Split Thickness Skin Grafts
Split thickness skin grafting is a technique that has been around for a long time because it works! With a skin graft, the surgeon will take a partial thickness piece of skin and transplant it to the wound bed. This procedure is done in the operating room. There will be a new wound on the thigh that will need to heal. If successful, the skin graft will take and can lead to wound healing in as little as two weeks.
Skin Grafts May Help Heal Diabetic Foot Ulcers And Reduce Amputations
Skin grafts and tissue replacement products can help heal diabetic foot ulcers in some cases, and may also slightly reduce the numbers of future amputations. Foot ulcers are common and can be hard to treat, but failure to heal them carries high risk for amputation and mortality.
This review showed skin grafts or tissue replacement moderately increased the healing rate of the most amenable diabetic foot ulcers in people with diabetes that is, in those who had sufficient blood flow in their feet. Two trials reported slightly fewer amputations in people with diabetes compared to usual care at 12 weeks.
The review identified the most relevant trial evidence available. These trials showed some limitations. For example, most trials were linked with product manufacturers. However, given that the treatments are recognisable to patients and staff, its difficult to eliminate all potential causes of bias.
Currently recommended treatments of wound dressings and foot infection control dont always achieve complete wound healing and are expensive for long term use, so this review added to understanding about better approaches. We still need more information about cost and long-term effectiveness of the treatments.
What Did It Find
- Fourteen trials found that skin grafts and tissue replacement products use in the trials increased the healing rate for people with diabetes by approximately 55% compared to usual care . Complete ulcer healing at 6 to 16 weeks was 423 per 1,000 people using skin grafts or tissue replacement, significantly more than the 273 per 1,000 achieved in standard care. Despite this improvement, fewer than half of all ulcers were healed by 16 weeks.
- Four trials directly comparing skin graft or tissue replacement products with one another found no specific type was more effective than another.
- Two trials looking at the rate of lower limb amputations found around half the rate of amputations in the skin graft or tissue replacement groups compared with usual care . There was imprecision in reporting of amputations rates.
- No trials reported significant differences in adverse events between skin graft or tissue replacement products compared to usual care, based on 16 trials.
- No trials reported on quality of life or compared the cost benefits of skin grafts or tissue replacement compared with usual care.
Also Check: What Medicine Is Best For Stomach Ulcers
Fish Skin Graft Rapidly Heals Diabetic Foot Ulcer Wounds Finds Study
USA: Acellular fish skin graft promotes wound healing in patients with diabetic foot ulcers , finds a recent study published in the journal Wounds. According to the study, DFU patients who received the graft experienced a rapid increase in wound healing during the initial 4 weeks following graft application.
“This review of the literature indicates that skin graft encourages wound healing by enabling the wound transition from chronic to acute stage of healing,” wrote the authors.
According to WHO, the South-East Asia Region is home to 26% of the worlds population with 44% burden of TB incidence. In 2017, an estimated 4.4 million people fell ill with TB and an estimated 638 000 died because of the disease which is more than half of global TB deaths. Six out of the 30 high TB burden countries are in the SEA Region: Bangladesh, Democratic Peoples Republic of Korea, India, Indonesia, Myanmar, and Thailand.
Due to this large patient population, diabetic wounds have become a growing problem and the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers creates a large financial burden in India annually. Therefore, extensive research in the treatment of DFUs is necessary to provide the most beneficial and cost-effective care.
The study involved 51 patients with a total of 58 DFUs treated with an acellular fish skin graft. The initial wound surface area at first application was compared with the final wound surface area to conclude the percentage of total wound healed over a 16-week treatment period.
