Ulcerative Colitis Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Ulcerative Colitis NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Ulcerative colitis is a medical condition that involves the inflammation and ulcer formation in the lining of the colon and rectum.
It is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that can have progressive symptoms over time and could be both debilitating and life-threatening if left uncontrolled.
There is no cure for ulcerative colitis yet, so the treatment is aimed at the reduction of signs and symptoms of this condition, and the prevention of complications.
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis: Care Plan 4 Diagnosis: Ineffective Coping
May be related to:
- Demonstrate necessary lifestyle changes to limit/prevent recurrent episodes.
As you continue, customnursingassignments.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order with us.
Nursing Care Plans for Ulcerative Colitis
Assessment Of Bowel Function
- Stool frequency, consistency, and presence of blood or mucus
- Patients with UC predominantly appear with symptoms of diarrhea mixed with blood and mucus, rectal bleeding, and frequent stools
- Pain associated with passing stools
Read Also: I Think I Have Ulcerative Colitis
Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel Disease 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to abdominal muscle spasms secondary to Inflammatory bowel disease as evidenced by a pain score of 10 out of 10, verbalization of abdominal pain and cramping, guarding sign on the abdomen
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate relief of pain as evidenced by a pain score of 0 out of 10, stable vital signs, and absence of restlessness.
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Interventions | Rationale |
| AnalgesicsVitamins and supplements | |
| Assess the patients vital signs and characteristics of pain at least 30 minutes after administration of medication. | To monitor effectiveness of medical treatment for the relief of heartburn and stomach pain. The time of monitoring of vital signs may depend on the peak time of the drug administered. |
| Teach the patient on how to perform non-pharmacological pain relief methods such as deep breathing, massage, acupressure, biofeedback, distraction, music therapy, and guided imagery. | To reduce stress levels, thereby relieving the symptoms of Inflammatory bowel disease, especially stomach pain and heartburn. |
| Help the patient to select appropriate dietary choices to reduce the intake of milk products, caffeinated drinks, alcohol and high fiber, high fat foods. | To relieve abdominal pain and cramping, alleviate diarrhea, and healthy food habits. |
Other possible nursing diagnoses:
Also Check: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
Causes And Risk Factors Of Ulcerative Colitis
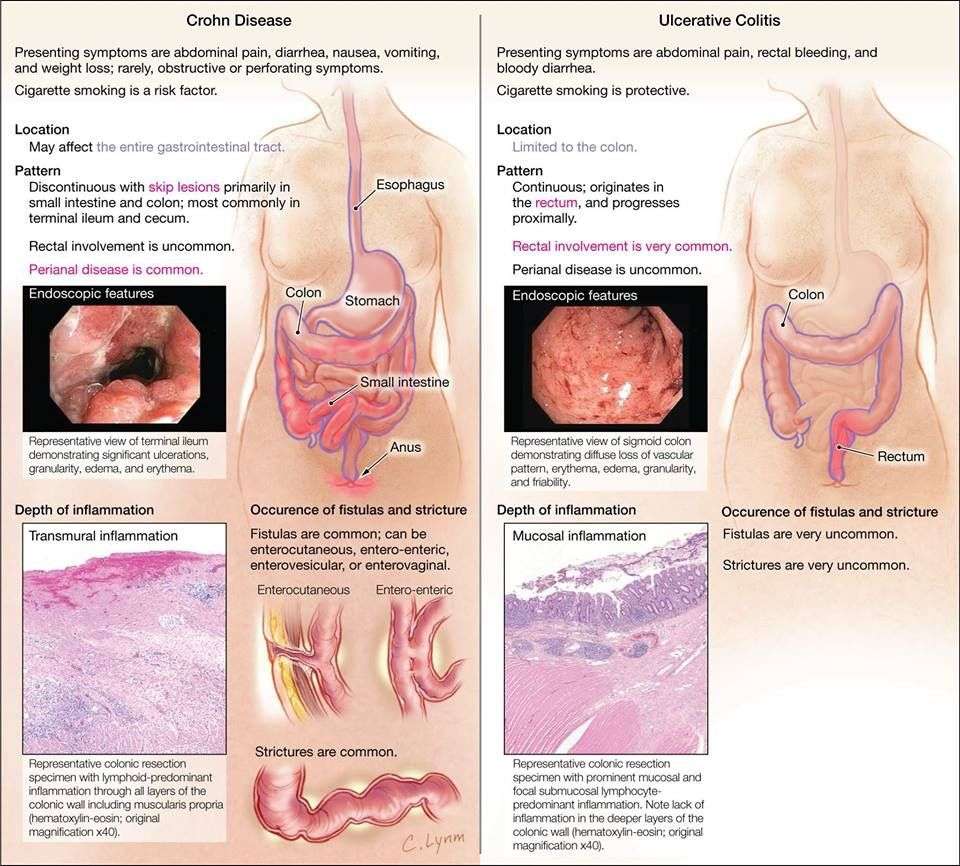
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is still unknown, but there are a few suspected conditions that may aggravate it.
