What Is Crohns Disease
Crohns disease is another type of inflammatory bowel disease . Like ulcerative colitis, Crohns also causes inflammation in your digestive tract. Inflammation caused by Crohns disease can involve different areas of the digestive tract in different people, explains the Mayo Clinic. The source also notes that the inflammation typically spreads into deeper layers of the bowel.
Crohns disease can also be debilitating and in some cases, it may lead to life-threatening complications. And just like ulcerative colitis, there is currently no cure. Luckily, certain treatments can help you manage the disease and may even bring about long-term remission and healing of inflammation, says the source.
Shutterstock/Michail Petrov
Treatment Of Ibd Complications
Treatment depends on the particular complication, but may include:
- complications caused by nutritional deficiencies vitamin and mineral supplements , changes to diet or a liquid diet in severe cases
- inflammation in other body areas usually ease when the bowel inflammation is controlled with medication
- fistulas small openings that often heal by themselves, with treatment to ease the inflammation. A person may need surgery to close a larger fistula. Abscesses may need antibiotics and surgical drainage
- intestinal obstruction in some cases, medical treatment to ease the inflammation will clear the obstruction. In severe cases, the person will need surgery
- toxic megacolon the person goes to hospital, and receives fluids and nutrients intravenously instead of by mouth, plus antibiotics and steroids to reduce inflammation. Sometimes, the doctor will remove the contents of the persons stomach with a slender tube . A ruptured bowel needs surgical repair or removal. In severe cases, the whole of the large bowel may need to be surgically removed.
Mild To Moderate Disease
First-line therapy in mild to moderate disease is the 5-ASA drugs, which can be administered as suppositories, enemas, or oral formulations . There does not appear to be any difference in efficacy or safety between different 5-ASA formulations.119 Sulfasalazine, which is metabolised to 5-ASA, appears to have similar efficacy to 5-ASA drugs, but tends to be less well tolerated.114 Patients with proctitis should be treated initially with 5-ASA suppositories since they directly target the site of inflammation and appear to be more effective than oral 5-ASA.114,118,120 In left-sided colitis, 5-ASA should be administered as an enema instead of a suppository in order to reach the splenic flexure. For patients with left-sided or extensive disease, it is recommended that oral 5-ASA be used in combination with topical 5-ASA to induce remission.114,118 Oral 5-ASA doses of 2 g or higher per day are more effective than lower doses at inducing and maintaining remission.121123 5-ASA can be started at a dose of 2.02.4 g per day and increased up to 4.8 g, if needed.114,123 Dosing of 5-ASA once a day has similar efficacy to divided doses and could increase adherence.114,123 Patients typically see a response within 14 days, but this response might take up to 8 weeks for symptomatic remission.114 5-ASA drugs have also been shown to be effective at maintaining remission, and patients who achieve remission with 5-ASA should continue on the same medication.114
Don’t Miss: Treating Leg Ulcers With Sugar
Ulcerative Colitis And Diverticulitis: Similarities And Differences
UC and diverticulitis both start out in the large intestine and share symptoms like belly pain and bloody poop. Both conditions are more likely the older you get, and both can range from mild to severe and vary for each person. But they differ in terms of what causes them and how your doctor might treat them.
UC is a lifelong condition that can lead to life-threatening problems. About a million Americans are affected by it. It can affect people at any age, including those in their 20s and 30s. If you have UC, you also might have weight loss or arthritis.
Diverticulitis, not a lifelong condition, is a complication of âdiverticulosis.â Itâs the term doctors use when one or more of the small bulging sacs grow on your colon wall. It usually starts in middle age and itâs common in older people. Diverticulitis can happen to you once and never happen again, or it might come and go. About 50% of those over the age of 60 have it, and almost everyone above 80 has it, too. Most are mild cases that donât cause any symptoms and arenât reasons to worry. Up to 30% of the people with diverticulosis go on to have diverticulitis. And among them, anywhere between 5%-15% will have symptoms like bloody poop.
