Living With Ulcerative Colitis
With careful management, most people with UC are able to enjoy life, including work, travel, recreation, sex and having children.
To keep healthy, consider:
- eating a nutritious diet to help with healing and reduce fatigue
- keeping a food diary to check if there are any foods that make your symptoms worse during a flare-up
- asking your doctor about supplements if you think you may be malnourished
- exercising regularly to lift your mood and help relieve stress
- learning some relaxation techniques to help manage stress
Pain Prevalence And Associated Factors
Slightly more than half of the entire group endorsed at least some pain over the previous two weeks before or during their index visit, with 108 people reporting a SIBDQ Pain Score of at least 4 . Considering the emphasis on frequency rather than severity, we correlated the SPS with the pain severity rating of the Colitis Activity Index, which showed a significant relationship between the two measures . Significantly more women than men described their pain as more frequent . Of note, 16 patients used opioids at the time of their index visit. Abdominal discomfort was the main reason for opioid use in 6 of these individuals, with the remaining patients receiving pain medications for joint, back, bone or muscle pains or chronic pancreatitis . In the remaining patients, no reason for opioid therapy could be identified. Opioid use was significantly more common in patients rating their pain as frequently or constantly present compared to those with no abdominal pain .
Abdominal Pain Prevalence in UC Patients with SIBDQ Scores. The histogram shows the distribution of pain scores, which are inversely related to pain frequency. The insert defines the fraction of patients with and without pain.
Prevent Bloating With A Change In Diet
The easiest way to prevent bloating is to avoid gas-causing foods as mentioned above. When changing your diet in a drastic way, please consult your doctor before doing so.
We hope that you use our tips on how to relieve ulcerative colitis, but if your abdomen feels tender, your bloating worsens or is accompanied by other symptoms, please seek immediate medical attention. If your symptoms dont go away, you will likely need medical interference. Stop by Village Emergency Centers in Katy, River Oaks, Clear Creek, or Jersey Village for the quality medical care that you deserve.
Further Reading:
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis And Mental Health
From Stabbing Sensations To Major Cramps Uc Pain Can Be Debilitating Heres What To Expectand How To Get Relief
by Health Writer
If youve recently been diagnosed with , you know: It can be hard to separate out symptoms of this gastrointestinal disease from the other aches and pains in your body. Is that stomachache due to a meal that didnt agree with you, or is caused by inflammation in your colon? Are those cramps related to your inflammatory bowel disease or your monthly cycle? Lets take a closer look at symptoms that make UC abdominal pain different from a run-of-the-mill stomachache, plus how to relieve the pain so you can get back to the things you love.
Anxiety And Control Over Activities
Participants acknowledged a large amount of anxiety resulting from a pattern of their symptoms controlling their lives and the resulting effects of their disease on their quality of life.
Ive got a full-blown flareup, and uh, I try and schedule things around when Ive got to go to the bathroom in a half hour, so lets not start this meeting or lets get this meeting over, um, excuse me, Ive gotta go.
if I dont go in the morning, then its in the back of my head, Ok, whens it going to hit? But if I go in the morning, right after I get up, I have no worries the rest of the day.
You end up planning your whole life around what your gut is doing.
I mean, you plan your life around it .
When it started, I just had to stay home because so often I couldnt handle it and it had absolutely no control, and when you teach, you cannot have that in the classroom.
You May Like: Best Fruits For Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
The most common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are abdominal pain and diarrhea that may contain blood, pus, or both.
The disease and these symptoms typically come on gradually.
As the disease progresses, other symptoms may include:
- Rectal pain, bleeding, or both
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pain
- Growth failure in children
If you have ulcerative proctitis which affects only the rectum your only symptom may be rectal bleeding. This form of the disease tends to be the least severe.
Proctosigmoiditis which affects the rectum and lower part of the colon tends to cause bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and difficulty defecating despite a strong urge to do so.
Left-sided colitis which affects the rectum and colon up to an area called the descending colon often causes bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain of the left side, and unintended weight loss.
If you have pancolitis which affects the entire colon youre likely to experience severe episodes of bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, and major weight loss.
Editor’s Picks
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Recommended Reading: Herbal Medicine For Stomach Ulcer
How Is Acute Bacterial Dysentery Differentiated From Acute Onset Of Ischemic Colitis
The degree of bloody diarrhea is variable in patients with ischemic colitis, and it may be difficult to distinguish between the two diseases. Clinically, the patient with ischemic colitis complains of sudden-onset abdominal pain, and an acute abdominal series may show thumbprinting of the colonic mucosa.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is the mainstay of diagnosis for ischemic colitis. The rectum is usually spared because of its collateral blood flow. Above the rectum, the mucosa becomes friable and edematous, and there may be hemorrhagic areas and ulcerations resembling those of Crohns disease. Angiography is not generally helpful in the evaluation of ischemic colitis ischemic colitis is a small-vessel disease compared with mesenteric midgut ischemia of the small bowel, which involves thrombosis or embolism in the superior mesenteric artery . A barium enema is contraindicated in patients with suspected ischemic colitis, because colonic expansion during barium instillation may promote further ischemia.
