How Do You Know If You Have A Perforated Ulcer
Symptoms of a perforated ulcer may include:
Can a perforated ulcer heal without surgery?
However complications of peptic ulcer disease either bleeding or perforation still frequently require surgical intervention. Although bleeding peptic ulcers can usually be treated with non-surgical means, 510% will require emergent surgery for hemostasis.
What causes perforated ulcer?
A hole in the stomach or duodenum is called a perforation. This is a medical emergency. The most common cause of ulcers is infection of the stomach by bacteria called Helicobacter pylori . Most people with peptic ulcers have these bacteria living in their digestive tract.
Signs And Symptoms Of A Perforated Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcers are erosions of the tissues lining the upper digestive tract, particularly the stomach and first portion of the small intestine, the duodenum.They are often caused by a bacterial infection that compromises your defense against the acid produced in the stomach. Peptic ulcers sometimes penetrate completely through the stomach or intestinal wall, resulting in a hole — or perforation — and spillage of acid, digestive enzymes and partially digested food into the abdominal cavity. Several signs and symptoms typically result, although they can occur with conditions other than a perforated ulcer.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
Treatment For A Perforated Ulcer
Treatment for a perforated ulcer starts with fixing the hole in your digestive tract. This may be done with surgery.
Other treatments are aimed at easing pain and removing the cause of the ulcer. Prescription medicines may help with the following:
-
Reducing the amount of acid the stomach makes
-
Coating the lining of the stomach and the duodenum
-
Treating infections
Your provider may also give you different medicines if your ulcer was caused by over-the-counter pain medicines. In some cases, these medicines cant be avoided. Check with your healthcare provider to see what is best for you.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Diabetic Ulcers On Toes
What Is Stomach Ulcer Surgery
Peptic ulcer surgery is an operation for repair of stomach damage that’s caused by an ulcer. A stomach ulcer is an erosion on the inside of the stomach lining, and it is also referred to as a peptic ulcer or a gastric ulcer. It can develop slowly, and you may have more than one at a time.
