Does Ulcerative Colitis Make You Immunocompromised
Ulcerative colitis doesnt make you immunocompromised. Some of the medicines that treat it may change the way your immune system responds. This change is different for each medication. Some of these changes may increase the risk of certain infections or other issues. A discussion with your health care team before starting a medication is the best way to understand these risks and ways to prevent them.
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Treated
Theres no cure for ulcerative colitis, but treatments can calm the inflammation, help you feel better and get you back to your daily activities. Treatment also depends on the severity and the individual, so treatment depends on each persons needs. Usually, healthcare providers manage the disease with medications. If your tests reveal infections that are causing problems, your healthcare provider will treat those underlying conditions and see if that helps.
The goal of medication is to induce and maintain remission, and to improve the quality of life for people with ulcerative colitis. Healthcare providers use several types of medications to calm inflammation in your large intestine. Reducing the swelling and irritation lets the tissue heal. It can also relieve your symptoms so you have less pain and less diarrhea. For children, teenagers and adults, your provider may recommend:
Children and young teenagers are prescribed the same medications. In addition to medications, some doctors also recommend that children take vitamins to get the nutrients they need for health and growth that they may not have gotten through food due to the effects of the disease on the bowel. Ask your healthcare provider for specific advice about the need for vitamin supplementation for your child.
You might need surgery that removes your colon and rectum to:
- Avoid medication side effects.
- Prevent or treat colon cancer .
- Eliminate life-threatening complications such as bleeding.
Is This My Fault
No. Scientists dont really know why your immune system starts to go haywire and inflames your bowel in ulcerative colitis. What seems fairly clear, though, is that it has little to do with what youve done in the past. You didnt catch UC from some infected person or from eating or drinking the wrong thing. Nor did you get it from simply being stressed out.
That said, both hard-to-digest foods and stressful situations can trigger or worsen a flare-up of UC symptoms, if you already have the disease. You can often improve your symptoms if you avoid certain high-fiber foods like uncooked veggies, nuts and seeds, as well as fatty or greasy foods like burgers and fries. Use common sense. If you find that certain foods upset your stomach, try to stay away from them.
It can also help to maintain balanced mental health and avoid unnecessary stress and anxiety. Proper sleep, quitting smoking, and regular exercise could also keep flare-ups at bay.
You May Like: Best Cure For Mouth Ulcers
New Genetic Markers For Ulcerative Colitis Identified
An international team led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers has identified genetic markers associated with risk for ulcerative colitis. The findings, which appear today as an advance online publication of the journal Nature Genetics, bring researchers closer to understanding the biological pathways involved in the disease and may lead to the development of new treatments that specifically target them.
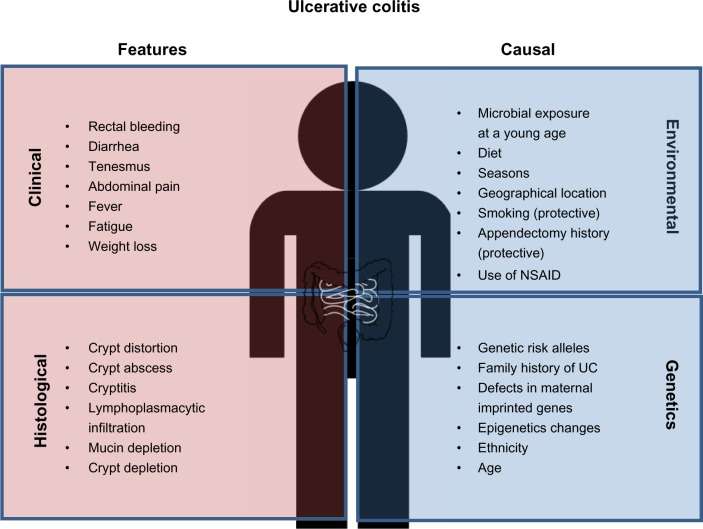
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, relapsing disorder that causes inflammation and ulceration in the inner lining of the rectum and large intestine. The most common symptoms are diarrhea and abdominal pain. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, another chronic gastrointestinal inflammatory disorder, are the two major forms of inflammatory bowel disease .
“Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are chronic conditions that impact the day-to-day lives of patients,” said senior author of the study Richard H. Duerr, M.D., associate professor of medicine and human genetics at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and Graduate School of Public Health. “IBD is most often diagnosed in the teenage years or early adulthood. While patients usually don’t die from IBD, affected individuals live with its debilitating symptoms during the most productive years of their lives.”
Explore further
What Is The Best Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Theres no single diet that works best for ulcerative colitis. If the disease damages the lining of the colon, your body might not absorb enough nutrients from food. Your healthcare provider may recommend supplemental nutrition or vitamins. Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Prednisolone Take To Work For Ulcerative Colitis
How Does Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Affect My Childs Mental/emotional Health
Like many conditions, ulcerative colitis can have a negative psychological effect, especially on children. They can experience physical, emotional, social and family problems. Because of the medications and/or general stress from the situation, your child may experience:
- Mood swings.
