Questions To Ask Your Health Care Provider
- How often do I need to see a gastroenterologist?
- How often do I need to undergo testing?
- What are my risks for colon cancer?
- Are there symptoms that should cause worry? If so, what are they?
If you dont know something at any point, ask for more information! For some, hearing that they have ulcerative colitis is a relief, a reason for symptoms and a light at the end of the tunnel. For others, it can be scary and daunting. Many will have a mix of feelings.All of this is completely normal.
Recommended Reading: What Treatment For A Stomach Ulcer
Daisys Story: Tips For Others
- Stay informed: Online resources from reputable sources can help a person understand ulcerative colitis better. It can help them prepare for test and appointments and may give them ideas of important questions to ask a doctor.
- Be open: Maintaining an honest and open line of communication with a doctor can speed up the diagnostic process. Do not dismiss the idea of lifestyle changes, which can make an enormous difference to symptoms, but be sure to follow the treatment advice doctors have given. Equally, make sure to tell a doctor in detail if a treatment does not seem to be working.
- Feel empowered: People should remember that their health condition does not define them. Some people find discussing bowel habits and colonoscopies embarrassing, and I definitely relate to that. However, it is important to remember that these are natural bodily processes and tests, and being open and honest can make a huge difference in managing symptoms successfully. It is important to make an invisible condition visible in this way.
- Stay mindful: Stress has always been a trigger for my symptoms, and the diagnosis process alone can be stressful. Try to make mindful activities part of the daily routine. This can help people learn to manage symptoms even after a flare-up has passed.
- Seek support: Several great support groups exist for people with ulcerative colitis. It can be helpful to know you are not alone and to learn more about current research and topics within this community.
Transmural Healing Role Of Mri Ct And Ius
There is no reference standard for CD activity, and any kind of diagnostic modality can only be used as a surrogate marker in this situation. CD is a transmural process thus full-thickness bowel healing or remodelling could be important endpoints.
Various studies have assessed the value of cross-sectional imaging techniques for therapeutic monitoring in CD affecting the small and large bowel. These studies assessed IUS, CT, or MRI.
The value of CT was assessed in a retrospective North American study on 63 infliximab-treated patients with CD. Of 105 lesions, 21 were colonic. Poor-to-fair correlation was found between CT enterography features of response and improved clinical symptoms , improved endoscopic appearance , and reduction of CRP . When comparing responders with non-responders, only the presence of the comb sign on the index CT enterography was predictive of radiological response . Even though CT in principle might be a suitable method to determine disease activity in CD, it should be noted that CT, due to radiation safety, should not usually be used for monitoring disease activity if MRI or IUS is available.
In a systematic review and analysis to identify MRE variables used to describe inflammation and damage wall enhancement, mucosal lesions and wall T2 hyperintensity were the most consistently useful for inflammation .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Cure Mouth Ulcers
What Are Common Tests For Ulcerative Colitis
Blood Tests
Even though blood tests alone cant diagnose ulcerative colitis, theyre an important tool in diagnosis and monitoring of the disease. These are only some of the blood tests used for UC. There are others your doctor may recommend.
These are used to detect infection, anemia , indicators of inflammation, and to identify deficiencies of vitamins or minerals.
Samples of stool may be tested for pathogenic bacteria and certain markers of inflammation. Your doctor will give you a container for collecting and storing the stool.
Imaging Tests
These are tests that take pictures of different parts of your body to provide a clearer view of your condition. They show your doctor areas of disease activity and possible complications. These are only some of the imaging tests used for UC. There are others your doctor may recommend.
A standard X-ray of your abdominal area can show narrowing, widening, or development of a perforation of the intestines or an intestinal blockagepossibly from inflammation or scarring. It may also be done to rule out certain UC complications.
This diagnostic test allows your doctor to evaluate your intestine by tracking the movement of a thick, chalky liquid called barium. The barium dye coats the lining of the bowelcreating a silhouette of your rectum, colon, and a portion of your intestine thats visible on an X-ray.
Biomarker Tests
Ways Biomarkers Can Help With UC Monitoring
Can Blood Test Detect Amoebiasis
An amoebiasis test is a blood test conducted to determine the level of parasitic infection of the intestines caused by entamoeba histolyca.
How is intestinal amoebiasis is diagnosed in lab?
What is amoebic colitis?
Amoebic colitis. Dr Rohit Sharma and Dr Hom Prasad Pant et al. Amoebic colitis is a type of infectious colitis, more common in tropical and subtropical areas. The causative agent is the trophozoite form of the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. In most cases of transmission, the cyst form lives in the colon as commensal and remains asymptomatic.
