Is There An Ulcerative Diet Listing Foods To Avoid And Foods That Relieve Symptoms
Proper nutrition is important for a person with ulcerative colitis. Foods do not cause ulcerative colitis, but certain food groups can cause symptoms to flare. Often it is a process of trial and error to find what foods need to be avoided. Although specific foods do not cause the disease, some types of food may trigger discomfort and diarrhea. Keep a food diary to help find foods that cause problems.
Counseling and education are important for both the patient and family a better understanding of how ulcerative colitis affects the body will allow the patient and physician to work together to control the symptoms.
Some Ingredients In Supplements
Some supplements are very beneficial for people with UC. These include calcium, folic acid, and iron. However, some ingredients in supplements may worsen the symptoms of UC.
According to the Crohns and Colitis Foundation, people should avoid supplements that contain:
All of these may aggravate a persons UC symptoms, particularly during a flare-up.
The Crohns and Colitis Foundation also adds that people should avoid taking any supplements on an empty stomach.
A person should check with a medical professional before taking any supplements, including herbal supplements, over-the-counter medications, and complementary therapies.
What Will You Need
Your needs will depend on your symptoms, and each person is different. Your ulcerative colitis could start out as mild, then stop for a while, only to come back worse than it was before. Or you may have only mild ulcerative colitis your entire life.
Plus, your body may not respond the same way to a drug as someone else’s. And over time, you may find that you need a different type of medicine. For example, something thatâs worked well for years may not work anymore. You may need a whole new treatment plan.
Let your doctor know how youâre really doing, and always tell them about any side effects that you have.
Show Sources
You May Like: When To Go To The Hospital For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis Treatment Options
Treatment of ulcerative colitis focuses on one of two goals: inducing remission during an active flare-up or maintaining remission. These goals are largely accomplished through medications that will be tailored to the severity and extent of the illness. Severe disease or complications may require surgical removal of part or all of the colon.
Working With A Healthcare Provider
UC doesnt have to be a battle between a patient and a severe digestive upset. For many people, remission is possible. But that goal can only be achieved when a patient works with a physician to create a treatment strategy and then sticks to that plan. While many UC patients require prescription medication to treat and control symptoms, some OTC medications can help when mild flare-ups occur. People diagnosed with UC should always speak with a doctor before incorporating new drugs to understand potential side effects.
Don’t Miss: Signs You May Have Stomach Ulcers
How To Take Tablets And Granules
You will either take the tablets or granules once a day, or as 2 or 3 smaller doses throughout the day.
Swallow the tablets whole with a drink of water or juice. Do not break, chew or crush them. This is because some tablets have a special coating to delay when they start to work, or to protect the medicine from the acids in your stomach.
For granules, open the sachet and tip the granules onto your tongue. Swallow them whole with a drink of water or juice. Do not chew them, as some granules have a special coating.
You can take some brands with food. Check the leaflet that comes with your medicine.
If you’re also taking indigestion medicines or remedies, leave a 2 hour gap before and after taking mesalazine. Indigestion treatments can affect how well the medicine works.
Ulcerative Colitis Remission Better Maintained After Infliximab Treatment
New data has investigators caution against the discontinuation of ulcerative colitis treatment, due to threat of relapse.
Taku Kobayashi, MD
A recent study found that maintaining ulcerative colitis remission was significantly more common in patients who continued treatment with infliximab, compared to those who discontinued treatment.
The use of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents is common in the treatment of refractory UC, but the long-term use of anti-TNF therapy can increase the risk of malignancy or infection.
No previous study trial has evaluated the safety of anti-TNF agent discontinuation in patients with UC in remission.
The team, led by Taku Kobayashi, MD of the Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato University Kitasato Institute Hospital in Tokyo, looked to compare outcomes in patients who continued and discontinued infliximab treatment.
Thus, investigators conducted an open-label, randomized controlled trial at 24 specialist centers in Japan.
The study enrolled patients with UC in remission who had been treated with intravenous infliximab every 8 weeks. Patients were required to have started treatment 14 weeks prior to enrollment in the study.
