Pharmacologic Management Of Ibd In The Setting Of Comorbidities
A particular challenge in the management of elderly IBD patients is selection and continuation of therapy in the setting of comorbidities and polypharmacy. For example, poor lung function in patients with comorbid chronic obstructive pulmonary disease may make an IBD patient more susceptible to developing pneumonia or have more severe outcomes as a consequence. Other conditions become more prevalent in the elderly population, including cardiovascular disease and diabetes, presenting distinct challenges for clinicians who manage patients with comorbid IBD. For example, patients with diabetes mellitus and ulcerative colitis share a host of complications including peripheral neuropathy, reduced bone density, infection, and thromboembolism that challenge both diagnosis and treatment.
Ultimately, minimizing unnecessary pharmacologic exposure that might exacerbate a comorbid condition is essential in all patients. The presence of comorbid conditions necessitates close collaboration among treatment providers for coordinated decision-making and optimal outcomes.
Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis
Changes in Lifestyle
The first thing you need to do if you are suffering from a colitis infection or ulcerative colitis is getting rid of unhealthy habits and adopting healthy ones. You do not exactly need to follow a certain diet plan for your remission of ulcerative colitis, but not consuming foods that you think inflame your gut is the first step to adopting a healthy lifestyle.
For some people, keeping a food journal helps. This way, they can keep a track of their meals and figure out what causes them rectal cramps or bloody diarrhea. Skipping fatty and high fiber meals, and replacing them with small, frequent portions of food high in probiotics will greatly reduce inflammation.
People with ulcerative colitis or UC get dehydrated easily as their large intestine does not do the best job at reabsorbing water and nutrients. Set a goal to drink enough water each day so you can go through your day without feeling symptoms of dehydration. Try using an electrolyte replacement or a meal replacement drink to control your stool symptoms of ulcerative colitis immediately.
Medical Therapyeffectiveness And Persistence
Every type of drug, from mesalazine through steroids, immunomodulators, and biotechnological therapies, used in adult UC are also indicated in older patients with UC limitations and contraindications depend on coexisting comorbidities. There is a lack of specific studies addressing efficacy of mesalazine, steroids, especially low bioavailability steroids, or immunomodulators in the older UC population. As shown by Kochar et al. in a recent systematic review , < 1% of patients included in randomized clinical trials were 65 years. The evidence reported in literature in real-life studies concerning effectiveness of available therapies and persistence in therapy is therefore summarized in Table Table2,2, divided into late-onset and older patients with long-standing disease .
Also Check: Is Flaxseed Good For Ulcerative Colitis
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Postoperative Complications And Prognosis After Surgical Treatment

It is generally recognized that older age regardless of disease is an independent risk factor for surgical mortality and morbidity . However, some cohort studies of patients with UC have suggested that those were similar among several age groups . Nevertheless, it is commonly agreed that infectious complications and venous thrombosis, known to be increasing in older patients regardless of surgical treatments, must be considered during treatment for UC . Although pouch surgery for UC has been shown to be safe, and surgical morbidity and mortality are similar regardless of age, emergent surgery and concomitant complications with other systematic diseases, such as heart disease or pulmonary disease, are shown to be prognostic factors in the surgical treatments for older patients . In a study conducted in Japan, surgical mortality in the older group who received an emergency procedure was at a rate of 26.7% within 30 postoperative days , though surgical morbidity and mortality were similar between patients of older age and younger age.
In conclusion, the rates of surgical morbidity and mortality may be increasing in older patients with UC in association with the method of surgical procedure, or concomitant complications with other systematic diseases. Notably, it is important to highlight that emergency surgery for older patients elevates the risk for surgical morbidity and mortality.
You May Like: What Can I Take For Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Living With Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
Your ulcerative colitis symptoms will likely come and go, with longer periods in between flares when you may not experience any discomfort at all. Those periods are called remission, and they can span months or even years. Because there is not yet a cure for ulcerative colitis, your symptoms will eventually return.
Ulcerative colitis is an unpredictable disease, and the length of periods of remission between flares can make it difficult for doctors to evaluate whether your course of treatment has been effective or not.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure A Bleeding Ulcer
Layers Of The Bowel Wall
The walls of your bowel have layers. The inner layers take in nutrients from food. The outer layers help move food through the gut and waste out of the body.
