Support Surfaces For Pressure Ulcer Prevention: A Network Meta
-
* E-mail:
Affiliation Division of Nursing, Midwifery & Social Work, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health, University of Manchester, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester, United Kingdom
- Jo C. Dumville,
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Division of Nursing, Midwifery & Social Work, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health, University of Manchester, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester, United Kingdom
- Nicky Cullum
Roles Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing review & editing
Affiliations Division of Nursing, Midwifery & Social Work, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health, University of Manchester, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester, United Kingdom, Research and Innovation Division, Manchester University NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, Manchester, United Kingdom
Was The Allocation Sequence Randomly Generated
Yes, low risk of bias
The investigators describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as: referring to a random number table using a computer random number generator coin tossing shuffling cards or envelopes throwing dice drawing of lots.
No, high risk of bias
The investigators describe a nonrandom component in the sequence generation process. Usually, the description would involve some systematic, nonrandom approach, for example: sequence generated by odd or even date of birth sequence generated by some rule based on date of admission sequence generated by some rule based on hospital or clinic record number.
Unclear
Insufficient information about the sequence generation process to permit judgement of either Yes or No to be made.
Support Surfaces For Treating Pressure Ulcers
What is the aim of this review?
The aim of this review was to find out whether different support surfaces such as specially-designed beds, mattresses or cushions can help to treat pressure ulcers. Researchers from Cochrane collected and analysed all relevant studies to answer this question, and found 19 relevant studies.
Key messages
We cannot be certain which support surfaces are most effective for pressure ulcer treatment as the studies comparing them did not involve enough people and were not well designed.
What was studied in the review?
Pressure ulcers are wounds to the skin and underlying tissue caused by pressure or rubbing. They typically form at points on the body which are bony or which bear weight or pressure, such as the hips, buttocks, heels and elbows. People who have mobility problems or who lie in bed for long periods are at risk of developing pressure ulcers. A range of treatments, including wound dressings and support surfaces like special mattresses and cushions, are used to treat pressure ulcers.
We wanted to find out which support surfaces were most effective in helping pressure ulcers to heal. We also wanted to compare different support surfaces in terms of cost, reliability, durability, and the benefits or harms for patients using them.
What are the main results of the review?
How up to date is this review?
We searched for studies that had been published up to September 2017.
Also Check: How To Check A Horse For Ulcers
Risk Of Bias In Included Studies
Details of the risk of bias of each individual trial are included in and shown in and .
Risk of bias graph: review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included trials.
Allocation
The method of randomisation was unclear in 29 of the 59 included trials. Although the majority of trials reported patient eligibility criteria, just over a third of the reports gave information that indicated patients were allocated with concealed allocation .
Blinding
Blinded outcome assessment is rarely used in wound care trials, and this was the case in these evaluations of support surfaces. It can be difficult or impossible to disguise the surface that a patient is on for assessment of outcome, and patients are often too ill to be removed from their beds for assessment of their pressure areas. Nevertheless, some trials minimise bias in outcome assessment by having a second assessor and presenting interrater reliability data, or by presenting photographic evidence of pressure area status which can then be assessed by an independent assessor blinded to treatment. Of the 59 RCTs in this review, we could be confident that blinded outcome assessment had been used in only twelve trials .
Incomplete outcome data
Selective reporting
Other potential sources of bias
Appendix 3 Ebsco Cinahl Search Strategy

S29 S23 and S28S28 S24 or S25 or S26 or S27S27 TI decubitus or AB decubitusS26 TI or AB S25 TI or AB S24 S23 S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 or S5 or S6 or S7 or S8 or S9 or S10 or S11 or S12 or S13 or S14 or S15 or S16 or S17 or S18 or S19 or S20 or S21 or S22S22 TI or AB S21 TI net bed* or AB net bed*S20 TI or AB S19 TI or AB S18 TI or AB S17 TI elevation N2 device* or AB elevation N2 device*S16 TI water suspension or AB water suspensionS15 TI air bag* or AB air bag*S14 TI air suspension or AB air suspensionS13 TI alternat* pressure or AB alternat* pressureS12 TI static air or AB static airS11 TI constant N2 pressure or AB constant N2 pressureS10 TI low pressure N2 support or AB low pressure N2 supportS9 TI low pressure N2 device* or AB low pressure N2 device*S8 TI pressure alleviat* or AB pressure alleviat*S7 TI pressure reduc* or AB pressure reduc*S6 TI pressure relie* or AB pressure relie*S5 TI or AB S4 TI or AB S3 TI or AB S2 S1
Also Check: Side Effects Of Ulcerative Colitis
Criteria For Considering Studies For This Review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials and quasirandomised trials comparing support surfaces, and which measured the incidence of new pressure ulcers were included. Trials that only reported subjective measures of outcome were excluded, as were trials that reported only proxy measures such as interface pressure. Trials were eligible for inclusion if they reported an objective, clinical, outcome measure such as incidence and severity of new pressure ulcers developed.
