Complications Outside The Bowel
Colitis doesnt just affect the bowel. As many as 1 in 5 people with Colitis develop problems in other parts of the body. Most affected are joints, eyes or skin. These are known as extraintestinal manifestations . They usually happen during a flare-up, but can occur without or before any bowel symptoms. These complications can often happen to people who dont have Colitis too. For many of the complications, there are things you can do to reduce your risk.
Joints
You may have pain and/or swelling in your joints. Around 1 in 6 people with Colitis experiences joint problems. For some, this will get worse during a flare, but will usually improve with treatment for Colitis. Others may have joint problems even when bowel symptoms feel better. Find out more in Joints.
Bones
People with Colitis are more at risk of developing thinner and weaker bones or osteoporosis. This can be due to ongoing inflammation, smoking, taking steroids or low levels of physical activity. Calcium is needed for bone formation, and this may be low if your diet doesnt contain enough dairy. Weight-bearing exercise, calcium and vitamin D supplements, not smoking and avoiding long-term steroid use can help. Some people may also take bisphosphonate medicines. Find out more in our information on Bones.
Skin
Colitis can affect the skin in different parts of the body.
Eyes
Anemia
Anaemia can make you feel very tired. If its more severe you may also have shortness of breath, headaches, and general weakness.
Liver
Diet And Lifestyle Changes
Although diet and stress do not cause ulcerative colitis, there may be times when changes in your lifestyle may help control your symptoms and lengthen the time between flare-ups. The following changes may help to ease your symptoms:
- Limit milk/dairy products. If you are lactose intolerant , milk and dairy products can produce symptoms of excess gas and diarrhea.
- Restrict intake of certain high-fibre foods: such as nuts, seeds, and raw vegetables.
- Limit intake of caffeine, alcohol, carbonated drinks and fatty foods. .
- Eat small, frequent meals, rather than large meals..
- Exercise regularly to promote movement of the colon and reduce stress..
- Minimize stress. Yoga, meditation and slow, relaxed breathing techniques can help people with ulcerative colitis manage stress..
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if one of these formulations may be right for you. It is important to take the probiotic in the dose and duration recommended by the manufacturer to achieve the best results.
Study Design And Inclusion Criteria
This is a cross-sectional study and includes all patients18years old with a primary diagnosis of acute diverticulitis in 2014. The ICD-9 CM codes used were 56211, 56201, 56213, and 56203. The database was then queried to include all patients with prior diagnosis of CD or UC . Patients included in the study were required to have a primary diagnosis of acute diverticulitis with a prior diagnosis of either UC or CD. Primary study outcomes included mortality, cost of hospitalization, and length of stay for diverticulitis with either UC or CD. A second comparison was made between those with CD and those without IBD. Various patient demographics , comorbidities, and hospital characteristics were obtained. The severity of the co-morbidities was analyzed via the Deyo modification of the Charlson comorbidity index . This index measures 17 common medical conditions and assigns different weights to compile a score from 0 to 33, which correlates with overall severity of illness.
You May Like: Can Stress Give You An Ulcer
Back Pain Often Comes Directly From Back Or Spinal Structures But Sometimes Its A Sign Of A Medical Condition Elsewhere In Your Body Heres What Else Could Be Causing Your Back Pain
Heres a scene that plays out every day, all over the world: Someone thinks they have a little back strain. Perhaps they lifted something wrong or moved the wrong way. It was just a twinge, so they waited it out a few days for the pain to go away. It doesnt, so they head to their doctor. Turns out, they hadnt lifted anything wrong at all. It was the start of a kidney infection, or a UTI, or pancreatitis.
Heres how to tell the difference between a back strain and something more serious going on.
How do you know when the root cause of back pain is elsewhere in your body? There are two types of pain we look at, explains Matthew Crooks, MD, a pain specialist at Pinnacle Pain and Spine in Scottsdale, Arizona: visceral pain and somatic pain. Visceral pain is pain from an organ or internal pain that can radiate to the spine with conditions like pancreatitis, ulcerative colitis or Crohns disease, gall stones, cancers, kidney pain, and urinary tract infection, says Dr. Crooks.