In Colitis, theres inflammation and swelling of the inner layer of the bowel wall. This can cause bleeding. More mucus may be produced by the inner layer of the bowel wall. Ulcers develop on the inner layer as the condition gets worse, but they can also go as the condition gets better.
The inflammation in Colitis affects how your body digests food, absorbs nutrients and gets rid of waste.
Everyone experiences Colitis differently. When youre having symptoms, its known as active disease, a flare-up or relapse. Symptoms may be mild or severe and are likely to change over time.
Your symptoms may vary depending on where Colitis is active in your bowel and how severe it is. Find out more in the section Types of Colitis.
The most common symptoms are:
Andy
Living with Colitis
Recommended Reading: Can Stomach Ulcers Cause Blood In Urine
When To See A Doctor
For people with ulcerative colitis, it can be challenging to know which symptoms are an emergency, which should prompt a call to the gastroenterologist, and which can wait.
After doing well and having few or no symptoms, when symptoms begin again, it is a reason to call the doctor and get evaluated for a potential flare-up. It may be necessary to change treatments or adjust the current care plan in order to get any inflammation under control quickly.
Ulcerative Colitis Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctors appointment to help you ask the right questions.
In general, symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, excessive bleeding, and signs of dehydration are a reason to seek medical care right away. When possible, calling the gastroenterologist before going to the hospital might help in deciding what level of care is needed.
However, if treatment is needed right away, going to the emergency department may be the best choice. If a serious condition such as a bowel perforation or toxic megacolon is suspected, it may be necessary to call 911, because these are medical emergencies.
Dont Miss: Is Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis The Same Thing
Iatrogenic Complications Adverse Drug Reactions And New Pathologies
Despite the similar use of steroid therapy in the two groups, iatrogenic complications were more common in the elderly . In particular, the most frequent ones were steroid diabetes and osteoporosis .
Unexpectedly, adverse drug reaction were less common in the elderly . . However, if we exclude patients on biological therapy, they were similar in the two groups . Globally, 10 adverse drug reactions developed in the elderly and 16 in the adult group, and the most frequent ones were skin reactions.
Fig. 3
During follow up, some conditions typical of old age were considered. A higher number of elderly patients developed cognitive impairment . Malignancy , deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism , myocardial infarction , stroke and depression were also more frequent .
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Ulcers
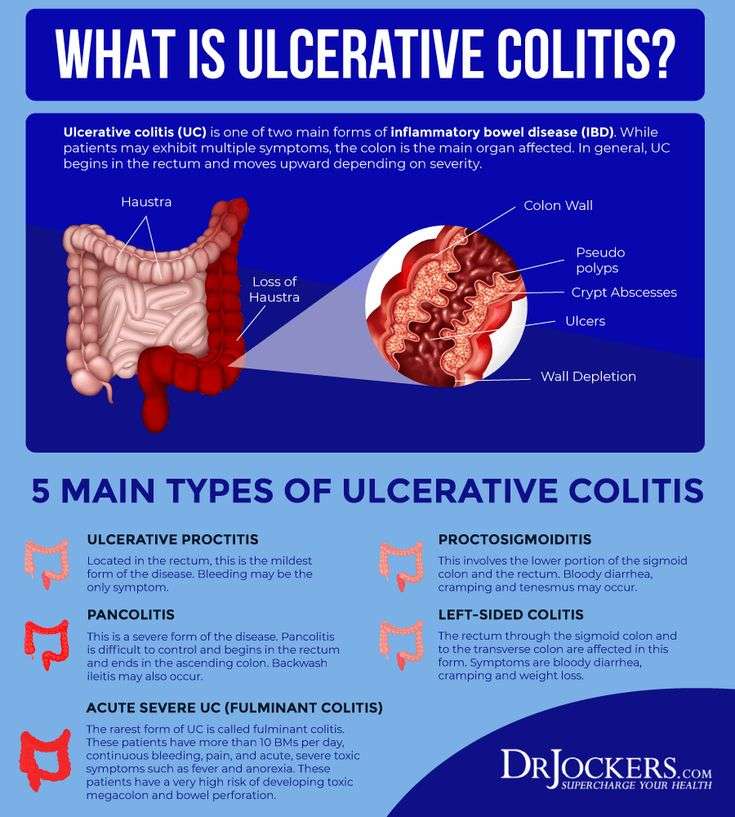
What Is Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease in which the lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed.
