Endoscopy And Mucosal Biopsy
Endoscopic examination with mucosal biopsy is essential to confirm a diagnosis of IBD and determine the extent of disease. The most widely reported endoscopic abnormalities seen with canine and feline IBD include mucosal friability, increased granularity, and mucosal erosions .7,33,46
FIGURE 5. Endoscopic images of dogs with IBD consistent with increased small intestinal friability, increased small intestinal granularity, and intestinal mucosal erosions. Endoscopic image showing the advancement of biopsy forceps to obtain partial-thickness biopsy samples in a dog with inflamed GI mucosa and IBD. Courtesy of Dr. Albert Jergens.
The association between endoscopic lesions and disease activity in small animal IBD has been investigated to a limited extent. In separate investigations, endoscopic abnormalities of the duodenum of dogs with IBD did not always correlate with clinical indices of inflammation.33,47 The presence of severe mucosal lesions of the duodenum, but not the colon, was associated with a negative outcome in one study.33
In contrast to dogs, cats with IBD have endoscopic abnormalities that correlate to both clinical disease activity and histopathologic lesions at diagnosis.6
The need to perform ileoscopy may be guided by the presence or absence of hypocobalaminemia, because cobalamin is absorbed in the ileum.
Serum Biochemistry And Specialized Serologies
Results from biochemical analysis rarely provide definitive evidence for IBD, but they do facilitate the recognition of abnormalities in other organs that may cause GI signs.
In cats with IBD, hyperproteinemia and mild elevation in liver enzymes are often reported.7,22,40
Dogs with PLE frequently have hypoalbuminemia and hypoglobulinemia, which may be accompanied by hypocholesterolemia and hypocalcemia. The presence of hypoalbuminemia correlates with a negative outcome in dogs.33,38
Cats with IBD may have increased serum pancreatic lipase concentrations . This association does not appear to influence clinical outcome, based on a recent report.41 However, increased serum pancreatic lipase concentrations in dogs with IBD have been associated with a poorer clinical outcome.42
Dogs and cats with chronic small bowel disease may have concentrations secondary to cobalamin malabsorption. Failure to recognize and correct hypocobalaminemia can delay clinical recovery, even with specific therapy for IBD.43 Hypocobalaminemia has also been correlated with a poor prognosis in dogs with chronic enteropathies.33
Diet For Dogs With Colitis
Diet plays a vital role in the treatment of colitis. Immediately there is a diagnosis for the condition, fast your dog for 24 to 48 hours.
Once this period lapses, slowly introduce a high fiber diet. This is more so if your dog suffers irritable bowel syndrome. A high dog fiber colitis diet increases stool bulk, improves contraction of colon muscles and binds fecal water. These with time normalize the dogs stool.
For colitis resulting from allergic reactions and sensitivity to specific foods, opt for hypoallergenic diets. These are available commercially and there also are some available on prescription. Duck, venison, and fish could be alternative sources of proteins which are beneficial.
In case the high fiber diet does not work, opt for highly digestible foods to treat colitis in dogs naturally. With these, smaller fecal mass is produced.
Don’t Miss: Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses Symptoms
Recovery Of Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis In Dogs
Supportive care is required to assist your pet back to good health. If your dog is on a course of medication, ensure that the medication is given as advised. Missing one dose may upset the whole recovery process and it may take longer to effect a positive result. Creating a calm quiet place for your dog to rest and gain his strength as well as providing nourishing but easily assimilated meals will enable the internal organs to recover and fight back against the disease. Often once a positive result has been seen, and your dog is bouncing around full of life again, it is easy to relax with the medications provided, but keep in mind this condition can reoccur with a vengeance so prevention is vital.
*Wag! may collect a share of sales or other compensation from the links on this page. Items are sold by the retailer, not Wag!.
How Is Colitis Diagnosed

The diagnosis of colitis is based on your pet’s clinical signs and history, microscopic evaluation of the feces, rectal examination, cytology, and blood tests. Additional testing such as radiographs to examine the colon and intestinal tract, colonoscopy and colon biopsies, fecal cultures, barium enemas, or ultrasound evaluation of the abdomen may be necessary in some cases. These tests are important to rule out conditions such as colonic tumors or polyps, irritable bowel syndrome, cecal inversion, and ileocecocolic intussusception .
You May Like: What Is An Ulcer Diet
Treatment Of Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis In Dogs
It depends on the severity of the disease as to the appropriate treatment. Young dogs who are only mildly affected usually only need dietary changes and a course of medication to overcome the condition. Medication in the form of sulfasalazine and corticosteroid therapy is the chosen way to treat HUC. Diets that include high fibre should be avoided as it will aggravate the condition. Your veterinarian can advise about dietary changes and how to include just moderately fermentable fibre supplements to maintain your dogs health. He will also discuss with you the possibility of the progressive nature of the disease and even if your dog responds well to treatment, that there may be reoccurrences later on in life.
