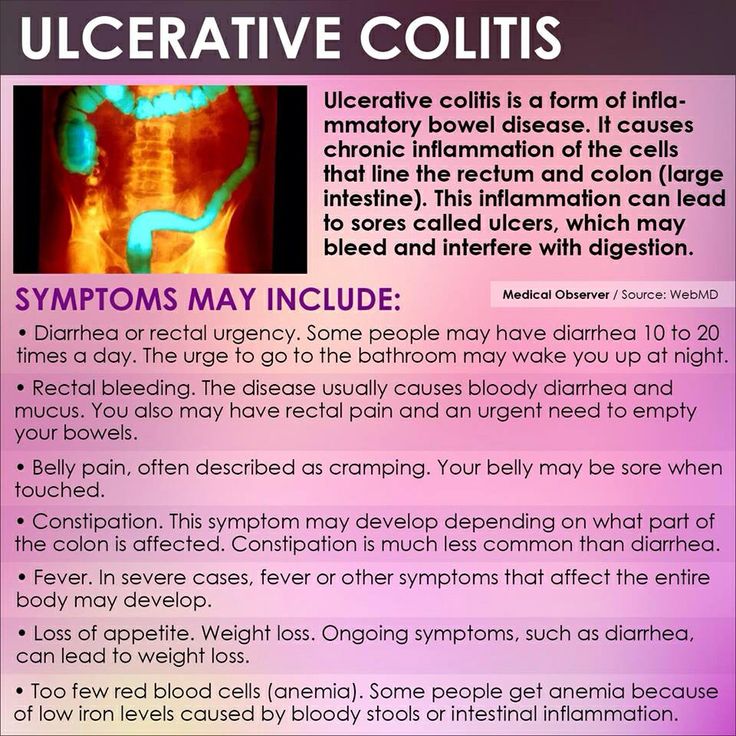
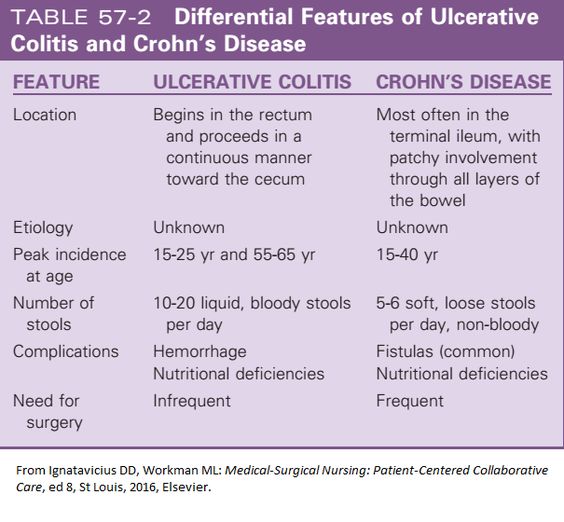
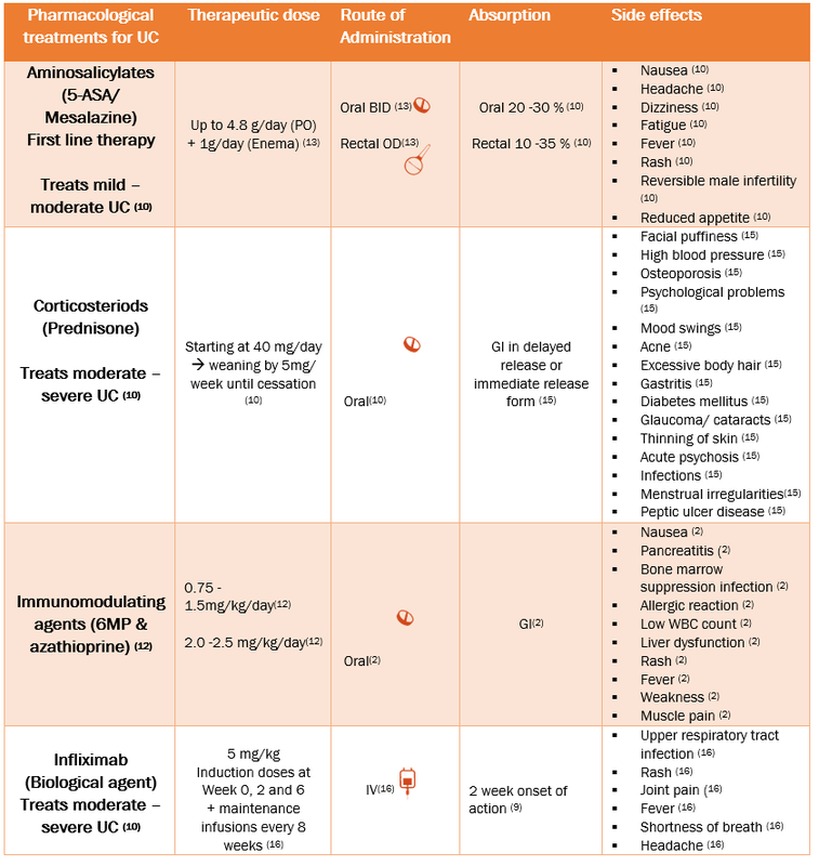
Pediatric Uc Epidemiology And Disease Features
Worldwide, the prevalence of UC is rising, and while the incidence is stabilizing in much of the Western world, rates are increasing in newly industrialized countries, specifically in parts of South Asia . To address the increasing disease burden, there is an urgent need to develop biomarkers that predict disease severity and disease course in a wide diverse population .
Features indicative of pediatric UC are well-described in the criteria set forth by the North American and European Societies for Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition . UC typically presents with a continuous inflammation of the rectum and colon proximally and is further categorized based on disease location and severity by the Paris pediatric modification of the Montreal classification of IBD . It is well-recognized that, in children, UC can present with atypical features, including macroscopic rectal sparing , backwash ileitis in association with severe pancolitis, and limited distal disease associated with mild cecal inflammation with an otherwise normal right colon . The presentation and natural history of pediatric UC are distinct from those of adult UC in that the majority of pediatric-onset UC presents with extensive colitis affecting the entire colon . On the contrary adults predominately present with left-sided colitis , with more than half in remission or with mild disease activity after initial presentation .
Procedure For Permanent Colostomy
This procedure is done when the damaged bowel cannot be restored after surgery, as in the case of colon cancer. In this procedure, the surgeon will create a stoma at the level of the damaged section of the colon and rectum and then staple or suture the remaining ends together. The stoma will be sealed from about 4-12 inches below the exit site. The goal is to divert stool away from the damaged area and prevent the accumulation of stool at the opening from the intestine to the skin surface.