Side Notes For Symptoms Of Crohns Disease
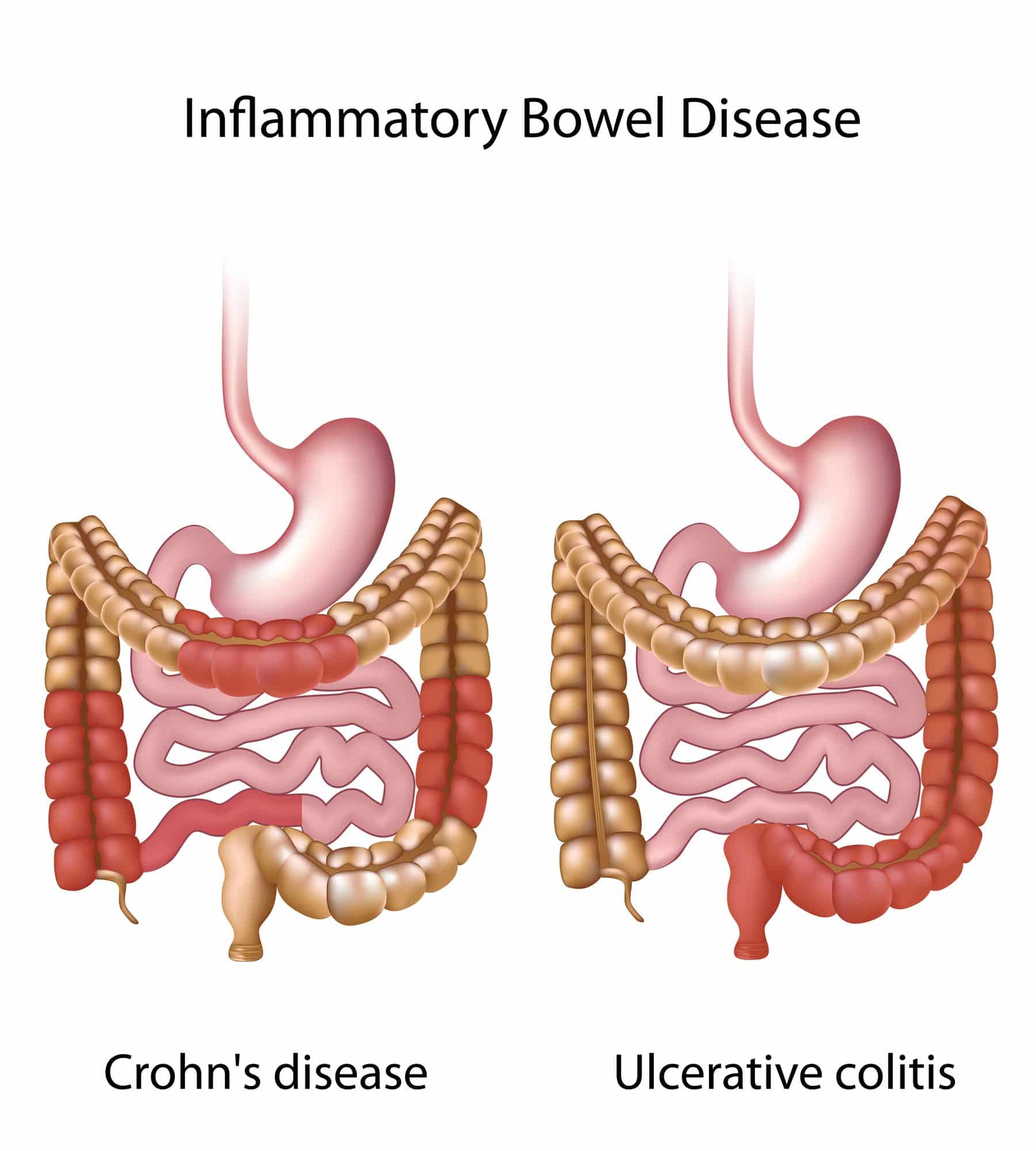
- Unlike U.C., Crohns disease is more likely to become a full gastrointestinal condition, where you can develop esophagus damage, small intestinal issues, and mouth sores.
- Skip lesions in the colon is one of the main signature findings for Crohns during a colonoscopy. U.C. tends to have more continuous damage of the colon.
