How Is Ibd Diagnosed
- A combination of endoscopy or colonoscopy and imaging studies, such as:
- Contrast radiography.
- Types of common medications to treat IBD:
- 5-aminosalicyclic acids.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Are You Struggling With Crohns Disease Ulcerative Colitis Or Celiac Disease
Are you or a loved one struggling with an inflammatory bowel condition? If so, the good news is, youre not at the mercy of your diagnosis. While we may not be able to cure these conditions, you have so much power over your own health. I cant overemphasize the importance and influence your diet, supplements, and lifestyle factors can have on your inflammation levels and symptoms.
So if youre ready to take your power and health back from one of these inflammatory bowel conditions, I recommend starting with the steps outlined in this article and seeking out the guidance of an experienced Integrative and Functional Medicine Practitioner. Theyll help you identify the root cause of your condition and come up with a personalized plan of action to begin healing.
And if youre hungry for more practical and research-backed tips on optimizing your health, you can head over to my blog and catch up on hundreds of articles that simplify healthy living.
You May Like: Medications Used For Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnosing Inflammatory Bowel Disease
To diagnose Crohns disease or colitis, we start with a comprehensive examination and collecting a thorough history. A number of tests are needed to confirm diagnosis. They may include:
- Colonoscopy and flexible sigmoidoscopy: Used for initial diagnosis, both use a thin, flexible tube with camera to examine different areas, including the colon, small intestine and large intestine to see any ulcers, bleeding and inflammation.
- Upper endoscopy: Uses a thin, flexible tube with camera inserted through the mouth, following the tract to the stomach and upper small intestine to look for bleeding, ulcers and inflammation.
- Capsule endoscopy: A capsule containing a camera is swallowed by the patient to take pictures along the digestive tract not easily reachable by other procedures .
- Laboratory tests: Blood work plus stool samples to check for bacteria and intestinal bleeding.
- CT interography and MR interography: Specialized radiology tests that evaluate the small intestine, an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is beyond the reach of colonoscopy and upper endoscopy, but is often where Crohns disease is present.
- Imaging tests: Collaborating with experts in Radiology for imaging and interpreting gastrointestinal abnormalities, including abdominal x-rays, barium enema, computed tomography , fistulogram and MRI.
Recommended Reading: What Can Cause Ulcers In Your Mouth
What Are Nonsurgical Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatments
IBD treatments vary depending on the particular type and symptoms. Medications can help control inflammation so you dont have symptoms . Medications to treat IBD include:
- Aminosalicylates minimize irritation to the intestines.
- Antibiotics treat infections and abscesses.
- Biologics interrupt signals from the immune system that cause inflammation.
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, keep the immune system in check and manage flares.
- Immunomodulators calm an overactive immune system.
You may also benefit from these over-the-counter IBD treatments:
- Antidiarrheal medication.
- Vitamins and supplements like probiotics.
What Is The Prognosis For People With Crohns Disease
Most people with Crohns disease enjoy healthy, active lives. While there isnt a cure for Crohns disease, treatments and lifestyle changes can keep the disease in remission and prevent complications.
Lifestyle changes can include changes to your diet. People with Crohns disease often need to adapt their diets so that they get enough calories each day. Lactose intolerance can also be an issue for those with Crohns disease. You may need to avoid certain dairy products if you find that youre having issues with this dietary intolerance. You should also avoid smoking if you have Crohns disease. Smoking can only make your condition worse.
Your healthcare provider might recommend you receive preventative colonoscopies after youre diagnosed with Crohns disease. Talk to your provider about how often you should have colonoscopies and what your risks are for other medical conditions.
Also Check: How To Heal Ulcers Fast
Complications Caused By Nutritional Deficiencies
Some of the complications of malnutrition include:
- Dehydration diarrhoea causes your body to lose fluid, which can lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia reduced iron in the diet combined with losing blood from the bowel can lead to anaemia .
