What Should You Eat When You Have Ulcerative Colitis
When it comes to food, theres no known dietary cause of ulcerative colitis, but different foods may aggravate or help limit symptoms of the disease.
Youre more likely to need to change your diet during periods of active disease , when eating soft, bland foods can help limit symptoms like cramping and diarrhea. With guidance from a doctor, a liquid meal replacement diet known as an elemental diet, can also help achieve remission from active disease.
During flares, you may also want to avoid or limit high-fiber and high-fat foods, as well as alcohol, dairy products, and spicy foods.
If youre losing nutrients and water in your diet due to diarrhea, you may need to focus on increasing your fluid intake and getting enough calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals from foods or supplements.
Editor’s Picks
Outlook For People With Ulcerative Colitis
If you have UC, a doctor will need to monitor your condition, and youll need to carefully follow your treatment plan throughout your life.
The only true cure for UC is removal of the entire colon and rectum. Your doctor will usually begin with medical therapy unless you have a severe complication that requires surgery. Some people will eventually require surgery, but most do well with nonsurgical therapy and care.
Inflammation In Other Areas
Some people with IBD have painful inflammation in other areas of the body, including:
- joints of the fingers, hands, feet, ankles and knees
- joints of the spine, including vertebrae and sacroiliac joints
Two specific skin problems that can occur as a result of IBD are:
- pyoderma gangrenosum small, sunken ulcers on the skin
- erythema nodosum painful, small, reddened nodules on the skin .
Read Also: Oats For Horses With Ulcers
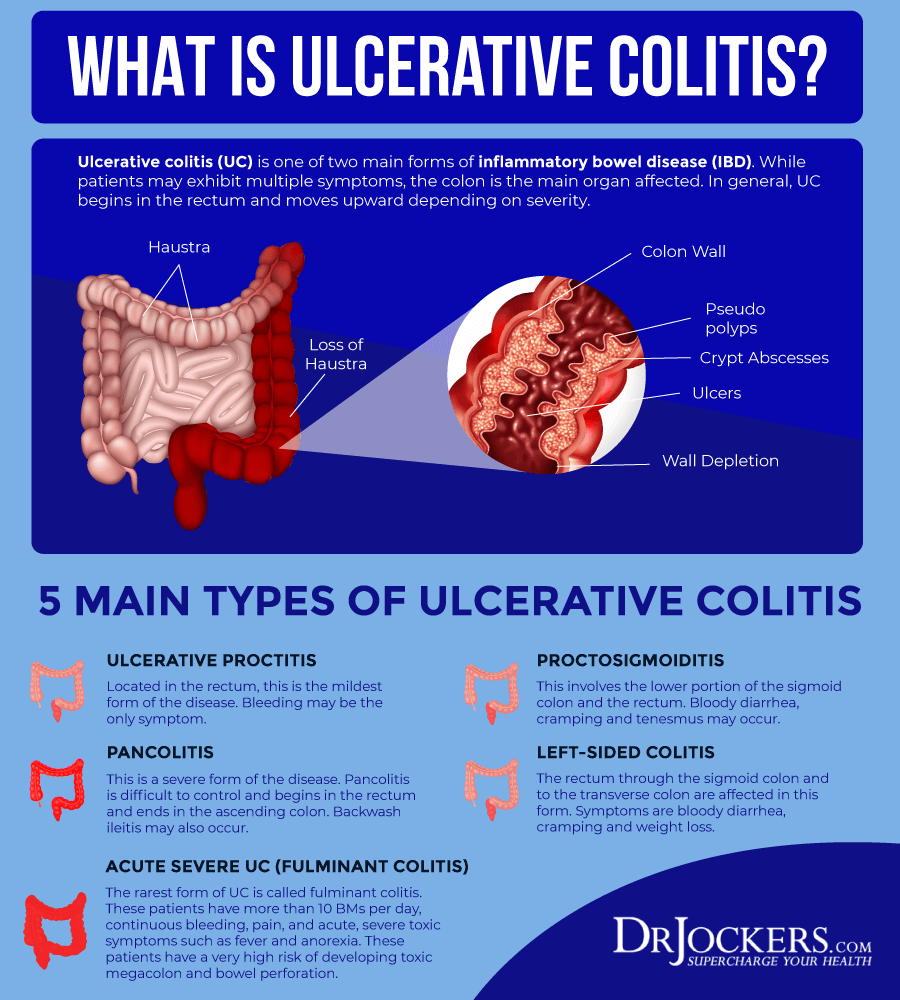
What Is Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease in which the lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed.
