What Is Trapped Wind
Trapped wind can be common after surgery, as a symptom of IBD and of course, a result of eating and drinking. It can be incredibly painful, especially when you have active inflammation, strictures, or scar tissue, and it can last an awfully long time if action is not taken to shift it!
As is often the case with Crohnâs disease or ulcerative colitis, what works for one person may not work for another, but there are so many tips and tricks which get shared repeatedly, that I would hope at least one will work for you!
Personally, I have found that sometimes one thing will help and then the next time it doesnt! I know, IBD likes to keep us on our toes doesnt it?!
Donât Miss: Infliximab Vs Adalimumab Ulcerative Colitis
How Can Sulphur Cause Harm
Bacteria that live in the bowel convert the sulphur in food into hydrogen sulphide, in a process known as fermentation. This highly toxic product is responsible for the foul odour associated with passing gas, can cause abdominal pain, and frequent, urgent trips to the toilet. Normally, the cells lining the colon absorb and detoxify the gas but in people with ulcerative colitis, there is a two-fold problem. Firstly, ulcerative colitis patients appear to produce more hydrogen sulphide than normal, and they have a more difficult time breaking down the gas . The extra gas present may further damage the lining of the colon.
Hydrogen sulphide may have a number of adverse effects on the bowel and may contribute to the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Hydrogen sulphide has been shown to increase the epithelial permeability and barrier function. In other words, it reduces the protective function of the cells lining the bowel. Other animal studies indicate high concentrations of the product can produce cell death, goblet cell loss, crypt architectural distortion, and superficial mucosal ulceration. It has also been shown to reduce the effectiveness of the immune system in trapping and killing unwanted bacteria. All of these examples point to the possible toxic effects of hydrogen sulphide on the cells lining the colon.
Is This My Fault
No. Scientists dont really know why your immune system starts to go haywire and inflames your bowel in ulcerative colitis. What seems fairly clear, though, is that it has little to do with what youve done in the past. You didnt catch UC from some infected person or from eating or drinking the wrong thing. Nor did you get it from simply being stressed out.
That said, both hard-to-digest foods and stressful situations can trigger or worsen a flare-up of UC symptoms, if you already have the disease. You can often improve your symptoms if you avoid certain high-fiber foods like uncooked veggies, nuts and seeds, as well as fatty or greasy foods like burgers and fries. Use common sense. If you find that certain foods upset your stomach, try to stay away from them.
It can also help to maintain balanced mental health and avoid unnecessary stress and anxiety. Proper sleep, quitting smoking, and regular exercise could also keep flare-ups at bay.
Don’t Miss: Over The Counter For Ulcer Pain
What Tests Are Used To Find The Cause Of Blood In Stools
Your doctor will talk to you, examine you, and should arrange some tests to investigate the cause. The doctor will choose the right test for you based on your age, symptoms and medical history. Possible tests include:
