What Do Chills Feel Like With Ibd
Many people with IBD experience chills. MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam members describe this symptom in different ways. As one shared, Its like I cannot get warm.
Some people find that chills are accompanied by other symptoms, like fevers: I get flu-like episodes which come on suddenly, wrote one member. Headache, very sore neck and back, big spike in temperature, alternating sweats and chills. Its gone by the next morning. Another shared, The night sweats are horrible! My sheets are soaked every morning.
Sometimes, these chills and other flu-like symptoms are what spur a person with IBD to see a doctor in the first place. If a persons gastrointestinal symptoms are not particularly severe, fever and chills might be the first indication that something is wrong. As one member commented, Fevers and chills were part of what led to my Crohns diagnosis.
These symptoms may occur during IBD flares in some cases, even without accompanying gastrointestinal symptoms. Fever and chills are part of the symptoms of a Crohns flare-up I had, shared one member. These were the only symptoms for about a week.
However, some people with IBD experience these symptoms on a regular basis. For the past month or so, I have been getting chills while I have a bowel movement, and they are getting worse each day, one member wrote.
Symptom Development And Flares
The symptoms of UC usually start out fairly mild, such as slightly looser or more frequent bowel movements. The symptoms may become more severe as inflammation worsens and open sores develop in the bowel. Eventually, a person with UC might experience fatigue, fever, nausea, and weight loss.
Some people experience ulcerative colitis constantly. However, it is more common to have flare-ups, during which symptoms begin or worsen, followed by periods of remission, when symptoms go away or improve for a while.
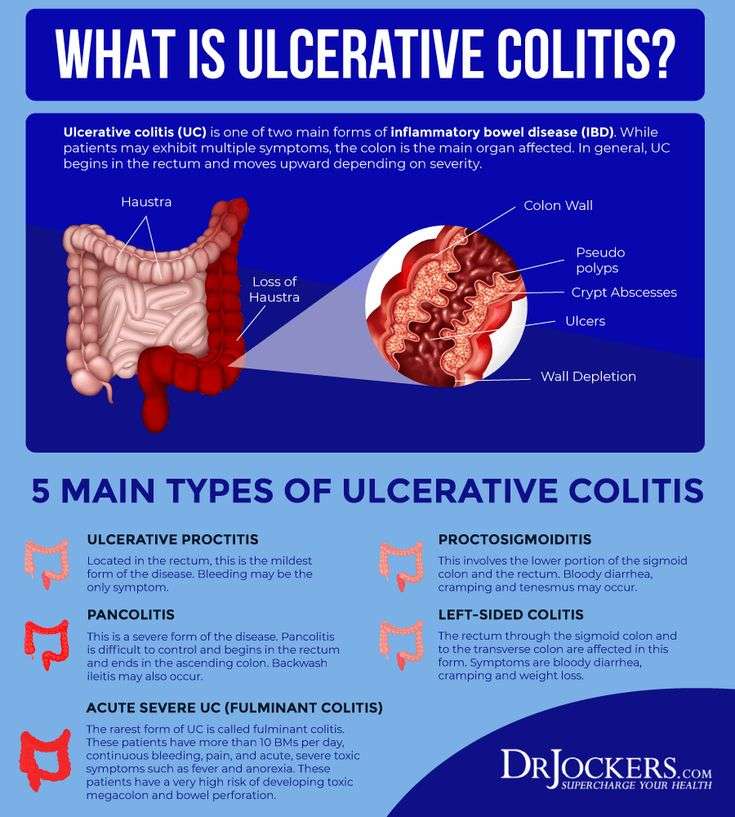
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis causes irritation and ulcers in the large intestine . It belongs to a group of conditions called inflammatory bowel disease . It often causes diarrhea with blood, cramping and urgency. Sometimes these symptoms can wake a person up at night to go to the bathroom as well.
The inflammation in ulcerative colitis usually starts in the rectum, which is close to the anus . The inflammation can spread and affect a portion of, or the entire colon. When the inflammation occurs in the rectum and lower part of the colon it is called ulcerative proctitis. If the entire colon is affected it is called pancolitis. If only the left side of the colon is affected it is called limited or distal colitis.