The colon then develops ulcers that produce blood, pus, and mucus.
The small intestine is rarely affected.
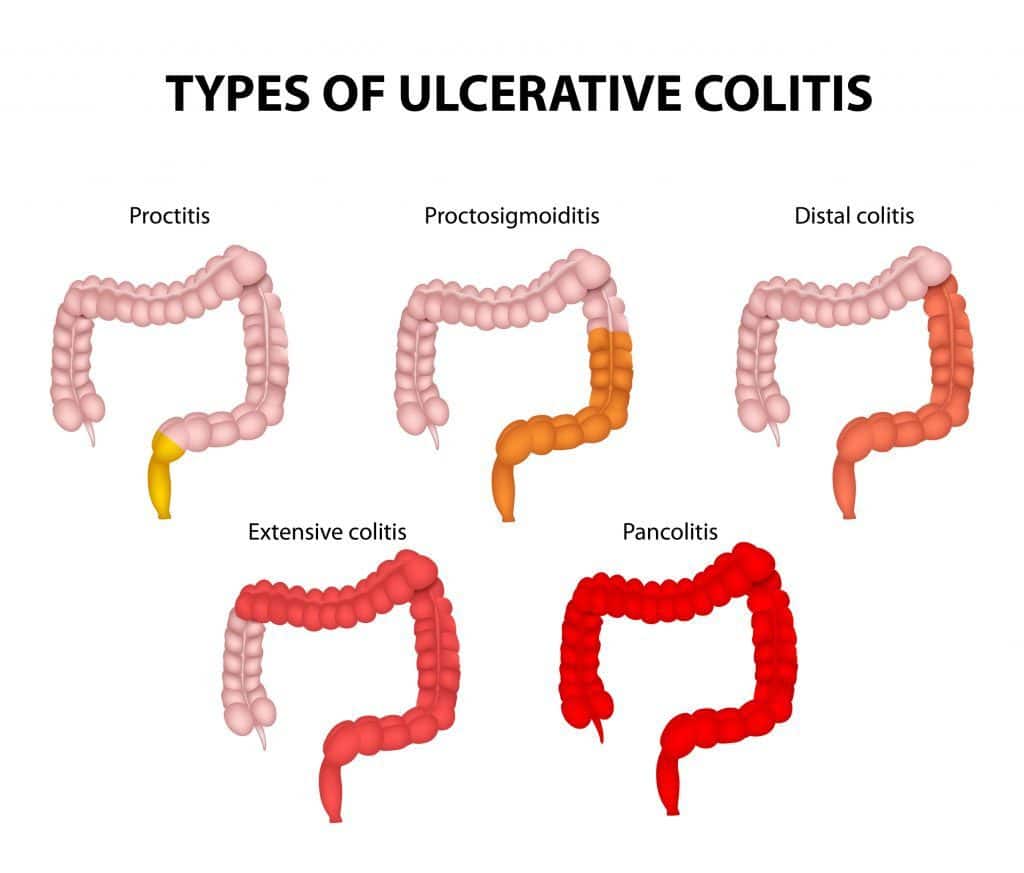
There are several subtypes of ulcerative colitis, which are named according to the part of the colon affected:
- Ulcerative proctitis, which affects only the rectum
- Proctosigmoiditis, which affects the rectum and lower segment of the colon
- Left-sided colitis, which affects the rectum, sigmoid colon, and descending colon up to the sharp bend near the spleen
- Pan-ulcerative or total colitis, which affects the entire colon
What Are Possible Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis In A Child
In rare cases, this condition can cause death. If your childs condition affects more than just his or her rectum and lower colon, your child has a higher risk for colon cancer. Your child is also at risk for a tear of the bowel wall. This needs to be fixed with surgery. Your child may also have periods of severe bleeding.