- sigmoidoscopy a procedure where your doctor uses a camera to check inside your rectum and most of your lower large intestine
- colonoscopy a physician uses a camera that sits within a tube to examine your entire colon
- gastroscopy a tube is inserted through the mouth to look at the oesophagus, stomach and first part of the small intestine
Some of these tests are done under sedation and anaesthetic. Ask your doctor for more information.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Duodenal Ulcer
Digestive Changes In Ulcerative Colitis
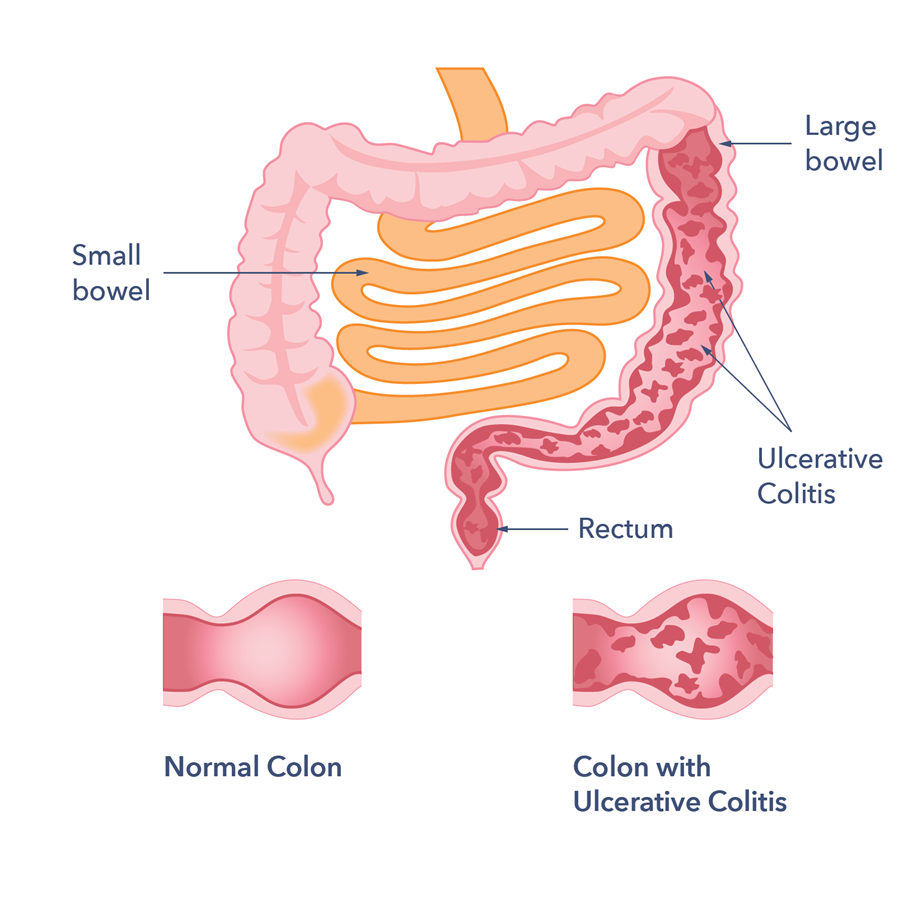
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition, meaning it comes on slowly over a long period of time. Currently, there is no known cure for UC.
With UC, inflammation and ulcers develop on the lining of the large intestine . Sometimes the rectum is affected, as well.
This inflammation can cause changes in bowel habits, including urgency, diarrhea, blood or mucus in the stool, and abdominal pain. When your large intestine is inflamed, it contracts and empties often, which is why you may have urgent bowel movements and diarrhea.
When chronic inflammation damages the lining of your colon, ulcers can develop. The ulcers can bleed, leading to blood in your stool. If you regularly lose a lot of blood in your stool, you might develop anemia .
Though diarrhea is more common, some people with UC experience constipation. Inflammation limited to the rectum, known as ulcerative proctitis, may result in constipation.
Other symptoms of UC include painful bowel movements, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, unintentional weight loss, and fever.
You May Like: What Does Stomach Ulcer Pain Feel Like
Who Diagnoses Ulcerative Colitis
If you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis, your regular healthcare provider will probably refer you to a specialist. A gastroenterologist a doctor who specializes in the digestive system should oversee the care for adults. For young patients, a pediatric gastroenterologist who specializes in children should manage the care.
How To Treat Symptoms
In a given year, 70 percent of people with active disease will have another episode the following year. But only 30 percent of people in remission will have active disease the next year.
Basically, the longer youre in remission, the less likely you are to have a flare-up the next year. And that means less diarrhea. Thats why its so important to find a treatment plan that works for you.
Medications to control UC symptoms include:
- aminosalicylates
- immune modifiers
There are also medications to help with diarrhea. Antidiarrheal agents help slow movement through the intestines, which helps your body absorb the fluids and nutrients you need. These include:
Fiber supplements may also be helpful in reducing diarrhea, but avoid them if youre in the middle of a flare-up. Check with your doctor if youre not sure whether these supplements are suitable for you.
Its also important to speak with your doctor under the following conditions:
- Before adding any over-the-counter treatments or dietary supplements to your regimen. Some have the potential to interfere with the medications youre currently taking.
There are a few ways to help manage urgent or frequent bowel movements. For example, you can set regular times to move your bowels. Choose times that are convenient, so youre not rushed.