Other medications may include the use of antimicrobials and anti-inflammatory drugs. Diet plays a major role in the health of your dog and even once he is healthy, maintaining a varied nourishing diet is important. Your dog is genetically geared to try to eat many things that may not be good for them, essentially they will scavenge if they can. In a country setting, this includes eating anything they find such as half rotten carcasses of birds or small animals, so an awareness of this habit is advisable.
Recovery And Management Of Colitis In Dogs
In cases of acute colitis, full recovery typically happens within a few days. Chronic colitis usually takes a longer time, requiring further diagnostics and trials of different medications and diets to see what helps.
Depending on the underlying cause, chronic colitis in dogs might not be curable, but it can often be managed and controlled through one or more of the following: diet, fiber supplements, antibiotics, and corticosteroids/anti-inflammatories/immune modulators.
Also Check: Stelara Dosing For Ulcerative Colitis
Causes Of Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis In Dogs
- The true cause seems to be a debatable issue among veterinarian and researchers
- Histiocytic ulcerative colitis seems to be a breed-related disease affecting usually the Boxer types although it can affect other breeds
- Acute stress seems to be an acknowledged cause of this disease
- Other causes include internal infections
- Parasites such as whipworms or Giardia
- Allergic reaction to a particular food
- Contact with other infected dogs
- Eating contaminated food
Diagnosis Of Boxer Colitis
Its important to distinguish between a bout of acute, regular colitis and the more severe, chronic form that is Boxer colitis.
Acute colitis will typically resolve within a few days with minimal treatment.
A short fast of 24-48 hours may be all thats required .
Chronic colitis, however, will recur and worsen over time.
Definitive diagnosis of histiocytic ulcerative colitis in a Boxer usually involves a colonoscopy, a procedure whereby a tube with a camera is inserted via the anus into the lower digestive tract.
Colonoscopy will typically reveal:
- Irregularities in the mucosal surface
During the procedure, biopsies will be taken.
The classic finding when the tissue is examined is the presence of large macrophages that stain in a certain way under the microscope.
Prior to doing the colonoscopy, your vet will usually perform:
- Poop test to look for worms and other parasites
- Blood tests to rule out other causes of colitis
- Abdominal scans to check for masses or tumors, fecal impaction or abnormalities like thickening of tissues in the large intestine
If E. coli is detected, a diagnosis of Boxer colitis is likely.
A culture is is recommended prior to commencing treatment, to identify the particular strain of E. coli and to confirm which antibiotics will work against it.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Eat If You Have Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment For Colitis In Dogs
Do not give any medications at home. Dogs do not metabolize medications the same as humans, so giving your dog a human medication is very dangerous. It can also be counterproductive without knowing the exact cause of the colitis.
Take your dog to the veterinarian if you see any symptoms of colitis. They might initially provide some fluids under your dogs skin to help with hydration. Then, depending on their findings, they may prescribe one or more of the following treatment options.
Enrofloxacin Treatment For Colitis In Boxer Dogs
As mentioned above, acute colitis can typically be resolved by fasting for 24 hours or until symptoms resolve.
These days, the standard treatment for histiocytic ulcerative colitis involves antibiotics for four to eight weeks, namely enrofloxacin , which is a gram-negative, broad spectrum antibiotic of the quinolone class, dosed at 5mg/kg once a day.
Dogs with GI issues should not have further:
- Drugs including chemical wormers and flea/tick preventives
To quote the prominent integrative veterinarian Dr Karen Becker, Any chemical that goes into your pets body has the potential to contribute to unaddressed sources of inflammation.
Note: before accepting a diagnosis of colitis, its important to make sure you are feeding a fresh, natural canine diet i.e. a raw meaty bone-based diet.
Kibble and other highly processed dog food is not an optimal diet for Boxers and can, it itself, cause an array of gastrointestinal disturbances that may look very much like colitis.
Owners who switch their Boxers to a properly composed raw diet often see all symptoms resolve.
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Venous Stasis Ulcer Left Leg
Dog Breeds That Are Prone To Colitis
Any dog can get colitis. However, young Boxers and French Bulldogs are more prone to a rare type of colitis called granulomatous colitis.
In granulomatous colitis, a bowel segment becomes thickened or partially blocked due to a bacterial invasion of the intestinal wall. It results in bloody diarrhea and weight loss. Treatment includes antibiotic therapy and dietary changes as well as corticosteroids.