- Fissures and strictures can be very problematic if they develop for Crohns. For example, a stricture occurs because of continuous damage and healing that leads to scar tissue build up. This can make it very difficult for food to pass through and can even lead to excessive vomiting and nausea.
Read Also: Natural Home Remedies For Ulcers In Stomach In Tamil
How Are Ibs Crohns And Ulcerative Colitis Different
The short answer is Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are both types of inflammatory bowel disease , which causes chronic inflammation of the intestines.
Irritable bowel syndrome , is a different noninflammatory condition that also affects the intestines .
If your heads spinning over gut disorders, dont worry, we gotchu. Heres the lowdown on Crohns and ulcerative colitis , and IBS.
Side Notes For Symptoms Of Both Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
- While it can be hard to absorb nutrients in general, usually fats and oils are the most difficult to absorb for IBD. This is because, while carbs and proteins get absorbed high up in the small intestine, fats need to latch onto bile acids and get absorbed in the colon. If you have colon inflammation, this can make it harder to absorb fats.
- If you would like to learn how to consume the right fats in the most optimal way for U.C. and Crohns, according to research, make sure you check out my FREE mini-course
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Pain Left Side Under Ribs
What Causes Ibs And Who Gets It
Someone you know fo sho has IBS, even if you dont know it. Thats because IBS is among the most common disorders diagnosed by doctors. About 11 percent of the population worldwide and about 12 percent of people in the U.S. have it, though some estimates are as high as 20 percent.
The cause of IBS remains unknown, and theres currently no known cure .
Those more likely to get IBS may include:
Women with IBS often report increased symptoms during their period.
The Difference Between Celiac Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Celiac disease and ulcerative colitis are two very different conditions. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the digestive system, while ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Heres a closer look at the key differences between these two conditions:
Celiac disease is caused by an intolerance to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with celiac disease eats gluten, their immune system reacts by damaging the lining of the small intestine. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is a chronic inflammation of the large intestine . The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system. Symptoms of ulcerative colitis include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
While both celiac disease and ulcerative colitis can be serious conditions, they are treated differently. There is no cure for celiac disease, but the condition can be managed by following a gluten-free diet. Ulcerative colitis, on the other
You May Like: Wheatgrass Spray For Leg Ulcers
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Colon Cancer Vs Ulcerative Colitis
Colon Cancer Symptoms and Signs
Some individuals with colon cancer have no symptoms, and if they do have symptoms they often are minimalized and overlooked until the cancer becomes more severe. Cancer screening tests for colon cancer thus are important in individuals 50 years of age and older. Colon and rectum cancer can have many different symptoms and signs. If you have any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical help. You may notice bleeding from your rectum or blood mixed with your stool. It usually, but not always, can be detected through a fecal occult blood test, in which samples of stool are submitted to a lab for detection of blood.
People commonly attribute all rectal bleeding to hemorrhoids, thus preventing early diagnosis owing to lack of concern over “bleeding hemorrhoids.” New onset of bright red blood in the stool always deserves an evaluation. Blood in the stool may be less evident, and is sometimes invisible, or causes a black or tarry stool.
Rectal bleeding due to colon cancer may not be noticeable or chronic, and may only show up as an iron deficiency anemia, not colon cancer. Colon cancer may be associated with fatigue and pale skin due to the anemia. Changes in bowel movement frequency also is a symptom of colon cancer.
If the tumor in the colon becomes large enough, it may completely or partially block your colon. Symptoms of bowel obstruction include:
Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms and Signs
Common symptoms of ulcerative colitis include:
Ibd And Changing Your Diet
Some dietary changes that may help a person with IBD include:
- Low-fibre diet when IBD is active, most people find a bland , low-fibre diet helps to ease diarrhoea and abdominal cramping. People with Crohns disease who have a narrowed small intestine may need to eat a low-fibre diet most of the time.
- Low-fat diet people with Crohns disease who experience steatorrhoea may benefit from a low-fat diet.