Also Check: Natural Cures For Gastritis And Ulcers
Surgery To Treat Ulcerative Colitis
Even with proper medication and diet, some children require surgery to attain the best possible quality of life. The decision to proceed with surgery is made in collaboration between the child and family, the gastroenterologist, and the surgeon specializing in IBD. Surgery is used to relieve severe, ongoing symptoms and to help children achieve growth and weight gain when medical management is no longer effective on its own. Unlike Crohns disease, in which surgery is a temporary solution, surgery can provide long-term relief with ulcerative colitis.There are multiple surgical options for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. At the Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease, our team will work closely with your family to determine if surgery is necessary, and our expert surgeons who specialize in IBD-related procedures will provide additional information and work to optimize your childs quality of life. Learn more about J-pouch Surgery and Bowel Resection Surgery.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Colitis
Complications usually result from severe, long-term, chronic colitis. They can include:
- Perforation. Chronic inflammation weakens your colon walls, making them more likely to rupture. An ulcer in your colon may wear a hole all the way through. This can cause bacteria from your colon to infect your abdominal cavity and possibly your bloodstream , which would be especially dangerous. Septicemia can lead to .
- Toxic megacolon. Severe inflammation can cause the walls of your colon to dilate and interfere with its natural muscle contractions . This can trap food and gas in your colon . Obstruction leads to painful abdominal distension and an increased risk of rupture.
- Increased risk of colon cancer. Long-term inflammation is associated with cellular changes in your colon wall that can sometimes progress to cancerous changes. The risk increases rapidly after the first decade of chronic colitis.
- Increased risk of other inflammatory diseases. People with inflammatory bowel diseases are more likely to have other inflammatory diseases in other parts of their bodies. Some examples include osteoarthritis and primary sclerosing cholangitis . It appears that uncontrolled inflammation in one area may trigger a similar process somewhere else.
Recommended Reading: Are Ulcerative Colitis And Ibs The Same
Complications Caused By Nutritional Deficiencies
Some of the complications of malnutrition include:
- Dehydration diarrhoea causes your body to lose fluid, which can lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia reduced iron in the diet combined with losing blood from the bowel can lead to anaemia .
- Weight loss reduced appetite and poor absorption of food nutrients can cause weight loss.
- Reduced growth inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can impair a childs growth and physical development.
Daily Life For People With Ibd
People with IBD lead useful and productive lives, even though they need to take medications. When they are not experiencing a flare-up of their disease, they feel quite well and are often free of symptoms.People with IBD can marry, enjoy sexual activity and have children. They can hold down jobs, care for families and enjoy sport and recreational activities.Even though there is currently no cure for IBD, medical therapy has improved the health and quality of life of most people with Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Research underway today may lead to further improvements in medical and surgical treatment, and even a cure.
Read Also: How Do You Get Rid Of Stomach Ulcers
Vitamin And Mineral Supplements For Ibd
A person with IBD who eats a healthy, varied diet does not usually need to take vitamin supplements. But if they have a dietary deficiency, they may need tablets or occasional vitamin B12 injections. For example, a person on a low-fibre diet may need extra vitamin C and folic acid because they dont eat enough fruit and vegetables.A person with Crohns disease who experiences steatorrhoea may need calcium and magnesium supplements. Most children with IBD should take supplements to help them grow and develop normally.
Dietary And Lifestyle Modifications
As most nutrients are absorbed higher up in the digestive tract, those with ulcerative colitis generally do not have nutrient deficiencies however, other factors might influence your nutritional state. Disease symptoms may cause food avoidance, leading to food choices that might not provide a balanced diet. If bleeding is excessive, problems such as anemia may occur, and modifications to the diet will be necessary to compensate for this.
Generally, better overall nutrition provides the body with the means to heal itself, but research and clinical experience show that diet changes alone cannot manage this disease. Depending on the extent and location of inflammation, you may have to follow a special diet, including supplementation. It is important to follow Canadas Food Guide, but this is not always easy for individuals with ulcerative colitis. We encourage you to consult a registered dietitian, who can help set up an effective, personalized nutrition plan by addressing disease-specific deficiencies and your sensitive digestive tract. Some foods may irritate the bowel and increase symptoms even though they do not worsen the disease.