The severity of UC depends on the amount of inflammation and the location. Everyone is a little different. You could have severe inflammation in the rectum or very mild inflammation in the entire colon .
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may notice a pattern of flare-ups , when symptoms are worse. During times of remission, you might have little to no symptoms. The goal with therapy is to remain in remission as long as possible .
Don’t Miss: What Foods Help Stomach Ulcers
Prognosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is usually chronic, with repeated flare-ups and remissions . In about 10% of people, an initial attack progresses rapidly and results in serious complications. Another 10% of people recover completely after a single attack. The remaining people have some degree of recurring disease.
People who have ulcerative proctitis have the best prognosis. Severe complications are unlikely. However, in about 20 to 30% of people, the disease eventually spreads to the large intestine . In people who have proctitis that has not spread, surgery is rarely required, cancer rates are not increased, and life expectancy is normal.
What Is The Best Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Theres no single diet that works best for ulcerative colitis. If the disease damages the lining of the colon, your body might not absorb enough nutrients from food. Your healthcare provider may recommend supplemental nutrition or vitamins. Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan.
You May Like: How Do You Heal A Bleeding Ulcer
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Effects Of Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Every person responds differently to IBD. The severity of symptoms will vary from time to time and from person to person. IBD is not a progressive disease . Rather, flare-ups can range from mild to severe and back to mild again. Some people will experience periods of relief from symptoms in between flare-ups.We cannot predict how long a person will stay free from symptoms, or when their next flare-up will occur. Some flare-ups settle down quite quickly with treatment. Other times, it may take months for a persons symptoms to respond to treatment.IBD interferes with a persons normal body functions. Signs and symptoms can include:
- pain in the abdomen
- delayed or impaired growth in children.
Also Check: What Is A Vascular Ulcer
Ulcerative Colitis And Colonoscopy
Doctors can use a colonoscopy to diagnose UC or determine the severity of the condition.
Before the procedure, a doctor will likely instruct you to reduce solid foods and switch to a liquid-only diet. Then youll fast for a period of time before the procedure.
Typical colonoscopy prep involves taking a laxative the evening before the procedure, too. This helps eliminate any waste still in the colon and rectum. Doctors can examine a clean colon more easily.
During the procedure, youll lie on your side. Your doctor will give you a sedative to help you relax and prevent any discomfort.
Once the medication takes effect, the doctor will insert a colonoscope into your anus. This device is long and flexible so it can move easily through your GI tract. The colonoscope also has a camera attached so your doctor can see inside the colon.
During the exam, the doctor will look for signs of inflammation and check for precancerous growth called polyps. The doctor may also perform a biopsy. The tissue can be sent to a laboratory for further examination.
If youve been diagnosed with UC, a doctor may conduct periodic colonoscopies to monitor inflammation, damage to your intestines, and healing progress.
These symptoms are sometimes associated with UC complications.
If you havent been diagnosed with UC, see a doctor if you experience multiple symptoms of the condition. They can help determine whether you may have UC or another bowel disease.
Digestive Changes In Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition, meaning it comes on slowly over a long period of time. Currently, there is no known cure for UC.
With UC, inflammation and ulcers develop on the lining of the large intestine . Sometimes the rectum is affected, as well.
This inflammation can cause changes in bowel habits, including urgency, diarrhea, blood or mucus in the stool, and abdominal pain. When your large intestine is inflamed, it contracts and empties often, which is why you may have urgent bowel movements and diarrhea.
When chronic inflammation damages the lining of your colon, ulcers can develop. The ulcers can bleed, leading to blood in your stool. If you regularly lose a lot of blood in your stool, you might develop anemia .
Though diarrhea is more common, some people with UC experience constipation. Inflammation limited to the rectum, known as ulcerative proctitis, may result in constipation.
Other symptoms of UC include painful bowel movements, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, unintentional weight loss, and fever.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Signs Of An Ulcer
What Foods Cause Colitis
Foods with high fiber content like brown rice, quinoa, oats can trigger the symptoms of Colitis especially Ulcerative colitis . It is difficult to digest high fiber foods which increase the bowel movements and abdominal cramps. Caffeine. Coffee, tea and other caffeine-rich drinks are known to flare up the UC.
Who Is At Risk For Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Most diagnoses of ulcerative colitis are in men between the ages of 15 and 35. The disease course for ASUC can be harder to predict, but it commonly appears between ages 34 and 48.