- Low-lactose diet the milk sugar lactose is broken down by the enzyme lactase, commonly found in the lining of the small intestine. Some people with Crohns disease lack this enzyme, so should avoid milk and other dairy products. Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed with a simple test ask your doctor.
- Liquid diet a person with severe Crohns disease may need a nutritionally balanced liquid diet.
- Plenty of water people with IBD need to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Also Check: Stomach Ulcer And Chest Pain
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease
Its not entirely known what causes ulcerative colitis or Crohns disease. However, experts believe it has something to do with genetic factors and environmental factors . Your gut microbiomethe bazillion bacteria that live in your digestive tractis thought to have influence as well. In fact, a 2020 study published in the journal Frontiers of Medicine, found that not only was the gut bacteria in people with IBD different from people without IBD, but it was also different between people with ulcerative colitis vs. people with Crohns disease.4
What is known is that something sets off your immune system to mistakenly attack healthy areas of your digestive tract, causing chronic inflammation.
This overreaction of the immune system can also affect areas outside of your digestive system and can include your skin, eyes, and other organs. This can occur with both ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, but ulcerative colitis is more likely to affect the skin, eyes, and bones, while Crohns disease is more apt to affect the kidneys and gallstones.1
Read Also: What Is Good For Ulcers
Webinar Safe Treatment Of Ibd Patients With Thiopurines: Tpmt Genotyping And Phenotyping
Thiopurine methyltransferase testing is important in the detection of individuals with altered TPMT activity who are at risk for severe hematopoietic toxicity when taking thiopurine medications . This webinar will outline the different tests to detect patients who are at risk for thiopurine-related toxicity and the advantages of each test. It is intended to educate clinicians and increase their confidence when treating patients with thiopurine medications.
Read Also: What Can You Eat With A Peptic Ulcer
What Are The Possible Complications Of Colitis
Complications usually result from severe, long-term, chronic colitis. They can include:
- Perforation. Chronic inflammation weakens your colon walls, making them more likely to rupture. An ulcer in your colon may wear a hole all the way through. This can cause bacteria from your colon to infect your abdominal cavity and possibly your bloodstream , which would be especially dangerous. Septicemia can lead to .
- Toxic megacolon. Severe inflammation can cause the walls of your colon to dilate and interfere with its natural muscle contractions . This can trap food and gas in your colon . Obstruction leads to painful abdominal distension and an increased risk of rupture.
- Increased risk of colon cancer. Long-term inflammation is associated with cellular changes in your colon wall that can sometimes progress to cancerous changes. The risk increases rapidly after the first decade of chronic colitis.
- Increased risk of other inflammatory diseases. People with inflammatory bowel diseases are more likely to have other inflammatory diseases in other parts of their bodies. Some examples include osteoarthritis and primary sclerosing cholangitis . It appears that uncontrolled inflammation in one area may trigger a similar process somewhere else.
How Is Treatment The Same And Different
In both conditions, treatments usually involve medications or, sometimes, surgery. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a combination of the two to bring your symptoms under control. Certain over-the-counter medications may ease some of your pain-related symptoms. These include:
- Anti-diarrheal medications
- Antispasmodics to ease cramps and bloating
- Iron supplements, especially if youâre bleeding
UC treatments may include:
Anti-inflammatory drugs. This is usually the first line of treatment. This can include drugs like 5-aminosalicylates and corticosteroids. Some newer drugs like sulfasalazine and 5-ASAs , which are called âsteroid-sparing,â can be safely taken long-term. Your doctor may not want you to take steroids long-term because of their side effects.
Immunosuppressant drugs. This helps to reduce inflammation in your colon and cut down the immune response that might attack your digestive cells.
Biologics. This targets the proteins made by your immune system.
Surgery. About 30% of people who have UC need surgery. Itâs sometimes the only cure, especially if medications donât ease your symptoms or they become too difficult to manage. Your doctor may consider a surgery called proctocolectomy.
In this procedure, your entire colon and rectum are removed. Most surgeries also involve a procedure in which your doctor will attach a pouch at the end of the small intestine or outside your body to pass poop directly into it.
Diverticulitis treatments may include:
Recommended Reading: Things To Eat With An Ulcer
Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis, defined as six or more bloody bowel movements per day and at least one of the following: pulse rate > 90 beats per min, temperature > 37.8°C, haemoglobin count < 10.5 g/dL, or ESR > 30 mm/h, should be admitted to a tertiary care centre.69 Acute severe ulcerative colitis is associated with significant morbidity and mortality of approximately 1%.138 Patients are initially treated with intravenous corticosteroids to which approximately 65% will respond.139 For patients not responding to intravenous corticosteroids within 3 to 5 days, rescue medical therapy with either ciclosporin or infliximab can be attempted. Both drugs are equally efficacious in acute severe ulcerative colitis.140,141 Delays in surgery can increase postoperative complications and mortality increases significantly after 7 days.142,143 If there is no response to one of these drugs, colectomy should be performed. Further discussion of acute severe ulcerative colitis is in the appendix.
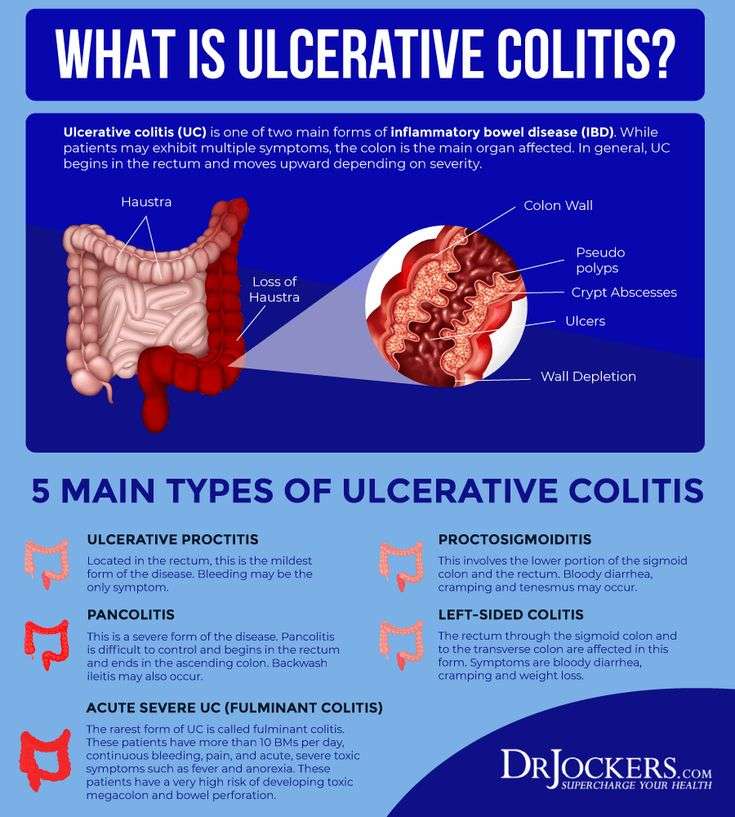
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Ulcerative Colitis
Can I Get Surgery For My Ulcerative Colitis
Surgery is an option if medications arent working or you have complications, such as bleeding or abnormal growths. You might develop precancerous lesions, or growths that can turn into colorectal cancer. A doctor can remove these lesions with surgery or during a colonoscopy.
Research shows that about 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery sometime during their life. About 20% of children with ulcerative colitis will need surgery during their childhood years.
There are two kinds of surgery for ulcerative colitis:
Proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch
The proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch is the most common procedure for ulcerative colitis. This procedure typically requires more than one surgery, and there are several ways to do it. First, your surgeon does a proctocolectomy a procedure that removes your colon and rectum. Then the surgeon forms an ileoanal pouch to create a new rectum. While your body and newly made pouch is healing, your surgeon may perform a temporary ileostomy at the same time. This creates an opening in your lower belly. Your small intestines attach to the stoma, which looks like a small piece of pink skin on your belly.
After you heal, waste from your small intestines comes out through the stoma and into an attached bag called an ostomy bag. The small bag lies flat on the outside of your body, below your beltline. Youll need to wear the bag at all times to collect waste. Youll have to change the bag frequently throughout the day.