Mild To Moderate Disease
First-line therapy in mild to moderate disease is the 5-ASA drugs, which can be administered as suppositories, enemas, or oral formulations . There does not appear to be any difference in efficacy or safety between different 5-ASA formulations.119 Sulfasalazine, which is metabolised to 5-ASA, appears to have similar efficacy to 5-ASA drugs, but tends to be less well tolerated.114 Patients with proctitis should be treated initially with 5-ASA suppositories since they directly target the site of inflammation and appear to be more effective than oral 5-ASA.114,118,120 In left-sided colitis, 5-ASA should be administered as an enema instead of a suppository in order to reach the splenic flexure. For patients with left-sided or extensive disease, it is recommended that oral 5-ASA be used in combination with topical 5-ASA to induce remission.114,118 Oral 5-ASA doses of 2 g or higher per day are more effective than lower doses at inducing and maintaining remission.121123 5-ASA can be started at a dose of 2.02.4 g per day and increased up to 4.8 g, if needed.114,123 Dosing of 5-ASA once a day has similar efficacy to divided doses and could increase adherence.114,123 Patients typically see a response within 14 days, but this response might take up to 8 weeks for symptomatic remission.114 5-ASA drugs have also been shown to be effective at maintaining remission, and patients who achieve remission with 5-ASA should continue on the same medication.114
What Is The Best Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Theres no single diet that works best for ulcerative colitis. If the disease damages the lining of the colon, your body might not absorb enough nutrients from food. Your healthcare provider may recommend supplemental nutrition or vitamins. Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan.
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Also Check: Normal Colon Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Does Uc Have Serious Complications
It canespecially if left untreated or if you dont follow directions for your medications. Common complications of UC include:
-
Rectal bleeding, which can lead to anemia
-
A perforated colon, a dangerous condition where large intestine ruptures
-
Increased risk of colon cancer the chronic inflammation can increase the likelihood of cancerous cells developing. Depending on how long youve had UC symptoms, you may need more frequent colonoscopies to screen for this cancer, according to a study in Clinical Endoscopy.
-
Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin. These deficiencies can lead to things like anemia and bone loss in the form of osteopenia or osteoporosis.
-
Inflammation throughout the body, such as the eyes, skin, and joints. This can lead to things like dry eye, rashes, and arthritis.
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
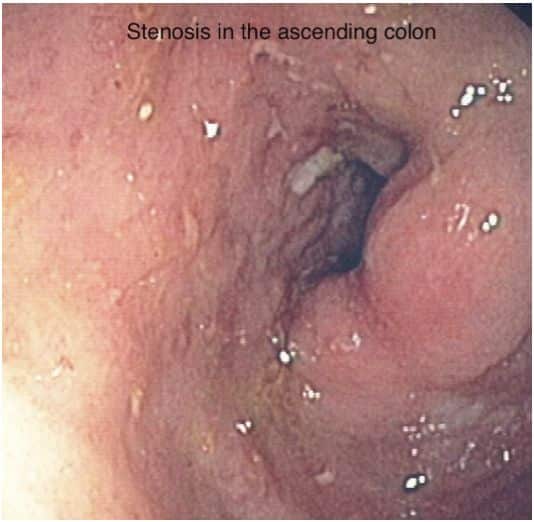
UC and Crohns disease are the most common forms of IBD. Both conditions are thought to be the result of an overactive immune system.
They also share many symptoms, including:
However, UC and Crohns disease do have distinct differences. Understanding the key differences between them can help you obtain a proper diagnosis.
Location
These two conditions affect different portions of the GI tract.
Response to treatment
Similar medications are prescribed to treat both conditions. Surgery is also a treatment option. Its a last resort for both conditions, but it can be a cure for UC, whereas its only a temporary therapy for Crohns.
Also Check: What Foods Not To Eat When You Have An Ulcer
What Should I Ask My Doctor On Behalf Of My Child Or Teenager
Ask your healthcare provider the following questions in addition to the ones listed above:
- What vitamins should my child take?
- Will my other children have pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child at risk for other conditions?
- Can you recommend a psychiatrist or therapist to help my child with emotional issues related to pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child growing at a normal rate?
- What can I do to help my child cope at school?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
When you have ulcerative colitis, its essential to work closely with your healthcare team.
Take your medications as prescribed, even when you dont have symptoms. Skipping medications youre supposed to take can lead to flareups and make the disease harder to control. Your best shot at managing ulcerative colitis is to follow your treatment plan and talk to your healthcare provider regularly.
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis And What Causes It
Colitis can develop at any age, but usually first appears in people aged 15 to 30.
Experts are not sure why UC or Crohns disease occurs in some people. It may be due to a combination of genetic, environmental and infectious factors that cause a fault in the immune system leading to inflammation of the bowel.