- Worry about appearance and physical stamina.
- Vulnerability because their body doesnt function normally.
- Poor concentration.
- Misunderstandings with friends and family.
Children need mutual support from all family members. Its helpful for the entire family to learn about the disease and try to be empathetic. Seek out a psychiatrist and therapist to help your child manage such challenges of their ulcerative colitis.
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Read Also: What To Eat To Help Stomach Ulcers
The Intensity Of Your Symptoms Might Vary Over Time
The most common ulcerative colitis symptoms are diarrhea containing blood or pus and abdominal pain, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases says. Theres a lot of cramping, Cristal Steuer, 38, who was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis while she was in college, tells SELF. You might also experience things like fatigue, fevers, nausea, unintended weight loss, joint pain, and rashes. Whichever symptoms you do have, they may wax and wane, the NIDDK explains. You may have periods when youre in remission interspersed with periods when your symptoms are worse. But some people experience constant symptoms from ulcerative colitis.
Just because you can’t see it doesn’t mean that it’s not hard every single day, Tatiana Skomski, 26, who was diagnosed at 21 after years of unexplained fatigue and pain when an especially bad flare-up nearly caused her to bleed to death, tells SELF.
I’ve had to increase my tolerance for what is a background level of pain, Sam, 22, who was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis in the summer of 2019, tells SELF. I’ll have sharper moments where I can’t functionbut for the most part, it’s more like a constant level of chronic pain.
If pain or other ulcerative colitis symptoms are really interfering with your life, make sure your health care provider knows so that you might be able to tweak your treatment plan if necessary.
Family History Is Biggest Risk For Crohns And Colitis
Talking about irritable bowel disease isnt easy, especially at a family gathering. Theres no better setting in which to have this conversation though, because IBD runs in families. If your family has a medical history of IBD, make it a point to discuss facts about the disease and explain the importance of treatment.
Here are some answers to questions your family members may ask:
What are Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis?
Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are the two most common types of irritable bowel disease, a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the digestive tract. Crohns disease can form anywhere along the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. However, ulcerative colitis only affects the colon and the rectum.
How do my genes affect my risk of IBD?
Family history of inflammatory bowel disease is the most influential risk factor for developing IBD. About 12 percent of people with Crohns disease and about 9 percent of people with ulcerative colitis have a confirmed family history.
Can I calculate my own risk for IBD?
Your risk for IBD depends on which family member is affected. Having a first-degree relative with IBD increases your risk more than having a second-degree relative with the disease. If your mother and your father have IBD, you have a one in three chance of being affected. Your risk for IBD is highest if you have three or more relatives who are affected.
Make an Appointment with a Gastroenterologist
You May Like: I Think I Have Ulcerative Colitis
Things No One Tells You About Life With Ulcerative Colitis
People who have never experienced ulcerative colitis may think it means getting the occasional bad stomachache or having a fussy gastrointestinal system. But as anyone with ulcerative colitis knows, the effects of this inflammatory bowel diseasein which sections of the large intestine develop inflammation and ulcerscan be severe and disrupt many aspects of your life. After a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis, it can be incredibly hard to navigate the reality of your new normal. Knowing the following seven facts about life with ulcerative colitis might help make the whole experience a little bit easier.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Liver disease.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms Back Pain
What Role Does Diet And Nutrition Play In Ulcerative Colitis
Diet does not cause the development of ulcerative colitis nor can any special diet cure the disease. However, the foods you or your child eat may play a role in managing symptoms and lengthening the time between flareups.
Some foods may make symptoms worse and should be avoided, especially during flareups. Foods that trigger symptoms are different from person to person. To narrow down what foods affect you, keep track of what you eat each day and how you feel afterward .
Problem foods often include:
- High sugar foods and drinks.
- Carbonated beverages.
- High-fiber foods.
- Alcohol.
In addition to the problem foods listed above, infants, children and teenagers can also experience issues with:
- Salt.
- Dairy products.
Keep a careful eye on your childs diet and nutrition. Their appetite may decrease during a flareup and they might not eat enough to stay healthy, and grow. Also, the inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis may keep their digestive tract from absorbing enough nutrients. This can also affect your childs health. For these reasons, you may have to increase the amount of calories your child consumes.
Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan if you or your child has ulcerative colitis.
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
To diagnose ulcerative colitis in children, teenagers and adults, your healthcare provider has to rule out other illnesses. After a physical exam, your provider may order:
- Blood tests: Your blood can show signs of infection or anemia. Anemia is a low level of iron in your blood. It can mean you have bleeding in the colon or rectum.
- Stool samples: Signs of infection, parasites , and inflammation can show up in your poop.
- Imaging tests: Your healthcare provider may need a picture of your colon and rectum. You may have tests including a magnetic resonance imaging scan or computed tomography scan.