Skin Grafting And Tissue Replacement Effective For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
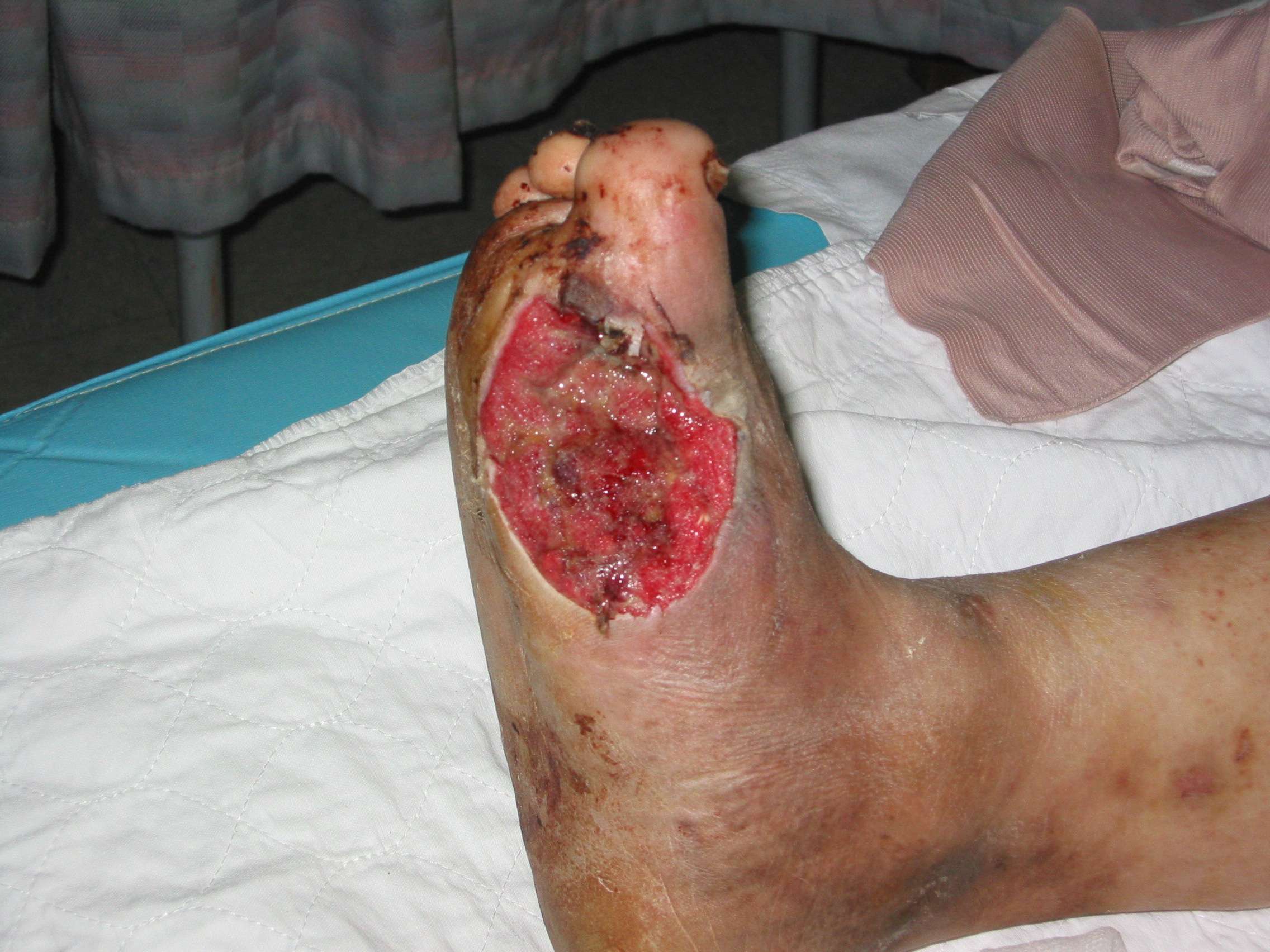
How effective are skin grafting and tissue replacement for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes?
Skin grafts and tissue replacements, used in conjunction with standard care, increased the healing rate of foot ulcers and led to slightly fewer amputations in people with diabetes, compared with standard care. Evidence of long-term effectiveness was lacking and cost-effectiveness was uncertain. There was not enough evidence to be able to recommend a specific type of skin graft or tissue replacement. No differences were found for ulcer recurrence and incidence of infection between groups. There were no differences in the occurrence of adverse events between the intervention and the control group.
For the outcome incidence of complete closure of the ulcer quality of evidence was low, and for total incidence of lower limb amputations quality of evidence was very low. The potential benefits of skin graft and tissue replacements should be weighed against the high costs of these products.
Foot ulceration is a major problem in people with diabetes and is the leading cause of hopitalisation and limb amputations. Skin grafts and tissue replacement can be used to reconstruct skin defects for people with diabetic foot ulcers in addition to providing them with standard care. Skin substitutes can consist of bioengineered or artificial skin, autografts , allografts or xenografts .
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
Outcomes In Chronic Venous Leg Ulcers
CVLUs amount to 70% of all CLUs and consist of excavation located in lower leg skin because of the loss of inflammatory necrotic tissue as a result of insufficient venous blood circulation because of structural abnormalities of the vein draining the legs. These abnormalities can be detected in the superficial veins, the communicating veins or the deep veins and mostly consist of faulty valves unable to ensure forward progression of blood. This alteration leads to an increased venous pressure with progressive dilation of the veins and egress of proteins, such as fibrinogen. The resulting fibrin complexes compromise the microcirculation and cause the phlogosis onset. Finally, cell death and necrotic tissue evolve into venous ulcerations. CVLUs consist of irregular, shallow and painful lesions usually located over bony prominences such as medial malleolus, with granulation tissue and fibrin present in the ulcer base. Other important findings may be oedema, varicosities, hyperpigmentation and lipodermatosclerosis with thickening and fibrosis of the adipose layer under the skin .
Furthermore, Salomè et al. showed how split-thickness skin grafting resulted in better health-related quality of life and self-esteem in patients with venous leg ulcers than did different treatments.
Also Check: What Is Best Medicine For Ulcer
What Does Current Guidance Say On This Issue
NICEs 2015 guidance on Diabetic foot problems: prevention and management recommends that usual care includes one or more of the following treatments: offloading , control of foot infection, control of ischaemia and wound dressings.
It also recommends considering skin grafts or skin substitutes in addition to usual care for diabetic foot ulcers only when healing has not progressed and on the advice of the multidisciplinary foot care service.
Also Check: How Effective Is Humira For Ulcerative Colitis
What To Expect From A Biosynthetic Skin Graft
Bioengineered skin is composed of a dermal layer, an epidermal layer, or a combination of both layers embedded into a cellular or acellular matrix. The matrix is a support structure that is composed of materials such as collagen, hyaluronic acid, and fibronectin.Heres how biosynthetic skin grafts are used to treat foot ulcers:
Healing time for a diabetic ulcer treated with a biosynthetic skin graft depends on factors such as wound size, location, and pressure applied from standing or walking. Healing may occur within a few weeks or require several months of recovery. You can speed up the process by carefully managing your blood glucose levels and following all of your podiatrists wound care recommendations.
In some cases, Dr. Scudday may recommend additional treatment to help prevent additional ulcers from occurring. For example, surgery to correct hammertoes or bunions might be required to keep you from developing another foot ulcer.
What Is A Skin Graft
Skin grafts and tissue replacement can be used to treat foot ulcers in people with diabetes by reconstructing the skin defect. Skin substitutes need to be placed on a prepared wound bed to ensure contact between the wound bed and the graft and they take on the functions of the missing skin layer. Furthermore, diabetic foot wounds are a serious issue that needs immediate treatment. Many diabetics walk around with wounds on their feet that are not getting properly treated. A highly trained Family Foot & Ankle Physician can evaluate and treat these wounds. After making sure there are no underlying issues that are contributing to the wound, we will advise you on how to treat your diabetic foot wound.
The topic of skin grafting will come up as a treatment for diabetic foot ulcers when other means have been exhausted or you are past the point of more conservative treatments.
Typically, larger wounds require a skin graft, which is successful in covering skin defects and allows your wound to heal more effectively. If you have questions about skin grafts and our process, please contact Family Foot & Ankle Physicians to review your conditions and discuss skin graft treatment options.
If you or a loved one has a wound of the foot, ankle or lower leg call us today to see if you are a candidate for this procedure.
Don’t Miss: What Pain Reliever Is Safe For Stomach Ulcer
Management Of Systemic And Local Factors
Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers requires management of a number of systemic and local factors.
Precise diabetic control is, of course, vital, not only in achieving resolution of the current wound, but also in minimizing the risk of recurrence. Management of contributing systemic factors, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerotic heart disease, obesity, or renal insufficiency, is crucial. Management of arterial insufficiency, treatment of infection with appropriate antibiotics, offloading the area of the ulcer, and wound care are also essential.
References
Amin N, Doupis J. Diabetic foot disease: From the evaluation of the foot at risk to the novel diabetic ulcer treatment modalities. World J Diabetes. 2016 Apr 10. 7 :153-64. . .
Naves CC. The Diabetic Foot: A Historical Overview and Gaps in Current Treatment. Adv Wound Care . 2016 May 1. 5 :191-197. . .
Rice JB, Desai U, Cummings AK, Birnbaum HG, Skornicki M, Parsons NB. Burden of diabetic foot ulcers for Medicare and private insurers. Diabetes Care. 2014. 37 :651-8. .
Gentile AT, Berman SS, Reinke KR, Demas CP, Ihnat DH, Hughes JD, et al. A regional pedal ischemia scoring system for decision analysis in patients with heel ulceration. Am J Surg. 1998 Aug. 176:109-14. .
Mills JL Sr, Conte MS, Armstrong DG, et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: risk stratification based on wound, ischemia, and foot infection . J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan. 59 :220-34.e1-2. . .
Treating Your Diabetic Wounds With Stem Cell Grafting
Dr. Rambacher and his team have seen incredible results by combining stem cell therapy with skin grafting to treat diabetic foot ulcers. In this in-office procedure, our doctors use a skin graft made with placental tissue to cover your diabetic wound or ulcer.
Getting this treatment is similar to getting a traditional graft on your ulcer, but it comes with significant additional benefits once our team has placed the graft. Not only do stem cell grafts promote faster, less painful healing, they also help your ulcer regrow new skin as part of the healing process.
The stem cells in the graft help generate new skin and tissues in your body, revitalizing your foot with healthy, new cells. This helps restore your foots health as part of the healing process.
As part of your treatment, our team creates a personalized treatment plan for your diabetic ulcer, including choosing the right stem cells for your ulcer. Our team is always happy to be your guide throughout this cutting-edge procedure, including answering all your questions and ensuring you understand what is happening throughout.
If you keep getting diabetic foot wounds and would like a treatment that is faster, more effective, and less painful, stem cell grafts could be right for you. To learn more, schedule your appointment with our team online or by phone.
You Might Also Enjoy…
Recommended Reading: Humira For Ulcerative Colitis Reviews
Research Design And Methods
We searched the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register , MEDLINE , EMBASE , and CINAHL using a combination of text and keywords in addition to a filter for controlled clinical trials. The last update of searches was performed on 30 September 2007. We included trials if the allocation of participants was described as randomized, with participants of any age and in any care setting having diabetic leg or foot ulceration. We included studies that compared the following types of grafts with any other intervention: 1) autografts , 2) allografts , 3) xerografts, and 4) bioengineered skin.
Two reviewers independently evaluated reports for eligibility and assessed methodological details and results of the studies. Disagreements were resolved by discussion.
The prespecified primary end point was complete healing rate at the end of the trial. Results are presented as odds ratios . We used standard fixed-effects meta-analysis and Cochran’s Q test for heterogeneity . Analyses were performed using Stata .
Skin Grafting And Your Feet
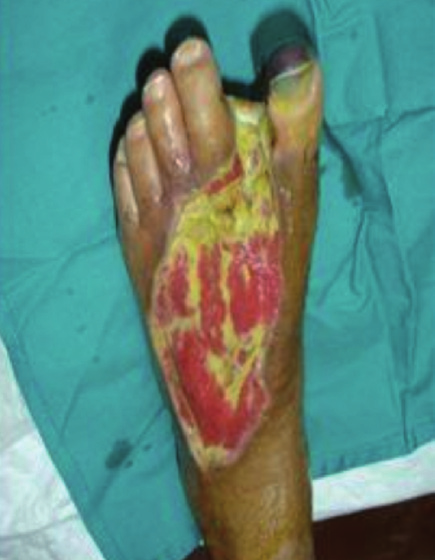
Skin grafting for those with advanced foot conditions can provide for great benefits including reinstating mobility, promoting movement and even saving limbs. Patients with diabetes in particular greatly benefit from this type of treatment as the graft replaces tissue on their feet to help heal foot ulcers. This can actually save the foot and prevent amputations!
Skin grafts can be produced from living or non-living tissue. Once the graft is placed over an open wound, it will steadily provide for viable skin growth. Skin grafting for foot ulcers is accomplished by taking healthy skin from other areas of the body and covering the ulcer with it. Burn victims or those with severe injuries may also benefit from skin grafts. Due to the many benefits of skin grafting, this treatment should be utilized immediately when required.
The foot surgeon will work with you to determine if a thinner or thicker graft is more appropriate for your wound. Thick grafts are more durable, retain more of the skins natural pigmentation and also allow for more sensation to be preserved. Areas directly on top of tendons, cartilage or bone should be avoided because they will not receive enough blood for proper healing.
A skin graft should stick to the wound successfully a week after the grafting surgery. Keep the area around the wound moist and apply abundant anti-microbial materials.
Also Check: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
Why Was This Study Needed
Foot complications are common in people with diabetes with around 10 to15% experiencing a diabetic foot ulcer at some point in their lives. NICE also estimate that around 50% of people die within five years of developing a diabetic foot ulcer and ulcers precede more than 80% of diabetes-related amputations.
They are also costly. A 2012 NHS Diabetes report estimated that around £650 million is spent on foot ulcers or amputations each year.
Despite the variety of current treatments for diabetic foot ulcers – including control of foot infection and wound dressings – up to 60% of ulcers fail to heal completely.
This review looked to see whether treatments involving skin grafts and tissue replacement would improve ulcer healing rates compared to usual care.
Acellular Matrix Skin Graft Better Than Standard Care For The Treatment Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Fran Lowry
April 27, 2009 Treating diabetic foot ulcers with an acellular matrix skin graft resulted in faster and more complete healing than standard treatment, according to the results of a randomized controlled trial published online April 2 in the International Wound Journal.
“Bioengineered skin grafts, including grafts, are promising alternatives for diabetic lower extremity wounds that often are unresponsive to traditional wound management modalities,” write Alexander Reyzelmen, DPM, from Advanced Clinical Research, LLC, Castro Valley, California, and coauthors. “While several studies have reported outcomes in chronic wounds, most are not randomized controlled studies specifically evaluating AM therapy use in diabetic foot ulcers.”
The primary aim of the study was to compare the proportion of ulcers that completely healed at 12 weeks in patients receiving AM therapy and those receiving standard wound management. A secondary aim was to compare the mean time to healing between the 2 treatment groups. Complete healing was defined as 100% re-epithelialization without drainage.
The authors reported outcomes from 46 patients randomly assigned to AM therapy and 39 patients randomly assigned to standard management. Most of the patients had type 2 diabetes and were obese . Metabolic control was maintained in all patients throughout the duration of the study.
The mean ulcer size at presentation was 3.6 cm2 in the AM group and 5.1 cm2 in the standard management group.
Also Check: How Long Does Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is a type of treatment that uses your bodys own natural healing abilities as part of the recovery process. Using stem cells speeds up your healing process and can be used to treat a variety of foot conditions, including diabetic foot ulcers.
Your stem cell treatment is noninvasive and takes place right in the Podiatry Hotline Foot & Ankle office. To complete the procedure, our podiatrists use highly effective and ethically sound placental tissues.
After getting stem cell therapy, your body not only heals your area of concern more quickly, it also decreases inflammation and reduces your pain. Youll also regrow fresh, new tissues in the area, often resolving the problem permanently.
Recommended Reading: How Is Ulcerative Colitis Caused