Establishing Extent Of Infection
Early recognition of the area of involved tissue can facilitate appropriate management and prevent progression of the infection . The wound should be cleansed and debrided carefully to remove foreign bodies or necrotic material and should be probed with a sterile metal instrument to identify any sinus tracts, abscesses, or involvement of bones or joints.
Plantar foot ulcers with a deep space infection.
Figure 3.
Plantar foot ulcers with a deep space infection.
Osteomyelitis is a common and serious complication of diabetic foot infection that poses a diagnostic challenge. A delay in diagnosis increases the risk of amputation.13 Risk factors associated with osteomyelitis are summarized in Table 1.3,1316 Visible bone and palpable bone by probing are suggestive of underlying osteomyelitis in patients with a diabetic foot infection.1314 Laboratory studies, such as white blood cell count and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate , have limited sensitivity for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis is unlikely with normal ESR values however, an ESR of more than 70 mm per hour supports a clinical suspicion of osteomyelitis.13 Definitive diagnosis requires percutaneous or open bone biopsy. Bone biopsy is recommended if the diagnosis of osteomyelitis remains in doubt after imaging.3
Wound lacking purulence or any manifestations of inflammation
Diagnosis Of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis
Preventive Care And Treatment
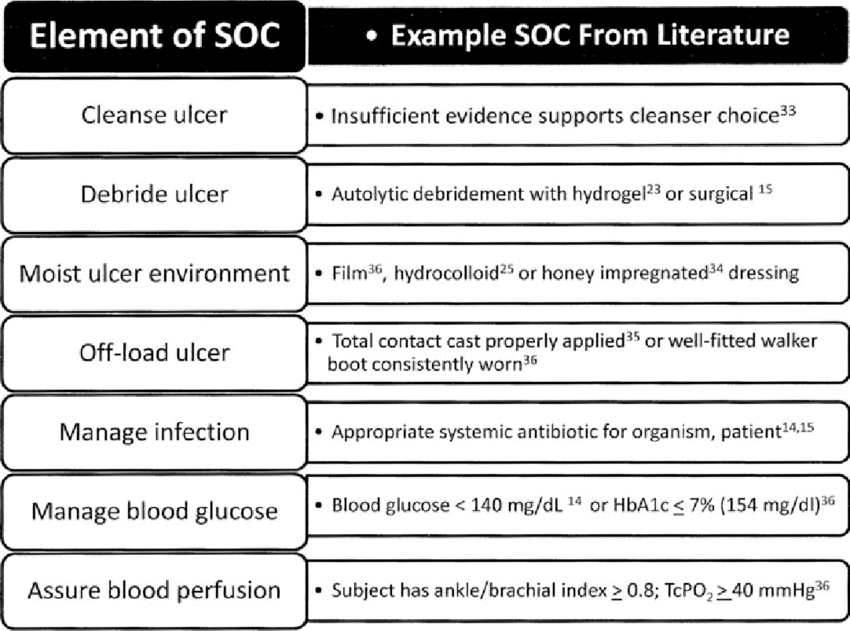
Preventive measures against the risk of amputation include regular foot examination, evaluation of amputation risk, regular callus debridement, patient education, professionally fitted therapeutic footwear to reduce plantar pressure and accommodate foot deformities, and early detection and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers . Many studies that have assessed interventions to prevent and treat diabetic foot ulcers have had limited quality of supportive evidence because of problems in study design and methods . However, the treatment of foot ulcers typically is most effective with an interprofessional approach and includes measures to improve glycemic control, decrease mechanical pressure with off-loading, treat infection, ensure adequate lower-extremity arterial inflow and provide local wound care .
| Table 3 |
|---|
|
Treatment of the acute Charcot foot requires immobilization of the foot, typically for several months, in a total contact cast, removable walker boot or custom orthosis until consolidation occurs . Surgical stabilization may be indicated for Charcot arthropathy associated with marked instability, deformity or nonhealing ulcers. Although bisphosphonates have been considered for the treatment of Charcot arthropathy, further studies are necessary to fully evaluate these agents and other medical therapies in the routine treatment of Charcot arthropathy .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Cure Mouth Ulcers
What Is A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, 6 percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
Diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations in the United States, and approximately 14-24 percent of patients with diabetes who develop a foot ulcer will require an amputation. Foot ulceration precedes 85 percent of diabetes-related amputations. Research has shown, however, that development of a foot ulcer is preventable.