Whats more, thanks to aging, injury, or a sedentary lifestyle, almost everyone has some wear and tear in the spine and pain in the musculoskeletal system . When you do develop visceral pain, it can flare up your somatic pain. And thats separate from the pain thats radiating from an organ, says Dr. Crooks. It can be activated from overall inflammation and the stress of the body dealing with the medical issue. Its the BOGO special that you never want.
Donât Miss: Succeed For Horses With Ulcers
What Causes Diverticular Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis
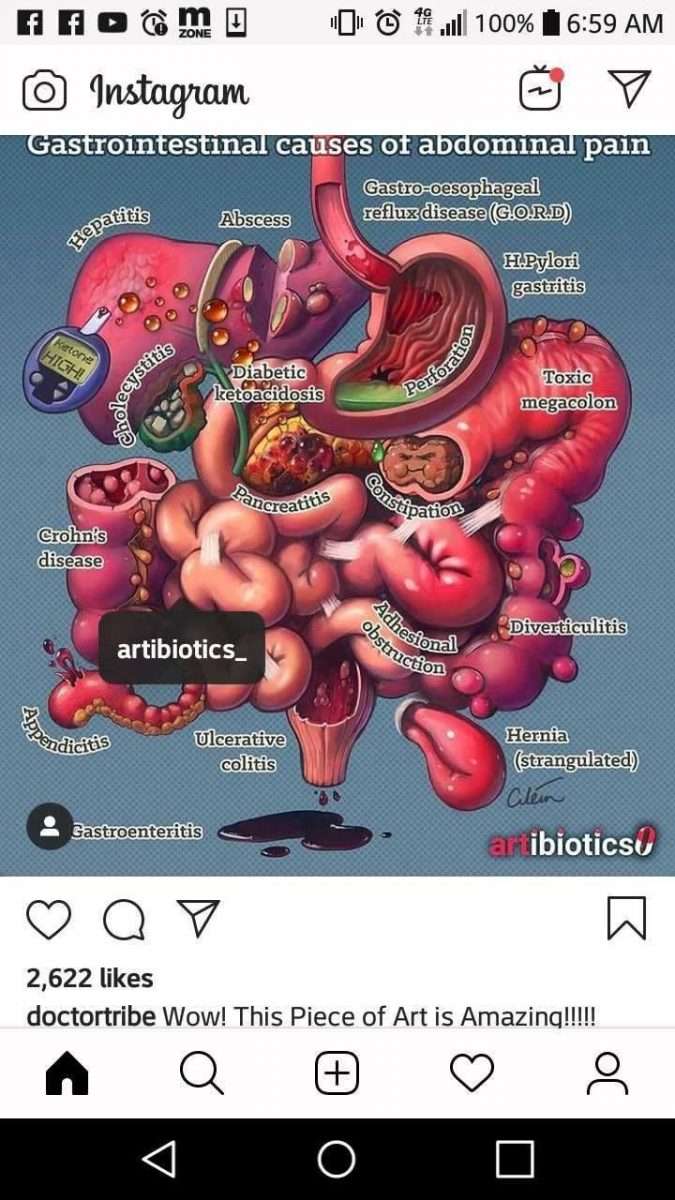
Causes of Diverticular Disease
Diverticulosis is thought to be caused by increased pressure on the intestinal wall from inside the intestine.
- As the body ages, the outer layer of the intestinal wall thickens. This causes the open space inside the intestine to narrow. Stool moves more slowly through the colon, increasing the pressure.
- Hard stools, such as those produced by a diet low in fiber or slower stool “transit time” through the colon can further increase the pressure.
- Frequent, repeated straining during bowel movements also increases the pressure and contributes to the formation of diverticula.
Diverticulosis in developed countries is blamed largely on a diet low in fiber.
- Fiber is found in fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and legumes .
- There are two types of fiber soluble and insoluble.
- Soluble fiber forms a soft gel-like substance in the digestive tract.
- Insoluble fiber passes through the digestive tract nearly unchanged.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The cause of ulcerative colitis is uncertain. Researchers believe that the body’s immune system reacts to a virus or bacteria, causing ongoing inflammation in the intestinal wall. Although UC is considered to be a problem with the immune system, some researchers believe that the immune reaction may be the result, not the cause, of ulcerative colitis.