Diet and stress are two risk factors that can make Ulcerative colitis worse, but not necessarily cause it.
Some research studies are focused on the nature of ulcerative colitis being an autoimmune condition.
The immune system is the bodys way to protect itself by attacking foreign bodies like viruses and bacteria.
This process sometimes fails due to certain factors, making the body attack its own cells. Cells in the digestive tract may be mistakenly attacked, causing ulcerative colitis.
Another cause thought to explain ulcerative colitis is heredity. It is noted that family history is apparent in some, but not all, people with ulcerative colitis.
Statistics suggest that ulcerative colitis equally affects men and women. Its risk factors include the following:
Also Check: Is Coconut Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Treat To Target And Overall Severity Scoring
In an effort to move from a reactive, disease activitydriven approach to a proactive treatment approach to improve patient outcomes, 2 major concepts have recently been promoted: treat to target, and overall disease severity scoring.
In 2018, a group of IBD specialists convened to develop an overall severity index for both CD and UC using a modified RAND panel with an adaptive choice-based conjoint processes.72 These methods helped the panelists to identify key variables of IBD disease severity, break these variables into categorical levels, rank them relative to each other, and assign relative point values to each variable.
What Can Happen If I Have Diarrhea
Acute diarrhea is uncomfortable but rarely dangerous in healthy adults and children. However, diarrheal stools may contain viruses and bacteria that spread infections. For example, the bacterium Escherichia coli causes about 9% of all foodborne infections in the United States. If there is severe diarrhea with vomiting, dehydration can occur. This occurs when there is excessive water loss from your body due to diarrhea and/or vomiting. Severe dehydration may be life-threatening.
- Avoid eating contaminated food- If food poisoning is suspected to be a cause of your diarrhea, contact a local health department or call your doctor for instructions.
- Maintain hygiene -Keep hands clean by washing with soap and warm water for 20 seconds.
Follow these steps to prevent dehydration:
1. Drink plenty of water and other liquids. Water is important because your body loses water when you have diarrhea. Fluids that contain electrolytes are also helpful.
2. Avoid coffee and tea while you have diarrhea because they may worsen the problem by irritating the bowel wall, causing pain and inflammation, and increasing fluid loss.
Get the following premium features for free after ordering a custom nursing assignment from us:
Read Also: Foods That Make Ulcerative Colitis Worse
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis happens when the immune system makes a mistake. Normally, it attacks invaders in the body, like the common cold. But when one has UC, the immune system thinks food, good gut bacteria, and the cells that line the colon are the intruders. White blood cells that usually protect the body attack the colons lining instead. They cause inflammation and ulcers.
Doctors arent sure why people get the condition. Genes may play a role the disease sometimes runs in families. Other things in the world around may make a difference too.
As you continue reading remember that our top and qualified writers are here to help with any of your assignment. All you need to do is place an order with us.
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
-
Design strengths included comparing hospitalisations 1year before and 1year after the introduction of an inflammatory bowel disease nurse position.
-
The extraction of patients with IBD with two information systems allowed exhaustiveness.
-
The major limitation was that costs were only attributed to the reduction of hospitalisation.
Read Also: Bland Diet Recipes For Ulcers
You May Like: Feeding Beet Pulp To Horses With Ulcers
Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel Disease 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements related to altered absorption of nutrients secondary to Inflammatory bowel disease, as evidenced by diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to achieve a weight within his/her normal BMI range, demonstrating healthy eating patterns and choices.
Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis
There is a wide array of treatment options for patients with ulcerative colitis.
Treatments usually involve pharmacologic therapy and surgical procedures. Alternative treatments are also widely available.
Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs. These are the first line of treatment for people with ulcerative colitis.
5-Aminosalicylates can be given by mouth or as suppository depending on the affected part of the colon.
On the other hand, corticosteroids are commonly prescribed if other treatments cause no response.
Immune system suppressors. These drugs work by prohibiting inflammatory response through suppressing the immune system.
They usually work better in combination with other drugs.
They usually require regular checking of the liver and pancreatic functions. Cyclosporines, like corticosteroids, are not indicated for long term use due to their side effects.
However, it is also the choice of drug when other treatments fail to work.
Biologics. Also called monoclonal antibodies, these drugs are usually prescribed to people with ulcerative colitis who cannot tolerate other treatments.
They work by stopping proteins in the body from causing inflammation.
Other medications can be used to treat symptoms related to ulcerative colitis. Examples are anti-diarrheal drugs, pain relievers, antispasmodics, and iron supplements.
Surgery
A more sophisticated procedure called ileoanal anastomosis can be done to prevent the patient from needing an external pouch to collect stool.
Also Check: What Can Cause Ulcers In The Intestines
Ulcerative Colitis Nclex Review
This NCLEX review will discuss ulcerative colitis.
As a nursing student, you must be familiar with ulcerative colitis, the pathophysiology, major signs and symptoms, and the nursing care for a patient experiencing this condition.
These type of questions may be found on NCLEX and definitely on nursing lecture exams.
Dont forget to take the ulcerative colitis review quiz.
You will learn the following from this NCLEX review:
- Definition of ulcerative colitis
- Signs and Symptoms of ulcerative colitis
- Nursing Interventions
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
Complications of ulcerative colitis can include:
Bleeding. This can lead to anemia.
Osteoporosis. Patients bones might become weak because of the diet or if they take a lot of corticosteroids.
Dehydration. A patient might need to get fluids through a vein if the large intestine cant absorb enough.
Inflammation. This can affect the joints, skin, or eyes.
Fulminant colitis. If UC attack is severe, the colon might burst, or infection could spread through the body. The intestines stop moving waste, and the belly swells.
Megacolon. Fulminant colitis can cause the large intestine to swell or burst. This is a dangerous complication, and a patient will probably need surgery.
Liver disease. The bile ducts or liver could become inflamed or could get scar tissue.
Colon cancer. Ulcerative colitis puts a patient at higher risk of getting colon cancer, especially if the whole large intestine is affected or if UC persists for a long time.
Don’t Miss: How To Eat With Ulcerative Colitis
You Are Reading A Preview
Activate your 30 day free trial to continue reading.
Image result for ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
Image result for ulcerative colitisUlcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation and ulcers in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
Also Check: Foods To Avoid During Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Caring For The Patient Undergoing Stoma And Ilealanal Pouch Formation
The Advanced IBD Nurse is well placed to support the patient in the peri-operative period by being a source of education and referring to appropriate members of the MDT, particularly the stoma nurse. Psychologists, sexual therapists and country-specific patient organizations can help with information provision and psychological support .
Many patients are understandably distressed at the thought of undergoing either planned or emergency surgery, and the Advanced IBD Nurse plays a key role in coordinating health-care professionals. Patients may undergo a colonic resection without stoma formation, or require further surgery to include restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouchanal anastomosis . The main indication for IPAA is in patients with medically refractory UC,372,373 or dysplasia or cancer developed from underlying UC.
For any complex surgical procedure, the patient is best managed within an MDT including the Stoma Care Nurse. In the event of stoma formation, the Stoma Care Nurse provides essential support and education for the patient and their family prior to surgery, during the hospital stay and following discharge.374
Stoma and IPAA surgery provide numerous benefits, including long-term symptom relief,372,375 although recent evidence suggests that while outcomes are often better than anticipated, some patients require a long time to decide about stoma surgery and find benefit from pre-operative contact with another patient with IBD living well with a stoma.29
Don’t Miss: Good Foods To Eat With Stomach Ulcer
Diagnosing Ulcerative Colitis In Children
At Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital at NYU Langone, doctors in the Pediatric Gastroenterology Program diagnose ulcerative colitis in children. In this form of inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, the lining of the colon, or large intestine, becomes chronically inflamed. This condition can occur in any part of the colon.
Signs and symptoms include bloody stools, abdominal pain, ulcers in the colon, diarrhea, and weight loss. Without treatment, symptoms can worsen over time. Children with ulcerative colitis often experience flare-ups between periods of remission, which is an absence of symptoms.
The causes of ulcerative colitis in children arent fully understood, but genetics, environment, and an autoimmune response are all thought to play a role.
Ulcerative colitis is not the same as irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS. In IBS, a collection of symptoms occurs together. These may include abdominal cramping, constipation, and diarrhea. Unlike with inflammatory bowel disease, IBS does not lead to inflammation that damages the gastrointestinal tract.
Another form of IBD is Crohns disease, which mainly affects the small intestine and colon but can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. The symptoms of these two types of IBD can be similar. For this reason, our doctors perform a physical exam and extensive testing when diagnosing ulcerative colitis in children.
Recommended Reading: Diet For Someone With Stomach Ulcers
The Advanced Ibd Nurses Role In The Planned Review Care And Follow
The Advanced IBD Nurse can conduct regular patient reviews face to face, via telephone or electronically in order to monitor treatments, and arrange appropriate investigations as required, in accordance with local policy or guidance . The limitations of remote contact must be considered and skilled judgement used in knowing when further assessment is required .
Patients with IBD require long-term outpatient follow-up and surveillance. Disease activity often fluctuates over time, requiring maintenance therapy and acute interventions for disease flares. Complex disease management requires a specialized MDT approach that enhances the level of continuous care and improves outcomes. In this dedicated team, a key role for the Advanced IBD Nurse is increasingly being recognized.259 Advanced IBD Nurses are consistent team members who work with patients over a period of time. This continuity is one of the advantages, over other groups of health-care professionals, of Advanced IBD Nurses involvement in follow-up.260,261
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Pressure Ulcers On Heels
How The Intervention Might Work
The cause of the abdominal pain could require a targeted approach.
Pharmacological interventions
Antispasmodics often have mixed mechanisms of action, but generally they tend to suppress intestinal spasms resulting from inflammation or obstruction . Pharmacological interventions may have associated adverse effects. For example, it is widely known that NSAIDs may increase the risk of disease flareup or exacerbation in IBD patients . In addition to offering shortterm relief, there seem to be concerns among IBD sufferers about the stigma of addiction associated with the use of opioids.The use of psychoactive drugs can also lead to heavy dependence on them and a higher risk of mortality . In IBD patients, tapering off narcotics could trigger withdrawal symptoms which mimic IBD symptoms , thus complicating further treatment. Therefore, longterm use for IBD pain relief is not recommended.
Nonpharmacological interventions
Stool Bulking Agents Or Laxatives
Colonic motility is affected by inflammation and rapid transit occurs through the inflamed colon. In left sided disease, distal transit is rapid but proximal transit is slowed, which can result in proximal constipation. Relief of proximal constipation by stool bulking agents or laxatives may help induce remission in proctitis.
Also Check: What To Use For Stomach Ulcer
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
There are different types of ulcerative colitis depending on the affected location:
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
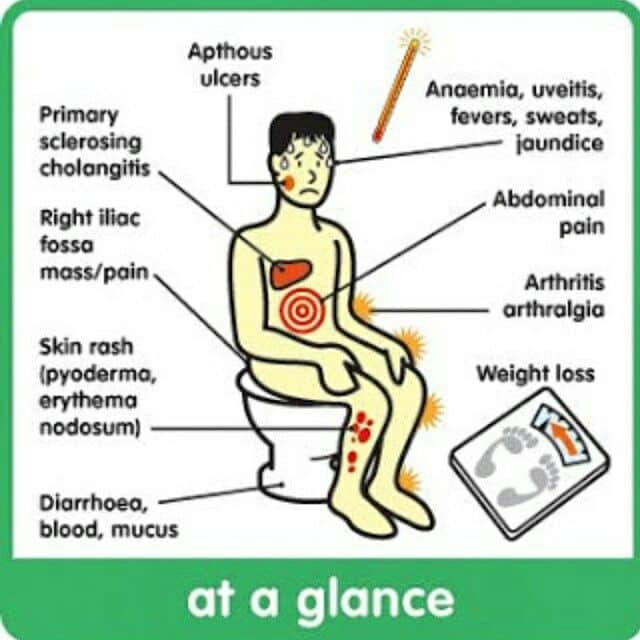
The main symptom of ulcerative colitis is bloody diarrhea. There might be some pus in the stools too.
Other problems include:
- Feeling like you havent completely emptied your colon after using the bathroom.
- Waking up at night to go
- Not being able to hold stool in
- Pain or bleeding with bowel movements
You May Like: Skin Graft Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
A doctor will use tests to tell if a patient has UC instead of another gut disease.
Blood tests can show if a patient has anemia or inflammation.
Stool samples can help the doctor rule out an infection or parasite in the colon. They can also show if theres blood in the stool.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy lets the doctor look at the lower part of the colon. Theyll put a bendable tube into the lower colon through the bottom. The tube has a small light and camera on the end. A doctor might also use a small tool to take a piece of the lining of the lower colon. This is called a biopsy. A doctor in a lab will look at the sample under a microscope.
Colonoscopy is the same process as flexible sigmoidoscopy, only the doctor will look at the whole colon, not just the lower part.
X-rays are less common for diagnosing the disease, but a doctor may want a patient to have one in special cases.