Don’t Miss: What Helps Ulcers In Your Mouth
Immunomodulators In The Treatment Of Cmv Colitis
The continued use of immunomodulators, including corticosteroids, thiopurines, and biologics, during antiviral therapy for CMV remains controversial. The European guideline recommends that cessation of all immunomodulatory therapies, including steroids, should be considered until the CMV colitis symptoms are controlled, and that no immunomodulator should be prescribed for patients with systemic CMV disease . However, the evidence level for these recommendations is 5 . Ciccocioppo suggested that steroids should be quickly tapered and discontinued, but immunosuppressants and biological agents with long-lasting effects should be maintained in patients with viral colitis and those exhibiting reactivation of latent infection . On the other hand, it has been suggested that any already initiated IBD treatment should be continued during antiviral therapy for CMV colitis . Sager et al. proposed that conventional corticosteroid therapy should be combined with antiviral therapy, and medical rescue therapy using immunosuppressants should be prescribed when necessary. Therefore, additional studies are required to explore the effects of immunomodulators employed to treat UC complicated by CMV colitis.
Several studies have shown that ganciclovir is essential for patients with steroid-refractory or -dependent UC and histologically high-grade CMV infections. Concomitant anti-TNF therapy to treat the UC may also be appropriate .
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Diagnosed
Ulcerative colitis has symptoms similar to many other digestive conditions, which can make diagnosis challenging. Because treatment is needed to induce remission and to prevent the disease from worsening, getting an accurate and timely diagnosis is important.
Gastroenterologists may use a variety of tests in order to understand whats going on with a patient who is suspected of having ulcerative colitis, but it is typically a colonoscopy with biopsies that is used to make the diagnosis.
Also Check: Wound Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The Causal Role Of Antioxidants Minerals And Vitamins In Uc
Genetically predicted higher lycopene levels were associated with reduced risk of UC in IIBDGC, and the associations were directionally consistent in UK Biobank . For a 1 μg/dl increase in the genetically predicted lycopene levels, the combined OR of UC was 0.91 . Higher genetically predicted phosphorus, zinc and selenium levels were statistically associated with a decreased risk of UC, whereas genetically predicted calcium and magnesium levels were positively associated with the disease . The combined ORs per 1-SD increase in genetically predicted circulating levels of these minerals were 0.69 for phosphorus, 0.91 for selenium, 1.46 for calcium and 1.24 for magnesium. Genetically predicted folate and vitamin E levels were inversely associated with risk of UC in the meta-analyses .
FIGURE 3
Results from the sensitivity analyses were generally consistent with the primary analysis, though they did not always reach a significant level. Associations between SNPs on magnesium and risk of UC showed evidence of heterogeneity in IIBDGC, and the direction of the association did not alter after removing one outlier in MR-PRESSO analysis .
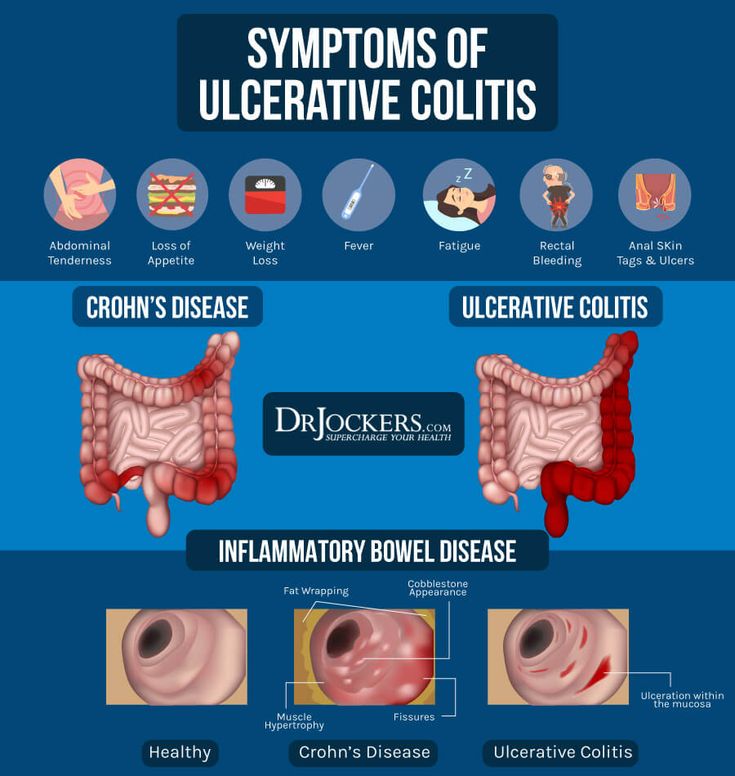
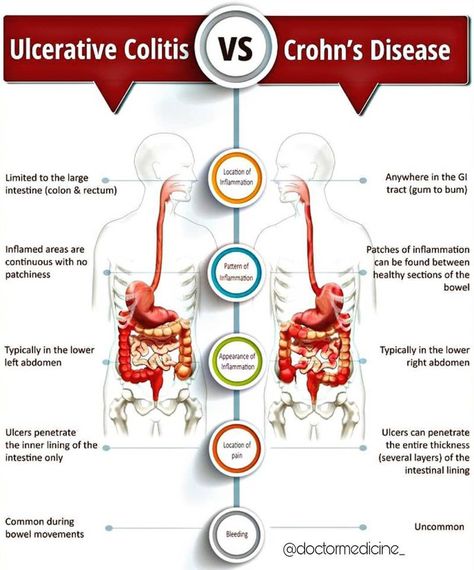
Diagnosing Ulcerative Colitis In Children
At Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital at NYU Langone, doctors in the Pediatric Gastroenterology Program diagnose ulcerative colitis in children. In this form of inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, the lining of the colon, or large intestine, becomes chronically inflamed. This condition can occur in any part of the colon.