The colon then develops ulcers that produce blood, pus, and mucus.
The small intestine is rarely affected.
There are several subtypes of ulcerative colitis, which are named according to the part of the colon affected:
- Ulcerative proctitis, which affects only the rectum
- Proctosigmoiditis, which affects the rectum and lower segment of the colon
- Left-sided colitis, which affects the rectum, sigmoid colon, and descending colon up to the sharp bend near the spleen
- Pan-ulcerative or total colitis, which affects the entire colon
Why Are Cases Of Uc Increasing In Older Populations
There are several factors that could explain why the incidence of UC is increasing in the older population.
Cases may be increasing because doctors are better able to diagnose UC. Cases of UC in older populations are increasing at a faster rate in higher-income urbanized environments, so better access to healthcare can partially explain this phenomenon.
However, people who live in cities and densely populated towns also tend to eat a more westernized diet, which is high in saturated fat and refined carbohydrates. When people routinely eat these types of foods, they disturb their microbiota and increase their risk of UC.
Other environmental factors that can increase a persons UC risk include air pollution, lack of sleep and exercise, and high stress levels.
You May Like: Do Tums Help Ulcerative Colitis
Indications For Surgery & Surgical Risk
Additionally, approximately, 25% of all intestinal surgeries for IBD are performed in patients 55 years old.19 Most of the surgeries for older patients with IBD are elective,20 with disease progression through medical management being the most common indication.21,22 Improving the quality of daily living over long-term sequelae of the disease is paramount and consultation with a surgeon before progression of the disease may allow the patient to make a better-informed decision about continuing medical therapy versus surgery.14 Unlike the young population, procedural risk must be balanced with cancer surveillance with age over 75 years as an additional risk factor for hospitalization after endoscopy.11,23 E-IBD patients are more than twice as likely to suffer from surgical complications, with an increased hospital length of stay compared to younger patients.24 Dysplasia and cancer are major concerns in the elderly population and are frequent reasons for surgery in some UC series.25
Efficacy Of Medical Therapy For Elderly Uc Patients
Despite a few reports comparing the efficacy of individual medical treatments in non-elderly UC patients to that in elderly UC patients, there is no clear evidence that the efficacy obtained in non-elderly UC patients cannot be expected in elderly UC patients . Therefore, all medical treatments are thought to be potential treatment options in elderly UC patients as well. In fact, medical treatments used in non-elderly UC patients are also selected for elderly UC patients in Japan .
However, when considering medical treatments in elderly UC patients, one should pay attention to the interaction between comorbid diseases and their treatments furthermore, a treatment needs to be decided whilst considering the characteristics of each patient, including susceptibility to infection and cancer risk. In fact, the frequency of adverse events such as infection and tumorigenesis is high in elderly UC patients who are treated with corticosteroids, thiopurine agents, or biological agents, and careful attention should be paid when administering these drugs . Therefore, when selecting a medical treatment for elderly UC patients, risks associated with treatment should be considered on a case-by-case basis, especially as many new treatment options for IBD become available in the future dosages may have to be kept low in elderly UC patients and one should note that the efficacy may consequently decrease.
Don’t Miss: Foods For Acid Reflux And Ulcers
What Are The Possible Complications Of Colitis
Complications usually result from severe, long-term, chronic colitis. They can include:
- Perforation. Chronic inflammation weakens your colon walls, making them more likely to rupture. An ulcer in your colon may wear a hole all the way through. This can cause bacteria from your colon to infect your abdominal cavity and possibly your bloodstream , which would be especially dangerous. Septicemia can lead to .
- Toxic megacolon. Severe inflammation can cause the walls of your colon to dilate and interfere with its natural muscle contractions . This can trap food and gas in your colon . Obstruction leads to painful abdominal distension and an increased risk of rupture.
