Consensus Statement #: Vascular Management Infection Management And Prevention And Pressure Relief Are Essential To Dfu Healing
The acronym VIP is a useful tool to recall key concepts in the management of DFUs, and it is often cited in the wound care literature.1–3 Evidence suggests that if the clinician aggressively manages the VIPs, then the wound-healing trajectory will progress.1,2,5 In patients with diabetes, neuropathy is the primary risk factor for DFU. Without proper off-loading and pressure relief, successful healing outcomes will be unlikely.1,2 However, off-loading alone will fail to present optimal outcomes if vascular disease or infection is not appropriately managed.20
Appendix 1
Seach Algorithm for Each of the Topics
Vascular assessment requires a combination of physical examination and laboratory tests or screenings, which can include palpation of pulses, ankle or toe brachial index, skin perfusion pressure, and transcutaneous oximetry.1,9,11,13,23,26,29 However, the poor reliability of blood pressure indices in the diabetic population, such as the ankle brachial index , means that these indices should not be used as the only means of vascular assessment. Consultation with a vascular specialist is prudent for evaluation and appropriate intervention when vascular disease is suspected.1
Consensus Statement #: Tcc Is The Preferred Method For Off
Although the ability to redistribute pressure most effectively over the entire foot through off-loading is supported by a moderate level of evidence, including multiple RCTs34,36 and systematic reviews10,38 , the panel agreed that TCC is likely the most ideal method of off-loading. Total contact casting is indicated for ulcers associated with neuropathy, Charcot’s foot, and postoperative off-loading.50 Inappropriate application may result in new ulcerations or other complications thus, proper training in application is paramount. General guidelines recommend weekly changing of the TCC because there can be volume changes in the affected extremity.
Comparing TCC with removable devices, TCC has been found to be more successful in healing outcomes because it enforces adherence by virtue of irremovability.34 Several RCTs have shown that for a removable device to be as effective as TCC, it must be modified to be nonremovable.36,46
The Complexity Of The Pathogenesis
DFUs are caused by multiple factors, including those that predispose to ulceration, those that trigger it, and those that prevent healing once ulceration occurs. Neuropathy and PAD are among the many factors that predispose to ulceration, and trauma is the principal trigger. But the failure of an established ulcer to heal can be the result of a number of further factors, and different ones among all of these may dominate at different times of the prolonged healing process. These are listed in , but our understanding of many of these processes is currently very limited.
Impact of the Complex Pathogenesis on Trial Design
This complexity of the mechanisms involved also undermines the attempt to establish the benefit of any intervention because interventions will generally be directed at a specific defect in the foot care process . And as this defect may be dominant only in certain people or intermittently in the same person at different times, it greatly increases the chance that the result of any trial to document benefit will be neutral .
The Complexity of the Care Process
The Impact of the Complexity of the Problem on Industrial Investment
Also Check: Black Tarry Stools Ulcerative Colitis
Dressings And Topical Products
Alginate and other dressings
Alginate dressings are derived from seaweed and come in the form of calcium alginate or calcium sodium alginate or alginic acid. These alginate products form a highly absorbent gel that can absorb large volume of wound exudates to avoid skin maceration yet still maintain a moist environment. A Cochrane review and meta-analysis in 2013 showed no significant difference in ulcer healing with alginate products when compared with basic contact dressings or silver hydrocolloid dressings. Another systematic review in 2016 also found no difference in healing time between other synthetic active dressings and traditional dressings, including wet to dry saline moistened gauze, Vaseline gauze, and hydrofiber. As an exception, moderate-quality evidence suggested that hydrogel was more effective in healing DFUs.