Types of participants
People receiving health care who were deemed to be at risk of developing pressure ulcers, in any setting. Some trials involved people who had existing pressure ulcers, however, only the incidence of new pressure ulcers was examined.
Types of interventions
Trials which evaluated the following interventions for preventing pressure ulcers were included:
1. “Lowtech” CLP support surfaces
-
Standard foam mattresses.
-
Alternative foam mattresses/overlays : these are conformable and aim to redistribute pressure over a larger contact area.
-
Gelfilled mattresses/overlays: mode of action as above.
-
Fibrefilled mattresses/overlays: mode of action as above.
-
Airfilled mattresses/overlays: mode of action as above.
-
Waterfilled mattresses/overlays: mode of action as above.
-
Beadfilled mattresses/overlays: mode of action as above.
-
Sheepskins: proposed mode of action unclear.
2. “Hightech” support surfaces
3. Other support surfaces
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Secondary outcomes
Current Recommendations And Practice For Preventing And Treating Pressure Ulcers
The 2014 NICE clinical guideline in the UK Pressure ulcers: prevention and management, has recommended using foam mattresses for preventing pressure ulcers in adults at risk of having a pressure ulcer, and for treating pressure ulcers.
However, other types of support surfaces such as reactive air mattresses or overlays, and alternating pressure air mattresses or overlays, are also commonly used.
The NICE guideline does not contain evidence on how support surfaces compare, or evidence on which support surface is the most effective. This leaves decision-makers with a confusing array of devices to choose from but evidence uncertainty.
Also Check: How Long Does An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
Are Reports Of The Trial Free Of Suggestion Of Selective Outcome Reporting
Yes, low risk of bias
Any of the following:
-
The trial protocol is available and all of the prespecified outcomes that are of interest in the review have been reported in the prespecified way.
-
The trial protocol is not available but it is clear that the published reports include all expected outcomes, including those that were prespecified .
No, high risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
Not all of the trial’s prespecified primary outcomes reported.
-
One or more primary outcomes is reported using measurements, analysis methods or subsets of the data that were not prespecified.
-
One or more reported primary outcomes were not prespecified .
-
One or more outcomes of interest in the review are reported incompletely so that they cannot be entered in a metaanalysis.
-
The trial report fails to include results for a key outcome that would be expected to have been reported for such a trial.
Unclear
Insufficient information to permit judgement of Yes or No to be made. It is likely that the majority of trials will fall into this category.
Purpose And Function Of Support Surfaces
Support surfaces alone neither prevent nor heal pressure ulcers. They are to be used as part of a total program of prevention and treatment. When pressure ulcers deteriorate or fail to heal, the professional should consider replacing the existing support surface with one that will improve pressure redistribution and microclimate for the individual. Changing the support surface is only one of several strategies to consider. The individual and his or her pressure ulcer should be re-evaluated. Preventive interventions and local wound care should also be intensified as needed. A significant increase in risk status may also prompt such re-evaluation of the individual and the support surface.
Support surfaces as a general recommendation provide a support that is properly matched to the individuals needs for pressure redistribution, shear reduction, and microclimate control and would replace the existing mattress for the individual if she or he: cannot be positioned off the ulcer has pressure ulcers on two or more turning surfaces has limited turning options fails to heal or demonstrates ulcer deterioration despite appropriate comprehensive care is at high risk for additional ulcers and bottoms out on the existing support surface.
Limit the amount of positioning devices and incontinence pads that are compatible with the support surface because these often create pressure points that have a tendency to lead to new trauma areas on the delicate tissues of our older patients.
