Natural Treatments To Get Rid Of Hpylori Bacteria
You can take medication to treat H. pylori, but you will be taking many at once and the side effects can do more harm than good. Thankfully you can treat the infection naturally. Some of these treatments are even food items that you may already have in your kitchen and they are inexpensive. The others can easily be found in health stores, pharmacies and online.
Extra virgin olive oil is the best choice since it has kept its nutritional value, unlike the refined olive oils. Olive oil contains antioxidants called phenolic compounds. The phenolic compounds have antibacterial properties that fight the H. pylori bacteria. To maintain the health benefits of the olive oil, do not cook with it. Rather use it on salads or in dips.
What Is The Treatment For H Pylori
Treatment for H. pylori infection usually involves taking several medications for 14 days.
- Proton pump inhibitors to decrease the stomach acid production
Many patients with H. pylori have an infection that is resistant to antibiotics, so it is important to take the entire course of all medications prescribed and to get a blood or stool test to confirm the infection has been cleared.
How Are Hpylori Peptic Ulcers Treated
Drugs Used To Treat H. pylori Peptic UlcersAntibiotics: metronidazole, tetracycline, amoxicillin, clarithromycin. H2-blockers: cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, nizatidine. Proton pump inhibitors: omeprazole, lansoprazole. Stomach-lining protector: bismuth subsalicylate. |
H. pylori peptic ulcers are treated with drugs to kill the bacteria, to reduce stomach acid, and to protect the stomach lining. Antibiotics are used to kill the bacteria. Two types of acid-suppressing drugs might be used: H2-blockers and proton pump inhibitors.
H2-blockers work by blocking histamine, which stimulates acid secretion. They help reduce ulcer pain after a few weeks. Proton pump inhibitors suppress acid production by halting the mechanism that pumps the acid into the stomach. H2-blockers and proton pump inhibitors have been prescribed alone for years as treatments for ulcers. But used alone, these drugs do not eradicate H. pylori, and therefore do not cure H. pylori-related ulcers. Bismuth subsalicylate, a component of Pepto-Bismol, is used to protect the stomach lining from acid. It also kills H. pylori. Treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics, acid suppressors, and stomach protectors.
Early results of studies in other countries suggest that 1 week of triple therapy may be as effective as the 2-week therapy, with fewer side effects.
Also Check: Does Turmeric Help Ulcerative Colitis
What Is H Pylori And Is It Contagious
H. pylori are spiral shaped bacteria. H. pylori bacteria are unique because they produce the enzyme urease that allows the bacteria to live in the harsh environment of the stomach. The urease enzyme it produces reacts with urea to form ammonia that neutralizes enough of the stomach’s acid to allow the organisms to survive in the tissues.
H. pylori is considered to be contagious and passed from person to person by:
- saliva,
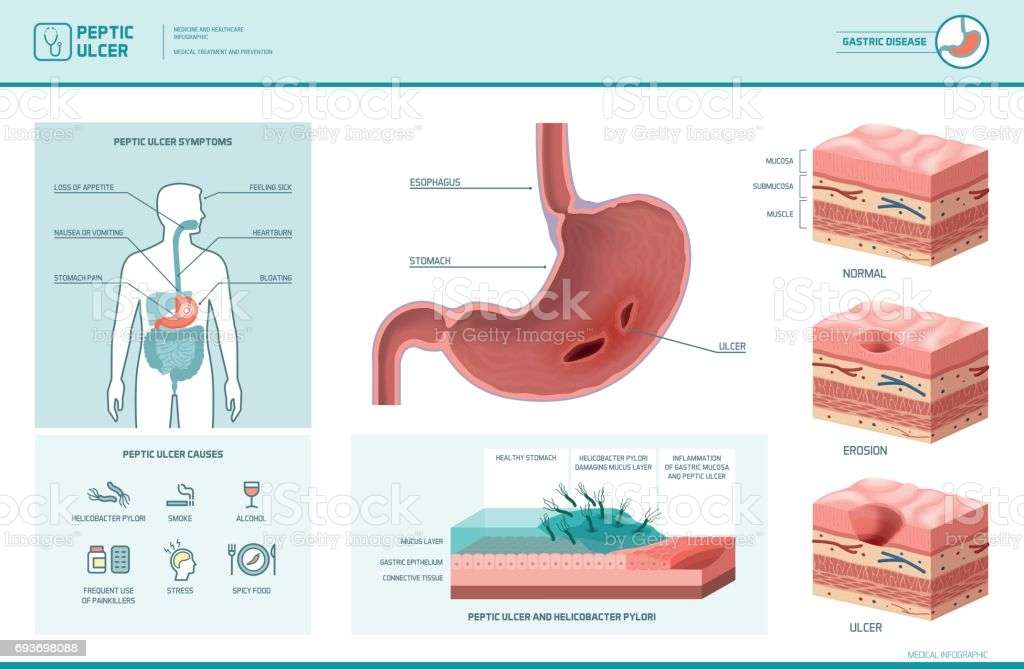
Often, these symptoms simply go away. However, those individuals who have more serious infection experience signs and symptoms of stomach and duodenal ulcers or severe gastritis which include:
Other symptoms may include:
Accurate and simple tests for the detection of H. pylori infection are available . They include blood antibody tests, urea breath tests, stool antigen tests, and endoscopic biopsies.