Glenn T. Furuta, in, 2004
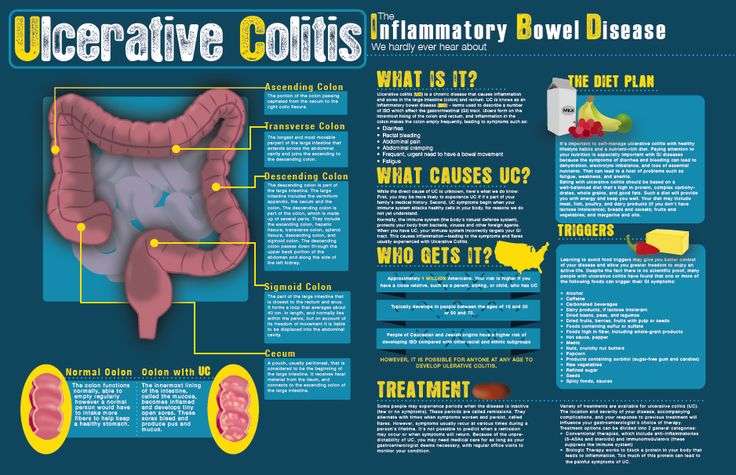
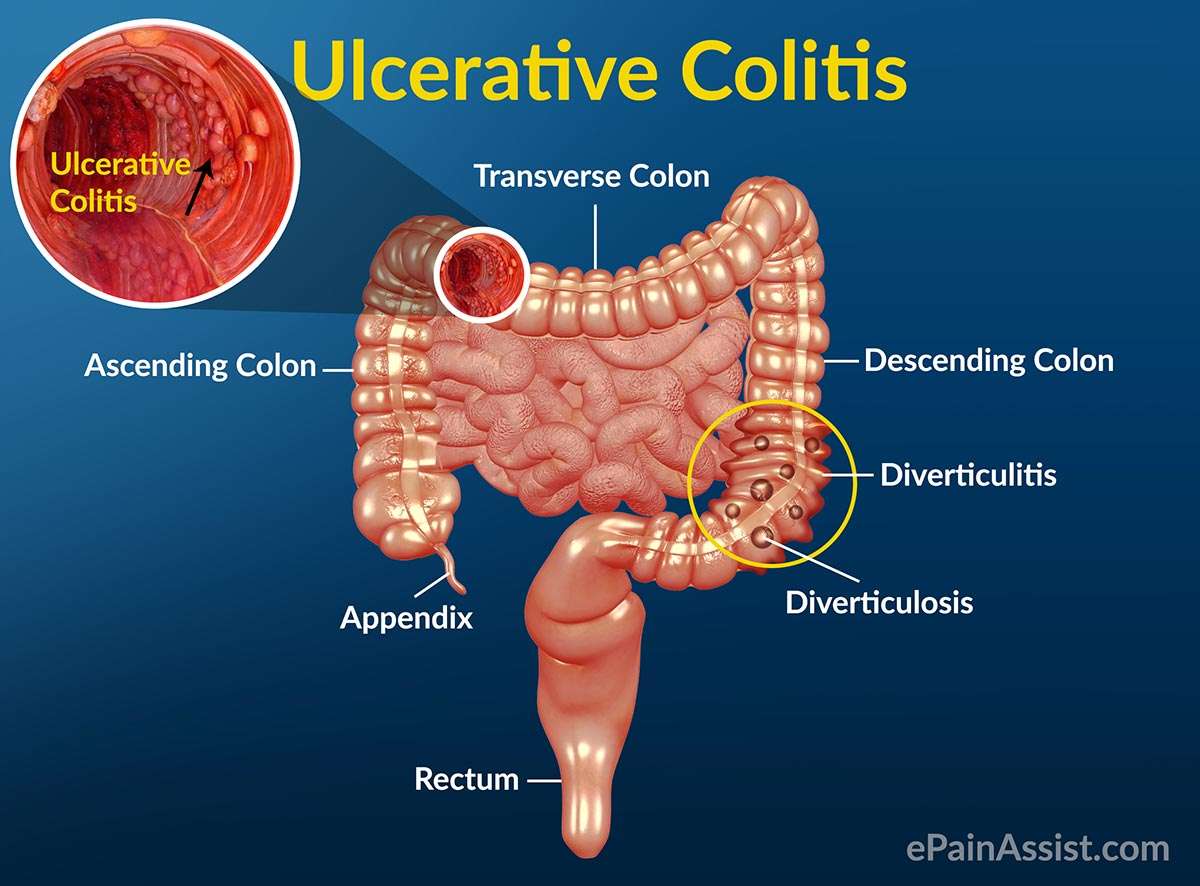
Colitis And The Anatomy Of The Colon
The colon, or large intestine, is a hollow, muscular tube that processes waste products of digestion from the small intestine, removes water, and ultimately eliminates the remnants as feces through the anus. The colon is located within the peritoneum, the sac that contains the intestine, located in the abdominal cavity.