Guidelines For Dressings In The Treatment Of Diabetic Ulcers
Preamble: There are a large number of topical therapies available for DFUs. Most dressings are used in combination with off-loading, debridement, and infection control. It is thought that a moist wound environment physiologically favors cell migration and matrix formation. There are several criteria that should be considered when selecting a dressing including the cost, potential for iatrogenic injury, and wound exudate management. First, dressings should not damage the wound. If the wound and surrounding tissue have continuous contact with wound exudate, the local tissue can become macerated and impede healing. Likewise, dressings that are not secure can cause friction injuries to the surrounding skin or wound bed. The cost of health care provider time, healing rate, and the unit cost of dressings should be considered when determining cost efficacy. Randomized clinical studies have not yet identified that any dressing approach is more effective than others to facilitate wound healing.
Guideline #5.1: Use a dressing that will maintain a moist wound-healing environment.
Principle: A moist wound environment physiologically favors cell migration and matrix formation while accelerating healing of wounds by promoting autolytic debridement.
Guideline #5.2: Use clinical judgment to select a moist wound dressing.
Guideline #5.3: Select a dressing that will manage the wound exudates and protect the peri-ulcer skin.
Guideline #5.5: Select a dressing that is cost effective.
Don’t Miss: Foam Boots For Pressure Ulcers
Guidelines For The Use Of Adjuvant Agents In The Treatment Of Diabetic Ulcers
Preamble: Many agents have been suggested to be used as adjuvants to dressings and off-loading therapy in the treatment of diabetic ulcers. These adjuvant agents can be divided into topical agents to be applied to the ulcer, devices aimed at accelerating ulcer healing, and systemic drugs to treat the patient. Several of these agents have enough evidence to allow guidelines regarding their use.
Peripheral Arterial Disease And The Dfu
Recommended Reading: Ways To Prevent Pressure Ulcers In Hospitals
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment: Iwgdf Guideline
M3 India NewsdeskApr 20, 2020
The International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot has issued an evidence-based guideline which lists out the principles of ulcer treatment. As per IWGDF, foot ulcers will heal in the majority of patients if the clinician bases treatment on the principles outlined. Patients with an ulcer deeper than the subcutaneous tissues may require intensive treatment and in some cases need to be hospitalised.
Diabetic foot disease is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus and ulcers are a frequent occurrence. The propensity of ulcer formation is high in diabetes patients presenting with two or more risk factors, with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and peripheral artery disease usually playing a key role.
Management Of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: A Literature Review
Angger Anugerah Hadi Sulistyo2483
Abstract
This article explores the effective management of diabetic foot ulcer. A literature review was conducted by analyzing scholar papers including systematic review, clinical and a randomized control trial published between 2000 to 2016 in the English language. Data were searched through CINAHL, PubMed, Proquest and Google Scholar. The keywords used were diabetic foot ulcer or diabetic foot ulcers or diabetic foot or neuropathic foot ulcer combined with assessment and treatment. There were two kinds of assessment used in diabetic foot ulcer which are risk assessment and wound assessment. The treatments that frequently used in diabetic foot ulcer are systemic treatment and local treatment. This literature review can be used as a guideline and literature for further experimental studies.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer, management of foot ulcer, assessment of foot ulcer, treatment of foot ulcer