In more severe cases, it might be necessary to allow the bowel time to rest and heal. Specialized diets, easy to digest meal substitutes , and fasting with intravenous feeding can achieve incremental degrees of bowel rest.
Recommended Reading: Can You Eat Oatmeal With Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Treated
Theres no cure for ulcerative colitis, but treatments can calm the inflammation, help you feel better and get you back to your daily activities. Treatment also depends on the severity and the individual, so treatment depends on each persons needs. Usually, healthcare providers manage the disease with medications. If your tests reveal infections that are causing problems, your healthcare provider will treat those underlying conditions and see if that helps.
The goal of medication is to induce and maintain remission, and to improve the quality of life for people with ulcerative colitis. Healthcare providers use several types of medications to calm inflammation in your large intestine. Reducing the swelling and irritation lets the tissue heal. It can also relieve your symptoms so you have less pain and less diarrhea. For children, teenagers and adults, your provider may recommend:
Children and young teenagers are prescribed the same medications. In addition to medications, some doctors also recommend that children take vitamins to get the nutrients they need for health and growth that they may not have gotten through food due to the effects of the disease on the bowel. Ask your healthcare provider for specific advice about the need for vitamin supplementation for your child.
You might need surgery that removes your colon and rectum to:
- Avoid medication side effects.
- Prevent or treat colon cancer .
- Eliminate life-threatening complications such as bleeding.
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
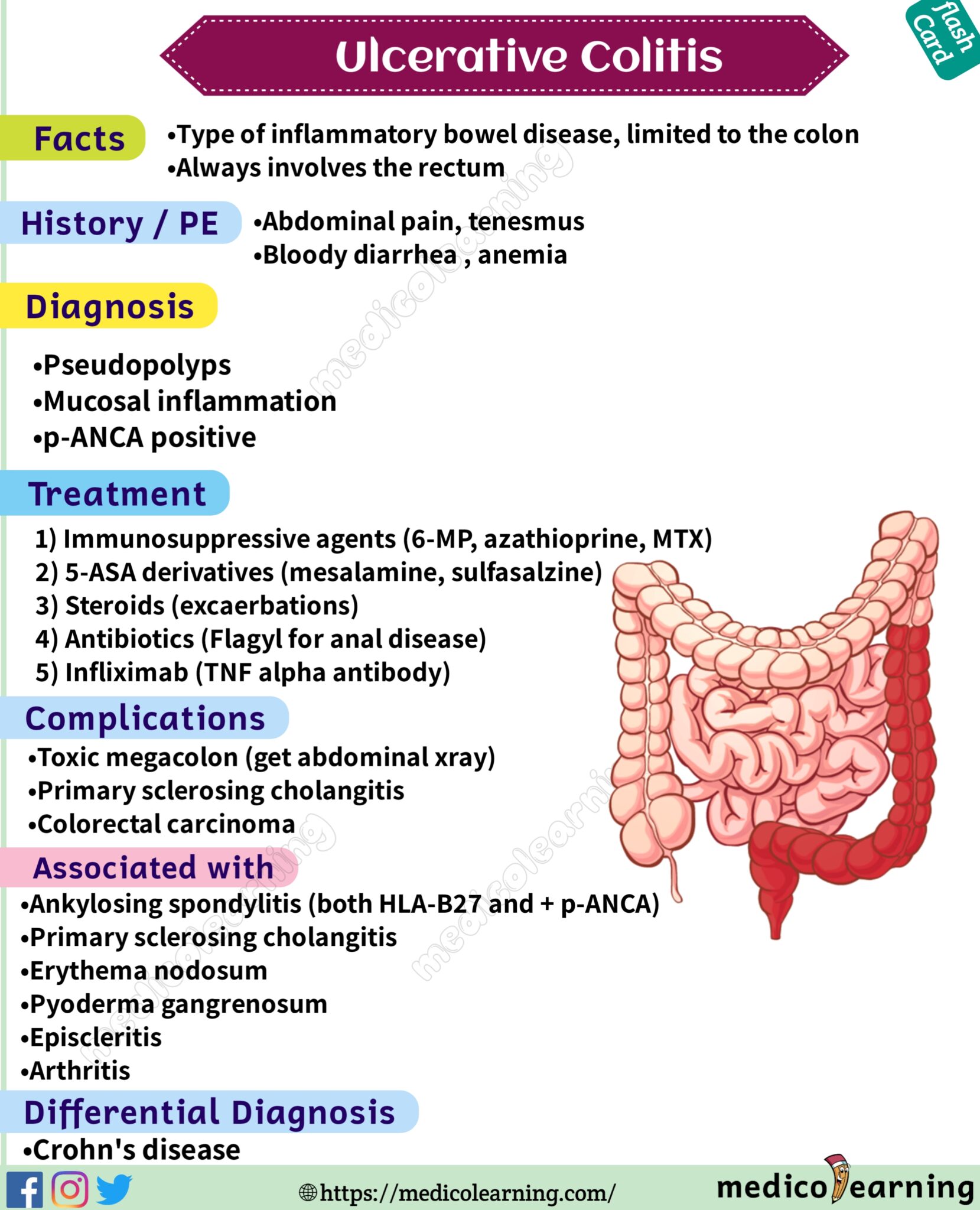
Colitis shares many symptoms with other common conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome, gastroenteritis and coeliac disease. Your doctor will examine you and take a detailed history of your symptoms to help rule these out.
There is no single test that can be used to diagnose UC, so a combination of tests is usually required:
- Blood tests help to rule out other medical conditions, and certain markers in the blood can indicate that inflammation is present.
- A stool sample may find other possible causes of diarrhoea and inflammation, such as an infection.
- A colonoscopy may be performed, where a thin, flexible tube that contains a tiny camera looks inside the bowel for ulcers, inflammation and bleeding.
- A biopsy may be taken from inside the bowel so a pathologist can examine it under a microscope to look for signs of disease.
Other types of imaging are sometimes used to help in the diagnosis and to help rule out other diseases.
Read Also: Mouth Ulcer Vitamin B Complex
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis Different