Also Check: Can I Eat Oatmeal With Ulcerative Colitis
Description Of The Intervention
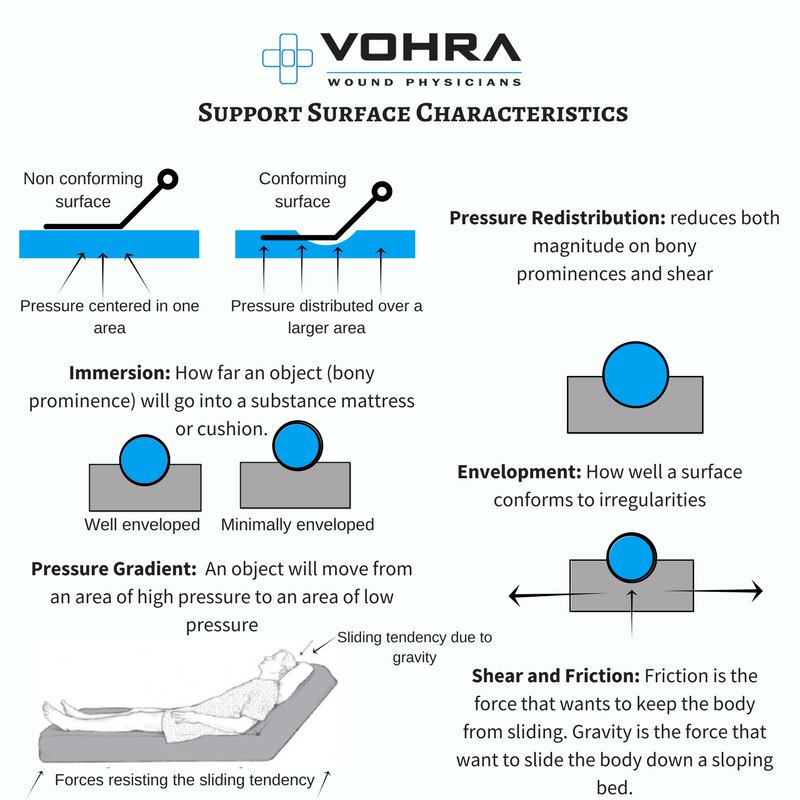
The aim of pressure ulcer prevention strategies is to reduce either the magnitude, or duration, of pressure between a patient and his support surface , or both. This may be achieved by regular manual repositioning , or by using pressurerelieving support surfaces such as cushions, mattress overlays, replacement mattresses or whole bed replacements, which are widely used in both institutional and noninstitutional settings. Often a combination of repositioning and support surface enhancement may be used. Support surfaces are used with the aim of redistributing pressure, reducing shearing forces and controlling the local microclimate. The cost of these interventions varies widely from over GBP 30,000 for some bed replacements, to less than GBP 100 for some foam overlays. Information on the relative costeffectiveness of this equipment is needed to inform use.
Mattress And Bed Support Surfaces For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Mattress and Bed Support Surfaces for Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Pressure redistributing support surfaces are designed to either increase the body surface area that comes in contact with the support surface or to sequentially alter the parts of the body that bear load, thus reducing the duration of loading at any given anatomical site.
1. Use a high specification reactive foam mattress rather than a non high specification reactive foam
mattress for all individuals assessed as being at risk for pressure ulcer development.
1.1. Review the characteristics of foam mattresses used in the facility for pressure ulcer prevention
to ensure they are high specification.
The below table 1 outlines consensus opinion on the minimum characteristics for a product to be considered a high specification foam mattress.
Table 1: consensus on Characteristics that constitute a high specification foam mattress.
Don’t Miss: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
Other Sources Of Potential Bias:
Yes, low risk of bias
The trial appears to be free of other sources of bias.
No, high risk of bias
There is at least one important risk of bias. For example, the trial:
-
Had a potential source of bias related to the specific trial design used or
-
Stopped early due to some datadependent process or
-
Had extreme baseline imbalance or
-
Has been claimed to have been fraudulent or
-
Had some other problem.
There may be a risk of bias, but there is either:
-
Insufficient information to assess whether an important risk of bias exists or
-
Insufficient rationale or evidence that an identified problem will introduce bias
Why It Is Important To Do This Review
Research indicates that pressure ulcers represent a major burden of sickness and reduced quality of life for patients, their carers , and their families . Often patients who develop pressure ulcers require prolonged and frequent contact with the healthcare system and suffer much pain , discomfort and inconvenience .
The presence of a pressure ulcer creates a number of significant difficulties psychologically, physically and clinically to patients, carers and their families. Clinicians, working in a variety of clinical and nonclinical settings, including primary care and acute trusts, also face challenges when providing holistic, personcentred services for the assessment and treatment of pressure ulcers. These challenges include clinical decisions regarding methods of assessment, and which treatments to use on individuals with an existing pressure ulcer.