There is data showing that 54% of those who developed ASUC get it within 1 year of their UC diagnosis 18% developed ASUC within 1 to 5 years of their initial diagnosis and 28% were diagnosed with ASUC more than 5 years after their UC diagnosis.
Additional studies show that those who were diagnosed before the age of 40 had an aggressive disease course, had large or deep ulcers on their colons, higher levels of inflammation, were prescribed steroid medications earlier in their disease, and were at a higher risk of severe disease, including ASUC. Men were at higher risk of needing a colectomy than women.
Recommended Reading: Best Anti Diarrhea Medicine For Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
To diagnose ulcerative colitis in children, teenagers and adults, your healthcare provider has to rule out other illnesses. After a physical exam, your provider may order:
- Blood tests: Your blood can show signs of infection or anemia. Anemia is a low level of iron in your blood. It can mean you have bleeding in the colon or rectum.
- Stool samples: Signs of infection, parasites , and inflammation can show up in your poop.
- Imaging tests: Your healthcare provider may need a picture of your colon and rectum. You may have tests including a magnetic resonance imaging scan or computed tomography scan.
- Endoscopic tests: An endoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera. Specialized doctors can slide the endoscope in through the anus to check the health of the rectum and colon. Common endoscopic tests include colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
How Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Treated
ASUC is a challenging condition to treat. Once you’re admitted to the emergency room, you’ll get a series of tests, including blood tests, stool tests, and an exam of your bowel called a sigmoidoscopy. You’ll also get intravenous fluids to boost hydration.
The average hospital stay for ASUC treatment ranges from 4.6 to 12.5 days. During this time, your health care providers may include a gastroenterologist, colorectal surgeon, dietitian, pharmacist, and stomal therapist. The goal of hospitalizing you is to end the flare, get your symptoms under control, and put the disease into remission. Your doctors will want to make sure that rectal bleeding and diarrhea have stopped and normal bowel movements have returned. Rehospitalization is common.
Intravenous steroid medications are the most common treatment for ASUC. For 30% to 40% of ASUC patients, steroid treatments donât work â and taking steroid medications for more than 10 days increases your risk of complications.
If the steroids donât help within 3 to 5 days, your health care team will start âmedical rescue therapyâ with immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or infliximab.
You might get an operation to remove part of your colon, called a colectomy, if your ASUC doesnât respond to steroids, immunosuppressants, or other medical treatments.
Read Also: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Body Aches
Predictors Of Outcomes In Asuc Response To Corticosteroid Therapy And Indicators For Rescue Therapy
Several markers have been studied as predictors of outcome in ASUC. These can be divided into clinical, biochemical, endoscopic and radiological and several indices and scoring systems have been developed, that can potentially predict disease outcomes and therefore guide patient management. Low albumin levels have been associated with an increased risk for colectomy and a CRP/albumin ratio of 0.85 on day 3 of intravenous steroid therapy was found to predict the need for colectomy with a sensitivity of 70% and specificity of 76% in one study . Endoscopic markers can also be used as predictors and severe endoscopic lesions including deep ulcers, extensive loss of mucosal layers, well-like ulcers or large erosions have been associated with non-response to corticosteroids and need for colectomy . As previously mentioned, a UCEIS of7 on admission is a predictor of the need of rescue therapy or colectomy . The use of faecal calprotectin as a predictor of failure of corticosteroid therapy has also been investigated. A prospective cohort study by Jain et al. found that all patients with UCEIS> 6 on admission and faecal calprotectin> 1000 g/g on day 3 failed steroid therapy .
Symptoms By Type Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis can be broken into subtypes depending on where the inflammation is in your colon.
- Ulcerative proctitis. Ulcerative proctitis affects your rectum, the part of your colon closest to your anus. Its the most common type and affects 30 to 60 percent of people with ulcerative colitis.
- Proctosigmoiditis. Proctosigmoiditis causes inflammation of your rectum and the lower part of your colon, called the sigmoid colon.
- Left-sided colitis. Left-sided colitis affects your rectum, your sigmoid colon, and the descending part of your colon on the left side of your body.
- Pancolitis.Pancolitis affects your entire colon.