Abstrak
Kata Kunci: luka kaki diabetes, manajemen luka kaki, pengkajian luka kaki, penanganan luka kaki
Keywords
Full Text:
References
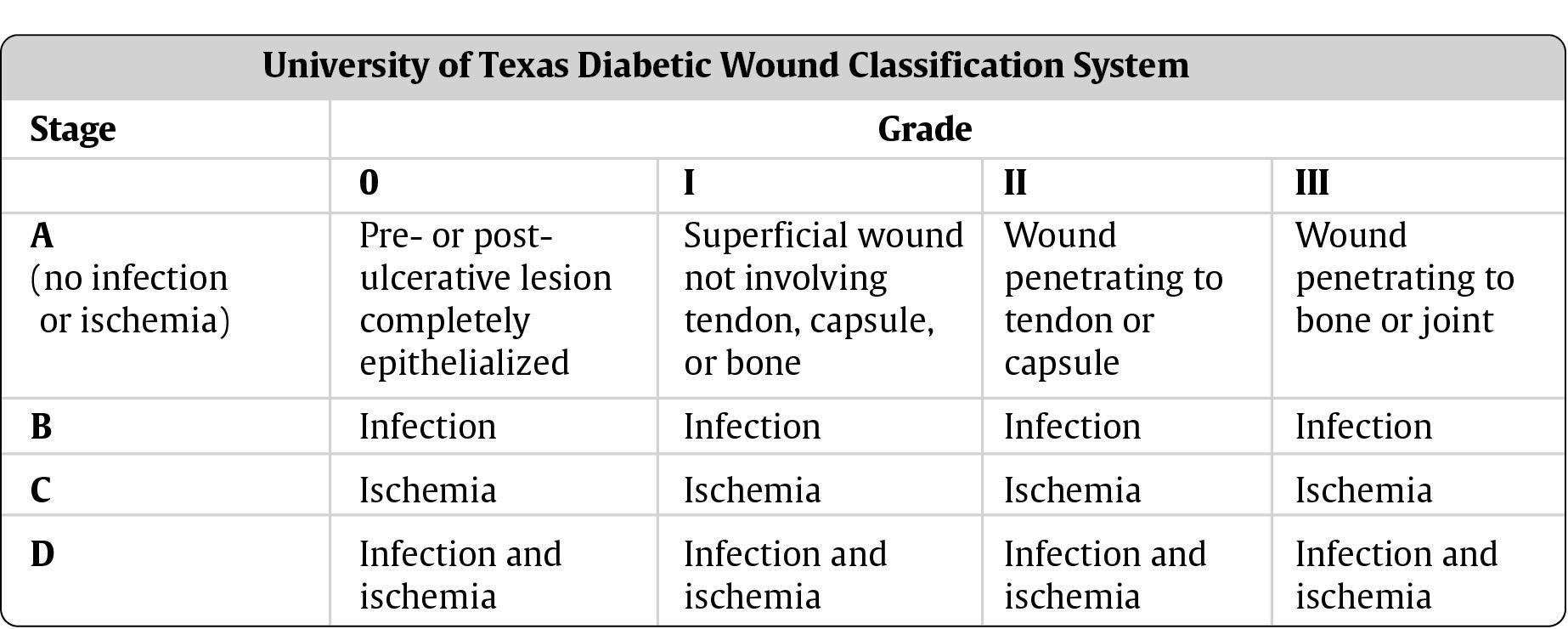
Abbas, Z.G., Lutale, J.K., Game, F.L., & Jeffcoate, W.J. . Comparison of four systems of classification of diabetic foot ulcers in
Tanzania. Diabetic Medicine, 25 , 134137.
Alexiadou, K., & Doupis, J. . Management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Therapy, 3, 4.
Bentley, J., & Foster, A. . Management of the diabetic foot ulcer: Exercising control. British journal of community nursing, 13 .
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Mouth Ulcers Fast
Guidelines For Wound Bed Preparation In The Treatment Of Diabetic Ulcers
Preamble: Wound bed preparation is defined as the management of the wound to accelerate endogenous healing or facilitate the effectiveness of other therapeutic measures. The aim of wound bed preparation is to convert the molecular and cellular environment of a chronic wound to that of an acute healing wound.
Guideline #4.1: Examination of the patient as a whole is important to evaluate and correct causes of tissue damage. This includes factors such as: systemic diseases and medications, nutrition, and tissue perfusion and oxygenation.
Principle: A general medical history, including a medication record, will help in identifying and correcting systemic causes of impaired healing. The presence of a major illness or systemic disease and drug therapies such as immunosuppressive drugs and systemic steroids will interfere with wound healing by alterations in immune functioning, metabolism, inflammation, nutrition, and tissue perfusion. Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, uncontrolled vasculitis, or pyoderma gangrenosum can all delay healing and may require systemic steroids or immunosuppressive agents before local wound healing can occur. Patients undergoing major surgery have a diminished wound-healing capacity as do chronic smokers. Smoking is associated with impaired wound healing and increased risk of infection.
Guidelines And Conflicts Of Interest
All members of the expert panel complied with the IDSA policy regarding conflicts of interest, which requires disclosure of any financial or other interest that might be construed as constituting an actual, potential, or apparent conflict. Members of the expert panel were provided a conflicts of interest disclosure statement from IDSA and were asked to identify ties to companies developing products that might be affected by promulgation of the guideline. The statement requested information regarding employment, consultancies, stock ownership, honoraria, research funding, expert testimony, and membership on company advisory committees. The panel was instructed to make decisions on a case-by-case basis as to whether an individual’s role should be limited as a result of a conflict, but no limiting conflicts were identified.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Vii When Should I Consider Imaging Studies To Evaluate A Diabetic Foot Infection And Which Should I Select
Recommendations
-
25.We recommend that all patients presenting with a new DFI have plain radiographs of the affected foot to look for bony abnormalities as well as for soft tissue gas and radio-opaque foreign bodies .
-
26.We recommend using magnetic resonance imaging as the study of choice for patients who require further imaging, particularly when soft tissue abscess is suspected or the diagnosis of osteomyelitis remains uncertain .
