Ulcerative Colitis Combined With Acute Interstitial Lung Disease And Airway Disease: A Case Report And Literature Review
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
Introduction
Case report
Clinical data
Physical examination on admission
Diagnosis and treatment
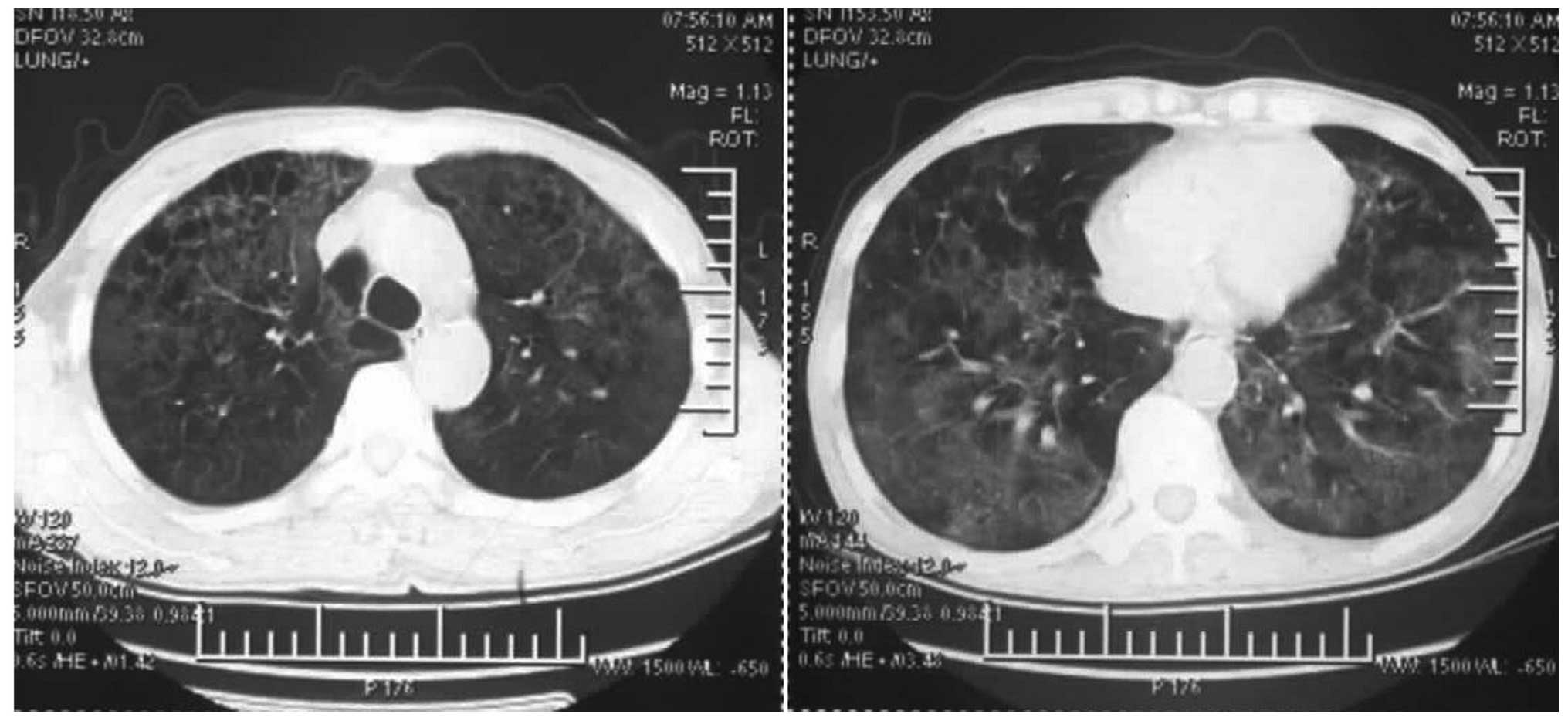
Subsequent to admission, 3 g cefoperazone-sulbactam,1 g vancomycin, 300 mg ganciclovir and 160 mg methylprednisolonewere intravenously infused once every 12 h. However, the conditionof the patient deteriorated and respiratory distress appeared. Theblood gas analysis revealed thefollowing results: pH, 7.35 PaCO2, 45 mmHg PaO2, 57 mmHg and HCO3 levels, 27mmol/l. The results of the repeated chest CT scan , performed on the21st day , showed that the bilaterallungs had changed to exhibit diffuse reticular or patchy shadows,with nodular shadows on the pulmonary hilar region and cyst shadowson the right upper lobe therefore, the use of vancomycin was ceased. On the 23rd day afterthe disease onset, pleural fiber deposition in the visceral layer,wide pleural adhesions and nodules on the lung surface wereobserved in the open lung biopsy taken from the right middle lobetissues.