The colon is surrounded by many layers of tissue. The innermost layer of the colon is the mucosa that comes into contact with the waste products of digestion. The mucosa absorbs water and electrolytes back into the blood vessels that are located just below the surface in the submucosa. This is surrounded by a circular layer of muscles and then another outer layer of longitudinal muscles that run along the length of the colon. The muscles work together to rhythmically squeeze liquid waste from the cecum through the entire length of the colon. Water is gradually removed, turning the waste into the formed stool so that it is excreted out of the anus in solid form.
The colon frames the organs within the peritoneum, and its segments are named based on their location.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat To Cure Ulcerative Colitis
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With Colitis
Patients with infectious diarrhea tend to get better relatively quickly with supportive care. Most infections will resolve with or without specific treatment and often do not require antibiotics. Those decisions depend on the patient’s diagnosis.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease probably will require lifelong treatment to help control their symptoms. The goal, as with any long-term illness, is to allow the patient to live a normal life with minimal symptoms from the disease.
Patients with ischemic colitis need to minimize their risk factors for progressive narrowing of the arteries. These are the same risks as for heart disease and require the same treatment approach, including controlling high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and smoking cessation. Patients with severe ischemia that leads to a dead colon require surgery to remove the gangrenous segment.
Will Surgery Cure A Peptic Ulcer
Medical therapy works in most people with peptic ulcers. Sometimes, medical therapy does not work, or a person cant take the therapy for some reason. Surgery is an alternative to medical therapy for these people.
Surgical operations often used in peptic ulcers include the following:
- Vagotomy: Cutting the vagus nerve, which transmits messages from the brain to the stomach, can reduce acid secretion. However, this can also interfere with other functions of the stomach. A newer operation cuts only the part of the nerve that affects acid secretion.
- Antrectomy: This is often done in conjunction with a vagotomy. It involves removing the lower part of the stomach . This part of the stomach produces a hormone that increases production of stomach acid. Adjacent parts of the stomach may also be removed.
- Pyloroplasty: This procedure also is sometimes done with vagotomy. It enlarges the opening between the stomach and duodenum to encourage passage of partially digested food. Once the food has passed, acid production normally stops.
- Tying off an artery: If bleeding is a problem, cutting off the blood supply to the ulcer can stop the bleeding.
You can treat an anal tear at home in several ways:
You likely wonât need surgery for an anal fissure, unless itâs ongoing. In that case, your surgeon might inject Botox into your anal sphincter, or cut a small part of the muscle to relax it and lessen spasms and pain.
Recommended Reading: Best Cure For Mouth Ulcers
More Tips To Ease Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
The best way to shorten a flare, of course, is to get treated by your doctor. But there are steps you can take at home too.
When you have a flare, try to follow a low-residue diet for several weeks, Damas says. The goal is to let the colon rest by avoiding fiber. That means staying away from seeds, nuts, fresh fruit, dried fruit, raw vegetables, whole grain bread and cereal, and tough meat.
Were learning more now about the influence that diet can have on control of inflammation, Damas notes. When patients are having an acute flare, its important in the short term to have a low-fiber diet. Many times, for a short period of time, until the flare-up is controlled, we recommend whats called a low FODMAP diet. However, this diet is not recommended long term, because it has no impact on inflammation itself and only on control of symptoms.
Indeed, once youre in remission, Damas says your doctor will likely recommend reintroducing fruits and vegetables as tolerated. Its better to cook vegetables without the skin and consume no more than 2 cups of milk a day.
If youre lactose intolerant, be sure you choose lactose-free dairy products. Its also a good idea to cut down on fat during this time to prevent bulky stools. Avoid other potential triggers, too, such as spicy foods.
Additionally, we recommend patients avoid eating processed foods, as well as those high in fat and animal protein, as these have been associated with inflammation in some studies, Damas says.
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medication such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. However, more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital to reduce the risk of serious complications, such as the colon becoming stretched and enlarged or developing large ulcers. Both of these can increase the risk of developing a hole in the bowel.
