How Is Treatment The Same And Different
In both conditions, treatments usually involve medications or, sometimes, surgery. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a combination of the two to bring your symptoms under control. Certain over-the-counter medications may ease some of your pain-related symptoms. These include:
- Anti-diarrheal medications
- Antispasmodics to ease cramps and bloating
- Iron supplements, especially if youâre bleeding
UC treatments may include:
Anti-inflammatory drugs. This is usually the first line of treatment. This can include drugs like 5-aminosalicylates and corticosteroids. Some newer drugs like sulfasalazine and 5-ASAs , which are called âsteroid-sparing,â can be safely taken long-term. Your doctor may not want you to take steroids long-term because of their side effects.
Immunosuppressant drugs. This helps to reduce inflammation in your colon and cut down the immune response that might attack your digestive cells.
Biologics. This targets the proteins made by your immune system.
Surgery. About 30% of people who have UC need surgery. Itâs sometimes the only cure, especially if medications donât ease your symptoms or they become too difficult to manage. Your doctor may consider a surgery called proctocolectomy.
In this procedure, your entire colon and rectum are removed. Most surgeries also involve a procedure in which your doctor will attach a pouch at the end of the small intestine or outside your body to pass poop directly into it.
Diverticulitis treatments may include:
Oral Signs Of Crohn Disease
The oral mucosa is commonly affected in Crohn disease with up to one third of patients reported to have oral changes, and even higher in children. In some studies, the oral changes preceded the diagnosis of Crohn disease in 60%. There may be a male predominance.
1. Specific oral mucosal changes: orofacial Crohn disease
In children with Crohn disease, orofacial Crohn disease can be an important presentation preceding the bowel diagnosis.
2. Nonspecific changes in the mouth and surrounding facial skin associated with Crohn disease:
Ibd Mimics: Most Common Conditions Misdiagnosed As Ibd
Since there is no single, gold standard diagnostic test for inflammatory bowel disease there are many disease processes that can be misdiagnosed as IBD, given its often non-specific symptoms. There is a broad differential diagnosis when considering IBD, however most of the etiologies generally fall into two categories: infectious and non-infectious. Some of these disease states affect a portion of the gastrointestinal tract which may help differentiate them from IBD and one another. First, we will review the non-infectious etiologies which include autoimmune disorders, vasculidities, ischemia, diverticular disease, drugs, cancer, and radiation-induced disease. It is important to note that while many of the etiologies discussed have histologic changes in colon biopsies in order to diagnosis IBD features of chronicity are warranted.
Non-infectious Mimics
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive condition where patients have oculocutaneous albinism, bleeding diathesis and other organ specific involvement including granulomatous colitis which can have features like CD. Patients with this condition who manifest GI disease usually have abdominal pain, fever, bloody stool and weight loss.6 The colon is most commonly affected, but like CD, may affect any part of the GI tract.
Infectious Mimics
Read Also: How To Treat Gum Ulcers
Main Differences Between Colitis And Diverticulitis
Diagnostic Focus And Assessment
The laboratory tests performed on the first day of admission revealed leukocytosis with neutrophilia , thrombocytosis , anemia , elevated inflammatory biomarkers , and low serum urea levels . The abdominal ultrasound examination was normal. Lower digestive endoscopy pointed out multiple ulcerations, hemorrhage, and edema of the sigmoid colon , thus suggesting a possible IBD however multiple orifices raised the suspicion of a CD, which was afterwards confirmed through a barium enema.
Figure 1. Initial aspect of the colon at colonoscopy.
Histopathological examination of the colonic biopsy specimens showed active inflammation associated with architectural changes of the colonic mucosa and crypt abscesses, which highly suggested a chronic inflammatory process, most likely UC. By taking into account the macroscopic aspect of the colonic mucosa and the histopathological results correlated with the presence of colonic diverticula, we were able to establish the diagnosis of SCAD.
Recommended Reading: Can Stress Cause Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
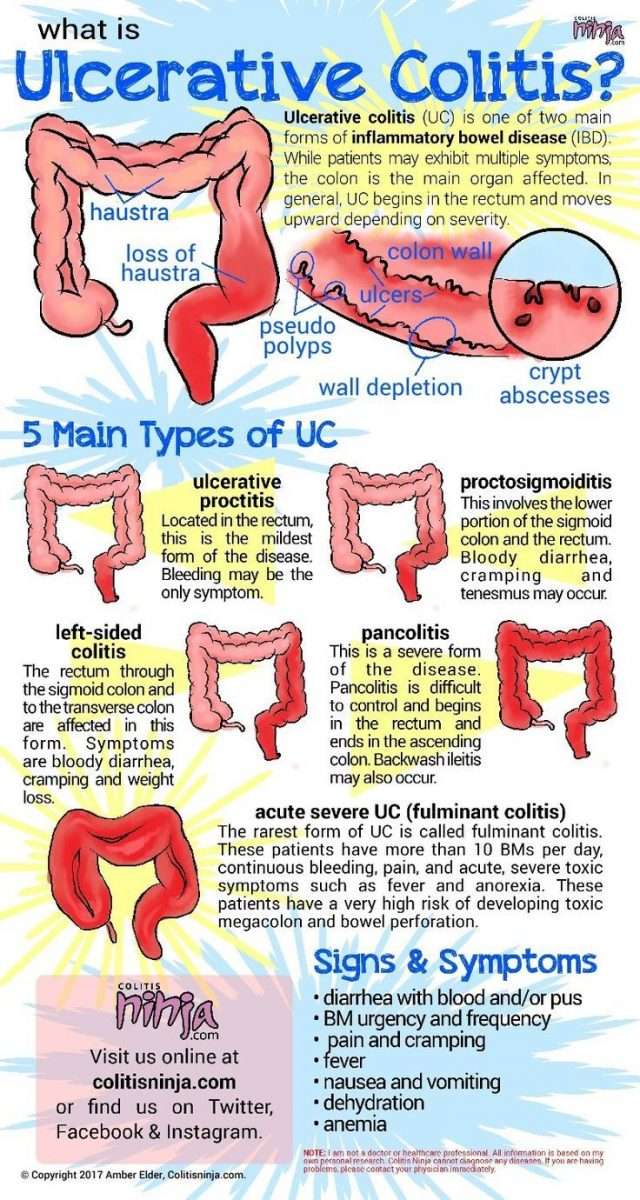
What Is Ulcerative Colitis
Defined as a chronic inflammation of the large intestine and rectum, ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease which can also give rise to inflammation in joints, spine, skin, eyes, and the liver and bile ducts, if the severity increases with time. This inflammatory process can also give rise to multiple tiny sores and ulcers in the affected areas, causing bleeding and discharge of pus.
This condition can affect individuals of any age, but symptoms will mainly be visible around the age of 15-30 and 50-70.
Even though the exact etiology for ulcerative colitis is not known yet, stress, heredity, and weakened immune system are thought to be playing important roles in the pathophysiology. People who are under the treatment of Isotretinoin, which is used to treat cystic acne are also at a high risk of developing this condition.
Patients with ulcerative colitis will usually experience abdominal pain, increased abdominal sounds, stools mixed with blood, diarrhea, fever, rectal pain, weight loss and malnutrition. Sometimes, there can be associated features such as nausea, vomiting, joint swelling and pain, skin ulcers and mouth sores depending on the affected systems.
According to latest research studies, ulcerative colitis is known to increase the risk of colon cancer. Therefore, it is highly important to carry out a colonoscopy in order to exclude a possible risk.
You May Like: Remicade Dosing For Ulcerative Colitis
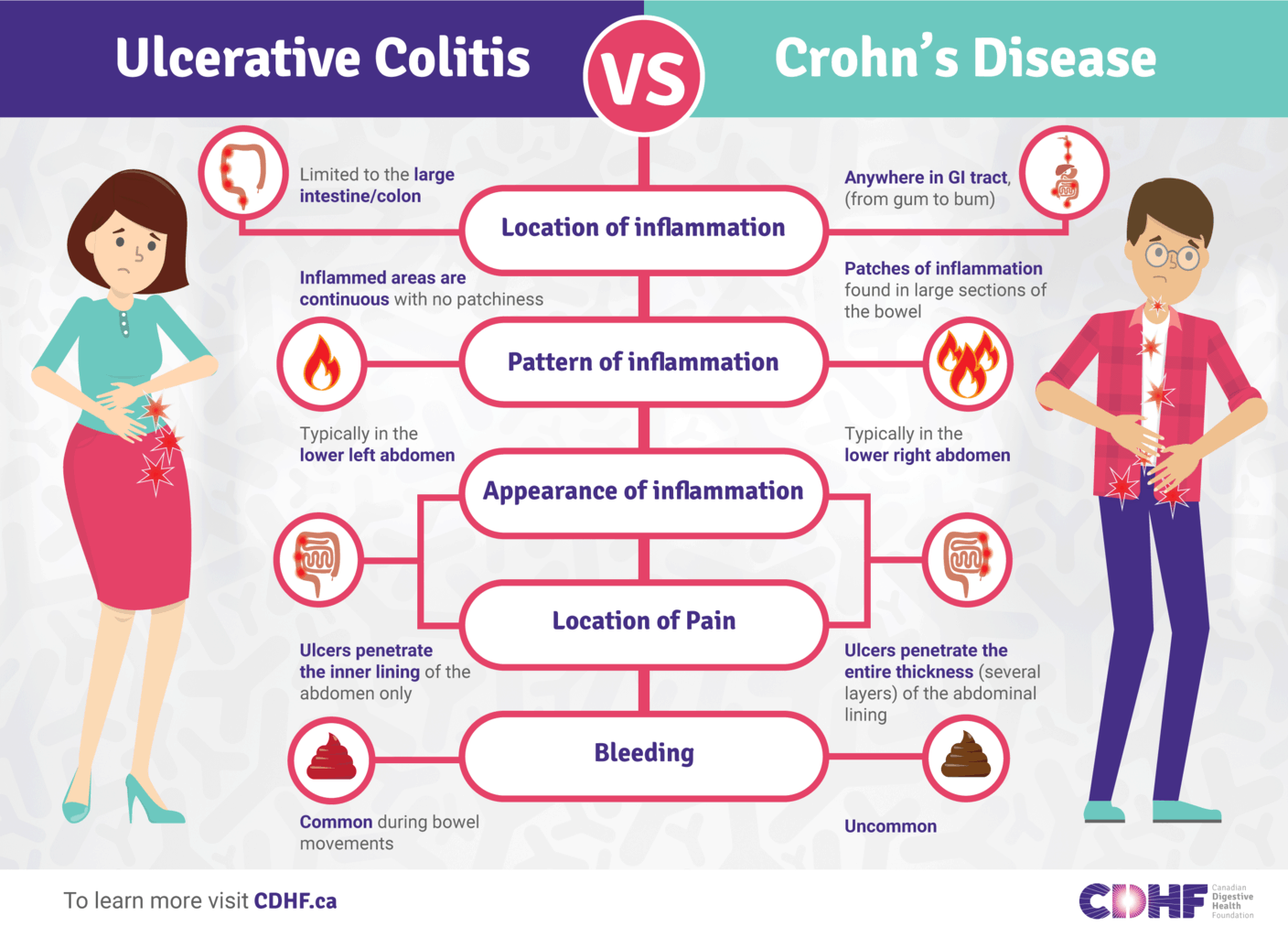
Ulcerative Colitis And Diverticulitis: Similarities And Differences
UC and diverticulitis both start out in the large intestine and share symptoms like belly pain and bloody poop. Both conditions are more likely the older you get, and both can range from mild to severe and vary for each person. But they differ in terms of what causes them and how your doctor might treat them.
UC is a lifelong condition that can lead to life-threatening problems. About a million Americans are affected by it. It can affect people at any age, including those in their 20s and 30s. If you have UC, you also might have weight loss or arthritis.
Diverticulitis, not a lifelong condition, is a complication of âdiverticulosis.â Itâs the term doctors use when one or more of the small bulging sacs grow on your colon wall. It usually starts in middle age and itâs common in older people. Diverticulitis can happen to you once and never happen again, or it might come and go. About 50% of those over the age of 60 have it, and almost everyone above 80 has it, too. Most are mild cases that donât cause any symptoms and arenât reasons to worry. Up to 30% of the people with diverticulosis go on to have diverticulitis. And among them, anywhere between 5%-15% will have symptoms like bloody poop.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Medication Not Working
Differentiating Crohns Disease And Diverticulitis Treatment
Crohns disease has a long list of treatment methods, because there is no exact cause to target. Treatment for Crohns disease may include corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressant agents, antibiotics, biologic agents, nutritional and dietary counseling, stress management, and, in severe Crohns disease cases, surgery to remove heavily affected areas of the intestines and colon.
Medical treatments for diverticulitis include antibiotics to treat infection, liquid diet to allow bowels to heal, and over-the-counter pain relievers. In complicated cases of diverticulitis, surgery may be required, such as primary bowel resection, where the affected part of the intestine is removed and the rest of it is reconnected. Another option is bowel resection with colostomy if it is impossible to reconnect the colon to the rectum due to inflammation.
If diverticulitis is causing pain, there are home remedies you can try for relief. To reduce muscle cramping caused by diverticulitis, you can apply heat to the abdomen. Meditation, too, may be beneficial in managing the associated pain. Lastly, if you need to opt for a pain reliever, stay away from ibuprofen and instead reach for acetaminophen .
There are also some preventative measures you can try to lower your risk of developing diverticulitis.
What Is The Difference Between Colitis And Diverticulitis
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Don’t Miss: How Does Humira Work For Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Diagnosis The Same And Different
If you think you have either UC or diverticulitis, talk to your doctor about it. You might be referred to a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in digestive issues, for a correct diagnosis.
Your doctor will first do a detailed medical exam. Theyâll ask you about your medical history including things like your diet, your bowel movements, and medications you might be taking.
Common tests to diagnose UC and diverticulitis include:
- Blood tests. This is done to check for infections
- Stool sample test. This checks for bacteria or parasites that might cause your stomach pain, cramps, or diarrhea
- Colonoscopy. The doctor will use a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the tip to explore your entire colon. They may take small tissue samples to test.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy. This is similar to a colonoscopy, except your doctor will only explore your rectum and s-shaped sigmoid colon â both of which are located at the lower end of your colon. This is usually done if you have severe inflammation.
- Barium enema. This test is also called lower gastrointestinal tract radiography. In this test, your doctor injects a liquid containing barium into your butt. The barium coats your entire colon and makes it easier to see clearly under an X-ray scan.
- CT scan. This test allows your doctor to scan your abdomen and pelvic area and spot inflamed areas in your colon. The scan can detect the irritated or inflamed pouches for diverticulitis and confirm the condition.
Comparing Ulcerative Colitis And Diverticulitis Signs And Symptoms
Ulcerative colitis symptoms include abdominal pain, increased abdominal sounds, blood stools, diarrhea, fever, rectal pain, weight loss, malnutrition, joint pain and swelling, mouth sores, nausea, vomiting, and skin ulcers.
Signs and symptoms of diverticulitis include severe pain that may last for days and takes place in the lower left side of the abdomen, nausea and vomiting, fever, abdominal tenderness, constipation, and in some cases diarrhea .
Recommended Reading: Can Duodenal Ulcer Cause Back Pain
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Diverticulitis: Us Prevalence
The CDC estimated that one to 1.3 million Americans are affected by IBD. Generally, ulcerative colitis is more prevalent in males than females.
Roughly two million people in the U.S. suffer from diverticular disease. Prevalence rate is one in 136, or 0.74 percent. Annually, 300,000 new cases of diverticular disease are diagnosed.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Diverticular Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms and Signs of Diverticulosis
- Pain in the belly
- Bloating
- Constipation
- Cramping
These symptoms are nonspecific. This means that similar symptoms are seen in many different digestive disorders. They do not necessarily mean that a person has diverticulosis. If an individual has these symptoms, he or she should see a healthcare professional.
Symptoms and Signs of Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a more serious condition and causes symptoms in most people with the condition that include:
- Pain in the abdomen, usually in the lower-left side
- Bleeding, bright red or maroon blood may appear in the stool, in the toilet , or on the toilet paper. Bleeding is often mild and usually stops by itself however, it can become severe.
- Fever
- Chills
- Constipation
- Worsening abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Constipation for an extended period of time
- Burning or pain during urination
- Bleeding from the rectum
Symptoms and Signs of Ulcerative Colitis
- Frequent loose bowel movements with or without blood
- The urgency to have a bowel movement and bowel incontinence
- Lower abdominal discomfort or cramps
- Fever, lethargy, and loss of appetite
- Weight loss with continuing diarrhea
- Anemia due to bleeding with bowel movements
Don’t Miss: What Are Leg Ulcers Caused By
Bloating Vs Weight Gain
Bloating is different than weight gain. Weight gain occurs over time when a person regularly eats more calories than they use through exercise and normal bodily activities.