- Weight loss reduced appetite and poor absorption of food nutrients can cause weight loss.
- Reduced growth inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can impair a childs growth and physical development.
Diagnosis And Assessment Of Disease Activity
The diagnoses of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are made on clinical grounds supplemented with objective findings of radiological, endoscopic, and histological examination. In some cases, the diagnostic evaluation must be repeated after a certain period of time has passed. There is no gold standard for diagnosis . When establishing the diagnosis, one must exclude other inflammatory, toxic, vascular, neoplastic, and infectious etiologies of enteritis and/or colitis .
Dont Miss: Ulcers On Legs From Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Is Olive Oil Good For Ulcerative Colitis
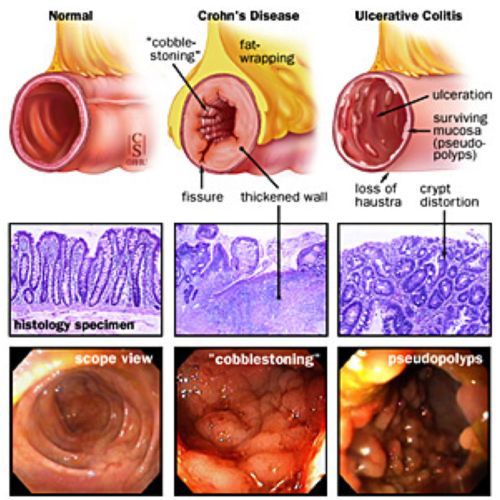
What Is Crohns Disease What Is Ulcerative Colitis How Are They Different And What Are Their Symptoms
There are two forms of IBD, Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Doctors distinguish between the two by determining what parts of the digestive tract have become inflamed and how many layers of the bowel wall are affected. Crohns disease, the more serious of the two, most commonly affects the end of the small bowel, but it can show up in any part of the gastrointestinal tract.
In contrast, ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon. And while ulcerative colitis causes inflammation to the innermost lining of the colon, Crohns can affect the entire thickness of the bowel wall.
How Can I Tell If I Have Ulcerative Colitis Or Crohns Disease
Its important that you, your healthcare provider, and a GI specialist work together closely to figure out whats causing your symptoms. This is especially important since the symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis can be similar. Your providers may check blood work and a stool sample. To get an accurate diagnosis, your GI specialist may do a colonoscopy, where a camera is pushed into the colon. Your provider will look at the inside of the colon and take tissue samples, which are important for making the right diagnosis. Your providers might get a CT scan or an MRI of your abdomen to check for complications related to your condition.
Don’t Miss: Hydrocolloid Dressing For Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have Crohns disease, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get Crohns disease?
- What form of Crohns disease do I have?
- Whats the best treatment for this disease type?
- How can I prevent flare-ups?
- If I have a genetic form, what steps can my family members take to lower their risk of Crohns disease?
- Should I make any dietary changes?
- What medications should I avoid?
- Should I take supplements?
- Should I get tested for anemia?
- Do I need to cut out alcohol?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Crohns disease flare-ups are unpredictable and can disrupt your daily life. Talk to your healthcare provider about the steps you can take to keep the disease in check. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage symptoms, avoid complications and live an active life.
Key Differences: The Symptoms
While the two diseases are similar, there are also a few notable differences that set them apart including some of their symptoms and where the inflammation develops. Only a health professional will be able to determine which type of IBD you have, so its important to explain all your symptoms to your doctor or GI specialist.
While their symptoms may seem similar on the surface, Everyday Health points out that ulcerative colitis is mostly characterized by blood stool with mucus and frequent diarrhea, whereas Crohns disease is often marked by nausea, weight loss, and vomiting, with only occasional rectal bleeding, and diarrhea. Crohns can also cause mouth sores, or inflammation of the skin, joints, and eyes which are not symptoms of ulcerative colitis.