Potential complications for permanent colostomy are infection at the site of an open wound, skin breakdown, stomal stenosis and fecal accumulation at the opening from the intestine to the skin surface.
This is a specific technique of undertaking a colostomy. The aim is to prevent fecal matter from leaking out of the stoma. This technique helps reduce pain, swelling and other complications after surgery.
Bowel technique procedure has a low risk of complications.
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
There is no single test to diagnose ulcerative colitis, so your childs doctor will first rule out other likely causes of symptoms. In addition to a standard physical exam and discussion of symptoms and family history, a combination of tests and procedures will be used to confirm a diagnosis. Those may include laboratory tests of blood and stool .
Other procedures include:
- Colonoscopy:Thedoctor uses a small camera mounted to the end of a lighted tube to examine the interior of the colon. This is done when your child is asleep under general anesthesia.
- Sigmoidoscopy: This is similar to a colonoscopy, but the physician only examines the rectum and the lower colon.
- Capsule endoscopy: The patient swallows a capsule that has a camera in it. The capsule travels through the small intestine, taking pictures that are transmitted to a receiver belt. The camera is expelled through a bowel movement and does not need to be retrieved.
- Imaging: The patient drinks a contrast dye and has an X-ray, Computed Tomography Enterography , or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Enterography.
Dont Miss: Does Alcohol Affect Ulcerative Colitis
Recommended Reading: How To Reverse Ulcerative Colitis
Nursing Interventions For Diarrhea
1. Encourage a liquid diet.Diarrhea normally requires bowel rest and the healthcare provider may order an NPO diet, but more likely a clear or full liquid diet.