These are the steps a vet will take to diagnose colitis in dogs.
Symptoms Of Boxer Colitis
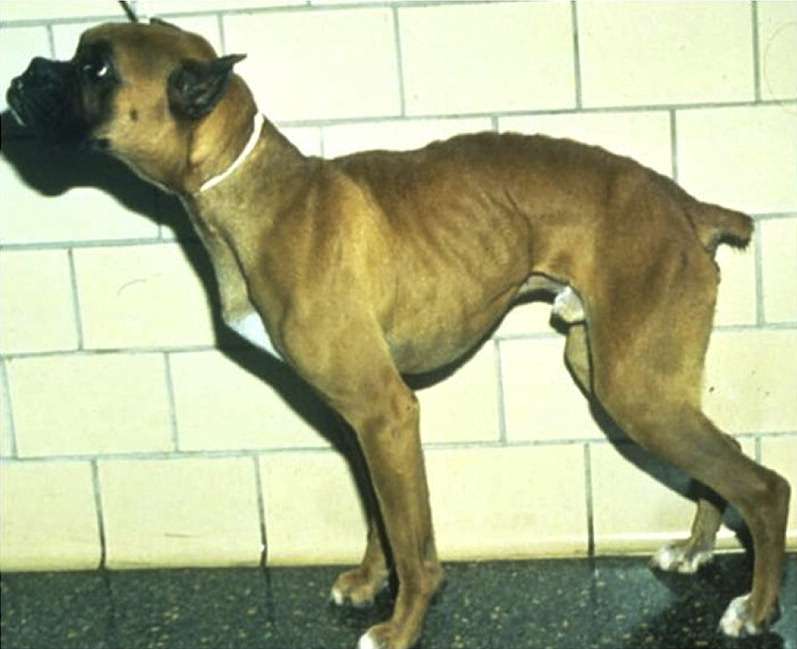
Colitis, in all its forms, presents as:
- Watery diarrhea possibly containing fresh red blood and mucus
- Urgency to get outside to poop
- Pain on defecation
- Increased frequency and urge to poop
- Nausea and vomiting
- Redness of tissues around the anus
- Soft, slimy and greasy loose poops
Once the condition becomes chronic, symptoms can include:
- Loss of appetite
- Substantial weight loss with an emaciated appearance
- Dehydration
- Cachexia or muscle wasting where the body overzealously breaks down skeletal muscle and fat tissue
- Extreme pain on rectal palpation and rectal mucosa may feel thickened and produce blood
- Behavioral changes like lethargy, lack of sociability
- Poor coat and body condition
- Black tarry stools
- Blood tests may reveal anemia and hypoalbuminemia
Another feature of Boxer colitis is that its often unresponsive to treatment with immunosuppressants.
Endoscopy will show an inflamed and ulcerated colonic mucosa .
Don’t Miss: What Foods Should You Eat If You Have An Ulcer
What Is The Best Food For A Boxer Dog With Colitis
Prominent integrative veterinarian Dr Karen Becker says she has seen a substantial amount of colitis in pets fed diets that arent compatible within their physiology, including prescription diets supposedly designed to address GI issues.
As mentioned above, its imperative to feed a biologically-appropriate diet to your Boxer.
This means a fresh, raw diet consisting of edible bone, lean muscle meat and a little offal .
Boxers experience various stomach problems when fed highly processed diets like kibble, and may appear to be picky eaters, until they are offered their natural diet.
History And Physical Exam
When a dog or cat is presented with diarrhea, questions to discern large bowel vs. small bowel and acute vs. chronic diarrhea are important for developing a logical differential list. Clinical signs of large bowel diarrhea may include increased urgency and frequency of defecation, tenesmus, mucus in feces, and hematochezia. Weight loss is much more characteristic of small bowel than large bowel disease, but weight loss is common with certain infections that primarily affect the large bowel. Historical questions of importance include a description of the frequency, consistency, and character of feces, any changes in diet, recent medications , recent stressors, travel history, and presence of other systemic signs of illness. A complete physical exam is warranted and may be normal or identify concurrent disease and/or clues to the cause of the large bowel disease. A rectal examination is an important component of the exam to allow evaluation of the rectal canal for masses, strictures, lymphadenomegaly, as well as to allow visualization of the fecal color and consistency.
Also Check: Is Okra Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms Of Colitis In Dogs
Signs of colitis in dogs include:
-
Urgency in needing to go to the bathroom
-
Soft or liquid stool
-
Straining or pain with defecation
-
More frequent bowel movements of smaller volume
-
Stool containing blood or mucus
Dog colitis symptoms will also vary depending on whether your dog has chronic or acute colitis.