Approaches used in stomach ulcer surgery include:
- Laparotomy: An open procedure with a large abdominal incision
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery: Involves a small abdominal incision and the use of a camera-equipped surgical device for visualization and repair
- Endoscopic procedure: A flexible tube is inserted into the throat and advanced down into the stomach to repair the ulcer with the assistance of a camera and surgical tools
This video has been medically reviewed by Anju Goel, MD, MPH.
Primary Repair Vs Sutureless
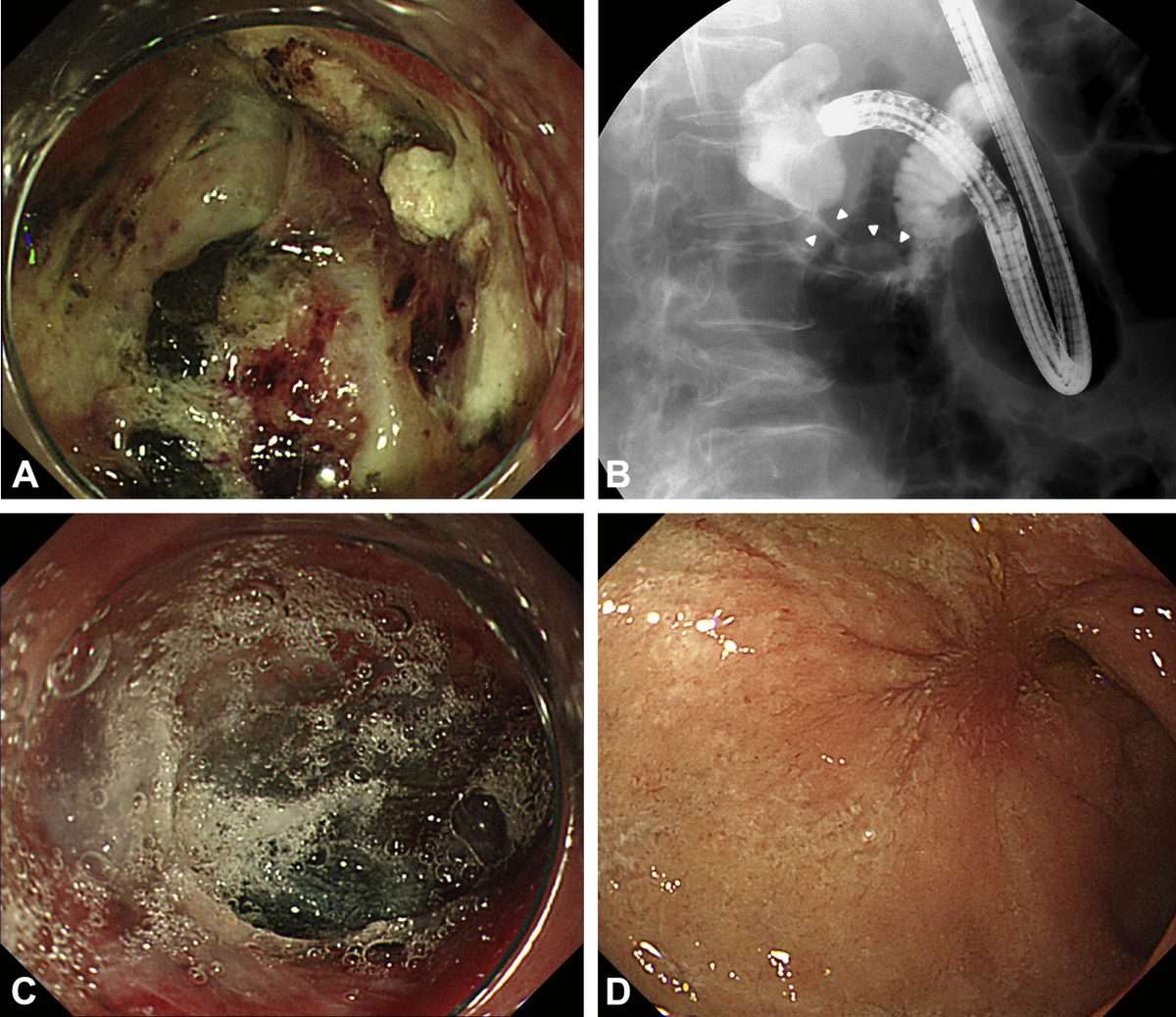
Laparoscopic sutureless repair was shown to take a significantly shorter time than laparoscopic suture repair. Laparoscopic sutureless repair has the advantage over laparoscopic suture repair because is technically much less demanding. The technique can be easily performed by those who have limited experience with laparoscopic surgery .
We suggest that Laparoscopic sutureless repair may be a viable option in presence of limited laparoscopic experience, only in presence of small size perforations without significant peritoneal contamination and for low risk patients.
We recommend primary repair in case of perforated peptic ulcer larger than 5 mm and smaller than 2 cm .
Additional file 3: Video 3: Technique of laparoscopic primary suture and repair of PPU larger than 1 cm Operating Surgeon Dr. Salomone Di Saverio MD.
We suggest routine use omental patch to further protect the suture line .
We recommend avoiding use of glue as only method of closure of PPU.
We suggest use of glue only as an adjunctive measure to protect suture line or the omental patch.
We suggest avoiding use of glue because of increased costs and risks of complications if serious doubts exist on the efficacy of primary closure.
We suggest conversion to open procedure if the primary repair is deemed to be done not efficaciously.
Don’t Miss: Urgent Care For Stomach Ulcer
When To Seek Medical Care
Seek medical evaluation as soon as possible if you experience symptoms that might indicate a peptic ulcer.Early diagnosis and treatment typically prevents the development of a perforation.
Emergency medical evaluation and treatment are necessary if you experience any signs or symptoms that could signal a perforated ulcer. Although another condition might be responsible for your symptoms, emergency medical care is needed to determine the cause, and ensure immediate and appropriate treatment.
Reviewed and revised by: Tina M. St. John, M.D.
- Seek medical evaluation as soon as possible if you experience symptoms that might indicate a peptic ulcer.
- Early diagnosis and treatment typically prevents the development of a perforation.
What To Do If You’re Worried
If you think you may have a stomach ulcer, you should visit your GP. And If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, seek urgent medical advice:
- Vomiting blood
- Passing dark, sticky, tar-like stools
- A sudden, sharp pain in your stomach that gets steadily worse
Tara’s family said a private funeral will be held on 27 February.
Also Check: Bone Broth For Stomach Ulcer
Treatment For A Stomach Ulcer
Special diets are now known to have very little impact on the prevention or treatment of stomach ulcers. Treatment options can include:
- medication including antibiotics, to destroy the H. pylori colony, and drugs to help speed the healing process. Different drugs need to be used in combination some of the side effects can include diarrhoea and rashes. Resistance to some of these antibiotics is becoming more common
- subsequent breath tests used to make sure the H. pylori infection has been treated successfully
- changes to existing medication the doses of arthritis medication, aspirin or other anti-inflammatory medication can be altered slightly to reduce their contributing effects on the stomach ulcer.
- reducing acid tablets are available to reduce the acid content in the gastric juices
- lifestyle modifications including quitting cigarettes, since smoking reduces the natural defences in the stomach and impairs the healing process.
How Is Gastrointestinal Perforation Diagnosed
To diagnose GP, your doctor will likely take X-rays of your chest or abdomen to check for air in the abdominal cavity. They may also perform a CT scanto get a better idea where the perforation might be. Theyll also order lab work to:
- look for signs of infection, such as a high white blood cell count
- evaluate your hemoglobin level, which can indicate if you have blood loss
In most cases, surgery is necessary to close the hole and treat the condition. The goals of the surgery are to:
- fix the anatomical problem
- fix the cause of peritonitis
- remove any foreign material in the abdominal cavity that might cause problems, such as feces, bile, and food
In rare cases, your doctor may forgo surgery and prescribe antibiotics alone if the hole closed on its own.
Sometimes, a piece of the intestine will need removal. The removal of a portion of either the small or large intestine may result in a colostomy or ileostomy, which allows intestinal contents to drain or empty into a bag attached to your abdominal wall.
Complications associated with GP include:
- bleeding
- conditions requiring steroids or biologic agents including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and similar conditions.
- other medical conditions such as heart disease, kidney or liver problems, and emphysema
If you experience pain or fever and youre at risk of having a GP, you should see your doctor. The sooner you see your doctor, the better your outlook will be.
You May Like: Best Treatment For Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
Can Ulcers Affect Bowel Movements
Rectal ulcers are sores that develop inside the rectum. These sores can be caused by several conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, solitary rectal ulcer syndrome and constipation. If you have a rectal ulcer, you may see blood in the stool, have rectal pain or experience painful bowel movements.
Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery
A NOTES approach may reduce the physiologic impact of therapeutic intervention after peptic ulcer perforation and provide a technically less challenging procedure. Experimental data suggest that the NOTES repair may be possible with lower intraabdominal pressure . Preclinical trials of endoscopic omental patch closures for upper gastrointestinal viscus perforations have been published . A retrospective review suggested that up to 50% of patients presenting with perforated ulcer might be candidates for a NOTES repair .
Bingener et al. present a pilot clinical study evaluating the feasibility of endoscopic transluminal omental patch closure for perforated peptic ulcers, with the hypothesis that the technique will be successful at closing ulcer perforations, as evidenced by intraoperative leak test and post operative water-soluble contrast studies.
Initial results from a laparoscopic-assisted NOTES approach for closure of perforated peptic ulcers appear promising and enable swift recovery in selected patients. This is especially important in elderly and/or immunocompromised patients. Technical details and patient selection criteria continue to evolve.
We do not recommend NOTES approach for PPU treatment until further experience and clinical evidence is gained.
Also Check: What Is Good For Mouth Ulcers
How Do You Know If You Have A Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcers sometimes penetrate completely through the stomach or intestinal wall, resulting in a hole or perforation and spillage of acid, digestive enzymes, and partially digested food into the abdominal cavity. Several signs and symptoms usually result, although they can occur with conditions other than a perforated ulcer.
What are the symptoms of a gastrointestinal perforation?
Peptic Ulcer Disease: Perforation
-
The epidemiology of peptic ulcer disease has changed dramatically.
-
The medical management of symptomatic peptic ulcer disease has improved.
-
There has been no decrease in ulcer perforations over the last decades.
-
Two main trends responsible for the unchanged rate of complications
-
Decrease in prevalence of Helicobacter pylori
-
Increase in use of NSAIDs
Ulcer perforations occur mostly in stomach or duodenum
One third to one half of ulcer perforations are associated with NSAID use
Clinical presentation tends to occur in 3 phases
Phase one: 02 h after onset, Initial sudden onset of severe abdominal pain
Phase two: 212 h after onset, Less abdominal pain
Phase three: > 12 h after onset, Increasing abdominal extension
Rapid diagnosis is essential!
Perforation is largely a clinical diagnosis: abdominal rigidity
Abdominal x-ray: look for free air no further examination necessary: this is an indication for surgical exploration
…
Read Also: Prednisone For Ulcerative Colitis Reviews
How Common Is A Perforated Ulcer
Perforated peptic ulcer disease is a serious complication of PUD and patients with PPU often present with an acute abdomen which carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality. The lifetime prevalence of perforation in patients with PUD is approximately 5%. PPU causes mortality ranging from 1.3% to 20%.
Can a perforated ulcer heal on its own?
The wound may heal on its own. If the ulcer is deep, it can cause severe pain or bleeding. Rarely, the acids contained in the digestive juices can pass completely through the stomach or the wall of the duodenum.
Causes Of Stomach Ulcers
A stomach ulcer can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Helicobacter pylori bacteria is thought to be responsible for around 60 per cent of stomach ulcers and at least 90 per cent of duodenal ulcers.
- Certain medications which include aspirin or clopidogrel, taken regularly to help prevent heart attack or stroke, and drugs for arthritis. Anti-inflammatory medications are thought to cause around two fifths of stomach ulcers.
- Cancer stomach cancer can present as an ulcer, particularly in older people.
Also Check: Can You Develop Ulcerative Colitis
Global Scope And Health Burden
Although there has been a substantial decrease, the estimated global number of deaths attributable to peptic ulcer disease in 2010 was 246 000 215 000 to 282 000). In context, this is seven times the death rate from appendicitis, considerably more than that for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, and similar to the death rate from cancers such as those of the prostate in men and ovarian and cervical cancer in women. Almost 70 per cent of deaths from peptic ulcer disease are the result of perforation.
Estimated annual incidence rates of peptic ulcer haemorrhage and perforation are 19·457·0 and 3·814 per 100 000 individuals respectively. Based on data from 11 European studies, there are between 4750 and 17 750 deaths from PPU every year. A study from 1993 to 2006, which captured 20 per cent of all hospital admissions in the USA, showed that the number of surgical procedures for perforation decreased by 21 per cent, from 15 000 to 12 000. The mortality rate from peptic ulcer disease was more than ten times higher than that from acute appendicitis and acute cholecystitis .
Sudden Severe Abdominal Pain
The first symptom of a perforated peptic ulcer is usually sudden, severe, sharp pain in the abdomen 1. The experience is typically so intense that most people precisely recall the exact moment the pain began. The pain is typically at its maximum immediately and persists. It is characteristically made worse by any movement, and greatly intensifies with coughing or sneezing. The pain is often generalized throughout the abdomen, but is sometimes focused in the upper abdomen. It may radiate to the shoulders or, less commonly, the hips.
- The first symptom of a perforated peptic ulcer is usually sudden, severe, sharp pain in the abdomen 1.
- The pain is often generalized throughout the abdomen, but is sometimes focused in the upper abdomen.
Recommended Reading: Ulcer Cause Blood In Stool
An Overview Of Gastroduodenal Perforation
- Department of Surgery, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Buea, Buea, Cameroon
Gastroduodenal perforation may be spontaneous or traumatic and the majority of spontaneous perforation is due to peptic ulcer disease. Improved medical management of peptic ulceration has reduced the incidence of perforation, but still remains a common cause of peritonitis. The classic sub-diaphragmatic air on chest x-ray may be absent and computed tomography scan is a more sensitive investigation in the stable patient. The management of perforated peptic ulcer disease is still a subject of debate. The majority of perforated peptic ulcers are caused by Helicobacter pylori, so definitive surgery is not usually required. Perforated peptic ulcer is an indication for operation in nearly all cases except when the patient is asymptomatic or unfit for surgery. However, non-operative management has a significant incidence of intra-abdominal abscesses and sepsis. Primary closure is achievable in traumatic perforation, but the management follows the Advanced Trauma Life Support principles.
Perforated Hiatus Hernia/gastric Volvulus
Perforated hiatus hernia or gastric volvulus, when part or all of the stomach is in the chest, present extremely difficult scenarios. Surgery in this situation may require thoracotomy, resection, and then a decision made regarding primary or delayed reconstruction . The influencing factors are the time since presentation, degree of mediastinal and pleural soiling, and the general condition of the patient .
Also Check: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Ulcerative Colitis
Is A Perforated Ulcer Life Threatening
Perforated peptic ulcer is relatively rare, but life-threatening with the mortality varying from 10% to 40% .
How long can you live with a perforated ulcer?
Overall 30-day mortality from perforated peptic ulcer was 25.3%, but it increased from 8.9% among patients younger than 65 years to respectively 28.5% and 46.0% among patients aged 6579 years and 80+ years .
Can perforated ulcer cause death?
Peptic ulcer perforation is well recognized as a cause of peritonitis and can result in death. Although amenable to surgery, delay in making the correct diagnosis results in increased mortality.
How long can you live with perforated ulcer?
Can ulcers cause death?
Peptic ulcer perforation is well recognized as a cause of peritonitis and can result in death. Although amenable to surgery, delay in making the correct diagnosis results in increased mortality. Accurate diagnosis has been hindered by demographic changes in the affected population.
Is a perforated ulcer serious?
Perforation is a hole in the wall of your stomach or small intestine. Its a serious condition in which an untreated ulcer can burn through the wall of the stomach. Digestive juices and food can seep through the hole into the abdominal cavity.
What is GP-B?
How Do They Fix A Perforated Duodenal Ulcer
Omental patching is a surgical procedure for treating perforated ulcers. It is also called a Graham patch after the surgeon who first performed this technique. This procedure uses a patch of the omentum to repair the injury because it is durable.
Omental patching may be combined with other procedures such as the resection of the vagus nerve that stimulates acid production to reduce acid production in the stomach or combined with other surgical procedures in case of very large ulcers.
The medical treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection and acidity is required. Diet and lifestyle modifications would have to be followed after the surgery to prevent the recurrence of ulcers. Sometimes, a perforated ulcer can seal itself by an adherent omentum. Hence, the patient may be managed with medical treatment instead of surgery.
An ulcer is discontinuation occurring on the external or internal surface of the body. Caused by trauma to the skin or a mucous membrane that does not heal, ulcers vary in width and depth. They can be painful and lead to severe complications. Ulcers can occur in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines .
The omentum is a double-layered fatty tissue that covers and supports the intestines and organs in the abdomen. The omentum is made up of the greater omentum that is important storage for fat and the lesser omentum that connects the stomach and intestines to the liver.
Also Check: Does Alcohol Affect Ulcerative Colitis