What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Adjusting Your Diet To Reduce Ulcerative Colitis Pain
There isnt one diet thats best for everyone with UC. It’s best to focus on getting balanced and diverse nutrition from a variety of foods. Cutting out whole food groups is unnecessary unless you have known food allergies or intolerances . For some people, following the guidelines of the Mediterranean diet is helpful.
Closely Monitor Your Symptoms
A sudden return of your symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, or bloody stools are likely to be a sign that you are experiencing a flare-up, and your treatment may need to be adjusted. However, sometimes, the symptoms of a flare-up may be subtler and not immediately apparent.
This is why it is essential to keep track of even the smallest change you feel. Let your doctor know if you experience any of the following:
- If you notice blood in your stool
- If you are having more bowel movements than usual
- If you see a change in the amount or texture of your bowel movements
- If you feel tired or seem to have less energy than usual
- If you are losing weight or if you notice a loss in appetite
- If you notice any other symptoms such as mouth sores or joint pain
It is a good idea to maintain a symptom diary to help keep track of your day to day condition. This will also help you explain your symptoms in detail to your doctor.
Read Also: Can Diet Help Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Liver disease.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With Colitis
Patients with infectious diarrhea tend to get better relatively quickly with supportive care. Most infections will resolve with or without specific treatment and often do not require antibiotics. Those decisions depend on the patient’s diagnosis.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease probably will require lifelong treatment to help control their symptoms. The goal, as with any long-term illness, is to allow the patient to live a normal life with minimal symptoms from the disease.
Patients with ischemic colitis need to minimize their risk factors for progressive narrowing of the arteries. These are the same risks as for heart disease and require the same treatment approach, including controlling high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and smoking cessation. Patients with severe ischemia that leads to a dead colon require surgery to remove the gangrenous segment.
Also Check: What Foods To Eat With Ulcerative Colitis
More Drugs That Work On Your Immune System
Other types of medicines for ulcerative colitis target your immune system, too. Your doctor may call these immunomodulators. They may be good options if 5-ASAs and corticosteroids havenât worked well for you.
The most common ones are azathioprine , mercaptopurine , and cyclosporine . Due to the risk of side effects, doctors usually save cyclosporine for people who donât have success with other meds. They may also try methotrexate paired with folic acid.
Ozanimod is an oral medication and is the first sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator approved for patients with moderately to severely active UC.
The goal is to lower inflammation in your colon.
These drugs can have side effects. They can damage your liver and make you more likely to get skin cancers, lymphoma, and infections. If you take them, your doctor will test your blood and check you for skin cancer regularly.
Cyclosporine is especially strong, but it works fast. Your doctor might prescribe it to get a severe flare under control, and then give you 6-MP or azathioprine afterward. The drug may cause kidney problems, gout, infections, and high blood pressure.
It can take several months for some of these drugs to work. So your doctor may give you a faster-acting medicine, like a low dose of a corticosteroid, to help in the meantime.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Last
Deal With Iron Deficiencies Too
UCs painful, even gut-wrenching symptoms dont always make it fun to eat. And, people with this chronic condition may lose blood in their stool, as well as absorb dietary iron poorly due to inflammation, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Additionally, foods rich in iron, like red meat, often trigger flareups. Together, this can cause anemia, a condition characterized by a low red blood cell count. Its a common issue with the UC communityand must be controlled to battle fatigue. If you have UC and super-low energy, talk to your doctor about iron supplements.
Also Check: Causes Of Bleeding Ulcers In Stomach
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
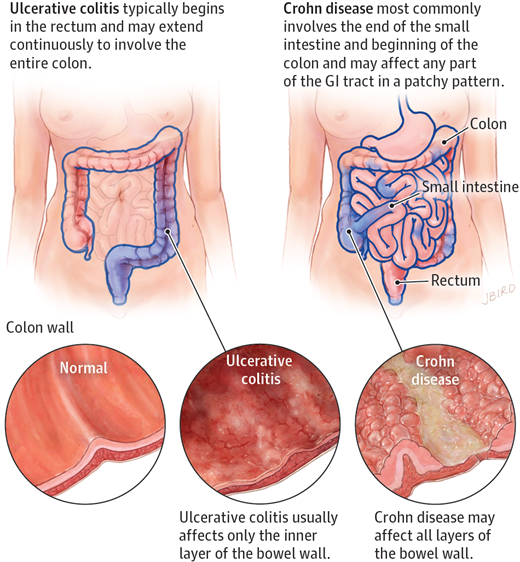
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Right Or Middle Abdomen Pain
A pain that feels like cramps in the middle of the abdomen or the lower right quadrant is typical of the types of Crohn’s disease known as ileocolitis and ileitis.
Ileocolitis is the most common form of Crohn’s disease and is defined by inflammation located in the last section of the small intestine and in the large intestine .
Ileitis is a type of Crohn’s disease that affects only the ileum and is the second most common form. People with ileitis may also find that their pain or discomfort appears within a few hours of eating a meal.
Also Check: Wound Care For Diabetic Leg Ulcers
What Are Common Inflammatory Sources Of Pain In People With Ibd
IBD is a condition caused by chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. This inflammation frequently causes symptoms and complications that are sources of pain, including:1
- Gastritis inflammation of the stomach lining
- Enteritis inflammation of the intestine
- Colitis inflammation in the colon, which is entirely different than ulcerative colitis
- Abscess an area of infection that is filled with pus
- Fistula a tunnel that forms between an organ and another part of the body
- Fissure a small tear in the tissues that line the anus
IBD can also cause symptoms and complications that occur outside of the digestive tract. These sources of pain are called extraintestinal, and can include:1
- Peripheral arthritis inflammation of the large joints of arms and legs
- Sacroiliitis inflammation in the area where the lower spine connects to the pelvis
- Ankylosing spondylitis inflammation that causes the vertebrae in the spine to fuse together
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis inflammation that scars and damages the bile ducts in the liver
- Erythema nodosum skin inflammation that causes red, painful lumps
- Pyoderma gangrenosum chronic, deep ulcers on the skin
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Also Check: How Do You Get A Peptic Ulcer
Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Some people with ulcerative colitis have only occasional symptoms. For others, the symptoms are constant. The symptoms a person experiences can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation and where it occurs in the large intestine.
Common symptoms include:
- diarrhea, often with blood and mucus
- cramping abdominal pain, especially in the lower abdomen
- a frequent sensation of needing to have a bowel movement
- little advance warning before a bowel movement
- the need to wake from sleep to have bowel movements
- feeling tired
- dehydration
- low red blood cell count
Some people with ulcerative colitis develop pain or soreness in the joints, irritated eyes, and rashes.
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis can suddenly get worse. This is called a flare. Then symptoms may fade away. This is called remission. Some individuals with ulcerative colitis have symptoms only rarely, others have flares and remissions, others have symptoms all or most of the time.
Ulcerative Colitis Medications: Biologics What To Avoid
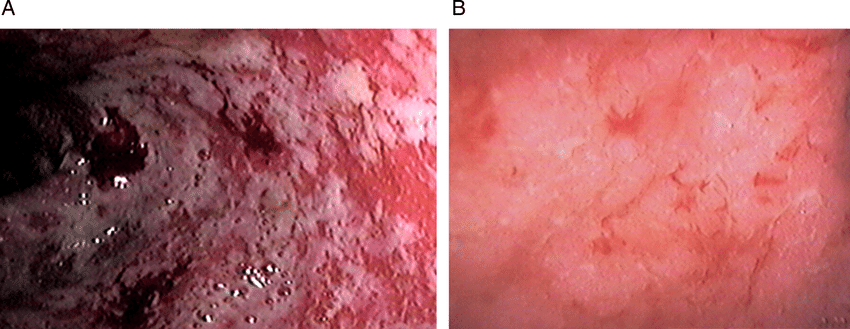
Ulcerative colitis is an idiopathic inflammatory condition of the colon which results in diffuse friability and superficial erosions on the colonic wall associated with bleeding. It is the most common form of inflammatory bowel disease worldwide. It characteristically involves inflammation restricted to the mucosa and submucosa of the colon Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that primarily affects the large intestine and colon. There is no proven cause for IBD, but recent research points to the possibility that the immune system attacks the lining of the intestines according to the Mayo Clinic Ulcerative colitis is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood. Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares
Recommended Reading: Best Foods To Eat When You Have A Stomach Ulcer
Where Does Ulcerative Colitis Pain Come From
Ulcerative colitis can be an unpredictable condition as the cause of it has yet to be uncovered. The illness is also associated with flare-ups, which can have unique triggers. Approximately 30% of people who are currently in remission will relapse in the next year.
It is believed that there is a genetic component that comes into play with this condition. Those with family members with ulcerative colitis are more likely to be afflicted by this condition. This disease can generally be found in any age group, but it is far more prevalent between the ages of 15 to 30, as well as 50 to 70. It is also believed that Caucasians are much more likely to develop this condition and the risk is even higher for those of Ashkenazi Jewish decent.
At one time, it was believed that ulcerative colitis was caused by stress and diet. Today, researchers believe these can be a trigger, but they no longer think it is a direct cause. Most studies are focused on searching the immune systems for a root cause for this condition. It is thought that the immune system might inadvertently attack the healthy cells in the GI tract when trying to fight off foreign invaders, which causes inflammation.
What To Look For When You Have Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Attacks from this condition vary greatly depending on the person, so it is important to know what a flare-up is to you. It can also affected by the severity of the inflammation as well as where in the large intestine it is.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms can be anywhere from mild to severe. They can slowly build or come on suddenly without warning. It is important to monitor this condition periodically as it can get worse over time even with treatment.
Some of the most common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are:
- Blood or pus in stool
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Frequent, uncontrollable bowel movements
There are other difficulties that can happen with this chronic condition. Some of these complications include rupture of the bowel, profuse bleeding, vitamin and mineral deficiencies, severe dehydration, and inflammation of the skin, joints, and eyes. The risk of colon cancer increases as well as the possibility for blood clots in veins and arteries.
Recommended Reading: What To Do When You Have A Stomach Ulcer
What Does A Uc Cramp Feel Like
People who have UC describe a pronounced sensation of squeezing and releasing in their abdomen, Dr. Ha says, that feels more like pressure than a stabbing pain.
Doctors diagnose UC based on where symptoms are occurring. Many people with the condition experience whats known as left-sided colitis, where the pain and inflammation occur on their left side, from the rectum up to the descending colon.
Cramps can also be accompanied by bloating and gas, which cause a feeling of pressure and knotting in your abdomen.
When Should Someone Contact A Doctor About Colitis
Diarrhea is a common sign of colitis. It is usually self-limited and resolves on its own with supportive care, including rest and a short course of a clear-fluid diet. However, seek medical care if diarrhea persists for more than two to three weeks, if there is blood in the stool, fever, or the person has signs of dehydration.
- Blood in the stool is never normal and should always be evaluated. Common causes of blood in the stool include hemorrhoids however, other serious causes of bleeding need to be investigated. Colitis is not the only cause of rectal bleeding. Other causes include diverticular disease of the colon , colon polyps, anal fissures, and cancer.
- Chronic diarrhea may lead to dehydration and changes in the electrolyte balance in the body. If it is severe enough, the dehydration may require treatment with IV fluids or oral rehydration therapy. The symptoms of dehydration may include
- lightheadedness , especially when changing from a sitting or lying position to a standing position
- weakness
You May Like: Exercising A Horse With Ulcers
Could My Symptoms Be Ibs
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a different condition from IBD, although some of the symptoms are similar. Like Crohn’s and Colitis, IBS can cause abdominal pain, bloating and bouts of diarrhoea or constipation. However, it does not cause the type of inflammation typical of Colitis, and there is no blood loss with IBS.
Some people with Colitis may develop IBS-like symptoms, for example experiencing diarrhoea even when their Colitis is inactive. These symptoms may need slightly different treatment from their usual IBD symptoms. IBS is more common in people with IBD than in the general population.
If you develop diarrhoea with bleeding and abdominal pain, your doctor may suspect you have Colitis, particularly if you are a young adult or have a family history of Crohn’s or Colitis. You will need tests and physical examinations to confirm a diagnosis. See Tests and Investigations for IBD.
You may need to have tests repeated from time to time to check on your condition and how your treatment is working.
Some drug treatments may also require a series of blood tests and, occasionally, x-rays or scans to check for any potential side effects. Your specialist will avoid giving you any unnecessary tests or investigations.
You may need more regular colonoscopies when you have had Ulcerative Colitis for a long time to check for any signs of cancer.
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medication such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. However, more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital to reduce the risk of serious complications, such as the colon becoming stretched and enlarged or developing large ulcers. Both of these can increase the risk of developing a hole in the bowel.
If medications aren’t effective at controlling your symptoms, or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
During surgery, your small intestine will either be diverted out of an opening in your abdomen , or used to create an internal pouch that’s connected to your anus .
Read more about:
You May Like: Natural Ways To Heal Ulcerative Colitis
What Kinds Of Pain Relievers Can Be Used By People With Ibd
The most common type of over-the-counter pain relievers are called NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen , aspirin, or naproxen. These medications are generally not recommended for people with inflammatory bowel disease because of the side effects that they can cause in the digestive tract. This means that taking NSAIDs for pain relief can cause the symptoms of IBD to get worse or trigger IBD flare-ups that can cause further damage to the digestive tract.1,2
Patients with IBD should consult their healthcare providers before taking any NSAID medications. In some cases, NSAIDs may be recommended for treating pain due to arthritis, but patients will be monitored closely for side effects. Instead of NSAIDs, people with IBD may be advised to try acetaminophen for pain relief.1,2
Opiates are a very strong type of medication that can be used to treat severe pain. They include morphine, hydrocodone with acetaminophen , oxycodone with acetaminophen , and codeine. While they can be very effective at treating severe pain in the short term, if they are taken long-term, opiates can cause serious side effects and can make a person physically dependent on them. For this reason, they should be taken only under close supervision from a healthcare provider.1,2