You May Like: What Is Peptic Ulcer Disease
Recognizing Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Also known as fulminant colitis, this complication affects less than 10 percent of people with ulcerative colitis and involves damage to the entire thickness of the intestinal wall, according to the Crohns and Colitis Foundation.
In fulminant colitis, the whole lining of the colon becomes inflamed, causing severe symptoms like bloody diarrhea and belly pain. Unless the inflammation is brought under control, patients with fulminant colitis are at risk of developing toxic megacolon, the most severe form of colitis.
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you notice your loved one is having more than six bowel movements per day that include a lot of blood, accompanied by any one of the following: a fast heart rate, a fever, a low temperature, and signs of anemia . These are signs that their ulcerative colitis has become severe, according to the American Gastroenterological Association.
Its essential for acute severe ulcerative colitis to be recognized early and that the patients condition is monitored closely while they receive intravenous corticosteroids, according to a review published in January 2019 in the BMJ Postgraduate Medical Journal. Patients will also need to receive fluids intravenously to replenish electrolytes.
You May Like: Whey Protein And Ulcerative Colitis
What Types Of Surgery Can Treat Ulcerative Colitis
There are different procedures. All are major surgery on your digestive system. Talk with your doctor about which one they recommend for you.
Hemicolectomy. This is an operation that removes part of your colon. There are two types, depending on where your problem area is:
- Right hemicolectomy: Removes the right, or ascending, part of your colon. The surgeon may also take out some other areas, like your appendix and part or all of your middle large intestine. Theyâll connect whatâs left of your colon to your small intestine.
- Left hemicolectomy: Removes the left, or descending, part of your colon. The surgeon will attach the right and middle parts to your rectum. This is the last place your bowel movements pass through on their way out.
Colectomy. This is surgery to remove the entire colon.
Proctocolectomy. This procedure removes both the colon and rectum.
Proctocolectomy is considered the standard treatment when surgery for ulcerative colitis is needed.
If the entire colon is removed, the surgeon may create an opening, or stoma, in the abdominal wall. The tip of the lower small intestine is brought through the stoma. An external bag, or pouch, is attached to the stoma. This is called a permanent ileostomy. Stools pass through this opening and collect in the pouch. The pouch must be worn at all times.
You May Like: Crohnâs Versus Ulcerative Colitis Pathology
Read Also: What Are The First Signs Of A Stomach Ulcer
Support For Ulcerative Colitis
When youre living with a chronic condition like ulcerative colitis, its important to get support from other people who understand your journey. At MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam, over 2,000 people have undergone a colectomy, and many have shared their experiences.
Are you or your doctor considering a colectomy for your ulcerative colitis? Join the conversation at MyCrohnsAndColitisTeam to share your own worries, experiences, and advice.
Uc And Your Mental Health
It almost goes without saying that UC can have a major impact on your mental health. The mind-gut connection is real, meaning that everyday stress can manifest in digestive symptoms. Of course, this relationship goes both ways, too: Stress can cause GI symptoms that can cause stress you get the idea.
Whats more is that research, like this study in the Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, shows that people with IBD are at increased risk of developing symptoms like anxiety and depression, and sometimes full-blown depressive or anxiety disorders.
Its no wonderliving with a condition like UC thats shrouded in stigma can be isolating, and the fear of symptoms flaring up unexpectedly is often anxiety-provoking and stressful. When your symptoms can interfere with your ability to go to work, go to school, or even just hang out with friends and family, it can take a serious toll on your mental health.
Building a strong support system of friends, family, and your health care team is important to remove some of that emotional burden. Working with a therapist is also a valuable optionthey can teach you techniques to reduce your anxiety, transform your mindset, and more.