Biopsies also may be cultured in the bacteriology laboratory for the presence of H. pylori however, this is done infrequently since other simpler tests are available.
In 2012, the FDA gave approval for the urea breath test to be done in children aged 3 years to 17 years old.
What Is Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori, is a spiral-shaped bacterium that grows in the mucus layer that coats the inside of the human stomach.
To survive in the harsh, acidic environment of the stomach, H. pylori secretes an enzyme called urease, which converts the chemical urea to ammonia. The production of ammonia around H. pylori neutralizes the acidity of the stomach, making it more hospitable for the bacterium. In addition, the helical shape of H. pylori allows it to burrow into the mucus layer, which is less acidic than the inside space, or lumen, of the stomach. H. pylori can also attach to the cells that line the inner surface of the stomach.
Although immune cells that normally recognize and attack invading bacteria accumulate near sites of H. pylori infection, they are unable to reach the stomach lining. In addition, H. pylori has developed ways of interfering with local immune responses, making them ineffective in eliminating this bacterium .
H. pylori has coexisted with humans for many thousands of years, and infection with this bacterium is common. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that approximately two-thirds of the worlds population harbors the bacterium, with infection rates much higher in developing countries than in developed nations.
Also Check: Is Constipation A Symptom Of Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Complications Of H Pylori
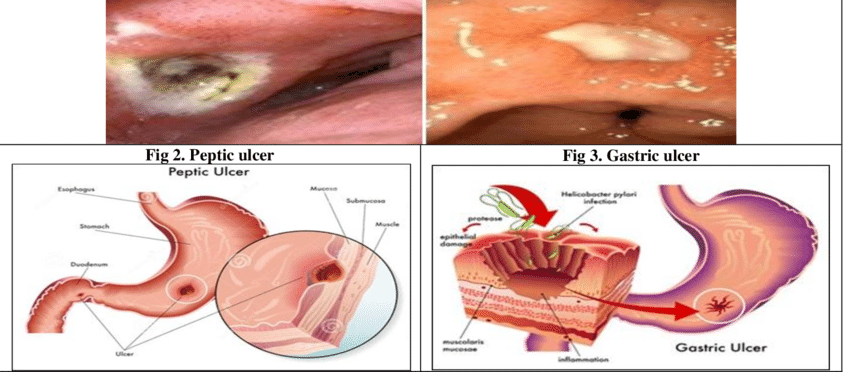
If you are infected with the bacteria you can get a painful sore called a peptic ulcer. These sores form in your upper digestive tract.
A very bad ulcer can wear away your stomach lining. It can also cause problems such as:
-
Bleeding when a blood vessel is worn away
-
A hole or perforation in your stomach wall
-
Blockage when the ulcer is in a spot that blocks food from leaving your stomach
H. pylori can also lead to stomach cancer.
Testing For Peptic Ulcers
Safe and effective tests are available to help your physician diagnose whether or not you have an ulcer. These include:
- Endoscopy: During an endoscopy, a flexible tube with a light and video camera on the end is gently inserted into your mouth and passed into the stomach and duodenum .Ulcers in the stomach or duodenum can be seen in real time with the camera during the procedure. Biopsies can be taken during the endoscopy. This is the most accurate test for ulcers.
- Upper Gastrointestinal X-ray: This is a special type of X-ray. To prepare for it, you will be asked to drink barium or a similar substance that outlines the inside of your esophagus , stomach and duodenum. Ulcers appear as defects in the barium that coats the lining of the stomach or duodenum. This test is not always accurate in showing ulcers, especially in children.