2. Educate on diet changes to prevent diarrhea.A bland diet with low fiber is needed to bulk the stools. This includes soft foods without added sugar or spices such as white rice, white toast, crackers, and eggs. Raw, fresh foods and caffeine are not recommended.
3. Review medications.Medications may need to be changed if diarrhea is an intolerable side effect. Review how a patient is taking their medications. If they are taking laxatives or stool softeners, educate on the appropriate use and to discontinue if diarrhea develops.
4. Administer antidiarrheals as appropriate.Once the cause of diarrhea has been determined and it is not contraindicated, administer antidiarrheals to stop diarrhea. These should not be given if the patient has a parasitic infection as the infectious process needs to be eliminated.
5. Correct electrolyte imbalances.Dehydration is common with diarrhea. Administer IV fluids if dehydration is severe. Replace electrolytes such as potassium if required.
6. Children may need oral rehydration.Children experiencing diarrhea may need oral rehydration solutions such as Pedialyte. These can also be concocted through a mixture of water, sugar, and salt to replace lost fluids.
Prognosis And Outcomes Of Ibd In Children
Given diagnosis in the first decades of life, infants and children have many decades of disease in front of them. Several recent cohorts have illustrated key aspects of the natural history and outcomes of IBD in children, with emphasis of key differences from adult-onset cohorts.
Immune reactivity based upon a series of specific serological responses, has been shown to associate with disease outcome in children. In this group of 796 children with CD, an increased number of serological responses were linked with more aggressive disease pattern and earlier progression of disease. Subsequently, Siegel et al have developed a tool to outline predicted disease course in children with CD, incorporating serologic responses, along with patient and disease factors. The need for surgery has also been linked with NOD2 mutations in children with CD. Risk scores have also been considered in paediatric UC: Moore et al showed that white blood count and haematocrit values at diagnosis were associated with colectomy at 3 years in a cohort of 135 children with UC.
You May Like: Home Remedies For Stomach Ulcer Pain
You May Like: How To Know If I Have Ulcerative Colitis
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis happens when the immune system makes a mistake. Normally, it attacks invaders in the body, like the common cold. But when one has UC, the immune system thinks food, good gut bacteria, and the cells that line the colon are the intruders. White blood cells that usually protect the body attack the colons lining instead. They cause inflammation and ulcers.
Doctors arent sure why people get the condition. Genes may play a role the disease sometimes runs in families. Other things in the world around may make a difference too.
Treat To Target And Overall Severity Scoring
In an effort to move from a reactive, disease activitydriven approach to a proactive treatment approach to improve patient outcomes, 2 major concepts have recently been promoted: treat to target, and overall disease severity scoring.
In 2018, a group of IBD specialists convened to develop an overall severity index for both CD and UC using a modified RAND panel with an adaptive choice-based conjoint processes.72 These methods helped the panelists to identify key variables of IBD disease severity, break these variables into categorical levels, rank them relative to each other, and assign relative point values to each variable.
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis Shortness Of Breath
Nursing Management Of Patients With Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease specialist nurse, Endoscopy Unit, University Hospital Aintree, Liverpool
Ulcerative colitis is a relapsing chronic disease that has an unpredictable course. A relapse in the condition requires timely intervention and expert monitoring. A severe flare-up will often necessitate admission to hospital. This article provides an overview of the medical management of severe ulcerative colitis and the nursing interventions required.
Nursing Standard.24, 17, 48-58. doi: 10.7748/ns.24.17.48.s59
Keywords :
Ulcerative Colitis Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Ulcerative Colitis NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Ulcerative colitis is a medical condition that involves the inflammation and ulcer formation in the lining of the colon and rectum.
It is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that can have progressive symptoms over time and could be both debilitating and life-threatening if left uncontrolled.
There is no cure for ulcerative colitis yet, so the treatment is aimed at the reduction of signs and symptoms of this condition, and the prevention of complications.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Peptic Ulcer
Peritonitis Nursing Care Plans
Peritonitisis the acute or chronic inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the visceral organs. Inflammation may extend throughout the peritoneum or may be localized as an abscess. Peritonitis commonly decreases intestinal motility and causes intestinal distention with gas. mortality is 10% with death usually a result of bowel obstruction.