Read Also: Best Smoothies For Ulcerative Colitis
Don’t Miss: What Can Cause Ulcerative Colitis Flare Ups
What Are The Main Types Of Ibd
| Crohns Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Location | Can affect any part of the GI tract Most often it affects the portion of the small intestine before the large intestine/colon. | Occurs in the large intestine and the rectum. |
| Damaged Areas | Damaged areas appear in patches that are next to areas of healthy tissue. | Damaged areas are continuous usually starting at the rectum and spreading further into the colon. |
| Inflammation | Inflammation may reach through the multiple layers of the walls of the GI tract. | Inflammation is present only in the innermost layer of the lining of the colon. |
Distinct Phenotype Of Peripheral Blood Pdc In Cd And Uc
Because we hypothesize that DC from IBD patients may induce and/or perpetuate inflammation, we investigated their native phenotype. We were particularly interested in their expression of co-stimulatory molecules. Expression of CD40 and CD86, two co-stimulatory molecules known to be up-regulated on mature, activated DC and critical for T cell activation was studied .
CD40
In UC, the fraction of CD40 expressing pDC was higher in UC patients in RM and reached statistical significance in acute FUs compared with controls . In CD, the fraction of CD40 expressing pDC was comparable between controls and CD patients in RM . However, the fraction of CD40 expressing pDC was significantly higher in flaring patients compared with controls .
Distinct phenotype of peripheral blood plasmacytoid dendritic cells in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. CD40: increased fraction of CD40 expressing pDC in flaring UC and CD patients compared with controls . CD86: increased fraction of CD86 expressing pDC in flaring UC and CD patients compared with controls . FACS plots from representative experiments. Quadrant thresholds were placed determined according to isotype controls. Asterisks denote statistical significance: **P< 0·01 ***P< 0·001.
CD86
CD83 and CD197
Overall, the fractions of CD83 and CD197 expressing pDC were very low and did not allow meaningful statistical comparisons .
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Mouth Ulcer
Types Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, is a condition in which there is chronic or recurring inflammation of the gastrointestinal, or GI, tract. In a type of IBD called ulcerative colitis, the condition is limited to the colon, also known as the large intestine. In another type known as Crohns disease, the condition most commonly affects the small intestine and colon, but it can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract.
Doctors at NYU Langones Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center use advanced diagnostic techniques to identify the type of IBD that is causing your symptoms and recommend the appropriate medical or surgical treatment to alleviate symptoms and achieve remission.
The cause of IBD is not known, but research suggests that in people with the condition, the bodys immune system may perceive food, bacteria, and other substances in the intestines as a threat. In response, the immune system sends white blood cells to the intestines, causing inflammation that triggers abdominal pain and other symptoms.
In addition, IBD prevents the intestines from absorbing essential nutrients in digested food, which can lead to malnutrition.
IBD can run in families, and men and women are diagnosed in equal numbers. Most people receive the diagnosis between the ages of 15 and 30. However, the condition can develop at any age.
Both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis often require lifelong medical treatment and monitoring to keep the disease and its symptoms under control.
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
The differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are:
- In Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is continuous inflammation of the colon
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls
Read Also: How To Treat Stomach Ulcers From Stress
What Are Surgical Treatments For Crohns Disease
As many as 7 in 10 people with Crohns disease eventually need surgery when medications no longer provide symptom relief. During a bowel resection, a surgeon:
- Removes the diseased bowel segment.
- Connects the two ends of the healthy bowel together .
After surgery, the remaining part of the bowel adapts and functions as it did before. Approximately 6 in 10 people who undergo surgery for Crohns disease will have a recurrence within 10 years. Another bowel resection may be a good option for you.
What Are The Differences And Similarities Between The Signs And Symptoms Of Crohn’s And Ulcerative Colitis
Differences between symptoms and signs of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
There are a few differences in the symptoms between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Frequently, doctors cannot diagnose the cause of either disease by symptoms alone. However, for people with ulcerative colitis, the abdominal pain is often confined to the left side of the abdomen, while Crohn’s disease may have abdominal pain anywhere in the abdomen.