You May Like: Crohn’s Versus Ulcerative Colitis Pathology
What Is Gastric Cancer
Gastric cancer, or cancer of the stomach, was once considered a single entity. Now, scientists divide this cancer into two main classes: gastric cardia cancer and non-cardia gastric cancer .
Gastric cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the world, killing approximately 738,000 people in 2008 . Gastric cancer is less common in the United States and other Western countries than in countries in Asia and South America.
Overall gastric cancer incidence is decreasing. However, this decline is mainly in the rates of non-cardia gastric cancer . Gastric cardia cancer, which was once very uncommon, has risen in incidence in recent decades .
Infection with H. pylori is the primary identified cause of gastric cancer. Other risk factors for gastric cancer include chronic gastritis older age male sex a diet high in salted, smoked, or poorly preserved foods and low in fruits and vegetables tobacco smoking pernicious anemia a history of stomach surgery for benign conditions and a family history of stomach cancer .
H. pylori has different associations with the two main classes of gastric cancer. Whereas people infected with H. pylori have an increased risk of non-cardia gastric cancer, their risk of gastric cardia cancer is not increased and may even be decreased.
What If I Have An Ulcer And H Pylori Infection
The medicines described earlier heal ulcers whether you have H. pylori infection or not. But, if you have H. pylori infection too, your doctor also will treat the infection. H. pylori is hard to get rid of. No single medicine can cure this infection. The best way to cure H. pylori infection is to take several medicines at the same time.
To treat an H. pylori infection, your doctor will prescribe several medicines: one or two antibiotics plus bismuth or a medicine to block stomach acid production. This means taking a large number of pills every day. Some combinations that use fewer drugs also might help. Tritec is a pill that combines bismuth and a drug to reduce acid in the stomach. It is used with an antibiotic. Helidac is another medicine that combines bismuth and two antibiotics. Your doctor will tell you which medicines you should take.
Also Check: Whey Protein And Ulcerative Colitis
Who Should Be Tested
The American College of Gastroenterology recommends testing in the following situations :
- Patients with active peptic ulcer disease
- A history of documented peptic ulcer
- Gastric MALT lymphoma
- Patients who have undergone resection of early gastric cancer.
Testing is not recommended for people who are asymptomatic or who have no history of peptic ulcer disease. However, certain population groups who are at risk for developing ulcers or stomach cancers may be considered for asymptomatic testing.
How Is H Pylori Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will look at your past health and give you a physical exam. He or she may also use other tests, including:
-
Blood tests. These check for infection-fighting cells that mean you have the bacteria.
-
Stool culture. This looks for any abnormal bacteria in your digestive tract that may cause diarrhea and other problems. A small stool sample is collected and sent to a lab. In 2 or 3 days, the test will show if you have any abnormal bacteria.
-
Breath tests. These can check if there is any carbon after you swallow a urea pill that has carbon molecules. If carbon is found that means that H. pylori has made the enzyme urease. This enzyme makes your stomach acids less acidic . It weakens your stomachs mucous lining.
-
Upper endoscopy, also called EGD . This test looks at the lining of your food pipe , stomach, and duodenum . It uses a thin, lighted tube or endoscope. The tube has a camera at one end. The tube is put into your mouth and throat. Then it goes down into your esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Your healthcare provider can see the inside of these organs. A small tissue sample is taken if needed. The tissue sample can show if you have the enzyme urease. It can also check the bacteria that is there.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Pressure Ulcers In Wheelchairs
Is Helicobacter Pylori Infection The Primary Cause Of Duodenal Ulceration Or A Secondary Factor A Review Of The Evidence
Vikram Kate
1Department of General and Gastrointestinal Surgery, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Pondicherry 605006, India
2Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Research Institute, Pondicherry 607402, India
3Division of Surgery and Interventional Science, University College London, London W1W 7ET, UK
Academic Editor:
Abstract
1. It Is the Primary Cause of Ulceration
1.1. Helicobacter pylori Is the Primary Cause of Duodenal Ulcer
The isolation of Helicobacter pylori from the gastric mucosa generated excitement when it was postulated by Marshall that these microorganisms could be the cause of gastritis and play an important role in the etiology of peptic ulcer disease . H. pylori infection is almost always associated with an inflammatory response however, peptic ulcer disease and gastric carcinoma occur only in a subset of individuals chronically infected with H. pylori. Presumably, both bacterial and host factors contribute to this differential response.