A key difference is what triggers colitis. For instance, IBD is usually an autoimmune issue. Thatâs when your immune system attacks healthy tissue in your body. Other kinds of colitis can be the result of outside factors, such as germs or medical treatments.
People with UC or other kinds of IBD may also have inflammatory symptoms alongside bowel problems, including:
But those arenât the only distinctions. Hereâs a breakdown by colitis type:
Ulcerative colitis . This type of IBD causes sores and constant inflammation in the inner lining of your large intestine. UC often starts in the rectum and extends through the left side of your colon. But some people have colitis throughout most or all of their colon. Thatâs called extensive colitis or pancolitis.
Crohnâs colitis. This is a feature of Crohnâs disease, another type of IBD. Crohnâs can impact any part of your gastrointestinal tract â thatâs your mouth to your . Unlike UC, you may have healthy tissue in between spots of inflammation. Crohnâs disease can also affect many layers of your GI tract.
Microscopic colitis. This is another type of IBD. Itâs not related to ulcerative colitis or Crohnâs disease, but itâs associated with other autoimmune diseases. Like the name suggests, your doctor has to use a microscope to see any evidence of this kind of colitis.
There are two main forms:
Some experts think collagenous and lymphocytic colitis may be different phases of the same condition.
Is Colitis A Serious Disease
There are different types of colitis, with different causes. Some are short-lived and easy to treat, like when you have a bacterial infection from food poisoning. Other types called inflammatory bowel diseases are more chronic and difficult to treat. Colitis is more serious when it doesnt go away. A severe case can do serious damage to your colon over time. It also affects your quality of life.
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Intestinal Ulcers In Humans
What Are The Different Types Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Ulcerative colitis is part of a group of disorders called inflammatory bowel diseases. Another common inflammatory bowel disease is Crohns disease. These two inflammatory bowel diseases have similar symptoms, such as diarrhea and abdominal pain. It can be hard for patients and health care providers to tell these conditions apart. However, there are important differences in the type and location of inflammation.3
When To Get Treatment
An increase in inflammation causes a flare, and the nature of inflammation means that you should treat it as quickly as you can. Inflammation grows exponentially, because inflammation itself causes an increase in inflammation. The longer you leave it untreated, the worse it will get. In addition, untreated inflammation not only leads to the symptoms associated with ulcerative colitis, it can also increase your risk of developing complications such as colorectal cancer down the line. Pay attention to your symptoms, and visit your physician if you notice that they change or increase even a small amount.
