Can Adults Get Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Yes. Hand, foot and mouth disease is very common and usually affects infants and children under the age of 5. But because its so infectious, it can spread among family members and also make older kids, teenagers and adults sick.
Can you get hand, food and mouth disease twice?
Yes. Because multiple viruses can cause hand, foot and mouth disease, it is possible to catch the virus multiple times.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hand
Several symptoms can be present and the disease does not present the same way in everyone. Generally, the symptoms include:
- Fever
- Painful ulcers in the mouth
- Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting and/or diarrhea
- Small red spots accompanied by blisters in the hands, under the feet, on the buttocks or even elsewhere on the body
How Is It Transmitted
- Hand, foot and mouth disease is spread by coming into contact with secretions from the nose and throat, saliva, fluid from blisters or stool of an infected person.
- It is spread through close personal contact , coughing and sneezing or from touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus.
Read Also: Best Ulcerative Colitis Diet Book
Serious Complications From Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Serious complications due to hand, foot and mouth disease are rare.
In rare cases, the virus can cause inflammation of the heart, the brain or the lung. In very rare cases these complications can cause death.
Take your child to your nearest hospital emergency department that treats children if they have hand, foot and mouth disease and any of the following symptoms:
- dislike of bright lights
- drowsy
- confusion
Causes Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
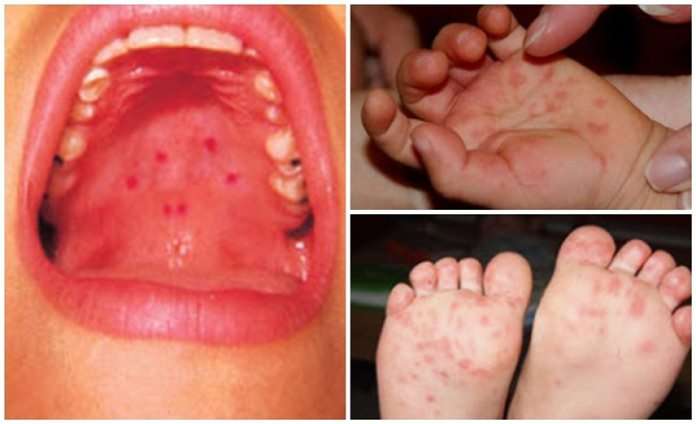
Hand, foot and mouth disease is usually caused by a group of viruses known as the coxsackieviruses. The one that most commonly causes the disease is coxsackie virus A16.
Another virus called enterovirus 71 can occasionally cause a more severe form of hand, foot and mouth disease. EV71 is uncommon in the UK.
The virus is very easily spread. Its passed from one person to another through coughing or sneezing and from direct contact with fluid from blisters. Its also passed on in an infected persons faeces they can spread it if they dont wash their hands properly after going to the toilet.
Recommended Reading: Offloading The Diabetic Foot For Ulcer Prevention And Healing
Treatment For Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Theres no cure for hand, foot and mouth disease. But most children get better quickly by themselves without any problems.
Paracetamol can help ease discomfort and pain.
Its important for your child to drink fluids to avoid dehydration. This can be hard if your childs mouth is sore. You could try an oral rehydration solution, which you can buy from any pharmacy.
If eating hurts your child, its best for him to stick to soft foods for several days, and to avoid tangy foods like tomatoes, lemons, grapefruit and oranges.
Dont try to pop the blisters. This increases the risk of getting a skin infection and spreading the virus to other children.
The Girl In The Vignette Has Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Accompanied By Meningitis
Aap red book hand foot mouth. Reflux solid foods sore throat No virus may be shed in the stool for several weeks. Small red spots and tiny water blisters.
Seen on the palms, fingers, soles and toes. From the american academy of pediatrics. At visit 2 the differential diagnosis should include the hand, foot, mouth syndrome with fever for > 3 days and no focus, likely a viral illness:
May see common cold signs or symptoms with fever, sore throat, runny nose, and cough.
Tiny blisters in the mouth and on the fingers, palms of hands, buttocks, and soles of feet that last a little longer than a week . Important complications to look for include dehydration, especially if your child has painful mouth ulcers and is not eating and drinking well. The diagnosis cannot be made without these.
2015 report of the committee on infectious diseases. During the summer and fall of 1963, 76 patients with exanthematous disease were studied and 6 cases of hand, foot, and mouth syndrome due to coxsackie a 16 virus were noted. However, empirical data to support this recommendation are limited.methods:.
Nine virus strains were isolated from the throat in five cases, vesicle fluid in. Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a clinical syndrome characterized by an oral enanthem and a macular, maculopapular, or vesicular rash of the hands and feet . Hand, foot, and mouth syndrome is caused by various viruses, including several types of coxsackieviruses.
Despite its scary name, this illness is generally mild.
Recommended Reading: Ulcerative Colitis And Blood In Urine
How To Prevent Hand
- Wash your hands multiple times a day, especially if you have been handling diapers or bathing an infected child.
- Do not touch your eyes, mouth, or nose with dirty hands.
- Avoid close contact with affected individuals.
- Do not share utensils with infected individuals until they have recovered.
- Disinfect common areas like toilets regularly.
- Infected individuals must avoid venturing out until advised by the doctor.
These tips will definitely help prevent the disease from spreading any further.
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease usually eases on its own. Treatment is offered to speed up the recovery. However, in some cases, the disease may take a drastic turn and lead to life-threatening complications like meningitis and encephalitis. Hence, it is recommended to look for worsening symptoms and avail medical intervention accordingly.
Hope this post has cleared most of your queries regarding hand-foot-and-mouth disease. For any more doubts, feel free to get in touch with us via the comments section below.
How To Stop The Condition Spreading
Hand, foot and mouth disease is easily passed on to other people. It’s spread in coughs, sneezes and poo.
You’re infectious from a few days before you have any symptoms. But you’re most likely to give it to others in the first 5 days after symptoms start.
To reduce the risk of spreading hand, foot and mouth disease:
- wash your hands often with warm soapy water and teach children to do so
- use tissues to trap germs when you cough or sneeze
- bin used tissues as quickly as possible
- don’t share towels or household items like cups or cutlery
- wash soiled bedding and clothing on a hot wash
Recommended Reading: How Effective Is Humira For Ulcerative Colitis
How Can I Prevent Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease is highly contagious. The infection often spreads before a person realizes theyre sick. You can slow or stop the spread of the illness through these good hygiene steps:
- Cover sneezes and coughs with the crook of your elbow.
- Disinfect high-touch items, such as toys, countertops and doorknobs.
- Dont share eating utensils, cups, towels, blankets or clothing.
- Keep infected children away from healthy children.
- Wash your child’s clothing, bedding and any other soiled items.
- Wash hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
Symptoms Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The virus infects children 4-6 days before symptoms appear.
Your child might have a mild fever for a day or two before the other symptoms appear.
Small mouth ulcers usually appear first on the cheeks, gums and sides of the tongue. Your child might also complain of a sore mouth or throat, or just go off her food and refuse fluids.
Your child might also have a headache and aching muscles, mild stomach pain or nausea.
Small blisters also appear on the hands and feet, usually on the palms and soles. Tiny red spots might appear on your childs bottom, but these usually dont form blisters except in babies.
The blisters and ulcers usually go away after 7-10 days.
Also Check: How To Heal Leg Ulcers Quickly
Who Is At Risk For Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Young children have the highest risk for getting HFMD. Risk increases if they attend daycare or school, as viruses can spread quickly in these facilities.
Children usually build up immunity to the disease after being exposed to the viruses that cause it. This is why the condition rarely affects people over age 10.
However, its still possible for older children and adults to get the infection, especially if they have weakened immune systems.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you or your child has hand, foot and mouth disease, you may want to ask your doctor:
- How long are we contagious?
- How long should my child stay home from school?
- How long should I stay home from work?
- Should I notify my childs school about the infection?
- What steps can I take to ensure other family members dont get infected?
- What can I do to make myself or my child more comfortable?
- What can I do to alleviate symptoms like an itchy rash or mouth pain?
- How long will the rash last?
- Can the infection come back?
- What steps can I take to prevent getting hand, foot and mouth disease again?
- Should I look out for any signs of complications?
Summary
Symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease tend to be mild and go away with minimal treatment in less than two weeks. Because the virus is highly contagious, its important to practice good hygiene and take steps to keep it from infecting others. Your doctor can provide suggestions for symptom relief and offer tips for keeping other people healthy and virus-free.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/08/2020.
References
Don’t Miss: New Meds For Ulcerative Colitis
Prevention Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Its difficult to stop your child from getting hand, foot and mouth disease. Theres no vaccine for it.
Careful handwashing, especially at child care and preschool, can help minimise the spread of the virus.
If your child is still in nappies, make sure to wash your hands after changing her nappies. Also make sure to properly wipe down the changing mat or table.
Your child shouldnt go to child care, preschool or school until the fluid in the blisters has dried up.
Can Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Be Prevented
To prevent the spread of HFM, keep kids home from school and childcare while they have a fever or open blisters on the skin and in the mouth.
Hand washing is the best protection. Remind everyone in your family to wash their hands well and often, especially after using the toilet or changing a diaper, and before preparing or eating food. Shared toys in childcare centers should be cleaned often with a disinfectant because many viruses can live on objects for a few days.
Also Check: Is Nexium Good For Ulcers
Signs And Symptoms In Children
A child with hand-foot-and-mouth disease can often develop reddish spots on the soles of feet and palms of hands, which quickly turn into bumps or blisters.
When a child gets hand-foot-and-mouth disease , most signs and symptoms clear within 7 to 10 days. Heres what you may see during that time:
Days 12
For one or two days, you may notice that your child feels unwell and has one or more of the following:
-
A mild fever
Days 37
After one or two days, the above symptoms tend to clear and you may see:
-
Mouth sores
-
An itchy rash, usually on the feet, hands, or both
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Mouth sores: Most children have a few painful mouth sores, which usually develop on the tongue. Sores can also appear elsewhere in the mouth, including the roof of the mouth. Mouth sores tend to begin as bright pink spots or tiny bumps, which turn into blisters. The blisters can be painful.
Itchy rash: While an itchy rash tends to develop on the hands or feet, it can appear elsewhere on the body, such as the knees or elbows.
While a child can develop all of these signs and symptoms of HFMD, most children only have a few.
Painful mouth sores may cause your child to stop drinking, which can lead to dehydration. If you notice that your child wont drink, contact your childs doctor.
Living With Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Living with hand, foot, and mouth disease is a short-term challenge since the symptoms go away in about a week. As a parent caring for a child who has the virus, your primary goals are to keep your child comfortable and hydrated. It is best to keep them at home to rest and to avoid situations that will infect others.
Recommended Reading: What Are Some Symptoms Of An Ulcer
What Is The Cause Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand foot and mouth disease is due to an enterovirus infection, usually Coxsackie virus A16. Other viruses causing HFM include:
- Enterovirus 71, linked with severe infections that may involve the nervous system
- CVA6, causing increasingly common and severe infection worldwide
- CV A5, A7, A9, A10, B2, and B5
- Echovirus
- Coxsackievirus.
When To Call The Doctor
- Neck pain or chest pain
- Pus, drainage, swelling, or a large area of redness around any sores
- Trouble swallowing
- An infants soft spot pulling in
- No tears, sunken eyes
- No wet diaper for 4 to 6 hours
- Very dark urine, or
- No urination in 6 to 8 hours
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have A Stomach Ulcer
How To Treat Hand Foot And Mouth Disease In Children
To help with the symptoms:
- drink fluids often to prevent dehydration avoid acidic drinks such as fruit juice
- eat soft foods like soup, mashed potatoes and vegetables, smoothies and ice cream
- avoid hot or spicy foods
- avoid acidic fruits like tomatoes and citrus fruits
- rinse your mouth with warm, salty water and spit it out. Only give this to your child if they are old enough to spit it out
If your child is unwell or uncomfortable with a fever, giving them paracetamol or ibuprofen can help. Only give your child ibuprofen if they are older than 3 months. Adults who are unwell can also take paracetamol or ibuprofen.
You cannot take antibiotics or medicines to cure hand, foot and mouth disease.
Oil Pulling With Coconut Oil
Shutterstock
1 tablespoon of cold-pressed coconut oil
What You Have To Do
How Often You Should Do This
You can do this once daily, preferably every morning.
Why This Works
Oil pulling with coconut oil can help alleviate the painful and inflamed blisters inside the mouth. This is due to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of coconut oil .
Don’t Miss: How To Eat With A Stomach Ulcer
Signs And Symptoms Clear Quickly
While most signs and symptoms of HFMD clear within 7 to 10 days, children younger than 2 years of age may be sick longer. It can take more time for their bodies to get rid of the virus.
You can find out how HFMD spreads from person to person and how youre most likely to get the virus at: Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: Who gets & causes
ImagesImage 1: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 69:736-41Image 2: Getty images
ReferencesBelazarian L, Lorenzo ME, et al. Exanthematous viral diseases. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, et al. Fitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine . McGraw Hill Medical, New York, 2008: 1867-9.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Hand-foot-and-mouth disease. Last updated December 22, 2017. Last accessed May 25, 2018.
Lott JP, Liu K, et al. Atypical hand-foot-and-mouth disease associated with coxsackievirus A6 infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 69:736-41.
What Are The Complications Of Hand
Complications are uncommon. They include:
- Dehydration due to inadequate fluid intake
- Fingernail and toenail changes are often noted about 2 months after CVA6 infection:
- Transverse lines that slowly move outwards
- Nail shedding about 2 months after the illness.
- Eventually, the nails return to normal.
Serious enteroviral infection can lead to:
- Widespread vesicular rash
Don’t Miss: What Causes Venous Stasis Ulcers
What Are The Clinical Features Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The typical incubation period of HFMD is 3-5 days but has been known to range from, 2-7 days.
Symptoms usually include:
- Lesions on the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the hands and feet. The progression is from flat pink patches to small, elongated greyish blisters, and, within a week, these peel off leaving no scars.
- Small vesicles and ulcers in and around the mouth, palate, and pharynx. These are sometimes painful, so the child eats little, frets, and may complain of a sore throat or mouth sores.
- Red macules and papules on the buttocks and sometimes on the arms. Lesions can also occur on the genitalia.
Atypical hand foot and mouth disease results in a more widespread rash. Features may include:
- Red, crusted papules
- Involvement of unusual sites such as the ear
- In children with atopicdermatitis, lesions may select skin affected by eczema .
Flat pink patches on the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the hands and feet are soon followed by small elongated greyish blisters. These resolve by peeling off within a week, without leaving scars.
Usually, there are also a few small oral vesicles and ulcers. These are sometimes painful, so the child eats little and frets. There may be a few on the skin around the mouth. In young children, a red rash may develop on the buttocks and sometimes on the arms.
Atypical hand foot and mouth disease due to Coxsackie A6 results in a more widespread rash, larger blisters and subsequent skin peeling and/or nail shedding.