Discussion
References
Related Articles
Definition And Pathogenesis Of Ibd
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are usually referred to with the common label of inflammatory bowel diseases due to their similar inflammatory nature and unknown cause. However, many differences in the clinical and pathologic features of these two chronic intestinal diseases have been found. Ulcerative colitis involves the rectum and may affect part or all of colon, and the inflammation is typically restricted to the mucosa. Crohn’s disease, on the other hand, is generally limited to the ileum and colon, not rarely in a patchy manner, and the inflammation is mostly transmural, with consequent stenosis and fistulae.
IBD result from an impaired barrier function of the intestinal mucosa characterized by increased permeability and defective regulation of tight junctions . The failure of this barrier, determining an exposition to fecal antigens, may induce an inappropriate activation of the acquired mucosal immune system . As a matter of fact, antibodies against intestinal bacteria are frequently detected in serum of patients with IBD but, although many pathogens have been incriminated, none has been demonstrated to play a causative role . The initial fast, generic response to intestinal microbes is supplied by the innate immune system, while the adaptive immune system recognizes individual bacteria through antigen-specific receptors.
The Link Between Ulcerative Colitis And Joint Pain
UC is a type of inflammatory bowel disease . Arthritis is the most common non-GI complication of IBD. The reason for the link may lie in genes that make people with IBD more susceptible to arthritis.
Two types of conditions can affect the joints of people with UC. Arthritis is joint pain with inflammation . Arthralgia is pain in the joints without any inflammation.
Arthritis that occurs with UC is a bit different than regular arthritis. For one thing, it typically starts at a younger age.
In addition, arthritis in people with UC doesnt usually cause long-term joint damage. The joints swell up and become painful, but they return to normal once intestinal inflammation is under control.
A few types of arthritis can affect people with UC:
You May Like: Foam Boots For Pressure Ulcers
Which Individuals Are At Greatest Risk Of Developing Pulmonary Involvement In Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Any patient with IBD can develop respiratory manifestations. Until proven otherwise, patients with IBD who have persistent or unstable respiratory symptoms without identifiable cause should be considered to have a pulmonary manifestation of IBD or a complication of medical therapy for IBD. Patients with IBD with acute onset of breathlessness should be urgently evaluated for thromboembolic disease. Respiratory manifestations of IBD should be considered in patients with concomitant flares of pulmonary and intestinal symptoms.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Childhood
The age of onset of pulmonary involvement may vary in a wide range. The incidence of symptomatic bronchopulmonary involvement in children suffering from IBD seems to be much lower than in adults . The spectrum of lung pathologies is quite similar, and available reports comprise nodules consisting of non-caseating granulomas , cavitating lesions , pleuritis , lymphocytic infiltrations and organizing pneumonia in patients with CD and UC .
Read Also: How Do I Know If I Have A Peptic Ulcer
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Bronchoscopy Bal And Biopsy Results
The BAL cellular pattern is usually abnormal, but changes are not specific. Increased total cell count and mild lymphocytosis are the most typical findings . Some authors reported an increased percentage of BAL eosinophils . Patients without clinical evidence of pulmonary involvement may have alveolar lymphocytosis . Diagnosis is usually confirmed by surgical lung biopsy, but transbronchial peripheral lung biopsy may be sufficient . Therefore it is always worth trying as a less invasive method.
The possible pathological patterns are listed in .
You May Like: Different Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
Pulmonary Hypertension And Ulcerative Colitis
Pulmonary Hypertension is a rare but severe condition that causes high blood pressure in the lungs by damaging the pulmonary arteries. The vessels transport blood from the heart to the lungs, but because of the disease they become narrow and thick. When the normal blood flow becomes compromised, the heart is forced to work under stress to pump blood, which makes the heart weak and enlarged. There are numerous risks associated with this condition, including right heart failure and death.
When the cause of a specific case of pulmonary hypertension is unknown, the condition is known as idiopathic. When the disease is caused by a primary medical condition, it is called associated pulmonary hypertension. Common primary diseases include lung and heart diseases but inflammatory bowel disease ulcerative colitis which affects the digestive track, can also be a cause.
Conditions Related To Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an autoimmune disease that results in damage to the inner lining of the colon, or large intestine, and rectum. The cause of UC is believed to be an abnormal immune response that causes the body to attack itself. Like Crohns disease, it is a type of inflammatory bowel disease . Unlike Crohns, the primary disease is limited to the colon and rectum and does not involve the small intestine.
Gastrointestinal symptoms of IBD can have a significant impact on quality of life these symptoms include abdominal pain and cramping, diarrhea, and intestinal bleeding. However, UC affects more than just the digestive tract. Like many autoimmune diseases, its effects can be felt throughout the body.