Topical antiseptics and antimicrobials
Other topical products
Footwear And Offloading Interventions To Prevent And Heal Foot Ulcers And Reduce Plantar Pressure In Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review
S. A. Bus
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Correspondence to: Sicco A. Bus, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Room A01-419, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
J. E. A. Lewis
Cardiff and Vale University Health Board and Cardiff School of Health Science, Cardiff Metropolitan University, Cardiff, UK
S. A. Bus
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Correspondence to: Sicco A. Bus, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Room A01-419, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
J. E. A. Lewis
Cardiff and Vale University Health Board and Cardiff School of Health Science, Cardiff Metropolitan University, Cardiff, UK
Read Also: Best Way To Treat Mouth Ulcers
Causes Of Diabetic Foot Ulcer:
Patients with chronic diabetes are more likely to develop leg injuries:
- Peripheral Neuropathy Decreased cognition of the feet .
Peripheral Neuropathy: Neuropathy reduces the sensation of the feet. Even if the foot comes in contact with something hot or cold, the patient does not understand it. A small wound is formed, which later becomes larger. Again, due to lack of understanding, the patient does not understand even if there is a small injury in the leg or something breaks in the leg. Large wounds are made from there.
- Peripheral Vascular diseases- Decreased blood flow to the legs
Peripheral vascular disease: The bones of the feet, the flesh that is, the right amount of blood flow is needed to keep the tissues or cells of the feet alive. In diabetic patients, this blood flow is disrupted, resulting in sores on the legs easily, and the sores formed do not heal easily. When the blood flow is completely stopped, the legs rot, which is called gangrene. If immediate action is not taken when the blood flow is stopped, that part of the leg may have to be amputated.
- Cracks or wound- Infiltration of germs through small wounds or cracks in the soles of the feet etc.
Cracks in the soles of the feet: In long-term diabetic patients, cracks are formed by drying the skin on the soles of the feet. These fractures cause bacterial infections and can lead to osteomyelitis.
Future Directions New Guidelines
Much has been achieved in the last two decades with the incidence of major amputation being very much reduced, at least in some countries, but there is evidence that even more can be achieved. There is wide variation in the outcome of management, even in industrialized countries and those with nationalized health care systemssuggesting that many people do not receive optimal care. Two broad strategies are key to improving overall outcome. The first is a major investment in the conduct of the high-quality clinical trials that are necessary to improve the evidence base for routine clinical care. The second is to ensure that those responsible for the design and delivery of care for people with DFUs comply with such evidence-based guidance as is available.
Also Check: Best Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Offloading Techniques For Diabetic Foot
Simerjit Singh, Ming Yoong, Avneet Kaur
Department of Orthopaedics, Asia
Correspondence: Simerjit Singh, Department of Orthopaedics, Melaka Manipal Medical College, Asia
Citation: Singh S, Yoong M, Kaur A . Offloading techniques for diabetic foot. J Diabetes Metab Disord Control. 2017 4:84-88. DOI: 10.15406/jdmdc.2017.04.00112
Diabetic Foot Care Has Been Traditionally Neglected
Despite the high morbidity and mortality associated with diseases of the foot in diabetes and despite its cost to both health care providers and the patient and their families , it is a topic that has generally failed to attract the same level of interest by health care professionals as other diabetes complications. Not surprisingly, the field continues to attract relatively few clinicians who are interested in research.
Read Also: What Not To Eat With Bleeding Ulcers
What To Do To Prevent Diabetic Foot Ulcer:
Evidence Base For Wound Care Treatments
There is currently little evidence to justify the adoption of very many of the products and procedures currently promoted for use in clinical practice. Guidelines are required to encourage clinicians to adopt only those treatments that have been shown to be effective in robust studies and principally in RCTs. The design and conduct of such RCTs needs improved governance because many are of low standard and do not always provide the evidence that is claimed. There should be new guidance on the conduct of RCTs in this field, and it should embrace items such as those covered in the 21-item checklist of study quality reproduced as . Clinicians need to be able to assess the relative validity of published work, including its strengths and limitations in trial design, conduct, and reporting.
Don’t Miss: Ulcer On Eye From Contact Lens
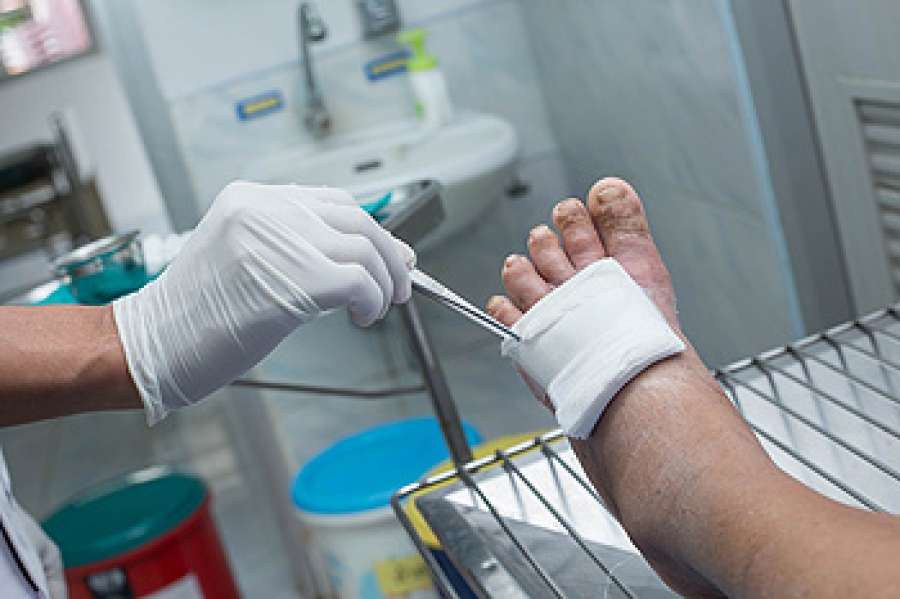
Ways Of Offloading To Prevent And Heal Foot Wounds
If using crutches or a wheelchair interferes too much with your everyday life, you may opt for a TCC or a removable cast walker.
A TCC evenly distributes weight across the entire sole of your foot so that a diabetic ulcer can heal without added weight strain.
A removable cast walker also helps redistribute weight and also allows you to easily dress and inspect your wound.
In addition to TCCs and removable cast walkers, there are special shoes and other types of footwear that help distribute your weight to prevent ulcers or help existing wounds heal.
If you have recurring foot ulcers or other diabetes-related foot problems, be sure to work with your physician to get the best foot care and protection available.
To schedule an appointment with a specialist at Main Line Health, or use our secure online appointment request form.
Geographic Differences In Clinical Outcome

There is also wide variation in clinical outcome within the same country , suggesting that some people are being managed considerably less well than others. Among the many possible reasons is the lack of emphasis placed on DFUs in basic training and continuing education of doctors and nurses .
There is thus a clear need for acceptance of standard components of care , as well as standard pathways for referral between general practice and specialty care and between different specialist groups. Such principles have been published by the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence however, adherence by professionals is not generally monitored, and the lack of a firm evidence base to underpin many aspects of management means that treatment choice is still very much influenced by opinion, as was illustrated in one small but important study .
You May Like: Low Residue Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Primary Prevention: Reducing The Incidence Of New Dfus
Data on community-wide ulcer incidence are very limited. Overall incidences of 5.8 and 6.0% have been reported in selected populations of people with diabetes in the U.S. while incidences of 2.1 and 2.2% have been reported from less selected populations in Europeeither in all people with diabetes or in those with type 2 disease alone . It is not known whether the incidence is changing, but it can be predicted that when expressed per total local population with diabetes, it is likely that there will be a short-term fall resulting from the impact of increased ascertainment of early diabetes through screening. But without major improvements in ulcer prevention, it can be predicted that this fall will be followed by a rise in the number of DFUs that will increase in step with the global epidemic of type 2 diabetes.