You May Like: Ulcerative Colitis What Vitamins Can I Take
You May Like: What Causes Ulcers On The Feet
Crohns & Colitis Uk Local Networks
Our Local Networks of volunteers across the UK organise events and provide opportunities to get to know other people in an informal setting, as well as to get involved with educational, awareness-raising and fundraising activities. You may find just being with other people and realising that you are not alone can be reassuring. Families and relatives may also find it useful to meet other people with Crohn’s or Colitis. All events are open to members of Crohns & Colitis UK
How Can I Prevent Inflammatory Bowel Disease
While there isnt anything you can do to prevent IBD, certain dietary and lifestyle changes may control the symptoms. You can:
- Eat smaller meals every two to four hours.
- Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, movement like tai chi, listening to music or going for a walk.
- Get plenty of sleep and stay physically active.
- Keep a food diary to identify foods that trigger IBD flares. You may find you have a food intolerance, such as lactose intolerance. If so, your body has a harder time digesting certain foods, which causes stomach upset.
- Reduce foods that irritate the intestines, such as those that are fibrous, spicy, greasy or made with milk. During flares, choose soft, bland foods that are less inflammatory.
- Cut back on caffeinated, carbonated and alcoholic beverages. Drink more water to prevent dehydration.
Recommended Reading: Diet To Control Ulcerative Colitis
Learn What The Phrase Chronic Condition Means When It Refers To The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Ibd
Medically reviewed in July 2021
In medical terminology, chronic means lasting a long time. But the meaning of lasting a long time can have different meanings depending on the condition that you are referring to. For example:
- Chronic migraine refers to having 15 or more migraines a month for three months or longer.
- Chronic Hepatitis C refers to a liver infection from the hepatitis c virus, an infection that can be cured but will not go away on its own without treatment.
- Chronic kidney disease is a condition where the kidneys stop working. There is no cure and treatment focuses on slowing the progression.
Ulcerative colitis is considered a chronic condition because it is a lifelong illnessthere is no cure and it requires ongoing treatment and management.
Here, we take a closer look at ulcerative colitis and what its status as a chronic condition means for people living with UC.
Ulcerative colitis is a form of IBD Along with Crohns disease, UC is one of the two main types of inflammatory bowel disease . Both conditions can cause a number of painful and uncomfortable symptomsabdominal pain, frequent diarrhea, bloody stools, fatigue, and weight loss. Both conditions can also result in a number of complications, including permanent damage to sections of the GI tract.
Healthcare researchers have not identified the exact cause of UC or Crohns disease but believe the causes to be a combination of environmental triggers and genetic factors.
Medically reviewed in July 2021.
Search Strategy And Selection Criteria
We searched for relevant manuscripts in PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Central from their inception until March 1, 2016. The search combined the MeSH terms ulcerative colitis and inflammatory bowel disease with the subheadings epidemiology, etiology, physiopathology, innate and adaptive immunity, diagnosis, genetics, diagnosis, endoscopy, therapy, surveillance, and complications. Bibliographies of included articles were searched and experts in inflammatory bowel disease were consulted to identify additional studies. Relevant articles and abstracts published in English were critically reviewed. Priority was given to manuscripts published in the past 5 years, randomised placebo-controlled trials, and meta-analyses.
Also Check: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Acid Reflux
Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease The Telltale Symptoms
Symptoms also include fatigue, which manifests itself as severe tiredness with no cause and has a profound impact on the patients personal, social and working life.
Joint, skin, eye and liver problems can also be associated with these diseases: these are immune-mediated extra-intestinal manifestations, which in some cases can even anticipate the typical symptoms of the disease by a few years.
What Is The Medical Term For Intestinal Inflammation
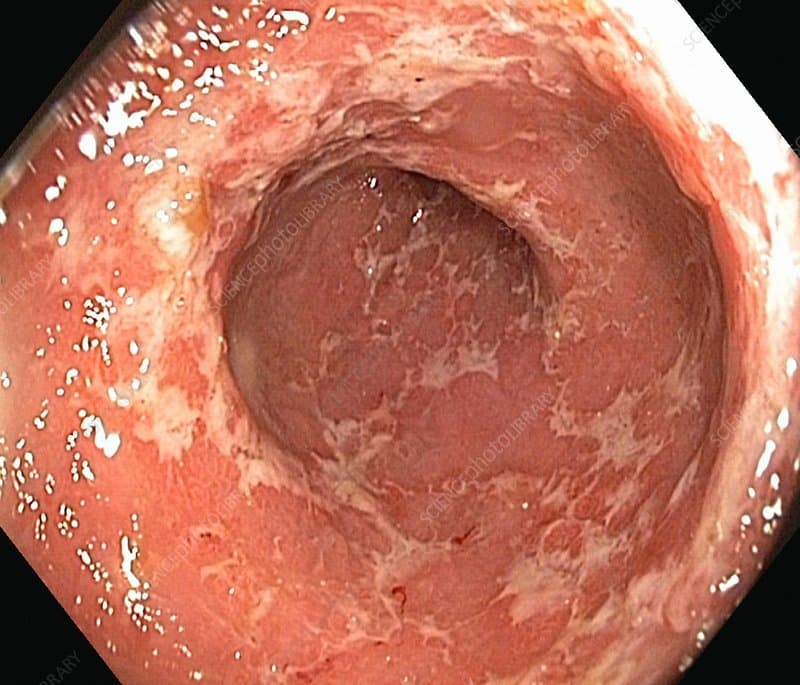
IBD refers to two illnesses that are characterized by persistent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Although they are both called IBD, they have different causes and treatments.
The terms irritable bowel syndrome and functional bowel disorder are also used to describe patients who experience abdominal pain or discomfort along with diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and mucus in their stools. IBS can be diagnosed based on a patient’s history and physical examination findings there are no lab tests to confirm the diagnosis. For FBD, additional testing may be needed to rule out organic causes for the patient’s symptoms.
Medical terms can be hard to understand! Do not worry if you do not understand everything at first. As you become more familiar with health concepts, you will learn how things work inside the body and these new discoveries will help you better understand diseases and treatments. In time, you will be able to explain these ideas to others.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Leg Ulcers Quickly
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
UC may affect the mouth. About 8% of individuals with UC develop oral manifestations. The two most common oral manifestations are aphthous stomatitis and angular cheilitis. Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by ulcers in the mouth, which are benign, noncontagious and often recurrent. Angular chelitis is characterized by redness at the corners of the mouth, which may include painful sores or breaks in the skin. Very rarely, benign pustules may occur in the mouth .
UC may affect the eyes. Inflammation may occur in the interior portion of the eye, leading to uveitis and iritis. Uveitis can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light . Untreated, uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss. Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye or the overlying connective tissue , causing conditions called scleritis and episcleritis. Uveitis and iritis are more commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, whereas episcleritis is more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease.
Future Directions And Controversies
The number of drugs modulating different disease pathways is expected to expand in the near future. There are at least 27 new drugs for ulcerative colitis with either recently completed or active trials.170 One example is the oral pan-janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib, which has shown higher rates of clinical remission than placebo in phase 2 studies.171 Etrolizumab, a subcutaneous monoclonal antibody that blocks the 7 subunit of the heterodimeric integrins 47 and E7 achieved higher clinical remission rates than placebo in a phase 2 trial.172 An oral anti-4 integrin therapy significantly increased clinical remission and endoscopic healing in a phase 2 trial.173 An oral drug inhibiting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors that blocks lymphocyte egress from lymph nodes has also shown efficacy.174 In a small trial of 5-ASA non-responders, curcumin increased endoscopic remission in mild to moderate ulcerative colitis as an add-on therapy.175 Biosimilar biological drugs should decrease the cost of therapy. Results from initial studies with an infliximab biosimilar, CT-P13, have shown efficacy at inducing endoscopic healing in ulcerative colitis.176 However, immunogenicity and efficacy remains a concern particularly in patients switching from the originator to the biosimilar.177
You May Like: What Is An Ulcer In Your Mouth
Treatment Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
There is currently no cure but there are medications that can help to:
- heal the bowels
- relieve symptoms
- control the inflammation
If the inflammation cannot be controlled with medication, sometimes surgery is needed. Early diagnosis and treatment may reduce the risk of needing surgery or having complications.
Is Ulcerative Colitis Considered An Autoimmune Disease
The immune system protects the body against infection. Many doctors think ulcerative colitis is an autoimmune disorder . Your body’s immune system contains different types of cells that protect it by fighting off foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. When the immune system fails to differentiate between “self” and non-self”, it causes autoimmune diseases.
Immune system disorders can be categorized as specific or non-specific. Specific immune system disorders involve problems with certain types of immune cells. These disorders can be diagnosed using blood tests. In contrast, non-specific immune system disorders involve problems with all types of immune cells. Non-specific disorders cannot be diagnosed using blood tests and require visual inspection of the body for signs of inflammation or infection. Ulcerative colitis is a non-specific immune system disorder.
People with ulcerative colitis have increased risks of developing cancers of the colon, breast, pancreas, and bladder. It is important to follow recommended screening procedures for these conditions.
Treatment for ulcerative colitis should not include surgery. Instead, focus your treatment on reducing your symptoms and waiting for the disease to heal on its own. This may take years for some people.
You May Like: Compression Stockings For Venous Leg Ulcers
In My Shoes: 24 Hours With Crohns Or Colitis App
In My Shoes is an immersive experience that allows anyone to find out first-hand what its like to have Colitis.