Signs and symptoms include bloody stools, abdominal pain, ulcers in the colon, diarrhea, and weight loss. Without treatment, symptoms can worsen over time. Children with ulcerative colitis often experience flare-ups between periods of remission, which is an absence of symptoms.
The causes of ulcerative colitis in children arent fully understood, but genetics, environment, and an autoimmune response are all thought to play a role.
Ulcerative colitis is not the same as irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS. In IBS, a collection of symptoms occurs together. These may include abdominal cramping, constipation, and diarrhea. Unlike with inflammatory bowel disease, IBS does not lead to inflammation that damages the gastrointestinal tract.
Another form of IBD is Crohns disease, which mainly affects the small intestine and colon but can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. The symptoms of these two types of IBD can be similar. For this reason, our doctors perform a physical exam and extensive testing when diagnosing ulcerative colitis in children.
You May Like: What Are The Warning Signs Of Ulcerative Colitis
How Long Will My Microscopic Colitis Flare Up Last
Its different for everyone, but flare-ups typically last for days to weeks. Many people find that they can reduce the length and severity of their flare ups by avoiding certain triggers, such as specific foods or chemicals, and medicating when necessary. Talk to your healthcare provider when your colitis is flaring.
Complementary Treatments And Therapies
You may consider these approaches in addition to what your doctor prescribes. But itâs important to talk to your medical team about any and all of them because some, like supplements, can interfere with treatments from your doctor. Letâs take a look at a few:
Mind-body therapies:Stress and anxiety are well-known triggers for many people with ulcerative colitis, so it is not surprising that mind-body relaxation techniques could help. These techniques help nurture a healthy connection between your mind and body as well as between you and the outside world. In some cases, they encourage behavior changes in your everyday life. They may be worthwhile if only to lessen anxiety and depression linked to UC and improve quality of life. In addition, there is some evidence that yoga, meditation, and gut-centered hypnotherapy could help with some physical symptoms or flare-ups of UC. Some of the techniques, like cognitive behavioral therapy and patient support groups, have been so successful that they have slowly become a part of mainstream treatment for IBD.
Keep in mind that the FDA doesn’t regulate supplements, so claims on packaging may not be accurate. Thatâs yet another reason why itâs important to talk to your doctor before you start taking any supplements for your UC.
Read Also: What Is Crohn And Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Amoebic Colitis Diagnosed
Colonoscopy may be helpful in the diagnosis of amebic colitis if antigen detection tests are negative. Colonoscopy is preferable to sigmoidoscopy for the diagnosis of amebic colitis because disease may be localized to the cecum or ascending colon.
What is amebic colitis?
Amoebic colitis is the most frequent clinical manifestation of invasive intestinal infection due to Entamoeba histolytica and a common cause of diarrhoea worldwide.
Is amoebic colitis and amoebic dysentery same?
Fulminant amebic colitis is a rare complication of amebic dysentery . It presents with the rapid onset of severe bloody diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, and evidence of peritonitis and fever.
Mri Scans And Mr Enterography
An MRI scan uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create two- and three-dimensional images of the body. MRI scans are especially helpful when doctors need to visualize soft tissues, such as the lining of the intestines. They may reveal small tears or ulcers, as well as irritation or bleeding.
To get a better look at the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor may ask you to drink a contrast agent just before the MRI. This is called MR enterography.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Yogurt Is Good For Ulcers
What Is Microscopic Colitis
Microscopic colitis is one of the lesser-known types of inflammatory bowel disease . These are chronic conditions of inflammation inside your bowels . Colitis means inflammation of your colon specifically, the inner lining. Many things can cause temporary colitis, but MC causes it on an ongoing basis. Its called microscopic because it can only be seen under a microscope.