Many different medical conditions frequently occur alongside UC, including:
- Arthritis
- Blood clots
- Anemia
About 43 percent of people with UC have extraintestinal manifestations of IBD, or conditions related to IBD that occur outside of the intestines. Some of these conditions are related to UC by underlying genetic factors or disease mechanisms, while others can occur as a side effect of treatments for UC. The symptoms of many of these related disorders worsen with UC flare-ups and resolve during periods of remission.
Sometimes these related diseases can develop before intestinal symptoms of UC appear. Here are some of the most common extraintestinal manifestations of UC.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Dysbiosis Of Intestinal Microbiota In Ibd
Dysbiosis has been associated with the development of IBD, although whether this is cause or effect is yet to be elucidated since most research to date has been correlative. Cross-sectional studies are the most common for assessing the microbiota of IBD patients but these only provide a snapshot in time . Instituting longitudinal studies could assist in establishing when dysbiosis occurs relative to the onset of intestinal inflammation and how this may change with the course of disease but this would require early and frequent sampling. Furthermore, the microbiome tends to be sequenced from fecal samples and while this is non-invasive for the IBD patient, this method could provide inaccurate measures, especially for CD patients where inflammation is often localized to the ileum or other portions of the gastrointestinal tract. This sampling method can also overlook mucosa-associated microbiota, and due to the variations in microbial composition that are apparent across the gastrointestinal tract, sampling methods need to be carefully considered when formulating studies . Nonetheless, the research that has been conducted to date has provided a solid foundation upon which future studies can expand to improve our understanding of dysbiosis in IBD.
Read Also: Can I Eat Oatmeal With Ulcerative Colitis
Possible Links Between Bowel And Lung Disease
Both the colonic and the respiratory epithelia provide the first barrier against microbial agents, antigens and toxins. Exposure to air pollutants, especially to particulate matter , was shown to increase morbidity and mortality related to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. This effect may be related to the induction of systemic inflammation, which is an important element in the pathogenesis of these diseases. Various pollutants may be swallowed and absorbed from the intestines, potentially inducing systemic and local inflammation. The incidence of IBD has significantly increased in the last five decades, probably reflecting changes in the industrialized environment . The idea of the impact of air pollution on the pathogenesis of IBD is intriguing, but evidence is scarce yet .
There are several papers documenting higher frequency of IgE-related and delayed-type hypersensitivity in IBD patients . Interestingly, colonic tissue eosinophilia was higher in patients with positive skin prick tests for food allergens . Based on such data, it may be suggested that atopy could be a common link between IBD and airway disease in some patients. Unfortunately, other data do not support this concept. For instance, asthma and atopy are Th2-mediated diseases, whereas CD is a Th1-mediated pathology .
Overlapping pulmonary and intestinal symptoms in UC and WG and high incidence of various ANCA autoantibodies in IBD patients may suggest the presence of a common autoantigen.
Evaluation And Management Of Ibd Patients With Suspected Pulmonary Involvement

IBD patients presenting with respiratory symptoms or even asymptomatic pulmonary findings on radiography should be approached with a high index of suspicion for drug-induced or IBD-related pulmonary disease. The history pertinent to IBD should include a careful review of the recent course of the disease, any history of extraintestinal manifestations, and medication use. 5-ASA medications may be resumed with caution, however re-challenge of the possible offending drug for the purpose of diagnosis of drug-induced pulmonary disease is not recommended.
Given these patients are often on immune-modulating drugs and that IBD itself is considered an immune-mediated disease, infection should initially be ruled out and the evaluation may require screening for tuberculosis or other diseases that IBD patients may be at increased risk for. Radiographic evaluation may begin with standard chest radiographs and should be followed by high-resolution CT in cases with pulmonary disease or high suspicion of pulmonary disease. Characteristic CT findings may be associated with specific diseases , as discussed above. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy was commonly utilized for tissue and further infectious disease evaluation, but was usually of low yield. In our observations, thoracoscopy with wedge biopsy is usually required to achieve the final diagnosis .
Don’t Miss: What Foods Should I Avoid With A Stomach Ulcer
Assessment Of The Risk Of Bias In The Included Studies
Two review authors assessed the risk of bias independently for each study using the criteria outlined in the ROBINS-I tool for nonrandomized studies . Any disagreement was resolved through discussion. The risk of bias was assessed according to the following domains: bias due to confounding variables such as smoking , sex , average age and observation bias bias due to selection of the participants bias due to classification of the intervention bias due to deviation from the intended interventions bias due to missing data bias in the measurement of the outcome and bias in the selection of reported results.
