerative colitis.
Statistics suggest that ulcerative colitis equally affects men and women. Its risk factors include the following:
Switching Between Infliximab And Cyclosporin
In cases of non-response to infliximab or cyclosporin, switching to either therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality and is not recommended. In the largest study of 86 patients on this aspect, 65 patients were administered infliximab after cyclosporin and 21 patients had cyclosporin after infliximab. Thirty three percent patients underwent colectomy within 3 mo and 1/3rd of the patients had adverse effects in form of infections.
Talk With Others Who Understand
MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam is the social network for people with ulcerative colitis and their loved ones. On MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam, more than 138,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their stories with others who understand life with ulcerative colitis.
Are you living with ulcerative colitis pain? What has helped you to manage it? Share your experience in the comments below, or start a conversation by posting on your Activities page.
Recommended Reading: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Uc Symptoms Can Get Worse Over Time
Because UC is a chronic disease, symptoms can change or get worse over time. Many people go through periods when they experience few or no symptoms, known as remission, as well as periods of flare-ups when they experience frequent and/or more intense symptoms.
If youre still experiencing symptoms, even while being treated for UC, it could be a sign that your symptoms are not under control.
Experiencing uncontrolled symptoms could mean its time to consider a new treatment.
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnosing And Treating Ulcerative Colitis
There are four ways to diagnose ulcerative colitis. It is usually treated through medications or surgery.
How ulcerative colitis is diagnosed:
- A review of the patients family history of UC
- Physical exam to check for swelling, listen for sounds in the abdomen, and check for tenderness or pain in the abdomen
- Lab tests of blood and stool that check for anemia, inflammation elsewhere in the body and other markers common to UC patients
- Use of an endoscope, a long, flexible tube with a camera, to look at the colon
: National Institutes of Health
Treatment options depend on the severity of the patients ulcerative colitis. Surgery may require removing the colon and rectum in the most severe cases.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Flareups
When youre in remission from ulcerative colitis, youll want to do everything you can to prevent a flareup. Things that may cause a flareup include:
- Emotional stress: Get at least seven hours of sleep a night, exercise regularly and find healthy ways to relieve stress, such as meditation.
- NSAID use: For pain relief or a fever, use acetaminophen instead of NSAIDs like Motrin® and Advil®.
- Antibiotics: Let your healthcare provider know if antibiotics trigger your symptoms.
Read Also: Best Vitamins For Ulcerative Colitis
When To See A Doctor
Bleeding from the rectum or blood in or on the stool is never normal. It should always be brought up to a doctor. However, its not always an urgent situation.
If the cause of the bleeding is from a chronic condition , it should be discussed with your gastroenterologist.
In the case of new bleeding, see a doctor as soon as possible. Rectal bleeding that wont stop is a reason to go to the emergency department. Additionally, if you feel faint from blood loss, get to the emergency department right away or call an ambulance.
Abdominal pain can come and go with ongoing conditions, like Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis. Its important to discuss pain at doctors visits. However, if abdominal pain comes on suddenly and is severe, you should go to the emergency room or see a doctor right away.
In infants, caregivers will want to take the baby to see a pediatrician as soon as possible after seeing blood in the stool or around the rectum. Allergic colitis may be a common reason for bleeding, but its important to have a doctor check it out to make sure theres not a more serious reason.
Ulcerative Colitis Questions To Ask Your Doctor
Whether youâre worried your symptoms are UC, or you already have the condition and want more information, here are questions to ask your doctor:
- Are my symptoms a sign of ulcerative colitis or another condition?
- Are there different kinds of UC? Do they have different symptoms?
- What tests will I need?
- If I have ulcerative colitis, what will my treatment plan be?
- Will changing my diet or lifestyle help ease my symptoms?
- How serious is my ulcerative colitis?
- If I take medication for ulcerative colitis, will there be side effects?
- Should I take nutritional supplements like probiotics?
- How often will I need to come in for checkups?