Healthcare professionals attempt to reduce the incidence of severe pressure ulcers by the identification of people at high risk, and the use of preventative strategies, such as the deployment of pressurerelieving equipment. It is essential that initiatives are based on the best available clinical and costeffectiveness evidence, and we have, therefore, undertaken a systematic review of the evidence for the effectiveness of pressurerelieving support surfaces such as beds, mattresses, cushions, and repositioning interventions.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should I Avoid With A Stomach Ulcer
Characteristics Of Excluded Studies
| Study | |
|---|---|
| This is a quasirandomised study. The method of randomisation is unclear and insufficiently described: The sample was randomized by alternating the application of each intervention when the patients were admitted to the unit. It appears that sequence generation took place by a rule based on admission time and therefore there is a high risk of bias. | |
| Whilst 8 surfaces were evaluated in this prospective trial, not all surfaces were in the trial at the same time, therefore, the surfaces were not truly compared with one another contemporaneously. Furthermore, it was possible for patients to be rerandomised back into the study, which occurred frequently, with a total of 457 mattress trials reported for only 238 patients. The data were not presented by patient only by mattress trial.Duplicate citation of Bliss 1994 . |
= greater than or equal to< = less than = less than or equal toA& E = Accident and Emergency departmentAP = alternating pressureFDA = Food and Drug AdministrationGA = general anaestheticITT = intentiontotreat analysisLAL = low air lossy = year
Acute Care Support Surfaces
Medlines comprehensive approach to pressure redistribution begins the moment a patient enters the hospital. Our full line of support surface products uses the most advanced pressure redistribution features with best-in-class technology to minimize the risk of facility-acquired pressure ulcers.
Self-Adjusting MattressesEqualizeAire mattresses provide you with an easy-to-use and easy-to-maintain mattress that can be used for high-risk patients for prevention and during treatment of pressure ulcers.
Therapeutic Foam MattressesTheraTech pressure redistribution mattresses feature independent load bearing cells, which allow the mattress to completely conform to the contours of the body, greatly reducing interface pressures and natural shear forces.
OR Table and Stretcher PadsPads help ensure optimal pressure redistribution before surgery transport, during surgery and after surgery transport. Our pads have three therapeutic layers that work together to provide excellent pressure redistribution. Custom sizing available.
Heel ProtectionMedline offers top-of-the-line heel protection devices, including our popular HEELMEDIX, that are designed to significantly reduce pressure, friction, and shear by elevating heels. Add these to your comprehensive skin management program.
Read Also: Different Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
Blinding Was Knowledge Of The Allocated Interventions Adequately Prevented During The Trial
Yes, low risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
No blinding, but the review authors judge that the outcome and the outcome measurement are not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
-
Blinding of participants and key trial personnel ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken.
-
Either participants or some key trial personnel were not blinded, but outcome assessment was blinded and the nonblinding of others unlikely to introduce bias.
No, high risk of bias
Any one of the following:
-
No blinding or incomplete blinding, and the outcome or outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding.
-
Blinding of key trial participants and personnel attempted, but likely that the blinding could have been broken.
-
Either participants or some key trial personnel were not blinded, and the nonblinding of others likely to introduce bias.
Unclear
Any one of the following:
-
Insufficient information to permit judgement of Yes or No to be made.
-
The trial did not address this outcome.
The Effect Of Support Surfaces On The Incidence Of Pressure Injuries In Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Cintia Magalhães Carvalho Grion
1Post-graduate Student, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Londrina, Brazil
2Registered Nurse, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Londrina, Brazil
3Registered Nurse, Associação Evangélica Beneficente de Londrina, Londrina, Brazil
4Medicine Graduate Student, Unicesumar, Maringá, Brazil
5Professor, Department of Internal Medicine, Universidade Estadual de Londrina, Londrina, Brazil
Academic Editor:
Abstract
1. Introduction
Patient safety involves all studies, practices, and actions promoted by health institutions to reduce or eliminate the risks of unnecessary harm to health care . In order to reduce adverse events related to health care, the World Health Organization together with the Joint Commission International has established global patient safety goals, which combine strategies focused on higher risk situations, among them the reduction in pressure injuries .
The presence of pressure injuries has been considered an indicator of quality in health services, and efforts have been made to establish guidelines that orientate practices to reduce the problem. Pressure injuries are an important public health problem with great repercussions in different areas, present at all levels of care and that affect mainly, but not only, critically ill patients hospitalized in the intensive care unit .
2. Methods
3. Results
| Total ( |
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcer