Can You Drink Alcohol With Crohns Disease
- Drinking alcohol is not recommended for most people with Crohns disease.
- Alcohol may irritate the lining of the intestinal wall, causing or worsening symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
- It also may contribute to malabsorption, further complicating nutritional deficiencies.
- Alcohol interacts with many medications, causing side effects that may be serious.
- Alcohol disrupts sleep cycles and can leave you feeling tired, and irritable the next day. However, if alcohol is well tolerated and not causing any complications, it can be consumed in moderation.
- Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration very easily.
- Dehydration makes you feel weak, tired, light-headed, or just blah.
- Alcohol can cause headaches, abdominal pain, and other symptoms. It also can place dangerous strain on your kidneys.
- Dehydration can be avoided by making a special effort to take in plenty of nonalcoholic fluids.
- You should take at least 8 full glasses of fluid every day.
- Try to stick to water, diluted fruit juice, sports drinks, decaffeinated beverages, and fruit and vegetable drinks.
- Avoid caffeinated beverages and sodas.
Ulcerative Colitis Complications Vs Crohns Disease Complications
When it comes to potential complications due to ulcerative colitis or Crohns disease, there are some that these two diseases share, and others that are more likely to occur in one versus the other, according to a 2017 study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology.6
- Colon cancer: People with ulcerative colitis, we well as people who have Crohns disease that affects most of their colon, do have a slightly increased risk of developing colon cancer.Screenings will typically be recommended 810 years after an IBD diagnosis, and your doctor will let you know how frequently youll need screening.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Inflammation can cause scarring of the bile ducts . This can lead to liver damage.
- Blood clots: Both people with ulcerative colitis and Crohns have a greater risk of blood clots, though it isnt entirely clear why. It may be due to genetic predispositions coupled with severe inflammation in the GI tract, according to Cedars Sinai.
- Medication side effects: The medications used to treat both conditions can potentially increase the risk for certain cancers, like lymphoma, when used long-term. Consistent corticosteroid use is also associated with things like high blood pressure and osteoporosis.
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
There are multiple contributing risk factors that can lead to ulcerative colitis and Crohns. Evidence does suggest that both are associated with an inappropriate immune response, which can arise from many different environmental factors, gut microbiome imbalance, as well as genetics .
The body creates temporary inflammation as part of a normal immune system response to threats and foreigners that may cause harm. An inappropriate immune response occurs when the immune system attacks something that is probably not harmful or overreacts to a possible pathogen. This creates unnecessary or excessive inflammation that can become chronic inflammation.
For example, in addition to toxins and infections, the immune system may attack food particles, beneficial gut bacteria, and, in the case of ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, the lining of the digestive tract [1
What might be causing the inflammation of the digestive tract and an inappropriate immune response?
Some of the contributing factors in IBD are:
Read Also: Is Soy Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
You May Like: Peptic Ulcer Food To Eat
Treating Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
Although there is no cure for ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, there are treatments available that can help you manage the condition and hopefully improve your symptoms. Both diseases are typically treated using drug therapy or surgery.
The type of medications you need will depend on the severity of the condition. The Mayo Clinic says one goal of treatment is to help reduce inflammation that triggers your system and another goal is to improve long-term prognosis by limiting complications.
Keep in mind, the source says there is no single treatment that works for everyone. One medication that works well for others may not work for you, which is why its vital that you work closely with your doctor.
Related Topics :
What Are Surgical Treatments For Ulcerative Colitis
After 30+ years of living with ulcerative colitis, about 1 in 3 people need surgery.
A surgeon:
- Removes the colon or the colon and rectum .
- Connects the small intestine and anus.
- Creates an ileal pouch that collects stool, which then exits through the anus.
Rarely, you may need an ileostomy instead of an ileal pouch. An ileostomy bag attaches outside of the belly to collect stool.
A proctocolectomy is curative. Symptoms wont return after surgery to remove the colon and rectum. However, you may have problems with the ileostomy or ileal pouch, such as pouchitis .
Dont Miss: Skin Graft For Foot Ulcer
Don’t Miss: Alternative Medicine For Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The recurring bouts of diarrhea and belly pain that sent people to the doctor are hallmark signs of both ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease. Despite their similarities, the two inflammatory bowel diseases can differ in how symptoms present.I have found that patients with ulcerative colitis tend to have more diarrhea, which can be bloody at times, says Rahul Nayak, MD, a gastroenterologist with Kaiser Permanente in Atlanta. Crohns typically presents with more abdominal pain but can also include diarrhea as well.
Mouth sores and fistulas are unique to Crohns disease. A fistula is an abnormal connection between two parts of the body, such as between the bowel and the skin, bladder, and other parts of the bowel.The symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease can be embarrassing, painful, and unbearable at times, but Dr. Nayak says that early and aggressive treatment can reduce or eliminate the possible symptoms and complications.
Treatment depends on the location of the inflammation in the body. Thats why its essential to know the different types of ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease and the specific symptoms they present.
You May Like: What To Avoid With An Ulcer
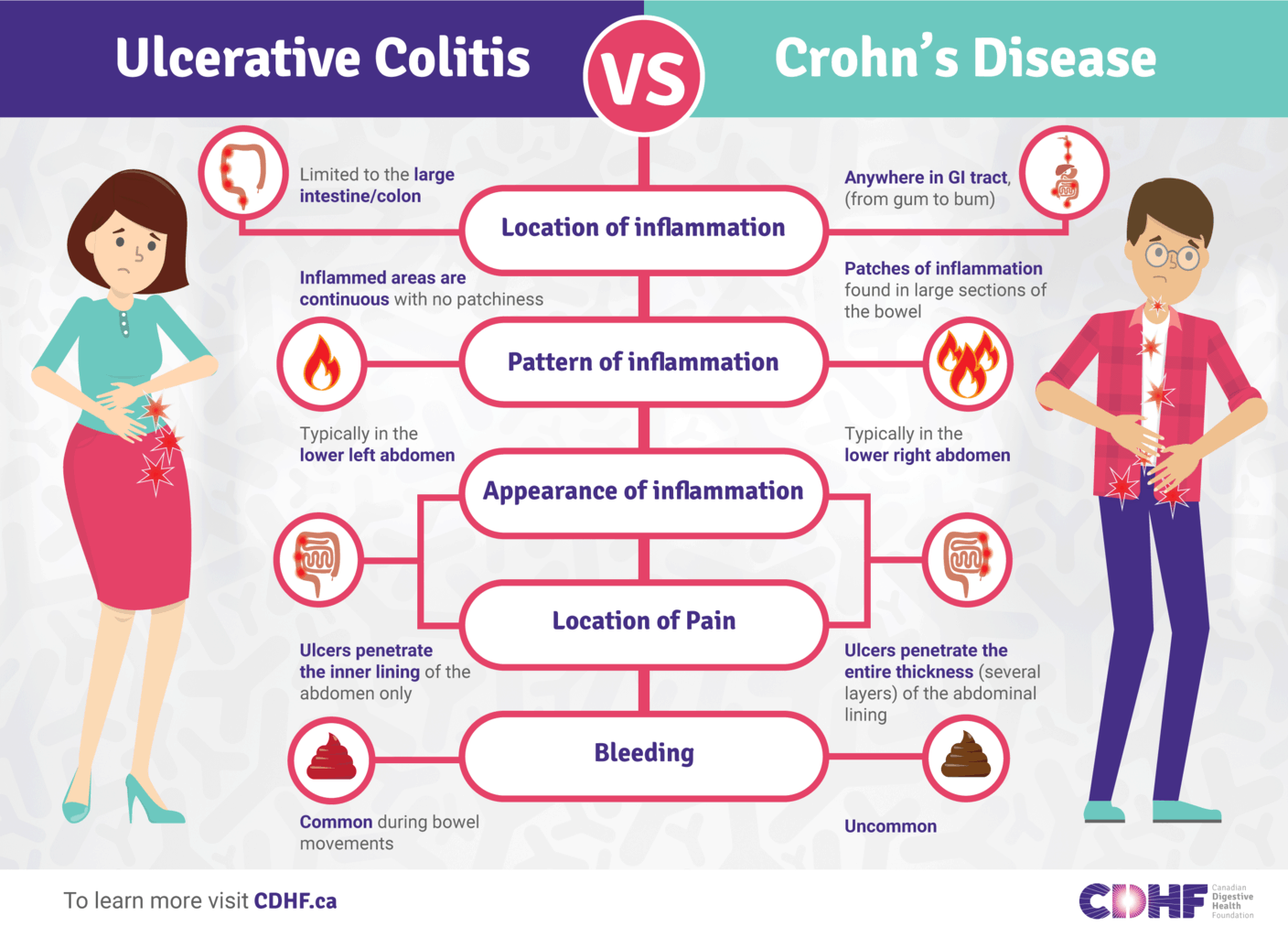
Key Differences: Where The Inflammation Develops
Another important difference between ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease is where the inflammation develops. Ulcerative colitis is isolated to the colon, whereas inflammation can develop anywhere between the mouth and the anus in Crohns disease, explains UCLA Health.
The source also notes that ulcerative colitis causes continuous inflammation in the colon, whereas in Crohns disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Finally, Crohns disease develops in all layers of the bowel walls and ulcerative colitis only affects the innermost lining of the colon.
Read Also: Natural Ways To Heal Stomach Ulcers
Diagnostic Tests And Tools: Getting The Right Diagnosis
The ultimate diagnosis and testing method for ulcerative colitis is colonoscopy, which is done using a thin tube with a light and camera at the end, allowing your doctor to examine the colon or/and take a tissue sample for biopsy.
If the doctor, during a colonoscopy, notices a continuous inflammation starting from the rectum, that could be a sign of ulcerative colitis. Otherwise, you might have Crohns disease if the inflammation is in other parts of your GI tract.
To ascertain whether or not you have Crohns, your GI specialist or gastroenterologist can use magnetic resonance imaging or CT scan if your small intestine is affected. They may also perform an endoscopy if the upper parts of your GI tract, like the esophagus, are involved in determining the site of inflammation. Other diagnosis methods for Crohns disease include capsule endoscopy.
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
The differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are:
- Ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere between the mouth and the anus
- In Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is continuous inflammation of the colon
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls
You May Like: Do Stomach Ulcers Cause Nausea
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
However, there are cases where the diagnosis of one form of IBD over the other is very difficult. At times, a final diagnosis is possible only after an event during the course of the disease or its treatment makes the form of IBD readily apparent.
Patients with IBD may be very confused as to the differences between these diseases. As with any chronic condition, education is an important tool to become an active participant in one’s own treatment plan.
If your diagnosis isn’t firm, don’t panic. In some people, it can take time to determine if the IBD is more like Crohn’s disease or more like ulcerative colitis. In about 5-20% of cases, people are diagnosed as having indeterminate colitis .
IBD is becoming increasingly treatable and there are now many medications in the arsenal that are helping people with all forms get greater control over their disease. The main differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are described below.
-
Smoking can worsen condition
Keep Up With Your Checkups
If you have either condition, you’ll need to keep up with your checkups, even if your symptoms start to ease up.
You may also need to get colonoscopies more often and start them at a younger age. A colonoscopy can check for cancer or polyps that need to come out. Experts recommend that you start these tests within 8 to 10 years of developing UC or Crohnâs symptoms, and then typically every 1 to 3 years after that. Your doctor will tell you a schedule that is best for you.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: Does Ulcerative Colitis Cause Fever
Whats The Difference Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Irritable Bowel Syndrome
IBD is a disease IBS is a syndrome, or group of symptoms. The causes and treatments are different.
IBS is a type of functional gastrointestinal disease. It affects how the bowels function, causing them to contract more often than usual. IBS is also known as spastic colon or nervous stomach.
IBS doesnt inflame or damage the intestines like IBD, so imaging scans cant detect it and it doesnt increase the risk of colon cancer. People with IBS rarely need hospitalization or surgery.
What Are The Differences Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
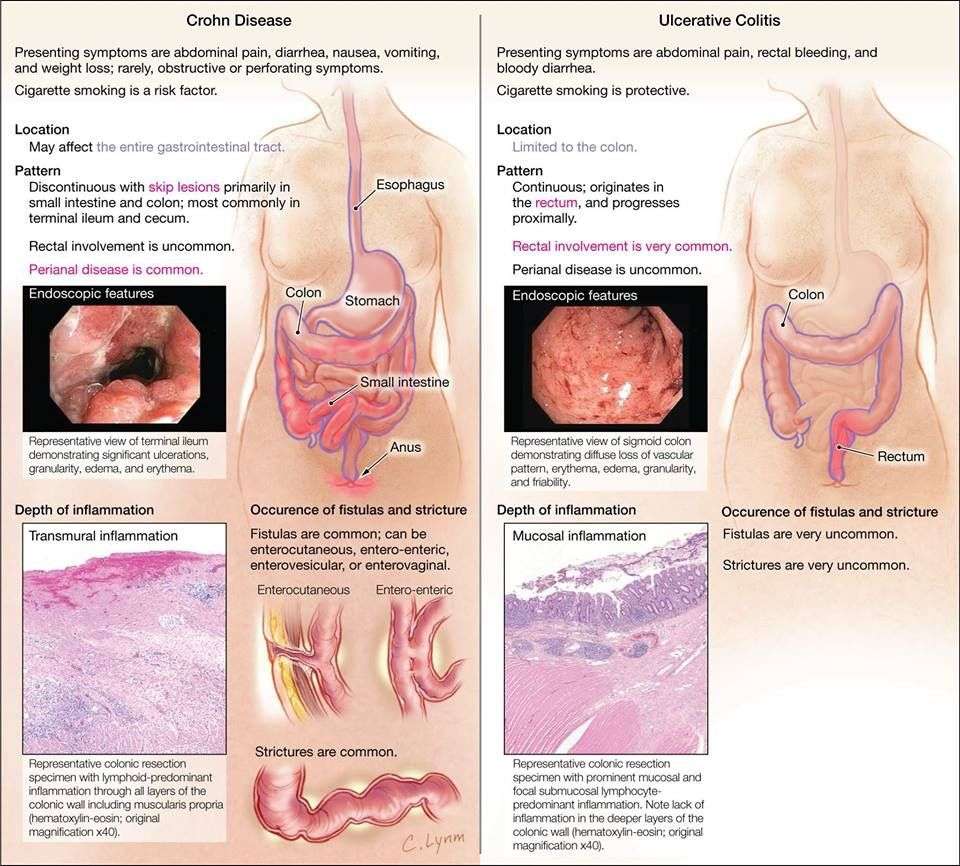
Although Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis have many similar symptoms, several things set them apart. These include:
Site of Inflammation
Crohns disease can affect and cause inflammation throughout your gastrointestinal tract. It can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus. However, it commonly develops in the small intestine, at the part leading to the large intestine or colon.
On the other hand, ulcerative colitis solely affects and resides within the large intestine. It varies among individuals, depending on what part of the colon is affected and the severity of the inflammation. Colitis affects everyone differently. The symptoms also vary in severity.
Inflammation Type
If you have Crohns disease, youll often have some healthy areas between inflamed parts. But, with ulcerative colitis, theres continuous inflammation of the colon, meaning there are no healthy areas between inflamed spots.
Affected Layers
Ulcerative colitis only affects the innermost lining of the large intestine. Crohns disease is characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract that can involve the deeper layers of the digestive tract leading to other complications. Individuals who have Crohns disease are more likely to have mouth sores between gums and lower lips, along with or under the tongue, ulcers, anal fissures, and fistulas these arent common in people with ulcerative colitis.
Symptomatic Differences
Read Also: Probiotics Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Symptomatic Differences Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
There are some subtle differences in symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. In Crohns disease rectal bleeding is less common, whereas in ulcerative colitis, bleeding from the rectum is much more common. In Crohns disease, continuous abdominal pain is more common and perianal problems such as fistulas, anal sores and skin tags, can occur. In contrast, people living with ulcerative colitis usually have intermittent pain coinciding with bowel movements. Perianal issues are uncommon in ulcerative colitis.
Clinical Trials Updates
Where Inflammation Occurs
Both illnesses are caused by inflammation in the GI tract, but where the inflammation occurs can lead a doctor to the correct diagnosis. The most basic difference is that Crohns disease can involve the entire GI tract, from the mouth all the way down to the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis is restricted to the colon, says Louis Cohen, MD, assistant professor of gastroenterology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City.