- What should I do if my symptoms suddenly get worse?
- How do I know if my ulcerative colitis is getting worse?
- How do I know if I should change my ulcerative colitis medication?
- Should I consider surgery? What does surgery involve?
- What is my risk of getting colon cancer?
Don’t Miss: What Is A Gastric Ulcer And What Is Its Cause
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis
Anyone at any age, including young children, can get ulcerative colitis. Your chance of getting it is slightly higher if you:
- Have a close relative with inflammatory bowel disease .
- Are between 15 and 30 years old, or older than 60.
- Are Jewish.
- Use frequent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen .
Clinical Presentation And Differential Diagnosis
Ulcerative colitis phenotypes by Montreal Classification
Extraintestinal manifestations can occur in about a third of patients with ulcerative colitis, and up to a quarter might have extraintestinal manifestations before inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis ., Peripheral arthritis appears to be the most common extraintestinal manifestation primary sclerosing cholangitis and pyoderma gangrenosum are more common in ulcerative colitis than in Crohns disease., The risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with inflammatory bowel disease is increased three to four times, and is greater when the patient is admitted with a flare or being treated with corticosteroids. Clinicians should have a high index of suspicion for venous thromboembolism, and hospitalised patients with ulcerative colitis should be prescribed venous thromboembolism prophylaxis.
You May Like: Best Ulcerative Colitis Diet Book
Common Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
While UC symptoms can vary over time and from person to person, the most common symptoms are diarrhea with blood and abdominal discomfort.
However, your symptoms may vary depending on where inflammation occurs in your GI tract and how severe it is.
Other signs and symptoms include:
- An urgent need to have a bowel movement
- Feeling tired
- Nausea or loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Anemiaa condition in which the body has fewer red blood cells than normal
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Also Check: How To Stop Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Meal Timing And Portion Sizes
For most people with IBD, eating small meals is easier on the digestive tract. For others, the simple act of eating can rev up the digestive system and make diarrhea worse. If your bowel movements subside when you take a break between meals, consider reworking your meal timing to include more substantial meals less often.
Since UC symptoms vary from person to person, theres no one-size-fits-all meal schedule. Pain can feel worse when you’re not well-rested. Choose meals that are easy to tolerate when its close to bedtime, or finish eating for the day a few hours before going to sleep.
What Else Should I Know About Ulcerative Colitis
Poor appetite, diarrhea, and poor digestion of nutrients can make it hard for teens with ulcerative colitis to get the calories and nutrients the body needs. Be sure to eat a variety of foods, get plenty of fluids, and avoid foods that make your symptoms worse. Some teens may need supplements, like calcium or vitamin D. Someone who isn’t growing well may need other nutrition support.
Recommended Reading: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Cancer
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
Aphthous ulcersPyoderma gangrenosum
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
UC may affect the mouth. About 8% of individuals with UC develop oral manifestations. The two most common oral manifestations are aphthous stomatitis and angular cheilitis. Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by ulcers in the mouth, which are benign, noncontagious and often recurrent. Angular chelitis is characterized by redness at the corners of the mouth, which may include painful sores or breaks in the skin. Very rarely, benign pustules may occur in the mouth .
UC may affect the eyes. Inflammation may occur in the interior portion of the eye, leading to uveitis and iritis. Uveitis can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light . Untreated, uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss. Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye or the overlying connective tissue , causing conditions called scleritis and episcleritis. Uveitis and iritis are more commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, whereas episcleritis is more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease.
Who Diagnoses Ulcerative Colitis
If you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis, your regular healthcare provider will probably refer you to a specialist. A gastroenterologist a doctor who specializes in the digestive system should oversee the care for adults. For young patients, a pediatric gastroenterologist who specializes in children should manage the care.
Also Check: Tofacitinib Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
What Are Natural Home Treatments For Ulcerative Colitis
Lifestyle modifications
- If the patient has been on steroids for a long time, the person may have some added risk because this medication reduces the bone mass.