1.2. Pathogenic Mechanisms and Virulence Factors
Levi et al. reported increased gastrin levels due to H. pylori infection which induced increased gastric acid secretion leading to duodenal ulcer . Eradication of H. pylori abolishes the hypergastrinemia suggesting that this is due to H. pylori infection.
1.3. Role of H. pylori in Duodenal Ulcer Disease
1.3.1. Uncomplicated Duodenal Ulcer
1.3.2. Helicobacter pylori and Complicated Duodenal Ulcer Disease
1.4. Conclusion
2.1. The Role of Acid
What Is Gastric Mucosa
Gastric MALT lymphoma is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is characterized by the slow multiplication of B lymphocytes, a type of immune cell, in the stomach lining. This cancer represents approximately 12 percent of the extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma that occurs among men and approximately 18 percent of extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma among women . During the period 19992003, the annual incidence of gastric MALT lymphoma in the United States was about one case for every 100,000 persons in the population.
Normally, the lining of the stomach lacks lymphoid tissue, but development of this tissue is often stimulated in response to colonization of the lining by H. pylori . Only in rare cases does this tissue give rise to MALT lymphoma. However, nearly all patients with gastric MALT lymphoma show signs of H. pylori infection, and the risk of developing this tumor is more than six times higher in infected people than in uninfected people .
Read Also: Hind Gut Ulcers In Horses Symptoms
Why Dont All Doctors Automatically Check For H Pylori
Changing medical belief and practice takes time. For nearly 100 years, scientists and doctors thought that ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Treatment involved bed rest and a bland diet. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids.Since H. pylori was discovered in 1982, studies conducted around the world have shown that using antibiotics to destroy H. pylori cured peptic ulcers. The National Institutes of Health released a consensus statement in 1994 confirming that H. pylori causes peptic ulcers. Despite the evidence, however, the medical community continues to debate H. pyloris role in peptic ulcers. If you have a peptic ulcer and have not been tested for H. pylori infection, talk to your doctor.
Causes And Risk Factors Of H Pylori
Doctors arent exactly sure how H. pylori infection is passed from person to person. Research shows that you can become infected with the bacteria by consuming contaminated food or water. H. pylori may also spread through contact with an infected persons saliva, vomit, or fecal matter.
H. pyloriH. pylori
- Sharing a crowded living space
- Living in a developing country
- Not having access to clean water
- Living with someone who has H. pylori
Read Also: Can Diet Help Ulcerative Colitis
Helicobacter Pylori Bacterial Infection
An infection that develops from Helicobacter pylori bacteria is one of most common causes of peptic ulcers. Its not clear how an H. pylori infection spreads, but it is believed that it may be transmitted from person to person through close contact. H. pylori bacteria may also enter the body through food and water.
This type of bacteria commonly live in the mucous layer that covers and protects tissues that line the stomach and small intestine. They can survive the acidic environment that occurs during the digestion process.
An overgrowth of these bacteria causes irritation in the stomach lining and weakens the protective coating. This can further lead to inflammation and infection, ultimately leading to an ulcer.
However, people who may get infected with H. pylori will not always develop ulcers. Only a few people infected with H. pylori will suffer from an ulcer in the coming days.
Real Causes Of H Pylori Infection And Its Natural Treatment
In this article, I will be explaining the causes of H pylori infection, the symptoms it causes, and the treatment for it. H. pylori are known as Helicobacter pylori in the medical community. It’s a bacterial infection that causes ulcers in your stomach and causes a lot of discomfort and digestive problems. It’s more common than you think. As much as 66% of people in the world have this infection, especially in the developing world. But what causes H. pylori infections and can you avoid it?
If you have ulcers in the stomach and the symptoms I have listed below then it is H.pylori. The biggest problem is that doctors especially in developing countries like in Asia, do not even check for H.pylori bacteria because it is expensive. The second biggest problem is that in order to kill H.Pylori if you have tested positive is, you have to eat like 20 medicines, which is not very safe. We are left here with only, one option.
How to increase stomach acid, as it will kill H.pylori automatically. This is catch 22. If you will increase stomach acid and have stomach ulcers, you will get burning sensation. So be very careful with the steps you take to naturally heal yourself and there is a protocol discussed later.
You May Like: Icd 10 Stage 4 Sacral Ulcer