Some items that can contribute to loose stools are:
Also Check: Probiotics Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Also Check: Ulcers In The Legs Or Feet
Mucosal Bacteria In Ulcerative Colitis
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 March 2007
- Microbiology and Gut Biology Group, University of Dundee, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
- E. Furrie
- Microbiology and Gut Biology Group, University of Dundee, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
- A. Kennedy
- Microbiology and Gut Biology Group, University of Dundee, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
- J. H. Cummings
- Division of Pathology and Neuroscience, University of Dundee, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
- G. T. Macfarlane
- Microbiology and Gut Biology Group, University of Dundee, Dundee, DD1 9SY, UK
- *
- *Corresponding author: Dr S. Macfarlane, fax +44 1382 633952
How Often Do I Need A Colonoscopy
Especially when you have symptoms or are just starting or changing medications, your doctor may want to periodically look at the inside of the rectum and colon to make sure the treatments are working and the lining is healing. How often this is needed is different for each person.
Ulcerative colitis also increases your chance of developing colon cancer. To look for early cancer signs, your healthcare provider may have you come in for a colonoscopy every one to three years.
Read Also: Best Wound Care For Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
Many tests are used to diagnose ulcerative colitis. A physical exam and medical history are usually the first step.
Blood tests may be done to check for anemia, which could indicate bleeding in the colon or rectum, or they may uncover a high white blood cell count, which is a sign of inflammation somewhere in the body.
A stool sample can also reveal white blood cells, whose presence indicates ulcerative colitis or inflammatory disease. In addition, a stool sample allows the doctor to detect bleeding or infection in the colon or rectum caused by bacteria, a virus, or parasites.
A colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy are the most accurate methods for making a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis and ruling-out other possible conditions, such as Crohns disease, diverticular disease, or cancer. For both tests, the doctor inserts a long
What To Do During A Flare
Most skin issues associated with UC are best treated by managing the UC as much as possible, as many of these rashes can coincide with UC flare-ups. Others may be the first sign of UC in someone who hasnt been diagnosed yet.
Corticosteroids can help with the inflammation that often causes the skin issues associated with UC. Eating a well-balanced diet can help promote overall health and may aid in preventing skin issues.
When you do experience a flare-up of UC skin rash, there are several things you can try:
- Keep the lesion clean to prevent infections.
- See your doctor for prescription antibiotic ointment or pain medication if needed.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get An Ulcer In Your Intestines
How Can Map Be Detected And Treated
The challenge with treating MAP is two fold:
Let’s talk about both of those challenges.
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is the result of several factors that are not yet well understood. Abnormal immune response, genetics, microbiome, and environmental factors all contribute to ulcerative colitis.
Research suggests that ulcerative colitis could be triggered by an interaction between a virus or bacterial infection in the colon and the bodys immune response.
-
Typically, the cells and proteins that make up your immune system protect you from infection.
-
A normal immune response would cause temporary inflammation to combat an illness or infection. The inflammation would then go away once you are healthy and free of the illness.
-
In ulcerative colitis patients, the inflammation persists long after the immune system should have finished its job. The body continues to send white blood cells into the lining of the intestines, where they produce chronic inflammation and ulcers.
Read Also: What To Eat To Help Stomach Ulcers
Bacterial Species Associated With Human Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Their Pathogenic Mechanisms
- 1School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 2Faculty of Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- 3School of Medical Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 4Gastrointestinal and Liver Unit, Prince of Wales Hospital, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract with unknown etiology. The pathogenesis of IBD results from immune responses to microbes in the gastrointestinal tract. Various bacterial species that are associated with human IBD have been identified. However, the microbes that trigger the development of human IBD are still not clear. Here we review bacterial species that are associated with human IBD and their pathogenic mechanisms to provide an updated broad understanding of this research field. IBD is an inflammatory syndrome rather than a single disease. We propose a three-stage pathogenesis model to illustrate the roles of different IBD-associated bacterial species and gut commensal bacteria in the development of human IBD. Finally, we recommend microbe-targeted therapeutic strategies based on the three-stage pathogenesis model.
Clostridium Difficile And Other Enteric Pathogen Infections In Inflammatory Bowel Disease
C. difficile is a Gram-positive spore-forming anaerobic bacterium, which is ubiquitous in nature and also colonizes the human intestinal tract . C. difficile causes diarrhea and colitis, often in individuals who have been treated with antibiotics for other medical conditions.