Bloating occurs when a persons gastrointestinal tract is full of air or other gases .
When bloated, a person may find that their stomach feels full and tight as though they have eaten a big meal. This sensation can be uncomfortable or even painful, and it may cause a persons stomach to appear bigger than usual.
There are several possible causes of weight gain in people with UC.
Ulcerative Colitis And Weight Gain
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and bloody stools. Although weight loss is a common symptom of UC, the condition can sometimes cause a person to gain weight.
UC is a relatively common long-term condition that causes the immune system to react abnormally. This immune reaction inflammation in the colon and causes ulcers to appear in the colons inner lining.
A person with UC may experience some of the following symptoms:
UC can cause various other symptoms, which include fatigue, a loss of appetite, fever, nausea, and anemia.
These symptoms often only appear during flare-ups, which usually appear before a period of remission. When a person is in remission, they may experience few or no symptoms.
Although it is common to lose weight as a result of UC, some people may gain weight due to the disease.
UC can cause both weight gain and weight loss.
UC can affect a persons ability to digest food properly and absorb nutrients from it. Due to this, it can lead to serious vitamin deficiencies and malnutrition. Both of these effects can cause a person with UC to lose weight.
However, there are several reasons why UC can also cause a person to gain weight. These include:
- issues eating certain foods
found that people with inflammatory bowel disease, which includes UC, had significantly worse belly pain, gas, and bloating than people in the general population.
Also Check: Ulcerated Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Crohns Disease Vs Diverticulitis: Us Prevalence
Prevalence of Crohns disease in the U.S. is 26 to 199 per 100,000 persons, and the incidence rate of Crohns disease is 3.1 to 14.6 cases per 100,000 person-years.
Roughly two million people in the U.S. suffer from diverticular disease. Prevalence rate is one in 136, or 0.74 percent. Annually, 300,000 new cases of diverticulitis are diagnosed.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Tongue Ulcers
Ibs Vs Diverticulitis: What Are The Differences
Irritable bowel syndrome vs Diverticulitis These are two different conditions that can cause issues with the digestive system.
People often get confused between them as their symptoms can be fairly similar, but they are in fact very different conditions.
So what are the differences between irritable bowel syndrome and diverticulitis? How do you know which one you have?
We have put together some useful information about the two conditions to help you understand the differences between them.
Read Also: How To Ease Stomach Ulcer Pain
What Causes Diverticular Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Causes of Diverticular Disease
Diverticulosis is thought to be caused by increased pressure on the intestinal wall from inside the intestine.
- As the body ages, the outer layer of the intestinal wall thickens. This causes the open space inside the intestine to narrow. Stool moves more slowly through the colon, increasing the pressure.
- Hard stools, such as those produced by a diet low in fiber or slower stool “transit time” through the colon can further increase the pressure.
- Frequent, repeated straining during bowel movements also increases the pressure and contributes to the formation of diverticula.
Diverticulosis in developed countries is blamed largely on a diet low in fiber.
- Fiber is found in fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes .
- There are two types of fiber soluble and insoluble.
- Soluble fiber forms a soft gel-like substance in the digestive tract.
- Insoluble fiber passes through the digestive tract nearly unchanged.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The cause of ulcerative colitis is uncertain. Researchers believe that the body’s immune system reacts to a virus or bacteria, causing ongoing inflammation in the intestinal wall. Although UC is considered to be a problem with the immune system, some researchers believe that the immune reaction may be the result, not the cause, of ulcerative colitis.
Diverticulitis & Colitis Diet
Fact Checked
Diet is an important part of the management of diverticulitis or colitis 1. In diverticular disease, small pockets or pouches form in the wall of the colon when these pouches get inflamed, the condition is called diverticulitis. Colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine this can be caused by irritable bowel disease, an inflammatory bowel disease like Crohns, or infections. When you have either of these conditions, you have to make some changes in your diet during the flare-ups to aid in your recovery.
Dont Miss: Best Ulcerative Colitis Diet Book
Recommended Reading: Cure For Stomach Ulcer Symptoms