-
27.When MRI is unavailable or contraindicated, clinicians might consider the combination of a radionuclide bone scan and a labeled white blood cell scan as the best alternative .
Guidelines For Infection Control In The Treatment Of Diabetic Ulcers
Preamble: Infection results when the bacteria: host defense equilibrium is upset in favor of the bacteria. Infection plays various roles in the etiology, healing, operative repair, and complications of diabetic ulcers.
Guideline #3.1: Remove all necrotic or devitalized tissue by surgical, enzymatic, mechanical, biological, or autolytic debridement. .
Principle: Devitalized tissue provides a safe haven for bacterial proliferation, a barrier for antibiotics to reach bacterial pathogens. In addition, it limits the body’s cellular defenses to fight infection. Removal of devitalized tissue reduces bacterial bioburden.
Guideline #3.2: If there is suspected infection in a debrided ulcer, or if epithelialization from the margin is not progressing within two weeks of debridement and initiation of offloading therapy, determine the type and level of infection in a debrided diabetic ulcer by tissue biopsy or by a validated quantitative swab technique.
Principle: High levels of bacteria impede wound healing and surgical wound closure. Reduction of the bacterial bioburden in the wound reduces the risk of clinical infection and improves wound healing. Cultures should be performed to isolate both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Guideline 3.8: If osteomyelitis is suspected, determine the type of bacterial pathogens by bone biopsy .
You May Like: What Is A Gastric Ulcer And What Is Its Cause
Data Sources And Searches
Since the 2006 guidelines, we sought to capture the highest quality of literature available regarding DFU diagnosis and treatment using a key word search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. Similarly, the citations of relevant articles were examined by hand. Key terms were generated from the existing guidelines. In this search as opposed to the previous data collection prior to 2006, we used human and disease specific data and limited to meta-analyses, systematic reviews, RCTs, retrospective series reviews, clinical case series, and expert panel recommendations published between January 2006 and present. References prior to 2006 supporting the original guideline recommendations are not included. Therefore, in some cases no additional updated references were included and the support for the guideline recommendation is based on evidence presented in the 2006 guideline. Therefore, no updated references are presented. It was further limited to only English publications. Any relevant additional references found after the formal search were also included.
The findings of these articles have been divided into one or more of the appropriate categories as performed in the original guideline
Evidence Reference:
-
- Retrospective series review
Ix In Which Patients With A Diabetic Foot Infection Should I Consider Surgical Intervention And What Type Of Procedure May Be Appropriate
Recommendations
-
38.We suggest that nonsurgical clinicians consider requesting an assessment by a surgeon for patients with a moderate or severe DFI .
-
39.We recommend urgent surgical intervention for most foot infections accompanied by gas in the deeper tissues, an abscess, or necrotizing fasciitis, and less urgent surgery for wounds with substantial nonviable tissue or extensive bone or joint involvement .
-
40.We recommend involving a vascular surgeon early on to consider revascularization whenever ischemia complicates a DFI, but especially in any patient with a critically ischemic limb .
-
41.Although most qualified surgeons can perform an urgently needed debridement or drainage, we recommend that in DFI cases requiring more complex or reconstructive procedures, the surgeon should have experience with these problems and adequate knowledge of the anatomy of the foot .
Recommended Reading: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Cancer
Treatment Of The Foot Ulcer Depends On The Severity Of The Wound
|
Severity |
|
|
|
|
Not infected |
|
|
Mild infection |
|
|
Moderate infection |
|
|
Severe infection |
|
Clinical Pathways And Assessment Forms For Diabetic Foot
Our Testimonials
-
I don’t have time to assess the quality of the many websites out there I would want to refer people to. Health Navigator solves this in one easy step. It is my “go to place” to send people for great information and self-management support.
Dr David Codyre
Primary care psychiatrist
-
Health Navigator provides the whole package of information on a topic. There is a high level of health literacy for the website itself and the information provided.
Christine Andrews
Quality Improvement Manager, Marlborough PHO
-
I was really impressed because health is covered in its entirety. Its a very useful site for clinicians or anyone interested in gaining knowledge around the current status of indigenous wellbeing here in Aotearoa.
-
I always recommend Health Navigator resources to my patients. It provides high quality, reliable, NZ relevant information in a clearly organized and easy to understand way. This means people can quickly get the key information or dig deeper when needed.
Dr Rebecca Grainger
Rheumatologist & researcher, University of Otago, Wellington
-
Health Navigator is such a valuable resource. Its useful for consumers, health professionals and health students as it covers a diverse range of topics, the explanations are easy to understand, and most importantly is credible and NZ focussed.
Dr Michelle Honey
You May Like: What To Eat When You Have Ulcers And Acid Reflux