Also Check: What Is Ulcerative Colitis Pain Like
Oral Vs Rectal Treatments
Most physicians prescribe ulcerative colitis patients oral versions of 5-ASAs or corticosteroids, since this is a patient-preferred delivery method of medication. However, even if they have a specially designed release mechanism, they might not reach and treat the area where the disease is most active.
For example, when you apply sunscreen to your skin, you need to make sure that you cover every exposed part to protect it from the sun. Similarly, when applying these treatments to your rectum and lower colon, you need to make sure that the product covers all of the inflamed areas.
Oral tablets might not be the optimal way to reach the end of the colon, where stool and the fact that ulcerative colitis patients have diarrhea, might interfere with its effectiveness. Unfortunately, this is also the area in the colon where a flare usually starts. The best way to reach this particular area is by inserting the drug directly into the rectum.
Rectal preparations are particularly good at treating urgency and bleeding, symptoms that often are very bothersome. A positive response often occurs within days of treatment.
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease Vs Irritable Bowel
Other gut diseases can have some of the same symptoms.
- Ulcerative colitis affects only your large intestine and its lining.
- Crohnâs disease causes inflammation, but it affects other places in your digestive tract.
- Irritable bowel syndrome has some of the same symptoms as UC, but it doesnât cause inflammation or ulcers. Instead, itâs a problem with the muscles in your intestines.
Recommended Reading: Is Aloe Vera Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease
Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease share similar symptoms and they are both types of inflammatory bowel disease , but they are not the same illness and they affect different areas of the GI tract.
- Can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall
- Only the colon and rectum are affected
- Affects the inner-most lining of the large intestine
- What is Ulcerative Colitis?
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Flareups
When youre in remission from ulcerative colitis, youll want to do everything you can to prevent a flareup. Things that may cause a flareup include:
- Emotional stress: Get at least seven hours of sleep a night, exercise regularly and find healthy ways to relieve stress, such as meditation.
- NSAID use: For pain relief or a fever, use acetaminophen instead of NSAIDs like Motrin® and Advil®.
- Antibiotics: Let your healthcare provider know if antibiotics trigger your symptoms.
Read Also: Best Natural Remedies For Stomach Ulcers
Ulcerative Colitis And Colorectal Cancer
Ulcerative colitis increases the risk of colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer often begins as small growths on the inside of the large intestine. The risk of colorectal cancer increases based on:
- the length of time a person has had ulcerative colitis
- how much of the colon is affected by ulcerative colitis
People with ulcerative colitis should have more frequent tests for polyps and colorectal cancer than people at average risk. The gold standard screening test is a colonoscopy. Polyps can be removed during a colonoscopy. This reduces the risk of colorectal cancer. Ask your doctor how often you should be checked for colorectal cancer.
Surgery to remove the entire colon eliminates the risk of colon cancer.
What Are The Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis may lead to complications that develop over time, such as
- anemia, a condition in which you have fewer red blood cells than normal. Ulcerative colitis may lead to more than one type of anemia, including iron-deficiency anemia and anemia of inflammation or chronic disease.
- bone problems, because ulcerative colitis and corticosteroids used to treat the disease can affect the bones. Bone problems include low bone mass, such as osteopenia or osteoporosis.
- problems with growth and development in children, such as gaining less weight than normal, slowed growth, short stature, or delayed puberty.
- colorectal cancer, because patients with long-standing ulcerative colitis that involves a third or more of the colon are at increased risk and require closer screening.
In some cases, ulcerative colitis may lead to serious complications that develop quickly and can be life-threatening. These complications require treatment at a hospital or emergency surgery. Serious complications include
Severe ulcerative colitis or serious complications may lead to additional problems, such as severe anemia and dehydration. These problems may require treatment at a hospital with blood transfusions or intravenous fluids and electrolytes.
Also Check: Can Mold Cause Ulcerative Colitis