If medications aren’t effective at controlling your symptoms, or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
During surgery, your small intestine will either be diverted out of an opening in your abdomen , or used to create an internal pouch that’s connected to your anus .
Read more about:
You May Like: How To Treat Gum Ulcers
What Are The Most Common Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
Early ulcerative colitis symptoms usually include things that could easily be overlooked. Dont be afraid to talk to a doctor if youre having any worries though, even if your symptoms seem mild. If symptoms are ongoing and start to feel more severe, like persistent pain in your abdomen or unintentional weight loss, you should seek medical treatment as soon as possible.
Here are some of the most common symptoms of ulcerative colitis to watch out for, per the NIDDK:
Okay, so this isnt the most pleasant one to start with, but it is actually the most common ulcerative colitis symptomits also a pretty good tip-off that something isnt quite right and that you should schedule an appointment with your doctor. Remember those ulcers we talked about earlier? Yeah, thats where the blood in your stool comes from, and you might also see mucus in there as well.
This is another pretty common symptom, and contrary to popular belief, those ulcers in the colon are not actually what causes the pain. Instead, its a combination of abdominal cramping and bowel distension that occurs due to the inflammation in the intestines, according to a 2013 study published in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.1
With all thats going on in the digestive tract with ulcerative colitis, nausea can sometimes be an issue. This occurs more often when symptoms are severe, or if the inflammation affects more of the large intestine, according to the NIDDK.
Five Tips For Dealing With Ulcerative Colitis Pain
There are ways to combat the pain that comes along with ulcerative colitis flare-ups. However, it is always best to get treatment from a doctor as they are most likely to efficiently and safely resolve your symptoms.
Here are five strategies you can use to help relieve symptoms and avoid a flare-up in the first place.
Also Check: Orange Juice And Ulcerative Colitis
What Does Your Stool Look Like With Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a disease that involves the inner lining of the large bowel. It causes abdominal pain and bleeds due to erosions and ulcers all over the large intestine and rectum. Inflammatory bowel disease is a lifelong illness with no specific cause or cure. Patients have repeated cycles of flare-ups and remission with potential extraintestinal manifestations. Flare-ups may last days to a few weeks. Remission might last for months or even years.
UC is a lifelong disease with constant periods of flare-ups and remission. Several treatment options and lifestyle modifications reduce the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Stool-related symptoms of UC include
- Diarrhea or loose stools more than four episodes a day
- Bloody stools, which may be bright red, pink or tarry
- Ribbon-like stools in case of narrowed intestines due to a long-standing disease
Diarrhea may be associated with cramps and abdominal pain. There may also be a constant feeling of the need to evacuate the bowels .
What Other Conditions Can Cause Abdominal Pain
There are dozens of conditions that can cause pain and cramping in the abdomen. Conditions that are sometimes confused with IBD are:7,8
- Appendicitis
- Stomach irritation
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional disorder. It causes similar symptoms as inflammatory bowel disease, including pain and cramping. However, irritable bowel syndrome does not damage the intestine the way Crohns disease does.
Read Also: How Do You Treat A Duodenal Ulcer
Be Diligent And Careful With Medication
A physician will usually prescribe an anti-inflammatory and medication to help with an overactive immune system with a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. This medication is vital to fight off flare-ups and missing a dose can be a trigger all by itself.
When taking medication for this condition, it is always wise to consult a doctor. Certain over-the-counter medications, like NSAIDs, can exacerbate ulcerative colitis as well as cause other issues.
Living With Uc: Probiotics
These friendly bacteria are similar to those that live in your intestine and prevent the growth of too many harmful bacteria. We need more research to know if probiotics can help with ulcerative colitis. You can find probiotics in some yogurts, milk, tempeh, and soy beverages. Or you can buy them as supplements.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcer
Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Colitis
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two types of inflammatory bowel disease that cause colitis. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are considered autoimmune diseases .
- Ulcerative colitis always begins in the rectum and may spread to the rest of the rest of the colon, spreading from the rectum to the sigmoid, descending, transverse, and finally the ascending colon and cecum in that order. Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, and symptoms include abdominal pain, and bloody, diarrheal bowel movements.
- Crohn’s disease may occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract , including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. In Crohn’s disease, there may be “skip lesions,” that is, abnormal segments of the GI tract interspersed with normal segments.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may have other organ systems involved in addition to the gastrointestinal tract.
Either collagen or lymphocytes infiltrate into the layers of the wall of the colon, presumably as a result of inflammation. This is an uncommon illness and maybe an autoimmune disease. Diarrhea often is watery, and no blood is present in the stool.