If you have microscopic colitis, the cells in your intestinal lining are irritated. The result is most commonly frequent, watery diarrhea. As with all chronic conditions, microscopic colitis may come and go. It may flare up in reaction to certain triggers, then subside on its own, and then return. While it’s a lifelong condition, it’s usually manageable with medical treatments.
Reasons To Be Open And Honest With Your Doctor
Having a good relationship with the right specialist for your UC can help you both have a clear idea of what is going on with your body and how to manage it.
Your doctor relies on what you tell him or her to get the full picture of how your disease is affecting your life. Use resources like the Doctor Discussion Guide to help make appointments go a little more seamlessly.
When you and your doctor have a good sense of whats going on with your UC, youll be able to confidently move toward a treatment plan thats right for you.
Learn about treatment options for ulcerative colitis.
Recommended Reading: Align Probiotic For Ulcerative Colitis
Also Check: How Can You Tell If You Have An Ulcer
How Is Microscopic Colitis Treated
Treatment can vary depending on your symptoms and how severe they are. They range from dietary and lifestyle changes to over-the-counter and prescription medications. For some people, symptoms flare up and then go away on their own. Some people are able to manage their symptoms well with dietary changes alone, while others may need to use medication intermittently or more frequently.
Common medications include:
- Bulking agents, such as psyllium, to make your poop more solid and slow down its transit time.
- Anti-diarrheals that slow down your bowel contractions, such as loperamide or diphenoxylate.
- Bismuth Subsalicylate for diarrhea, acid reflux, nausea and indigestion.
- Budesonide, a corticosteroid thats absorbed in your colon, where it reduces inflammation.
- Mesalamine, a medication designed to treat ulcerative colitis, for inflammation and pain.
- Bile acid sequestrants , if you have bile acid malabsorption.
If you don’t respond to the above medications, and if your doctor believes there is an autoimmune factor involved, they might suggest additional medications to target your immune response, such as:
Additional recommendations from your doctor may include:
- Adjusting your preexisting medications.
- Identifying your specific food intolerances.
Taking A Look At Your Gut
Crohns and Colitis cause painful sores and inflammation in your gut. Your doctor will need to take a look directly at your gut to check if you have these ulcers. This is done by an endoscopy.
In an endoscopy, a doctor or specialist endoscopist uses an endoscope a long, thin tube with a camera in its tip to examine your digestive system. There are several types of endoscopy which can have different names according to the part of the gut being examined. The main types are:
Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
This type of endoscopy goes through your mouth, and is used to examine the upper part of the digestive system the oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum . You may have this procedure if youre experiencing symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy goes through your bum to look at the whole of the large intestine, including rectum and colon.
Sigmoidoscopy
This is similar to colonoscopy but only examines the rectum and lower part of the colon.
If you have any worries about your endoscopy, discuss them in advance a with your healthcare professional. Endoscopies may be uncomfortable, so you may be offered a sedative to help you relax, but they are normally not painful. Biopsies are often taken during an endoscopy. These can then be examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Information from NHS Digital, licenced under the current version of the Open Government Licence.
You May Like: Is Colitis And Ulcerative Colitis The Same Thing
Ulcerative Colitis And Colorectal Cancer
Ulcerative colitis increases the risk of colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer often begins as small growths on the inside of the large intestine. The risk of colorectal cancer increases based on:
- the length of time a person has had ulcerative colitis
- how much of the colon is affected by ulcerative colitis
People with ulcerative colitis should have more frequent tests for polyps and colorectal cancer than people at average risk. The gold standard screening test is a colonoscopy. Polyps can be removed during a colonoscopy. This reduces the risk of colorectal cancer. Ask your doctor how often you should be checked for colorectal cancer.
Surgery to remove the entire colon eliminates the risk of colon cancer.
Getting Referred To A Gastroenterology Team
If your blood and stool tests show inflammation, you should be referred by your GP to a defined specialist gastroenterology doctor in an IBD service. They have expert knowledge of gut conditions like Crohns and Colitis, and can do specialist tests like endoscopies . In some areas, you may be able to have some choice over which hospital you go to if you have been referred through the NHS e-Referral Service.
It may take some time to get an appointment with your gastroenterology team. The IBD Standards state that you should have a specialist assessment within four weeks of being referred, but it may sometimes take longer. Your GP should let you know how long you can expect to wait contact your GP surgery if you havent heard from the hospital within that timeframe so that they can chase up for you. You can also talk to your GP about how best to manage your symptoms while you wait for an appointment, and what to do if you start to feel worse.
Read Also: Foods Not To Eat With Stomach Ulcer
Also Check: Best Prebiotic For Ulcerative Colitis