Symptoms typically become worse as inflammation spreads farther along your colon.
| Ulcerative proctitis |
show ulcerative colitis is slightly more prevalent in men, but most studies show no difference.
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis are similar regardless of sex, but unique issues may occur for some people.
Rectovaginal fistulas may develop, which are holes that allow stool to leak from the bowel to the vagina.
Ulcerative colitis may also lead to irregular periods or increased menstrual pain. Women may also be at a higher risk of anemia and osteoporosis, and ulcerative colitis can further increase this risk.
Recommended Reading: How To Apply Compression Bandages For Leg Ulcers
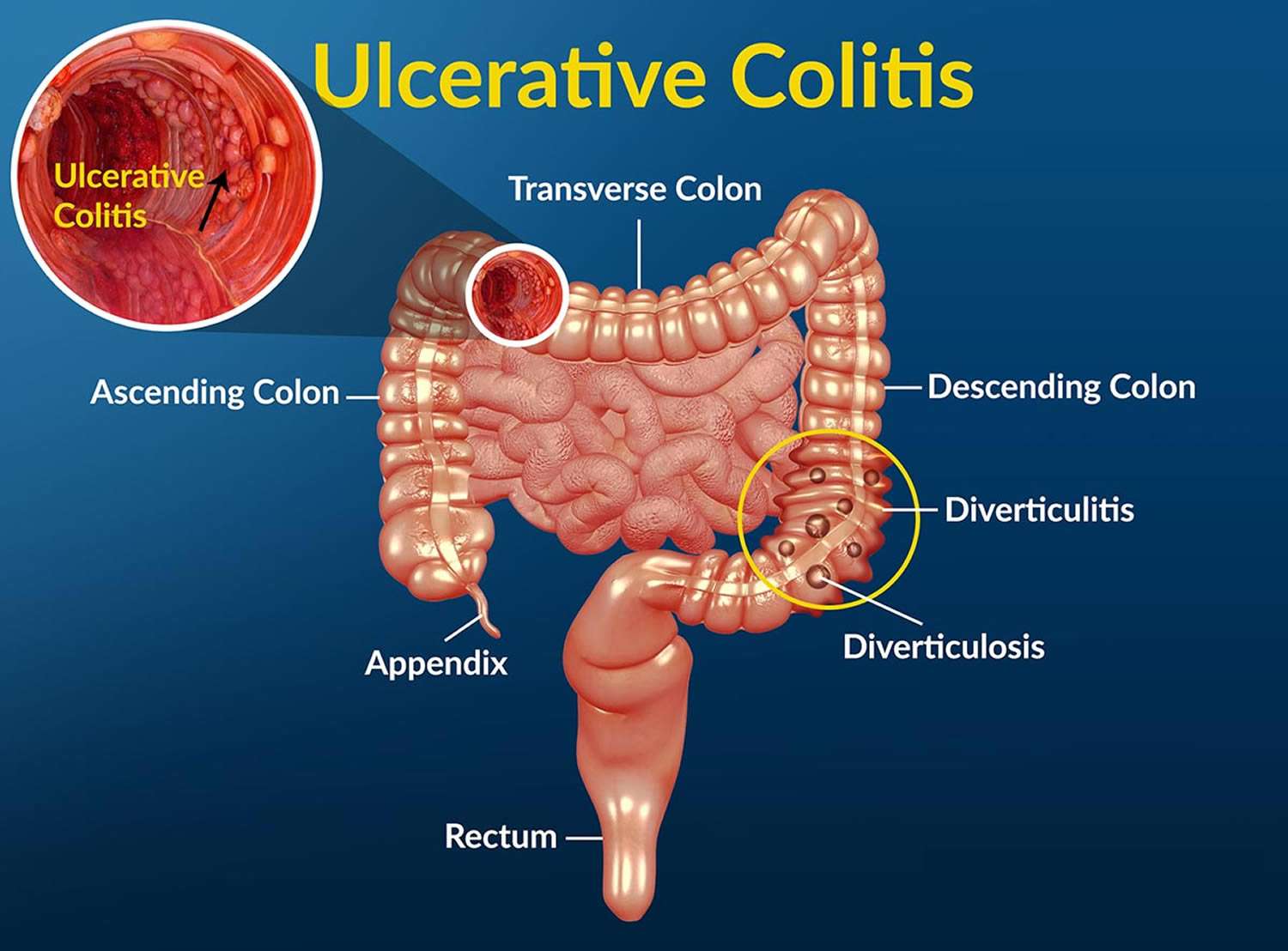
Where And How Does Ulcerative Colitis Start
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease . This chronic digestive disorder is characterized by inflammation in the colon and the rectum. People diagnosed with ulcerative colitis can develop sores on the inside of their large intestine, which can lead to bleeding, diarrhea, and other symptoms.