The major virulence factors of C. difficile are the two toxins encoded by tcdA and tcdB genes . These toxins inactivate host Rho and Ras family GTPase by glucosylation leading to the disruption of epithelial cytoskeleton and tight junctions, which may contribute to the increased epithelial permeability and luminal fluid accumulation associated with C. difficile infection . TcdA and TcdB toxins also cause cell death via caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis, further damaging the intestinal epithelial barrier . Both toxins also induce the production of proinflammatory cytokines in intestinal epithelial and immune cells, including IL-8, TNF-, IL-1, and IL-6 . By using multiomic analysis, it was found that the most discriminating metabolite between IBD and IBD infected with C. difficile was isocaproyltaurine, a covalent conjugate of a C. difficile fermentation product isocaproate and taurine from damaged tissue .
Also Check: What To Eat When You Have Gastric Ulcer
Ulcerative Colitis And C Diff Infection: What’s The Link
C. diff infection is a bacterial infection in the colon that can cause serious illness, even death. This increasingly common infection causes almost 500,000 illnesses each year in the United States. Many of those are repeat infections.
The CDC says 1 in 6 patients treated for a C. diff infection will get it again 2-8 weeks later. Up to 5.7% of people in the hospital with ulcerative colitis have a C. diff infection.
You may have heard the infection referred to as Clostridium difficile. The name was changed in 2016.
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Read Also: Can Colitis Turn Into Ulcerative Colitis
Do Ulcerative Colitis Causes And Crohns Disease Causes Overlap
In Crohns disease, areas of your digestive tract become irritated and inflamed. This can lead to symptoms like cramping, diarrhea, and unintentional weight loss, which heavily overlap with those of ulcerative colitis. While ulcerative colitis only affects your colon, Crohns disease can impact any part of your digestive tract. The most commonly affected areas are the last part of your small intestine, called the ileum, and the first part of your colon.
Much like ulcerative colitis, the exact causes of Crohns disease remain unclear. Similar factors are believed to play a role, including a dysfunctional immune response and genetics.
According to the NIDDK, the risk factors for Crohns disease include family history, smoking cigarettes, and being between the ages of 20 and 29. Its also possible that eating a high-fat diet or using medications like NSAIDs, antibiotics, or birth control pills may also slightly increase the risk of Crohns disease.
Environmental Factors And Ulcerative Colitis
A germ, like a virus in your environment, might raise your chances of getting ulcerative colitis.
If you use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, or birth control pills, your chances of having it may increase slightly. Its possible a high-fat diet is related to it, too.
A few other things could be related to the cause or might trigger a flare-up:
Don’t Miss: Gastric Ulcer Treatment In Horses
Diet For Ulcerative Colitis With Gas
Undigested food your body does not break down passes along the digestive tract into your large intestine, where it meets harmless bacteria. As the bacteria works to break down the food, gaseous hydrogen and carbon dioxide are produced, which are excreted from the rectum. In people with ulcerative colitis, a different form of gas is also created, causing foul odorous flatulence. A change in dietary habits can reduce the amount of gas you experience as well as reduce symptom flare-ups of the disease.
You May Like: What Does An Ulcer Look Like
Interactions Between Gut Microbiota And The Mucosal Immune System In Homeostasis
There are dynamic interactions between gut microbes and the mucosal immune system in healthy individuals, however, such interactions do not induce inflammation. In order to better explain the roles of different bacterial species in the pathogenesis of IBD, we firstly summarize the main strategies that maintain the homeostasis between gut microbiota and the mucosal immune system in healthy conditions.
The second strategy is the strategically arranged innate pattern recognition receptors in the intestinal epithelium. Intestinal epithelial cells express many different types of PRRs, located on the surface or inside of cells. These receptors recognize and respond to intruding pathogens but maintain a tolerance to gut microbiota and food components when under a homeostatic state. Such a tolerance is maintained by the low expression of these receptors and their spatial location in healthy conditions . For example, Toll-like receptor-4 and MD-2 are expressed at a low level in normal intestinal epithelial cells and they do not respond to lipopolysaccharide , a major component of Gram-negative bacteria . Furthermore, TLRs have a polarized distribution they are located at the basolateral surfaces instead of apical surface, which further limits the response of the intestinal epithelium to products of commensal gut microbes that have crossed the mucus layer .
Don’t Miss: Are Fermented Foods Good For Ulcerative Colitis