According to the UCLA Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Crohn’s disease usually results in healthy stretches of the intestine between inflamed areas. People who suffer from colitis experience continuous inflammation of the colon.
Recommended Reading: Foods To Eat When You Have An Ulcer
How Is Ibd Diagnosed
Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis cause similar symptoms. No single test can diagnose either condition.
To make a diagnosis, your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms. Your workup may start with a complete blood count and stool test to look for signs of intestinal inflammation.
You may also get one or more of these diagnostic tests:
- Colonoscopy to examine the large and small intestines.
- EUS to check the digestive tract for swelling and ulcers.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy to examine the inside of the rectum and anus.
- Imaging scan, such as a CT scan or MRI, to check for signs of inflammation or an abscess.
- Upper endoscopy to examine the digestive tract from the mouth to the start of the small intestine.
- Capsule endoscopy using a small camera device that you swallow. The camera captures images as it travels through the digestive tract.
What Can Be Learned From These Studies
Gene-expression profiling studies appear to hold much promise. In cancer studies, this promise has been met with the identification of many profiles that can be used to classify different tumor stages or to predict response to therapy. The gene-expression changes in tumor tissues are, in general, much more pronounced than those seen in other diseased tissues. A number of potentially interesting, new leads for therapeutic targets or disease diagnosis have come from Costello et al.’s study. Upregulation of cancer-related genes, such as TFF1 and the gene that encodes the Wnt signaling molecule CSNK1D, is very specific to the UC profile, and may point toward these genes playing a role in the increased risk of malignant transformation for patients with a long history of UC. Uthoff et al. also suggested a potential role for the Wnt signaling pathway in UC carcinogenesis in an earlier but much smaller study , but this needs to be further investigated. It is encouraging to learn that many of the genes now being identified confirm the ideas on disease pathogenesis that have developed recently as a result of genetic studies, namely, that there is impaired integrity of the epithelial barrier. Hence, Costello et al.’s study may further our understanding of the underlying disease mechanism.
You May Like: How Do You Stop A Stomach Ulcer From Hurting
Remission With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
People with inflammatory bowel disease strive to achieve remission statusmeaning there is no more inflammation or agonizing symptoms. Statistically speaking, about 50 percent of Crohns patients will be in remission or have mild disease over the course of five years past initial diagnosis.
Comparatively, in a given year, 48 percent of patients with ulcerative colitis are in remission, 30 percent have mild disease activity, and 20 percent have moderate disease activity.
Remission doesnt mean you should throw your care plan out the window.
Once remission has been accomplished, patients need ongoing medications to ensure that they stay in remission, says Dr. Nayak. Youll still want to avoid triggers and talk to your doctor about how often to get colonoscopies to screen for colon cancer, as the risk is higher with both ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease.
Diagnosing Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
If your doctor suspects you may have one of these diseases, they will likely request a colonoscopy, says Everyday Health. This involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the colon and allows your doctor to see the colon as well as take a biopsy of the inflamed tissue.
During the colonoscopy, if your doctor sees continuous inflammation from the rectum to the colon and then stops, this could be a key sign that you have ulcerative colitis. On the other hand, if your doctor sees patches of healthy tissue mixed with patches of inflamed tissue, this may indicate Crohns disease. Other possible tests include sigmoidoscopy blood, and fecal testing and computed tomography scan.
Don’t Miss: Nursing Care Plan For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
How Are They Similar
Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease are similar in a few ways. For starters, theyre both types of IBD and both cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. They also share many similar symptoms which is why you shouldnt try to self-diagnose. Its important that you see your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Both diseases commonly affect teens and young adults, however, they can also develop at any age. The disease also affects men and women equally, says UCLA Health. The source also notes, both diseases have similar types of contributing factors such as environmental, genetic and an inappropriate response by the bodys immune system.
Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis And Diet
Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD, and long-term special diets are not effective in treating IBD. However, adjusting your diet can help manage some of your symptoms, and can help IBD medications work better. A person with IBD has to pay close attention to their diet, since they may have malnutrition.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Treat Stomach Ulcers