- Endoscopic tests: An endoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera. Specialized doctors can slide the endoscope in through the anus to check the health of the rectum and colon. Common endoscopic tests include colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Recommended Reading: Foam Dressing For Pressure Ulcer
Large Studies Identify New Risk Genes For Ulcerative Colitis And Ibd
A large body of genetic research, published as two studies, promises to improve scientists understanding of the biology of inflammatory bowel disease and offers potential new drug targets. One study identifies 25 new genetic links to the digestive disease, while the other identifies a gene variant that doubles the risk of ulcerative colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease that leads to ulcers in the inner lining of the large intestine.
Both studies led by the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute at Hinxton in the United Kingdom are published in the journal Nature Genetics.
Inflammatory bowel disease is a group of chronic disorders that cause inflammation of the gut or gastrointestinal tract. There are two main types of IBD: ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, neither of which is currently curable.
Although the exact causes are unknown, scientists suspect that IBD is an autoimmune disorder that arises when the bodys own immune system mistakenly attacks tissue of the GI tract.
People with IBD often experience diarrhea and pain, and they may pass blood from the rectum. Because the disease impairs the ability of the gut to absorb nutrients, it can also lead to anemia.
Estimates suggest between 1 million and 1.3 million people in the United States are living with IBD. In the U.K., where the studies took place, the disease affects more than 300,000 people.
Signaling Pathways Enrichment And Functional Associations
Using the genes carrying the SNPs highlighted by our association analyses, gene-set lists were created as input to the PathwayConnector and the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins , a database of known and predicted proteinprotein associations platforms.
In Method 1, KEGG was selected as the default signaling pathway database, the top ten Enrichr pathways per set were considered as the initial seed pathways used in the complementary network analysis and edge betweenness was selected as the community detection algorithm for clustering on the complementary pathway network.
You May Like: Best Feed For Ulcer Prone Horses
The Heredity Implications Of Pregnancy With Ibd
If you or a relative has Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, you might wonder what role family history plays in IBD, especially when it comes to having children of your own. We’re here to help you understand how IBD can be passed down through families, so you can be informed as you prepare for the road ahead.
Of course, talking with a doctor who specializes in the treatment of IBD in pregnancy is the best way to understand your specific situation, but you can get more IBD information by exploring the questions and answers below.
Inheriting Crohn’s Vs Having A Predisposition
It is not clear whether Crohn’s disease is an inherited condition as a number of factors are involved in the development of the disease.
What is known, however, is that if a family member has an autoimmune disorderlike Crohn’sother members of that family are at risk of developing the same disease or another kind of autoimmune disease. But this does not necessarily mean that if one family member has Crohn’s disease, others will too.
You May Like: Ways To Prevent Pressure Ulcers In Hospitals
Can I Do Anything To Prevent Transmitting Ibd To My Child
Research is continuing to evolve in this area, but the reasons why IBD runs in families are not fully understood since genetics only explains a small fraction of how the disease is inherited. It is possible that other shared risk factors, like environment and/or the microbiome , also play a role.
It’s natural for parents to try to shield their children from anything that could potentially cause them pain. When it comes to IBD, there are no known steps you can take to decrease the risk of passing IBD on to your child. But, you can continue to learn about IBD and help your child manage the disease, should he or she inherit it. After all, you can pass down knowledge to your child, as well.
Environmental Risk Factors And Ulcerative Colitis
There is a limited effect of genetics on UC development and an increasing incidence of UC around the world, suggesting that environmental factors are likely more important to disease development and severity than genetic factors. Environmental risk factors may include:
- Former cigarette smoking
- Personal history of gastrointestinal, colorectal, or digestive diseases
- Use of some medications, such as birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Read Also: What Can I Eat When I Have Ulcerative Colitis
When To Get Medical Advice
You should see a GP as soon as possible if you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis and you have not been diagnosed with the condition.
They can arrange blood or stool sample tests to help determine what may be causing your symptoms.
If necessary, they can refer you to hospital for further tests.
If you have been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and think you may be having a severe flare-up, contact a GP or your care team for advice.
You may need to be admitted to hospital.
If you cannot contact your GP or care team, call NHS 111 or contact your local out-of-hours service.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
Researchers think the cause of ulcerative colitis is complex and involves many factors. They think its probably the result of an overactive immune response. The immune systems job is to protect the body from germs and other dangerous substances. But, sometimes your immune system mistakenly attacks your body, which causes inflammation and tissue damage.
Read Also: What To Eat When You Have Ulcers And Acid Reflux
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
Aphthous ulcersPyoderma gangrenosum
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
UC may affect the mouth. About 8% of individuals with UC develop oral manifestations. The two most common oral manifestations are aphthous stomatitis and angular cheilitis. Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by ulcers in the mouth, which are benign, noncontagious and often recurrent. Angular chelitis is characterized by redness at the corners of the mouth, which may include painful sores or breaks in the skin. Very rarely, benign pustules may occur in the mouth .
UC may affect the eyes. Inflammation may occur in the interior portion of the eye, leading to uveitis and iritis. Uveitis can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light . Untreated, uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss. Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye or the overlying connective tissue , causing conditions called scleritis and episcleritis. Uveitis and iritis are more commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, whereas episcleritis is more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease.