Stages Of Decubitus Ulcers
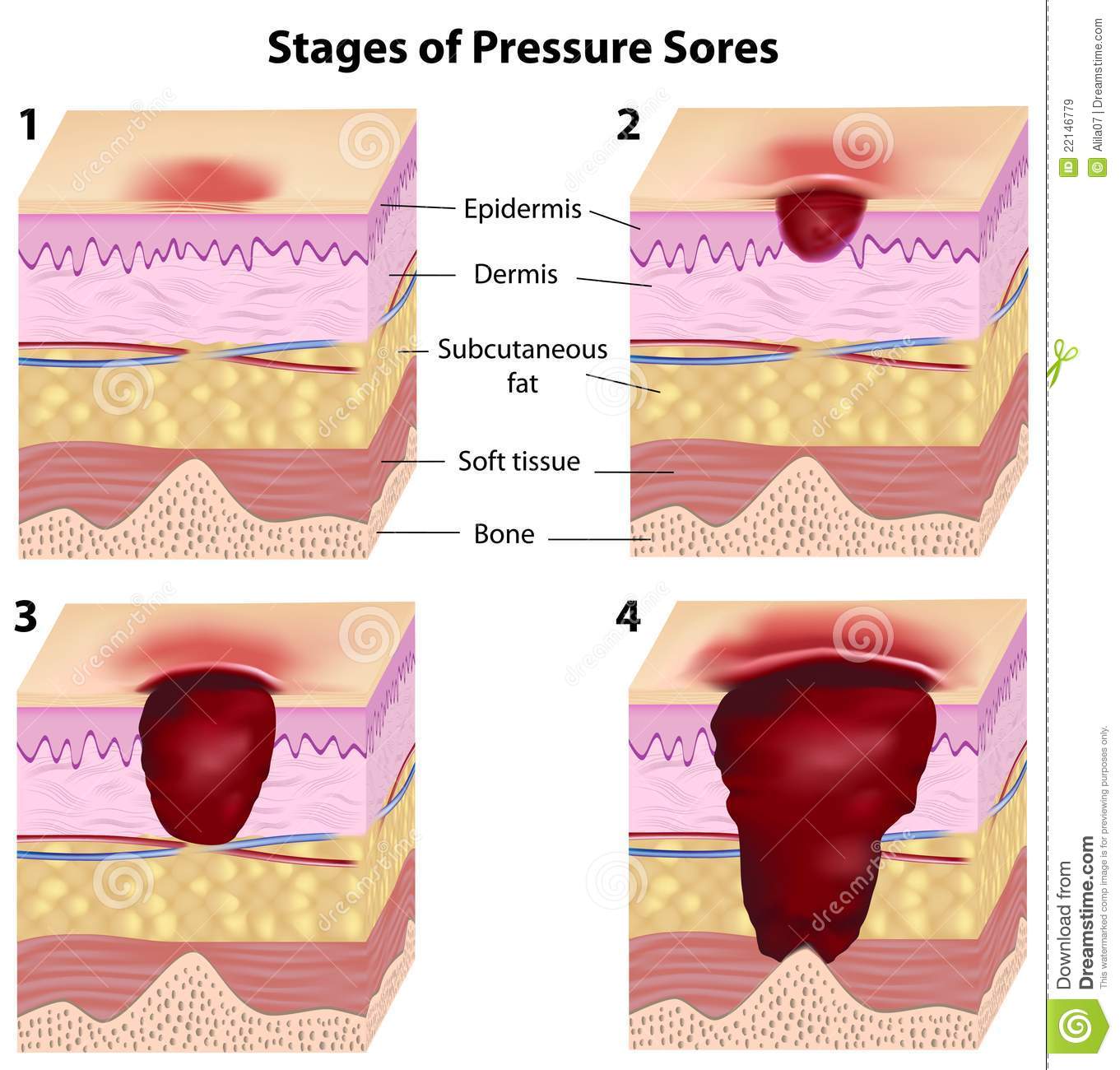
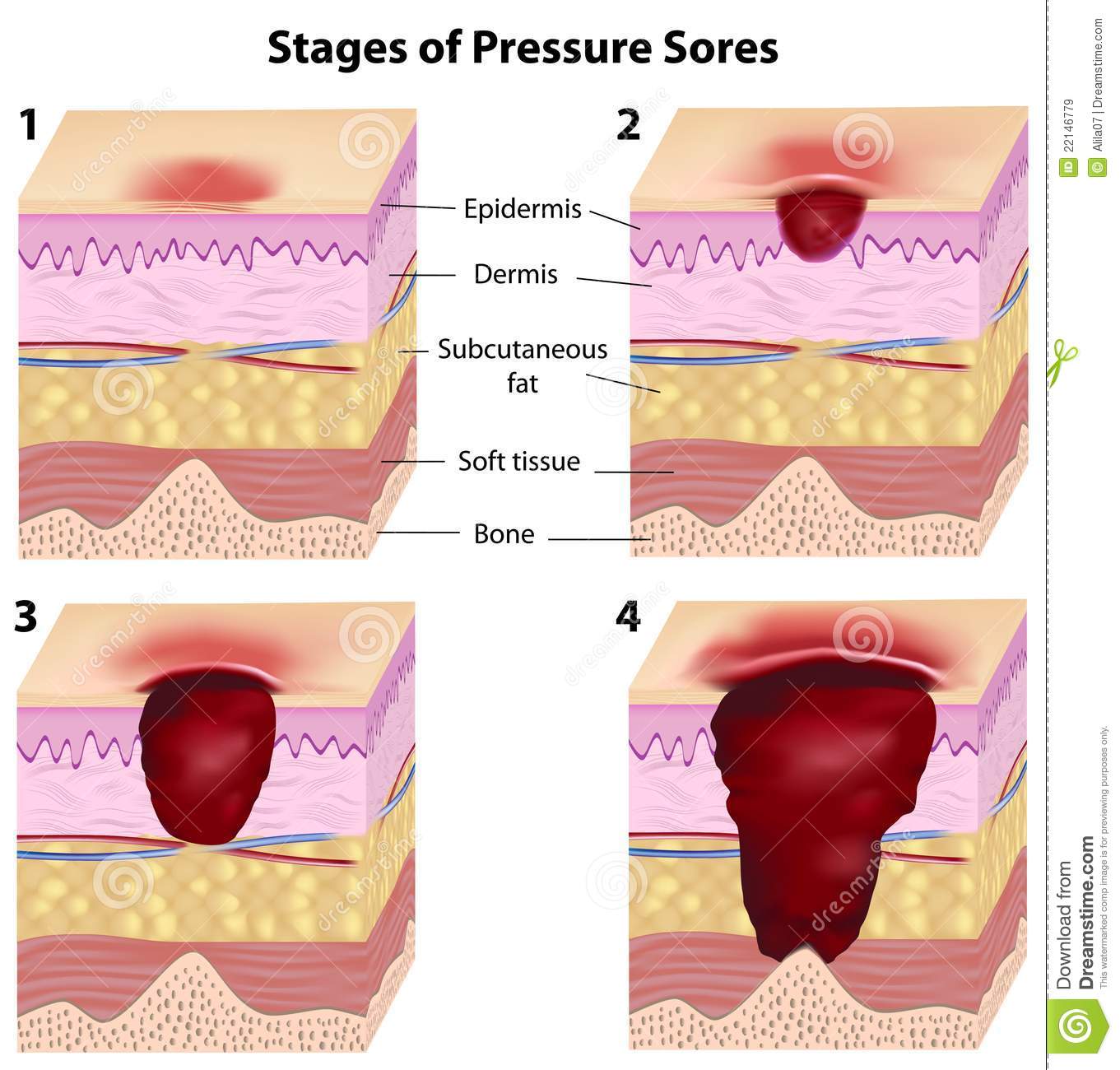
Stages of decubitus ulcers are classified from Stage I to Stage IV according to the severity of symptoms.
Stage Iâ In fair-skinned individuals, a defined skin area is characterized by persistent redness. Darker skin may come with hues of red, purple of blue. Compared to the other adjacent body area, the changes in the defined area involve skin temperature, sensation, and palpable or felt tissue consistency. When the define area is pressed, the skin does not turn to whiteâ a key indicator that decubitus ulcer has already started to occur.
Stage IIâ At this stage, the decubitus ulcer is still superficial. A blister, an abrasion, or a shallow crater or open sore has formed the surrounding area of which may appear to be irritated and red in color.
Stage IIIâ The superficial ulcer appears like a deep crater, where thick skin loss involves impairment in the skinâs underlying tissue. The depth of damage may reach the fascia, but does not pass through it.
Stage IVâ Further impairment takes place along with the fully thick skin loss. The depth of damage reaches the bone, muscle, or the supporting tendons and joint capsule. Furthermore, sinus tracts may also characterize Stage IV decubitus ulcers.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The main goal is to prevent a decubitus ulcer by decreasing the pressure acting on the affected site. This goal requires an interprofessional team, including primary care providers, wound care specialists, surgeons, specialty-trained wound nurses, physical therapists, and nurses aides. Nurses provide care, monitor patients, and notify the team of issues. Nurses aides are often responsible for turning and repositioning patients. Air-fluidized or foam mattresses should be used, frequent postural changes, provision of adequate nutrition, and treatment of any underlying systemic illnesses. Debridement should take place to remove dead tissue that serves as the optimum medium for the growth of bacteria. Hydrogels or hydrocolloid dressing should be used, which aid in wound healing. Tissue cultures are necessary, so the most directed antibiotic can be administered, which can involve the pharmacist and the latest antibiogram data. The patient should be kept pain-free by giving analgesics. They should try to increase physical activity if possible, which a nurseâs aide, medical assistant, or rehab nurse can facilitate. Frequent follow-ups are an absolute necessity and a team approach to patient education and management involving the wound care nurse and wound care clinician will lead to the best results. These interprofessional activities can help drive better outcomes for patients with decubitus ulcers.
Donât Miss: How To Get Rid Of Stomach Ulcer Pain
Pressure Ulcer Icd 10 Diagnosis
When admitted to an acute or chronic hospital, patients must undergo a thorough skin examination to determine whether they have developed a pressure ulcer ICD 10 and whether they have symptoms of previous pressure ulcer ICD 10 . The assessment of the skin can be done with various tools, but the most common is the use of the Braden scale. This assessment includes the presence of previous ulcers and an assessment of the risk of developing pressure ulcer ICD 10.
The scale checks the following sensory parameters:
- sensation of the skin
- assessment of friction forces
- shear forces on the affected skin
The Braden scale is rated by a factor of 1 to 4, with the exception of frictional shear, which has three points on its scale. Points are added up to get a score.
The highest possible Braden score is 23. A patient with a score of 18 or less is considered at risk for pressure ulcer ICD 10. The general health and nutritional status of the patients are also assessed. Particular care is required to prevent pressure-related skin changes and risks. If the patient has a pressure ulcer ICD 10, it should be an ulcer that can be documented with photographic evidence.
Read Also: What Does Ulcerative Colitis Affect
Whats The Icd 10 Code For An Open Wound
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized head to toe into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code S31.000: These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used.
Pressure Ulcer Icd 10 Symptoms
Early symptoms of a pressure ulcer ICD 10 include discoloration of skin. People with pale skin tend to have red spots and people with darker skin tend to have purple or blue spots.
Category 1 Pressure Ulcer ICD 10: Discolored stains may or may not turn white when pressed. The skin can feel warm and spongy. Pain or itching may occur in the affected area. Doctors and nurses refer to pressure ulcer ICD 10 at this stage as category 1 pressure ulcer ICD 10.
Category 2 Pressure Ulcer ICD 10: If the skin does not collapse, but the ulcer worsens, it may form an open wound or blister.
Category 3 Pressure Ulcer ICD 10: When the deep wound reaches deep into the skin layers.
Category 4 Pressure Ulcer ICD 10: When it reaches the muscles and bones.
Recommended Reading: What Medicine Is Good For Stomach Ulcer
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis Back Pain Treatment
Pressure Ulcer Icd 10 Causes
The three most important factors that contribute to bedsores are:
- Pressure: Ulcers are caused by pressure on the skin limiting blood flow to the skin. Constant pressure on any part of the body reduces blood flow to the tissues.
- Limited exercise: Lack of blood flow makes the skin more susceptible to damage that leads to the development of bedsores. Blood flow is crucial for supplying the tissue with oxygen and other nutrients. Without these nutrients, the skin and nearby tissues can be damaged and die.
- Friction:Friction occurs when the skin rubs against clothing or bed linen. Friction makes sensitive skin more susceptible to injury, especially when the skin is moist. Shearing occurs when two surfaces move in opposite directions. In people with reduced mobility, this type of pressure tends to occur in non-padded areas such as muscles, fat and low-lying bones such as the spine, coccyx, shoulder blades, hips, heels and elbows. For example, if the bed is lifted, the patients head slips onto the bed. When the tailbone moves, the skin around it stays in place but is pulled in the opposite direction. They are most common in bony parts of the body such as heels, elbows, hips and the base of the spine. They usually develop and form within a few hours.
Audit Considerations & Strategies
- The original coder did not code the pressure ulcer excision. Adding either the right or left hip excision would drive the case from a medical DRG to a surgical DRG
- The procedure code may have been overlooked because the surgeon documented that the tissue was excised rather than documenting that an excisional debridement was performed
- Documentation of excision or excised is sufficient to code PCS root operation: Excision
- Always carefully review the entire medical record including the Progress Notes for bedside procedures, especially for patients with pressure ulcers
- Per Coding Clinic1, the body part value for an excisional debridement performed on a muscle in the sacral region is the Hip muscle. If the documentation specifies that the right side or left side of the sacral ulcer was debrided, then a single code can be assigned. If the documentation does not specify laterality, assign codes for both the right and left hip muscles.
- Since only excision of sacral pressure sore was noted, both the 0KBN0ZZ and 0KBP0ZZ codes were assigned
- Coding Clinic likely allows coders to assume both the right and left hip muscles when laterality is not specified because sacral pressure ulcers often develop on the lower back which would include portions of the left and right hips
- Cases with a principal diagnosis of stage 3 or 4 pressure ulcer automatically result in DRG 592: Skin ulcers with MCC
- ICD-10 only requires one code to be assigned for the pressure ulcer and stage
Reference
Don’t Miss: Booties To Prevent Pressure Ulcers
Q& A: Clarifying New Guidance For Pressure Ulcers Deep
Q: Our coding department was told there were changes made for fiscal year 2020 when it comes to reporting healed/healing pressure ulcers and pressure-induced deep tissue damage. Can you explain any recent updates?
A: You are right, there have been updates to guidance surrounding these diagnoses.
First, the FY 2020 ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting have additional clarity on patients admitted with pressure ulcers documented as healed. The guidelines added the phrase at the time of admission. The guidelines now state that there is currently no code assignment for pressure ulcers that are completely healed at the time of admission.
In contrast, if the pressure ulcer is documented as healing but not yet healed, the coder is to code the pressure ulcer to the appropriate pressure ulcer stage at the time of admission. Meaning, if the pressure ulcer was to the bone but improves during the stay to only include the depth of the subcutaneous tissue , the pressure ulcer is to be reported as a stage 4 pressure ulcer, not a stage 3.
If a pressure ulcer was present on admission and is healed at the time of discharge, the site and stage of the pressure ulcer at the time of admission should be reported. Remember, healed at the time of admission is the only time a pressure ulcer would not be reported, because it no longer exists.
- L89.126, pressure-induced deep tissue damage of left upper back
- L89.156, pressure-induced deep tissue damage of sacral region
What Is The Icd Code For A Tailbone Pressure Ulcer
Pressure ulcer of coccyx Pressure ulcer of tailbone ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for L89.15 Pressure ulcer of sacral region The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code L89.15.
What is the ICD 9 cm diagnosis code for 2012?
Free, official information about 2012 ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 707.03, including coding notes, detailed descriptions, index cross-references and ICD-10-CM conversion.
Recommended Reading: What To Eat To Help Ulcers
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Pressure Ulcers
Treatment of Stage 3 and Stage 4 Pressure UlcersPatient should be repositioned with consideration to the individual’s level of activity, mobility and ability to independently reposition. … Keep the skin clean and dry.Avoid massaging bony prominences.Provide adequate intake of protein and calories.More items…
L899 Pressure Ulcer Of Unspecified Site
Pressure ulcer of unspecified site, unspecified stage
Pressure ulcer of unspecified site, stage 1
Pressure ulcer of unspecified site, stage 2
Pressure ulcer of unspecified site, stage 3
Pressure ulcer of unspecified site, stage 4
Also Check: Is Milk Good For Ulcers
Pressure Ulcer Of Unspecified Site Stage 4
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- L89.94 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L89.94 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L89.94 other international versions of ICD-10 L89.94 may differ.
- Healing pressure ulcer of unspecified site, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer with necrosis of soft tissues through to underlying muscle, tendon, or bone, unspecified site
- Applicable To annotations, or
Read Also: How To Use Aloe Vera Gel For Ulcerative Colitis
What Is A Stage 4 Sacral Wound
Stage 4 bedsores are the most severe form of bedsores, also called pressure sores, pressure ulcers, or decubitus ulcers. A stage 4 bedsore is characterized by a deep wound that reaches the muscles, ligaments, or even bone. They often cause residents to suffer extreme pain, infection, invasive surgeries, or even death.
Don’t Miss: I Think I Have An Ulcer In My Stomach
Can Bedsores Lead To Sepsis
What is the ICD-10 code for bed sores?
ICD-10-CM category L89 codes classify pressure ulcers, also known as bed sores, pressure sores or decubitus ulcers. Pressure ulcers are wounds caused by unrelieved pressure on the skin.
When do you code sepsis first?
When sepsis is present on admission and due to a localized infection , the sepsis code is sequenced first followed by the code for the localized infection.
What is the ICD code for a debridement sacral wound?
Postoperative And Rehabilitation Care
Postoperative care of patients who have undergone reconstructive surgery is of utmost significance as these ulcers have high rates of recurrence. A study done on characteristics of recurrent pressure ulcers showed that patients who underwent reconstructive surgery and developed post-operative, had an 11% to 19% chance of recurrence. Those without any postoperative complications had recurrence as high as 61%.
When medical staff shift patients from the operating table to their air-fluid beds, they must avoid excessive shearing, and stretch on skin flaps. For the first four weeks, patients are positioned flat on their support surfaces, after which they can place themselves in a semi-sitting position. The patient starts to sit for 10 minutes only after six weeks of the surgical procedure. After these sitting periods, the flap should be examined for discoloration and wound edge separation. Over two weeks, the sitting periods will increase to 2 hours in 10-minute increments. Patients will also learn to lift for 10 seconds every 10 minutes to relieve pressure. Meticulous skincare is necessary.
Recommended Reading: Snack Ideas For Ulcerative Colitis
Don’t Miss: Ulcerative Colitis Treatment In Elderly
L893 Pressure Ulcer Of Buttock
Pressure ulcer of unspecified buttock
Pressure ulcer of right buttock
Pressure Ulcer Of Other Site Stage 4
- 20162017201820192020202120222023Billable/Specific Code
- L89.894 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM L89.894 became effective on October 1, 2022.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L89.894 – other international versions of ICD-10 L89.894 may differ.
- Healing pressure ulcer of other site, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer with necrosis of soft tissues through to underlying muscle, tendon, or bone, other site
- Applicable To annotations, or
Recommended Reading: What’s The Difference Between Colitis And Ulcerative Colitis
Factors That Influence Sacral Ulcer Management
While wound management is a key part of sacral ulcer management, treating patients holistically is the key to success. Apart from ischemia, other factors that impede normal healing include poor nutrition, infection, edema, persistent moisture, fecal and urinary soiling, and shearing forces. One can look for, prevent, or minimize each of these risk factors. Of course, the patient should be frequently repositioned to avoid further tissue damage and to promote healing.
When selecting a dressing, the wound should be kept moist but not contain excessive amounts of exudate. Wound care professionals should consider the type of ulcer and any comorbid conditions that could complicate treatment . Arterial wounds generally require a moisture-retaining dressing, while wounds that arise from venous insufficiency usually require a dressing that absorbs excess moisture. All surfaces of the wound, including any tunnels, should be packed with the appropriate dressing.
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region Stage 4l89154
Chapter 12 – Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Other disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 4
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Read Also: Is Ulcerative Colitis Same As Crohn Disease
Diseases Of The Skin And Subcutaneous Tissuetype 2 Excludes
- Pressure ulcer of left foot stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of left lower leg stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of left toes, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of lower leg stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of right foot stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of right lower leg stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of right toes, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer of toes stage 4
- Pressure ulcer stage 4 of left lower leg
- Pressure ulcer stage 4 of lower leg
- Pressure ulcer stage 4 of right lower leg
- Pressure ulcer stage 4 of toes
- 573 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis with mcc
- 574 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis with cc
- 575 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis without cc/mcc
- 592 Skin ulcers with mcc
- 593 Skin ulcers with cc
- 594 Skin ulcers without cc/mcc