Similarities between symptoms and signs of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have many similar symptoms.
Doctors and researchers do not know what causes both diseases, but they speculate that several factors such as genetics, heredity, mucosal immunity, gut microbes, diet, environmental factors, vascular problems, psychosocial problems, and certain drugs may be triggers that may participate in causing these diseases.
Because the diseases have unknown causes, it is difficult to know what triggers their development. However, if you carefully note in a diary when symptoms reappear in Crohn’s disease orworsen in ulcerative colitis, you may be able to identify triggers that affect your disease.
Don’t Miss: Can Mold Cause Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Crohn’s Disease Diagnosed
Most people with Crohns first see a healthcare provider because of ongoing diarrhea, belly cramping or unexplained weight loss. If you have a child who has been experiencing the symptoms of Crohns disease, reach out to your pediatrician.
To find the cause of your symptoms, your healthcare provider may order one or more of these tests:
- Blood test: A blood test checks for high numbers of white blood cells that may indicate inflammation or infection. The test also checks for low red blood cell count, or anemia. Approximately one in three people with Crohns disease have anemia.
- Stool test: This test looks at a sample of your stool to check for bacteria or parasites. It can rule out infections that cause chronic diarrhea.
- Colonoscopy: During a colonoscopy, your doctor uses an endoscope to examine the inside of your colon. Your doctor may take a tissue sample from the colon to test for signs of inflammation.
- Computed tomography scan: A CT scan creates images of the digestive tract. It tells your healthcare provider how severe the intestinal inflammation is.
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: Your doctor threads a long, thin tube called an endoscope through your mouth and into your throat. An attached camera allows your doctor to see inside. During an upper endoscopy, your doctor may also take tissue samples.
- Upper gastrointestinal exam: X-ray images used during an upper GI exam allow your doctor to watch as a swallowed barium liquid moves through your digestive tract.
Overview Of Crohns Disease
Crohns disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract. Understanding Crohns disease can help you and your loved ones navigate the uncertainty that comes with a new diagnosis.
Calling all Crohns patients! Have you or a loved one been recently diagnosed? Or were you diagnosed with Crohns disease years ago but still dont fully understand your disease? Check out our latest video chat to learn more.
Video Length00:32:16
Video Chat: Crohns Disease 101
Crohns disease belongs to a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel diseases, or IBD. It is named after Dr. Burrill B. Crohn, who first described the disease in 1932 along with his colleagues, Dr. Leon Ginzburg and Dr. Gordon D. Oppenheimer.
Video Length00:07:09
Crohns 101 Overview This introductory video provides information on potential causes, symptoms, treatment and overall management of Crohns disease.
Don’t Miss: Can Stomach Ulcer Cause Fever
Watch A Video On The Basics Of Crohns
Youve been diagnosed with Crohns disease, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease in the gastrointestinal, or GI, tract.
But youve got this. And youre not alone.
Crohns affects 780,000 Americans. Diagnosis is most common between ages 15 and 35, but can occur at any age. It affects both men and women in equal proportions.
It can be overwhelming, but your journey towards remission begins by understanding your condition.
Crohns can cause redness, swelling and pain in your body, known as inflammation.
This leads to symptoms, including: abdominal pain and cramping, fatigue, and diarrhea.
Not all symptoms occur in everyone some are more common than others and can range in severity.
Crohns can cause inflammation through the entire GI tract other inflammatory conditions only affect a certain part of the GI tract. To get proper treatment, its important to know the difference.
We know its a lot, but youve got this. Youre learning, which is a great first step in your journey to remission.
When it comes to Crohns, the more you know, the more you can take control. If youve been recently diagnosed, or are curious about the condition, watch the Crohns 101 video for useful insight into an unpredictable disease.