Mouth And Skin Conditions
Diseases of the skin and oral mucosa, the lining of the mouth, can occur with UC. Erythema nodosum is the most common skin manifestation of IBD. It is seen in about 10 percent of people with UC and causes painful nodules in the skin, usually the legs.
The second-most common skin manifestation of IBD is pyoderma gangrenosum, which causes blisters in the skin. These blisters can grow quite large and become painful, ulcerating lesions.
Other skin diseases seen in UC and Crohns disease include:
- Pyostomatitis vegetans and aphthous stomatitis, which cause ulcers in the mouth
Skin and mouth conditions associated with UC tend to appear more when there is a flare-up of intestinal symptoms. Treatments vary by condition, but they can include steroids and biologic drugs.
Read Also: Does Smoking Cause Ulcers After Gastric Bypass
Development Of Pulmonary Hypertension Due To Ulcerative Colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease , ulcerative colitis included, causes irritation in the digestive tract which leads to diarrhea often with blood or pus, abdominal pain and cramping, rectal pain or bleeding, difficulties in normal defecation, weight loss, fatigue and fever. In addition, the disease can bring about a variety of respiratory complications, as explored in the study Pulmonary complications of inflammatory bowel disease, authored by Drs. Steven E. Weinberger and Mark A. Peppercorn.
According to the report: Case series vary in terms of the proportions of patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease who have associated lung disease . The pathogenesis of pulmonary parenchymal disease and serositis associated with IBD is unknown. However, the more common airway inflammatory changes are thought to represent the same type of inflammatory changes that occur in the bowel.
The correlation between pulmonary hypertension and ulcerative colitis is not fully disclosed but case studies indicate many instances of IBD- associated lung involvement.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Pulmonary Hypertension And Ulcerative Colitis
Since patients who suffer from ulcerative colitis are at risk of lung diseases and pulmonary hypertension, patients and physician should be aware of symptoms like shortness of breath , fatigue, dizziness or fainting spells , chest pressure or pain, swelling in the ankles, legs and abdomen , bluish color in lips and skin , or irregular heartbeat.
There is currently no cure for pulmonary hypertension, but there are treatments that can help patients ease symptoms and extend their lifespan. Blood vessel dilators , endothelin receptor antagonists, sildenafil and tadalafil, high-dose calcium channel blockers, anticoagulants, diuretics, and supplemental oxygen are the most used therapeutic options for patients with pulmonary hypertension. However, a tailored treatment taking into consideration the coexistence of the two conditions, the patients characteristics, and other medical information should be discussed with a specialized physician.
Note: Pulmonary Hypertension News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Read Also: Snack Ideas For Ulcerative Colitis
Bronchoscopy Bronchoalveolar Lavage And Biopsy Results
Mucosal edema and hyperemia are the most typical findings . Suppurative bronchitis is frequent, and in these instances chronic purulent expectoration is the main symptom . Tracheal or bronchial strictures have been described due to extensive submucosal fibrosis , inflammatory nodules or circumferential mucosal infiltration . Bronchial biopsy reveals mucosal hyperplasia , thickening of basal membrane and angioectasia , cellular infiltrations composed of granulocytes , T and B lymphocytes or non-specific chronic inflammatory infiltrates . Although the most typical finding in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of IBD patients is lymphocytosis, in tracheobronchial involvement BAL fluid may be dominated by neutrophils .
The classical form of small airway disease accompanying IBD is bronchiolitis. Non-necrotizing granulomas consisting of epithelioid, multinucleated giant and scattered mononuclear cells surrounding small bronchioles were described in patients suffering from CD . This and other similar findings recall similarities to sarcoidosis however, the coincidence of classical sarcoidosis with CD is probably incidental. In bronchiolitis related to UC, non-granulomatous inflammation has been found . Diffuse and fibrosing/sclerosing bronchiolitis of severe course has been described in UC .
What Laboratory Studies Should You Order To Help Make The Diagnosis And How Should You Interpret The Results
Start by evaluating for the presence of infection with sputum gram stain and bacterial culture, sputum AFB smear and mycobacterial culture for both typical and atypical mycobacterial disease, and sputum fungal culture. Consider serologic evaluation for endemic fungi based upon geographic location or exposure . Interferon gamma release assay and purified protein derivative skin testing for tuberculosis are difficult to interpret in the setting of immunosuppression.
Guide further evaluations by the distribution of pulmonary abnormalities on imaging studies. If VTE is suspected, an elevated d-dimer may be a nonspecific finding during flares of IBD. Consider an evaluation for autoimmune disease if there is diffuse parenchymal disease, organizing pneumonia, pulmonary vasculitis, bronchiolitis obliterans, or tracheal stenosis.
Also Check: How To Check A Horse For Ulcers