The peritoneum is sterile, despite the GI tract normally contains bacteria. When bacteria invade the peritoneum due to an inflammation or perforation of the GI tract peritonitis usually occurs. Bacterial invasion usually results from appendicitis, diverticulitis, peptic ulcer, ulcerative colitis, volvulus, abdominal neoplasms, or a stab wound. It may also be associated with peritoneal dialysis.
Diagnosing Ulcerative Colitis In Children
At Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital at NYU Langone, doctors in the Pediatric Gastroenterology Program diagnose ulcerative colitis in children. In this form of inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD, the lining of the colon, or large intestine, becomes chronically inflamed. This condition can occur in any part of the colon.
Signs and symptoms include bloody stools, abdominal pain, ulcers in the colon, diarrhea, and weight loss. Without treatment, symptoms can worsen over time. Children with ulcerative colitis often experience flare-ups between periods of remission, which is an absence of symptoms.
The causes of ulcerative colitis in children arent fully understood, but genetics, environment, and an autoimmune response are all thought to play a role.
Ulcerative colitis is not the same as irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS. In IBS, a collection of symptoms occurs together. These may include abdominal cramping, constipation, and diarrhea. Unlike with inflammatory bowel disease, IBS does not lead to inflammation that damages the gastrointestinal tract.
Another form of IBD is Crohns disease, which mainly affects the small intestine and colon but can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract. The symptoms of these two types of IBD can be similar. For this reason, our doctors perform a physical exam and extensive testing when diagnosing ulcerative colitis in children.
Recommended Reading: Diet For Someone With Stomach Ulcers
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
-
Design strengths included comparing hospitalisations 1year before and 1year after the introduction of an inflammatory bowel disease nurse position.
-
The extraction of patients with IBD with two information systems allowed exhaustiveness.
-
The major limitation was that costs were only attributed to the reduction of hospitalisation.
Read Also: Bland Diet Recipes For Ulcers
Nursing Care Plan For Ulcerative Colitis 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than Body Requirements related to altered absorption of nutrients secondary to Ulcerative colitis, as evidenced by diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to achieve a weight within his/her normal BMI range, demonstrating healthy eating patterns and choices.
You May Like: Besivance Dosage For Corneal Ulcer
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis:
Let the names help you, so you can understand where the ulcerative colitis is located:
Ulcerative proctitis : affects the rectum and is the most mild form of all types. It tends to have fewer complications due to being located just in the rectum.
Proctosigmoiditis: PROCT: COLON and SIGMOID: SIGMOID COLON and ITIS: inflammationinflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Pancolitis . It is a very severe form of ulcerative colitis.
Left-sided colitis: LEFT-SIDED: includes the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum and ITIS: inflammation.inflammation of the descending, sigmoid, and rectum.
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
There are different types of ulcerative colitis depending on the affected location:
Recommended Reading: What Foods Can You Eat When You Have An Ulcer
Eleanor Brown Case Study
Question 1. Describe the structural and functional changes in the disease process that led to Eleanors weight loss? Students answers must be supported by relevant academic references. References are not included in the word limit.
Question 2. Explain the pain pathway and how Morphine alters the conscious perception of pain. Students must support their answers with relevant academic references. References are not included in the word limit.
Question 3. Identify the clinical manifestations that may indicate the deterioration of Eleanors ulcerative colitis condition and explain why these may occur. Students answers must be supported by academic references. References are not included in the word limit.
Question 4. Explain the characteristics of the intravenous fluid that was ordered for Eleanor and the rationale for the administration of the IV fluid relating to Eleanors specific fluid balance. Students answers must be supported with academic references. References are not included in the word limit.
- Posted on : April 01st, 2018
How Do We Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis
The Digestive Health Center at Stanford Health Care delivers expert diagnosis for all forms of inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis. Part of what makes Stanford different is our expertise in measuring the degree of intestinal injury for each patient. This helps us understand the severity of your condition and how best to treat it.