- High-impact exercise such as aerobics or running may put too much stress on the fragile bones causing stress fractures or broken bones.
- Low-impact exercises may be more appropriate, such as cycling or swimming.
- A bone density screening arranged through a doctor can look at bone mass and assess if the patient is at risk.
- Strength training with moderate weights or machines, even stretch bands, may help build bone density.
Traveling with ulcerative colitis can be a challenge if the patient feels the need to use the bathroom frequently. Sometimes you simply “can’t wait,” so experts have some prudent suggestions:
Some patients will try alternative medicines to help treat ulcerative colitis. There is no evidence, as yet, that probiotics, fish oil, spices, and acupuncture are beneficial.
Ulcerative Colitis In Children
According to one study of IBD in the United States, 1 in 1,299 children between ages 2 and 17 years old were affected by the condition in 2016. Crohns disease was twice as common as UC, and boys were more likely to have IBD than girls.
For children with IBD, a diagnosis is more likely after 10 years old.
UC symptoms in children are similar to symptoms in older individuals. Children may experience bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and fatigue.
In addition, they may experience issues compounded by the condition, such as:
- anemia due to blood loss
- malnutrition from poor eating
- unexplained weight loss
UC can have a significant effect on a childs life, especially if the condition isnt treated and managed properly. Treatments for children are more limited because of possible complications. For example, medicated enemas are rarely used as a treatment method in children.
However, children with UC may be prescribed medications that reduce inflammation and prevent immune system attacks on the colon. For some children, surgery may be necessary to manage symptoms.
If your child has been diagnosed with UC, its important that you work closely with their doctor to find treatments and lifestyle changes that can help. Check out these tips for parents and children dealing with UC.
Don’t Miss: Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Colitis
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two types of inflammatory bowel disease that cause colitis. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are considered autoimmune diseases .
- Ulcerative colitis always begins in the rectum and may spread to the rest of the rest of the colon, spreading from the rectum to the sigmoid, descending, transverse, and finally the ascending colon and cecum in that order. Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, and symptoms include abdominal pain, and bloody, diarrheal bowel movements.
- Crohn’s disease may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract , including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. In Crohn’s disease, there may be “skip lesions,” that is, abnormal segments of the GI tract interspersed with normal segments.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may have other organ systems involved in addition to the gastrointestinal tract.