Symptoms Of Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis In Dogs
- Frequent straining and prolonged motions to pass feces but with limited results
- Diarrhea that is bloody and contains mucous throughout the sample
- Increasing need to defecate
- Soft unformed feces that are not normal
- Pain when passing stool
- Weight loss in later stages of the disease
- Lack of appetite
- Passing of gas
Types
- Although it primarily affects young Boxers it has also been reported in French Bulldogs, Alaskan Malamutes, English Bulldogs and Doberman Pinschers
- Colitis is a related disease and has similar symptoms but is a lot milder and easier to treat with diet
- The resultant diarrhea causes other problems such as redness and irritation around the anus
- The cause is unknown but a possible cause could be from a genetic basis
- Inflammation causing ulceration in the intestines is the result of the disease
- Intestinal cramping of the lower intestine causes discomfort for your dog
Recommended Reading: Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses Treatment
How Is Colitis Treated
The specific cause of colitis will dictate the appropriate treatment. Non-specific treatment includes fasting for 24 to 48 hours, feeding a low residue or hypoallergenic diet, increasing dietary fiber content, and adding fermentable fiber such as psyllium, beet pulp, or fructooligosaccharides to the food. Some dogs with colitis will do better on low-fiber diets. See the handout “Nutrition for Dogs with Colitis” for more information on the role of diet and nutrition for dogs diagnosed with colitis.
Antimicrobial drugs may be indicated, depending on your dog’s diagnosis. Anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive drugs may be used in cases of inflammatory or immune-mediated colitis. Drugs that modify the colon’s motility may also provide symptomatic relief.
Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis In Dogs
Ulcerative colitis in dogs affects the large intestines and is often associated with inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel disorder. With this condition, there is a malfunction of the immune system in which histiocytes penetrate the intestines of your dog.
Bulldogs and boxer breeds are prone to this condition and it is suspected to be as a result of a defect in the immunity system. Histiocytic ulcerative colitis is characterized by ulcers in addition to inflammation of the colon. It is mostly treated and managed through strict dietary schedules.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Stomach Ulcers At Home
What Is Colitis In Dogs
Colitis is a general term that refers to inflammation of a dogs colon, also known as the large intestine.
The colon is the last part of the gastrointestinal system, following the small intestine.
The colon also absorbs water, so when its inflamed and its cells arent functioning well, water isnt absorbed properly, and it is expelled as diarrhea.
Treatment Of Patients With Severe Ple

PLE is a recognized complication in a subset of chronic enteropathy cases, and hypoalbuminemia has been shown to be a poor prognostic indicator.33,38 Patients with albumin concentrations < 1.5 g/dL are at risk of developing ascites, pleural effusion, and subcutaneous edema. Many of these patients succumb to PLE within the first 1 to 2 months of starting prednisone treatment. Some studies have shown a better outcome with single-therapy cyclosporine,55 making it a better option for many of these patients. One recent study has shown that the combination of prednisolone and chlorambucil was superior to prednisolone and azathioprine for survival.56
Evaluation of hemostatic function in these patients is recommended to ascertain if hypercoagulability has developed as a consequence of enteric protein loss.57 Concurrent therapy with ultra-low aspirin 0.5 mg/kg PO every 24 hours or other platelet inhibitors, such as clopidogrel, is recommended in these patients to prevent thromboembolism.
Finally, these patients may be at risk of complications associated with intestinal biopsy by laparotomy. Therefore, plasma transfusion, human or canine albumin infusion, or synthetic colloid may be indicated during anesthesia for endoscopy.
Don’t Miss: How To Check A Horse For Ulcers
Mucosal Immune System And Immune Responses
The mucosal immune system, immune tolerance, and other innate and adaptive immune processes also play roles in the development of chronic inflammation of the GI tract.
Immunoglobulin A , important in the mucosal defense system, provides a barrier to keep luminal bacteria from crossing the luminal epithelial cells. Loosely and tightly adherent mucus produced by goblet cells and tight junctions between luminal epithelial cells also provide an immediate barrier. Any irregularity in these barriers can lead to the transposition of GI pathogens and commensals and result in chronic inflammation.
The focus of inflammation can exacerbate the degradation of tight junctions. T helper 1 cells and complementary T cell subsets are involved in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, whereas T regulatory cells antagonize proinflammatory states for appropriate homeostasis of the gut adaptive immune system. In IBD, this balance is lost.29
Intensive and hyperresponsive states of inflammation result from aggressive T-cell responses to antigens and pathogens with upregulation of inflammatory mediators, as well as defects in microbial extermination and downregulation of inflammatory control mediators.13,23