Donât Miss: Natural Ways To Heal Ulcerative Colitis
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Peptic Ulcer
Nursing Interventions For Colostomy
Colostomy irrigation is advised by the dietitian to be done at a frequency of 3 times per day in some cases, 2 times per day in others. Depending on the type of colostomy created, irrigation can be done with either saline or water solution.
The colostomy wound site should be cleaned with antibacterial soap and water prior to each irrigation session. The amount of fluid to be drained depends on the length of time between irrigations or the degree of diarrhea present.
Saline solution is recommended for a return type colostomy rather than tap water for its antibacterial action.
After irrigation, saline solution is used to clean the colostomy opening and surrounding skin surface.
After cleaning, a wafer-like dressing may be applied directly over the top of the wound opening for a permanent colostomy site. If gauze dressing is being used, it should be applied in such a way that an air hole is left open to prevent skin breakdown from continuous pressure.
A collection device may be needed for patients when bowel movements are infrequent or when circumstances such as the need to pass stool from the colon prevents evacuation of stool.
Patient respiration should be checked for 15 seconds after each irrigation session to prevent fluid from entering the lungs.
The patient needs to understand that their dietitian may prescribe 24 ounces of specific fiber supplement twice per day. This will depend on the amount and consistency of stool passed and the time between irrigations comes.
Future Applications Of Machine Learning
Machine learning has the potential to change practice in UC, a chronic disease as described above that has a variable disease course in individuals. Advances have been made in next-generation sequencing, and high-throughput omics, leading to a greater understanding of the molecular basis of pediatric UC. Innovations in the application of machine learning to derive not only automated learning of relevant features but also learning from patterns that are not obvious to human vision will advance the field further. Our reliance on multiple modalities such as endoscopy, histology, and imaging to ascertain the diagnosis and to monitor disease progression positions our field to capitalize on advances in machine learning. In leveraging computational approaches that can analyze large multimodal data, we could truly translate established and newly discovered predictive factors into the clinical setting. Incorporating a clinical decision support tool that, for example, supports patient stratification at disease onset and allocation of personalized therapies, all within the electronic health record, could provide data-driven solutions for individual patient encounters.
Recommended Reading: What Can You Eat If You Have Ulcerative Colitis
Read Also: How To Prevent Pressure Ulcers Nursing
Scheduled And Emergency Uc Surgery
Most UC surgery can be arranged at time thatâs convenient for you. Try scheduling it while your symptoms are calm to cut the chances of complications.
The risks are higher when you have emergency surgery. You may need it if you get toxic megacolon â a life-threatening condition when your colon rapidly swells and gas and bacteria build up inside. Get medical help right away if you have fever, belly pain, constipation, or swelling.
Recommended Reading: Best Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Inpatient Severe Disease Considerations
There are several disease scores used to determine the risk of requiring rescue therapy or colectomy in patients with severe colitis. Recent studies have shown a potential advantage of using the UCEIS scoring system, with 1 study showing improved accuracy of the UCEIS score in predicting the need for colectomy compared with the Mayo Score, with score greater than 7 showing a sensitivity of 60.3% with a specificity of 85.5%.98 Another study showed that a UCEIS score of 5 or more was associated with a 50% chance of requiring rescue therapy and 33% rate of colectomy compared with 27% and 9% for those with a score of less than or equal to 4. As mentioned previously, the commonly used Oxford index, developed in 1996, predicted the need for colectomy to be 85% in patients with a CRP level greater than 45 mg/L and 3 to 8 bowel movements a day after 3 days of IVCS treatment.24 Another score, developed in 1998 by Lindgren and colleagues99 using these same variables of bowel movements and CRP on day 3 after IVCS, showed favorable test characteristics for predicting the need for colectomy. The Ho index has also been used to risk stratify patients into low, intermediate, or high risk for colectomy.100 This index was derived from a cohort of patients from 1995 to 2002 and found aggregate scores of 0 to 1, 2 to 3, and greater than or equal to 4 from 3 variables correlated with a risk of progression to colectomy of 11%, 45%, and 85% respectively .
Read Also: Are Ulcerative Colitis And Ibs The Same