- Increased risk of colon cancer. Long-term inflammation is associated with cellular changes in your colon wall that can sometimes progress to cancerous changes. The risk increases rapidly after the first decade of chronic colitis.
- Increased risk of other inflammatory diseases. People with inflammatory bowel diseases are more likely to have other inflammatory diseases in other parts of their bodies. Some examples include osteoarthritis and primary sclerosing cholangitis . It appears that uncontrolled inflammation in one area may trigger a similar process somewhere else.
Also Check: Pressure Ulcer Wound Care Dressings
Selection Of Surgical Procedure
In elderly UC patients with impaired sphincter function or lower ADL, total colectomy+IRA or TPC is usually selected in consideration of postoperative functional outcomes. Stapled IPAA and IRA preserve the diseased mucosa therefore, it is important to pay attention to the risk for relapse or cancer . In the case of emergent surgery with poor general conditions, less invasive surgical procedures such as subtotal colectomy with end ileostomy, mucous fistula of the sigmoid colon, or Hartmanns operation should be selected first . Surgical procedures accompanied with stoma construction are more often selected in elderly UC patients compared with non-elderly UC patients .
Read Also: What Foods Irritate An Ulcer
Outlook For People With Ulcerative Colitis
If you have UC, a doctor will need to monitor your condition, and youll need to carefully follow your treatment plan throughout your life.
The only true cure for UC is removal of the entire colon and rectum. Your doctor will usually begin with medical therapy unless you have a severe complication that requires surgery. Some people will eventually require surgery, but most do well with nonsurgical therapy and care.
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medicine, such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. But more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital.
If medicines are not effective at controlling your symptoms or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
Don’t Miss: Budesonide Uceris For Ulcerative Colitis
Frailty In Ibd Trials
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.Clin Geriatr Med.Eur J Intern Med.Circ Res.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.Inflamm Bowel Dis.Curr Opin Immunol.J Crohn’s Colitis.
- Ananthakrishnan AN
Gastroenterology.
J Crohn’s Colitis.J Crohn’s Colitis.
- Ananthakrishnan AN
Gastroenterology.Aliment Pharmacol Ther.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
Dig Dis Sci.
Am Surg.Surgery.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.Gastroenterology.
- Ananthakrishnan AN
Dig Dis Sci.Lancet.J Am Med Dir Assoc.
Eo As A Factor Associated With The Long
Next, we investigated the factors associated with clinical remission or steroid-free remission after 8 and 52 weeks of anti-TNF treatment in patients with IBD by multivariate analyses. At 8 weeks, a C-reactive protein level of less than 0.30 mg/dl at week 0 was extracted as a significant factor for both clinical remission and steroid-free remission . Interestingly, after 52 weeks of anti-TNF treatment, EO and UC were extracted as a significant factor for clinical remission . In addition, EO and concomitant corticosteroid were extracted as a significant factor for steroid-free remission .
Table 2 Multivariate analysis of factors for clinical or steroid-free remission after 52 weeks of anti-TNF treatment .
Also Check: What Does A Duodenal Ulcer Feel Like
Ibd Looks Different In Older Adults
Hundreds of thousands of people whose IBD was diagnosed earlier in their lives are now living with the disease in older age. For many that means living with the damage the disease has done to their intestinal tract, and sometimes with the altering impacts of surgery done to manage it, such as ostomy pouches or increased incontinence. Not to mention continued flare-ups.
It used to be commonly thought that disease activity tapered off in older age, and some people do find their IBD becomes inactive later in life. But that isnt always the case, says Cleveland Clinic gastroenterologist Dr. Jessica Philpott. I certainly see some patients who develop more aggressive disease as they advance in age, she says.
For individuals who get IBD after they turn 60, the disease can look somewhat different than for those who have had it for decades. Whereas younger Crohns patients can have damage in any part of their intestinal tract, in older-onset cases it more often primarily affects the colon.
And because older adults have often already faced more health issues, they might not seek medical help as promptly. Crohns in particular can be trickier to pinpoint than ulcerative colitis, as it might present as intermittent abdominal pain and weight loss, which arent uncommon in older adults generally. These factors can sometimes delay proper diagnosis, and thus effective treatment, by years.