From low energy levels to managing pain, from rushing to the toilet to juggling work and a social life, the app will allow friends, family and anyone you want, to see first-hand how the condition can affect every part of your body, and every aspect of your life.
We have information for friends and family, employers, and colleagues. Find all our information online.
We have around 50 Local Networks across the UK that bring local people affected by Crohns and Colitis together. They are run by volunteers and host a range of events, from educational talks to socials. Check our website or call our Helpline to find your nearest Local Network.
Overview Of Ulcerative Colitis
While it can be overwhelming to receive a chronic disease diagnosis, learning all you can about ulcerative colitis will prepare you to manage your symptoms and live a full life.
Have you or a loved one been recently diagnosed with ulcerative colitis? Or were you diagnosed years ago but still dont fully understand your disease? Check out our latest video chat to learn more.
Video Length00:38:13
Video Chat: Ulcerative Colitis 101
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the large intestine, also called the colon, that affects the lining of the colon and causes small sores, or ulcers, to form.
Those ulcers produce pus and mucous, which cause abdominal pain and the need to frequently empty your colon.
Video Length00:06:55
Ulcerative Colitis 101 This introductory video provides information on potential causes, symptoms, treatment and overall management of ulcerative colitis.
Recommended Reading: Ulcer Cause Blood In Stool
Ulcerative Colitis Risk Factors
Most people with UC dont have a family history of the condition. However, about 12 percent of people with UC do have a family member with IBD, according to research from 2014.
UC can develop in a person of any race, but its more common in white people. If youre of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, you have a greater chance of developing the condition than most other groups.
Young people with IBD may also be dealing with acne at the same time. Some older studies have suggested a possible link between the use of the cystic acne medication isotretinoin and UC. However, newer research has yet to find a definitive causal relationship.
Theres no solid evidence indicating that your diet affects whether you develop UC. You may find that certain foods and drinks aggravate your symptoms when you have a flare-up, though.
Practices that may help include:
- drinking small amounts of water throughout the day
- eating smaller meals throughout the day
- limiting your intake of high fiber foods
- avoiding fatty foods
- lowering your intake of milk if youre lactose intolerant
Also, ask a doctor if you should take a multivitamin.
Panel: Major Differential Diagnoses In Diagnostic Examination Of Ulcerative Colitis74
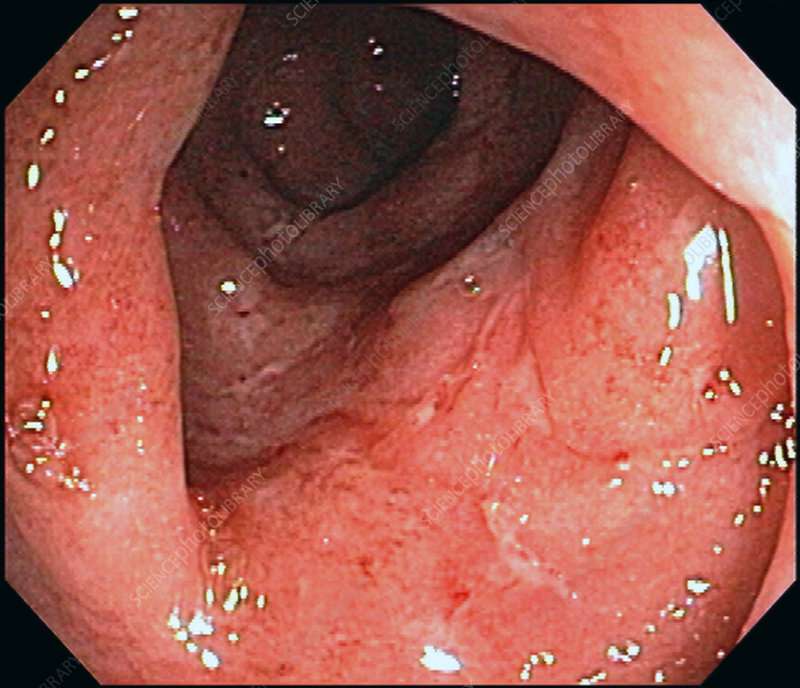
-
Infectious colitis: bacterial, viral, fungal , mycobacterial, and Clostridium difficile
-
Ischaemic colitis
-
Sexually transmitted diseases : Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, herpes, and syphilis
-
If predominant symptom is diarrhoea and not bleeding: coeliac disease, microscopic colitis, lactose or other food intolerances, and irritable bowel syndrome
Read Also: What Foods Should I Avoid With A Stomach Ulcer
Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
The main symptoms of ulcerative colitis are:
- recurring diarrhoea, which may contain blood, mucus or pus
- needing to empty your bowels frequently
You may also experience extreme tiredness , loss of appetite and weight loss.
The severity of the symptoms varies, depending on how much of the rectum and colon is inflamed and how severe the inflammation is.
For some people, the condition has a significant impact on their everyday lives.