Research Design And Methods
A diabetic foot management survey was sent to 5,200 private and academic practices and clinics in all 50 states and the District of Columbia in 2005. A total of 901 geographically diverse centers responded from 48 states and the District of Columbia. The data were analyzed by dividing the U.S. into four census regions based on regions described by the U.S. Census Bureau. The survey recorded information about the usage frequency and characteristics of assessment and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers in each center.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When Ulcerative Colitis Flares
Offloading Can Help Diabetic Foot Ulcers Heal
Offloading refers to minimizing or removing weight placed on the foot to help prevent and heal ulcers, particularly those caused by poor circulation to the feet due to diabetes. Offloading can be done by using a wheelchair or crutches, or through more practical means for the patient such as total contact casts or removable cast walkers. The idea is to protect your wound from getting worse or becoming infected because of added weight on the area.
Offloading In Ulcer Prevention And Its Relapse
- Jill Cundell
- , Neil Baker
- 2 Apr 2017
The term offloading is generally given to techniques employed in the treatment of active foot ulceration or immobilisation of acute Charcot neuroarthropathy. It can equally be used for modalities and strategies for the prevention of new and relapse ulcers. In this context, perhaps the term deleterious force management would be better suited. Preventing the first ulcer is the ultimate goal of risk screening and stratification thus understanding the mechanisms for ulceration should direct clinicians to employ timely and appropriate offloading strategies. The rate of ulcer relapse is very high with reported rates of 40% in 412 months and 70% in 3 years. Managing healed ulcers is complex and requires considerable understanding and sustained activity. Central to all of this is active patient involvement and unhindered, easy access to foot protection teams, as well as adequate resource allocation. It is the authors view that sadly perhaps more focus is placed upon ulcer healing rather than preventing relapse. This article will briefly explore the area of offloading in the prevention of ulceration and its relapse. When reading this article, it would be useful to bear in mind some of the concepts that were previously discussed in the authors article in The Diabetic Foot Journal 19, The principles and practicalities of offloading diabetic foot ulcers.
- The mechanism of ulceration
- What do we mean by offloading?
Don’t Miss: Snack Ideas For Ulcerative Colitis
Failure Of Dfus To Heal Promptly
The Condition of the DFU at First Expert Assessment
Ulcers that are graded as being more severe have a worse prognosis, and this is the basis of current grading schemes . Recent data have also shown a statistically significant association between ulcer severity and the time to first expert assessment, in both Norway and the U.K. . The longer the elapsed time to expert assessment, the more severe the ulcers and the worse the clinical outcomes.
Effectiveness of Existing Treatments
A number of systematic reviews of dressings and other treatments designed to accelerate healing have been conducted in recent years. The overall conclusion has been that with very few exceptions, the evidence available from published studies is of insufficient quality to recommend any particular treatment or dressing product in preference to any other. The main exception relates to the use of off-loading for plantar ulcers . The effectiveness of other treatmentssuch as the use of antibiotics for infection and the use of revascularization for peripheral artery disease is accepted even though the evidence to guide many of the precise circumstances of their use is not good .
The Incidence of Major Amputation
The Link Between DFUs and Established Renal Failure
Skin Grafts And Bioengineered Skin
Skin grafting and tissue replacement can be used to reconstruct skin defects in DFUs. There are various types of skin grafts, including autographs, allografts, xenografts, and bioengineered skin. Although the mechanism is unclear, it is thought to promote wound healing by adding extracellular matrices that induce helpful growth factors and cytokines. A 2016 Cochrane review and meta-analysis evaluated RCTs of a variety of skin grafts and tissue replacement products and found that there was increased healing rates of DFUs with these products compared with standard care. This paper notes that the quality of evidence was low and the impact of the intervention varied greatly depending on the product type. It was also noted that nearly all studies had connections to commercial organizations.
There is a growing interest in allografts originating from dehydrated human amniotic and chorionic membranes . There have been several recent studies comparing dHACM to standard of care that have found improved rates of wound healing and wound closure., Studies comparing dHACM to bioengineered skin substitutes have had various outcomes., Another area of interest is the use of cryopreserved umbilical cord as adjunctive therapy. Small retrospective studies show that it may be helpful in wound healing, but RCTs are warranted to evaluate its true efficacy.,
Also Check: How Long Does An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last