If youve experienced these symptoms or have been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis, you may be unsure exactly how the disease began. Heres what you need to know about where in the body ulcerative colitis starts and how.
Can The Immune Response To Covid
byKate Kneisel, Contributing Writer, MedPage Today March 1, 2022
A 50-year-old male patient presented to an outpatient clinic in the spring of 2020 with fever and dyspnea he told clinicians that the symptoms had persisted for the past 3 days.
Physical examination findings included a fever of 37.8°C , respiratory rate of 24 breaths/min, and heart rate of 105 beats/min. There was no organomegaly, and the patient was a non-smoker.
Initial laboratory test findings included:
- White blood cell count: 6.4 × 109/L
- C-reactive protein : 4.6 mg/L
- Ferritin: 162 ng/mL
- D-dimer: 842 ng/mL
Findings of a polymerase chain reaction test for SARS-CoV-2 were negative. However, the patients wife and two children had positive PCR test results and the patients CT chest scan revealed diffuse ground-glass opacities consistent with viral pneumonia. Clinicians diagnosed him with COVID-19, and he was started on a now-debunked 7-day regimen of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin. Once he was clinically stable, he was released with instructions to return for a follow-up assessment.
On follow-up assessment 1 week later, the patient reported no improvement in symptoms. His stool calprotectin level was 1800 g/g . Endoscopy revealed a diffuse, micro-ulcerated, granulated appearance that clinicians noted continued uninterrupted from the dentate line to the sigmoid colon, as well as distortion of the submucosal vascularization.
Discussion
Also Check: What Does A Mouth Ulcer Look Like
You May Like: How To Treat Ulcerative Colitis Pain
How Can I Help My Child Live With Ulcerative Colitis
Children with this condition need long-term care. Your child may have times when symptoms go away . This can sometimes last for months or years. But symptoms usually come back.
Your child should learn what foods trigger his or her symptoms and avoid these foods. You and your childs healthcare provider should make sure your child gets enough nutrients to grow and develop well. Support groups can help you and your child. Work with your childs healthcare provider to create a care plan for your child.
Who Diagnoses Ulcerative Colitis
If you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis, your regular healthcare provider will probably refer you to a specialist. A gastroenterologist a doctor who specializes in the digestive system should oversee the care for adults. For young patients, a pediatric gastroenterologist who specializes in children should manage the care.
You May Like: Bed To Prevent Pressure Ulcers
What To Look For
The key is to pay attention to your specific symptoms. The more you’re aware of them, the better able you are to spot changes.
And there are lots of ways your symptoms can change. You might get new ones. Or the ones you have may get worse, last longer, or come on more often.
Usually, a flare-up brings at least:
- An urgent need to poop
- Blood or mucus in your stool
- Cramps in your lower belly
If it spreads to more areas of the colon, everything gets more intense. You have more diarrhea. Cramps get more severe. You have more mucus, pus, and blood in your stool. Pain in your belly gets worse and more widespread, especially up the left side. It can also affect your desire to eat and cause you to lose weight.
And some of those symptoms may just be signs of a stronger flare-up. You’ll need to see your doctor to find out for sure. Read more on ulcerative colitis symptoms to look for.
Living With Ulcerative Colitis
With careful management, most people with UC are able to enjoy life, including work, travel, recreation, sex and having children.
To keep healthy, consider:
- eating a nutritious diet to help with healing and reduce fatigue
- keeping a food diary to check if there are any foods that make your symptoms worse during a flare-up
- asking your doctor about supplements if you think you may be malnourished
- exercising regularly to lift your mood and help relieve stress
- learning some relaxation techniques to help manage stress
Don’t Miss: How To Calm An Ulcer Attack