Either collagen or lymphocytes infiltrate into the layers of the wall of the colon, presumably as a result of inflammation. This is an uncommon illness and maybe an autoimmune disease. Diarrhea often is watery, and no blood is present in the stool.
What Imaging Tests And Procedures Diagnose Colitis
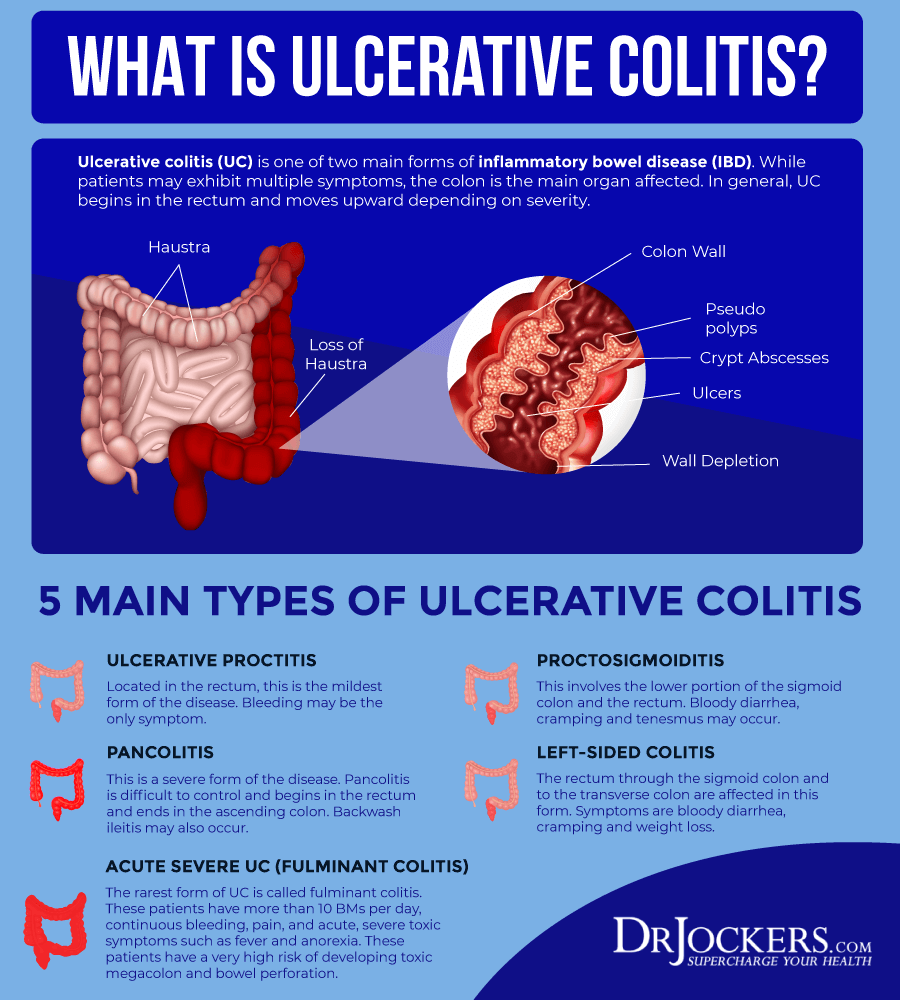
Colonoscopy: The length of the colon can be directly viewed by colonoscopy. A gastroenterologist uses a thin, flexible tube equipped with a fiberoptic camera to view the inside lining of the colon. The appearance of the colonic lining often allows the doctor to make the diagnosis and also provides the opportunity to look for tumors and polyps. Biopsies can be obtained from the mucosal lining during colonoscopy and evaluated under the microscope by a pathologist to determine the cause of colitis. A biopsy is the only way to diagnose microscopic colitis.
Computerized tomography and barium enema are tests that are sometimes ordered to help diagnose the potential cause of colitis. CT scan of the abdomen has become a more common test to evaluate patients with abdominal pain. However, it is important for the health care professional to balance the risk of radiation with the reward of the information that can be obtained. These tests usually are performed by a radiologist.
You May Like: Natural Supplements For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease Vs Irritable Bowel
Other gut diseases can have some of the same symptoms.
- Ulcerative colitis affects only your large intestine and its lining.
- Crohnâs disease causes inflammation, but it affects other places in your digestive tract.
- Irritable bowel syndrome has some of the same symptoms as UC, but it doesnât cause inflammation or ulcers. Instead, itâs a problem with the muscles in your intestines.
Ulcerative Colitis Risk Factors
Most people with UC dont have a family history of the condition. However, about 12 percent of people with UC do have a family member with IBD, according to research from 2014.
UC can develop in a person of any race, but its more common in white people. If youre of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, you have a greater chance of developing the condition than most other groups.
Young people with IBD may also be dealing with acne at the same time. Some older studies have suggested a possible link between the use of the cystic acne medication isotretinoin and UC. However, newer research has yet to find a definitive causal relationship.
Theres no solid evidence indicating that your diet affects whether you develop UC. You may find that certain foods and drinks aggravate your symptoms when you have a flare-up, though.
Practices that may help include:
- drinking small amounts of water throughout the day
- eating smaller meals throughout the day
- limiting your intake of high fiber foods
- avoiding fatty foods
- lowering your intake of milk if youre lactose intolerant
Also, ask a doctor if you should take a multivitamin.
Don’t Miss: Food To Avoid For Ulcer Patient