Also Check: What To Eat When You Have A Stomach Ulcer
Main Differences Between Colitis And Diverticulitis
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Also Check: Peptic Ulcer Vs Gastric Ulcer
Diverticulitis & Colitis Diet
Fact Checked
Diet is an important part of the management of diverticulitis or colitis 1. In diverticular disease, small pockets or pouches form in the wall of the colon when these pouches get inflamed, the condition is called diverticulitis. Colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine this can be caused by irritable bowel disease, an inflammatory bowel disease like Crohns, or infections. When you have either of these conditions, you have to make some changes in your diet during the flare-ups to aid in your recovery.
How Are Causes And Risk Factors The Same And Different
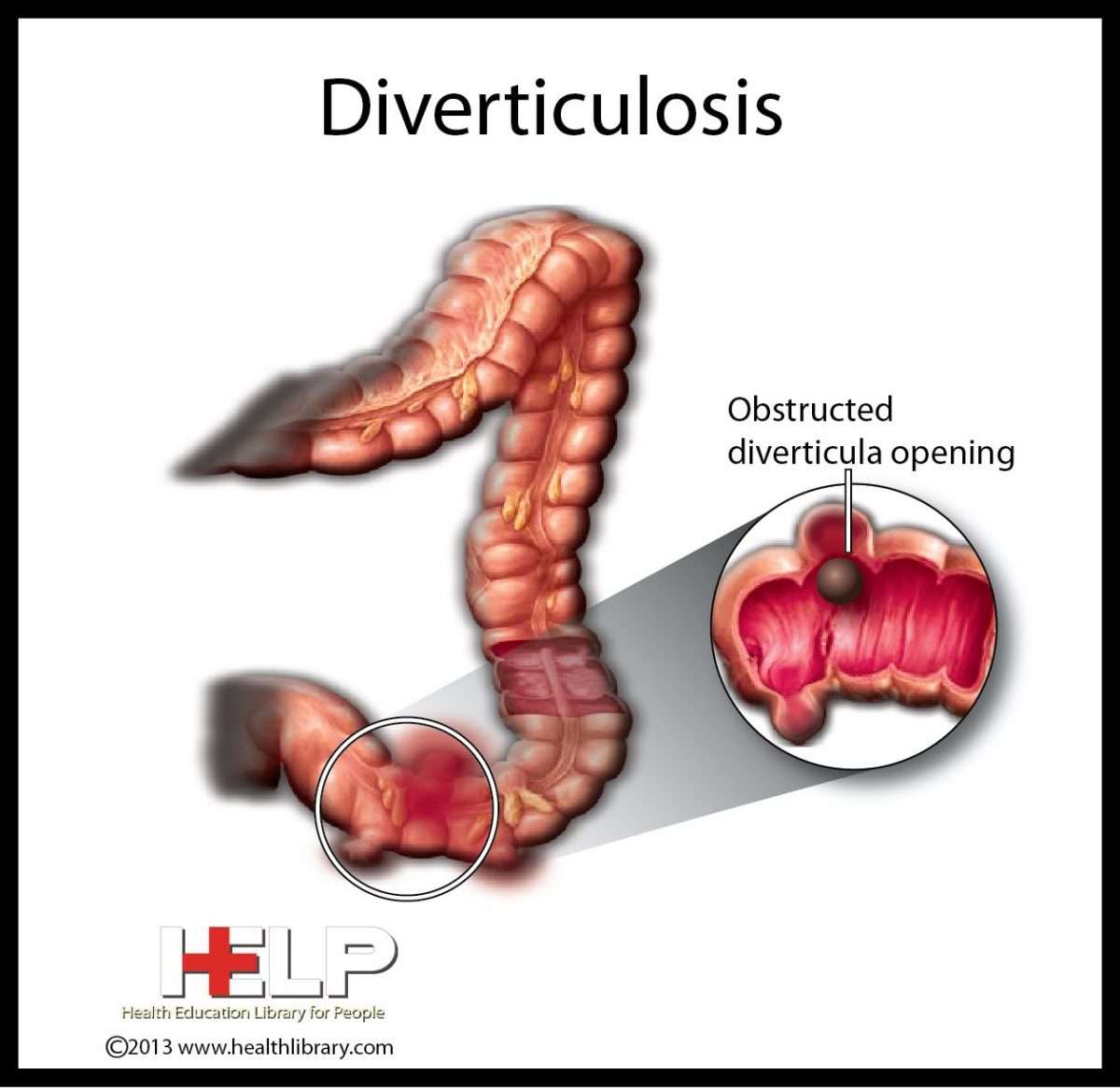
Doctors arenât sure what causes you to get UC or diverticulitis, but the two conditions have some common risk factors:
- Age. Your odds for either condition go up as you get older.
- Race. White people are more likely than those of any other race to have UC or diverticulitis.
UC might be caused by an abnormal immune response in your body. This means that if your immune system is fighting off a virus or bacteria, it may mistakenly attack cells in your digestive tract, too.
Genes might also play a role. If a close relative like your parent or sibling has UC, youâre more likely to have it, too. If you’re of Ashkenazi Jewish descent , your risk is even higher. Diet and stress donât cause UC, but they may trigger your symptoms and cause flare-ups.
As for what causes diverticulitis, experts believe bacteria found in your poop might get pushed into the bulging sacs as it passes through the colon. This causes the sacs to become infected or inflamed. Another theory is that your poop, especially if youâre constipated, might put a lot of pressure against the colon walls as it passes through. This can cause tears in the sacs and increase your chances of an infection.
Other risk factors for diverticulitis include:
- Diet low in fiber and high in animal fat
- Certain medications
Don’t Miss: Hospital Acquired Pressure Ulcers Reimbursement
Some Doctors May Use The Following Table To Classify Your Symptoms*:
*A patient does not need to have all of these factors to be considered in a specific category of disease
Ulcerative colitis symptoms are considered moderate when you experience between 4-6 stools per day which include a moderate amount of blood. Severe UC is when you experience 6-10 per day with a severe amount of blood when passing.
If youre concerned about any of your symptoms, talk to your doctor immediately.
How would you describe your symptoms?
Do your best to keep track of your symptoms so you can clearly describe them to your doctor. This information is key in helping your doctor determine the right treatment for you.
because of my UC symptoms, I wasnt able to socialize with my friends. Unfortunately I was missing out on a lot of plans.
Sarah, a real UC patient using HUMIRA
Changing your routine because of UC symptoms? Youre not alone. Hear from others who have been there.
Recommended Reading: What Are Infusions For Ulcerative Colitis
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis And What Causes It
Colitis can develop at any age, but usually first appears in people aged 15 to 30.
Experts are not sure why UC or Crohns disease occurs in some people. It may be due to a combination of genetic, environmental and infectious factors that cause a fault in the immune system leading to inflammation of the bowel.
Read Also: How Do You Get Ulcerative Colitis
Diet Management In Ulcerative Colitis
Its important to pay attention to what you eat if you have ulcerative colitis . Foods do not drive the condition, although they can induce flare-ups.
How can you avoid those triggers while still getting the nutrition you require? A nutrition plan can be beneficial in this situation. Here we discuss diet in Ulcerative Colitis, including what foods to eat and what foods to avoid.
How Is Diagnosis The Same And Different
If you think you have either UC or diverticulitis, talk to your doctor about it. You might be referred to a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in digestive issues, for a correct diagnosis.
Your doctor will first do a detailed medical exam. Theyâll ask you about your medical history including things like your diet, your bowel movements, and medications you might be taking.
Common tests to diagnose UC and diverticulitis include:
- Blood tests. This is done to check for infections
- Stool sample test. This checks for bacteria or parasites that might cause your stomach pain, cramps, or diarrhea
- Colonoscopy. The doctor will use a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the tip to explore your entire colon. They may take small tissue samples to test.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy. This is similar to a colonoscopy, except your doctor will only explore your rectum and s-shaped sigmoid colon â both of which are located at the lower end of your colon. This is usually done if you have severe inflammation.
- Barium enema. This test is also called lower gastrointestinal tract radiography. In this test, your doctor injects a liquid containing barium into your butt. The barium coats your entire colon and makes it easier to see clearly under an X-ray scan.
- CT scan. This test allows your doctor to scan your abdomen and pelvic area and spot inflamed areas in your colon. The scan can detect the irritated or inflamed pouches for diverticulitis and confirm the condition.
Also Check: Is Coconut Good For Ulcerative Colitis