Patients were also required to be in remission for more than 6 months, to be corticosteroid-free and have a Mayo Endoscopic Subscore of 0 or 1. The group was then randomized and put into either the infliximab-continued group or the infliximab-discontinued group.
Recommended Reading: Does Stelara Work For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis: Achieving And Maintaining Remission
US Pharm. 2008 33:30-37. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disorder characterized by diffuse mucosal inflammation of the colon. It affects between 250,000 and 500,000 Americans.1 Unlike Crohns disease, which may affect the entire gastrointestinal tract, UC is limited to the colon. UC almost always involves the rectum, but may extend proximally in a contiguous fashion to involve portions of, or the entire, colon . In the majority of new cases diagnosed, disease is limited to the distal or left side of the colon, and there is some evidence that aggressive pharmacotherapy early in the disease may prevent progression and extension of inflammation.2 This article will review the initial treatment options for UC and their place in therapy for both acute attacks and maintenance of remission.
Avoid Foods That Make Symptoms Worse
Diet does not cause ulcerative colitis flare-ups. You may, however, notice that some foods make your symptoms worse. If so, stop eating or drinking those foods. The most common foods that seem to exacerbate ulcerative colitis symptoms are dairy products, fatty foods, and spicy foods. High fiber foods also can worsen symptoms during a flare.
Also Check: What Are Stomach Ulcers From
What Is The Best Medication For Ulcerative Colitis
The severity and extent of ulcerative colitis will determine the most appropriate medications for the condition. For this reason, there is no best medication for ulcerative colitis. Instead, a patients medical situation and tolerance for side effects will determine the best medications for treating ulcerative colitis.
| Best medications for ulcerative colitis | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | |
| Administered weeks 0 and 4 then every eight weeks subcutaneously. | Upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, sore throat |
Many of the standard dosages above are from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or the National Institutes of Health . Dosage is determined by your doctor based on your medical condition, response to treatment, age, and weight. Other possible side effects exist. This is not a complete list.
What Are The Common Side Effects Of Ulcerative Colitis Medication
All ulcerative colitis medications may have side effects, but these side effects will differ depending on the drug. This is not a complete list, so please talk to a healthcare provider about any questions you have about possible side effects, drug interactions, or any other concerns.
Aminosalicylates are the first-line treatment for ulcerative colitis because they are generally safe medications with few side effects. Side effects are usually limited to headache, abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Sulfasalazine, however, is a sulfa drug, so it should not be taken by people with allergies to sulfa drugs.
Topical corticosteroids such as rectal suppositories, creams, or foams usually have few or only mild side effects. They most commonly provoke site reactions such as burning, irritation, and itching. Oral and injected corticosteroids, however, may produce side effects in many people including mood and behavior changes, increased appetite, weight gain, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, acne, thinning skin, fluid retention, and cataracts.
Immunosuppressants can weaken the immune system and decrease the bodys production of white blood cells that serve as the front-line defense against infection and cancer. The most serious side effects of immunosuppressants, then, are potentially severe infections and cancers. Other severe side effects might include liver, kidney, or lung damage.
Don’t Miss: Best Foods To Heal Stomach Ulcer
Medication For Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Gastroenterologists at NYU Langone’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center may prescribe one or more medications to reduce inflammation in the digestive tract caused by inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD. The goals of treatment are to improve symptoms and heal any damage to the intestines.
Our gastroenterologists develop a personalized treatment plan for you based on the type of IBD, the severity of the condition, and the results of diagnostic tests. These tests may have confirmed that you have Crohns disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, or ulcerative colitis, which only affects only the colon, or large intestine.
Medications work differently in different people, so your gastroenterologist closely monitors how well you respond to treatment. He or she adjusts the type or dose of medication as often as needed.
Medications for IBD can often reduce inflammation and promote healing in the intestines, resulting in remissionmeaning long-term symptom relief. However, for many people with IBD, the condition is chronic and treatment is lifelong. It is very important to follow up regularly with your gastroenterologist.
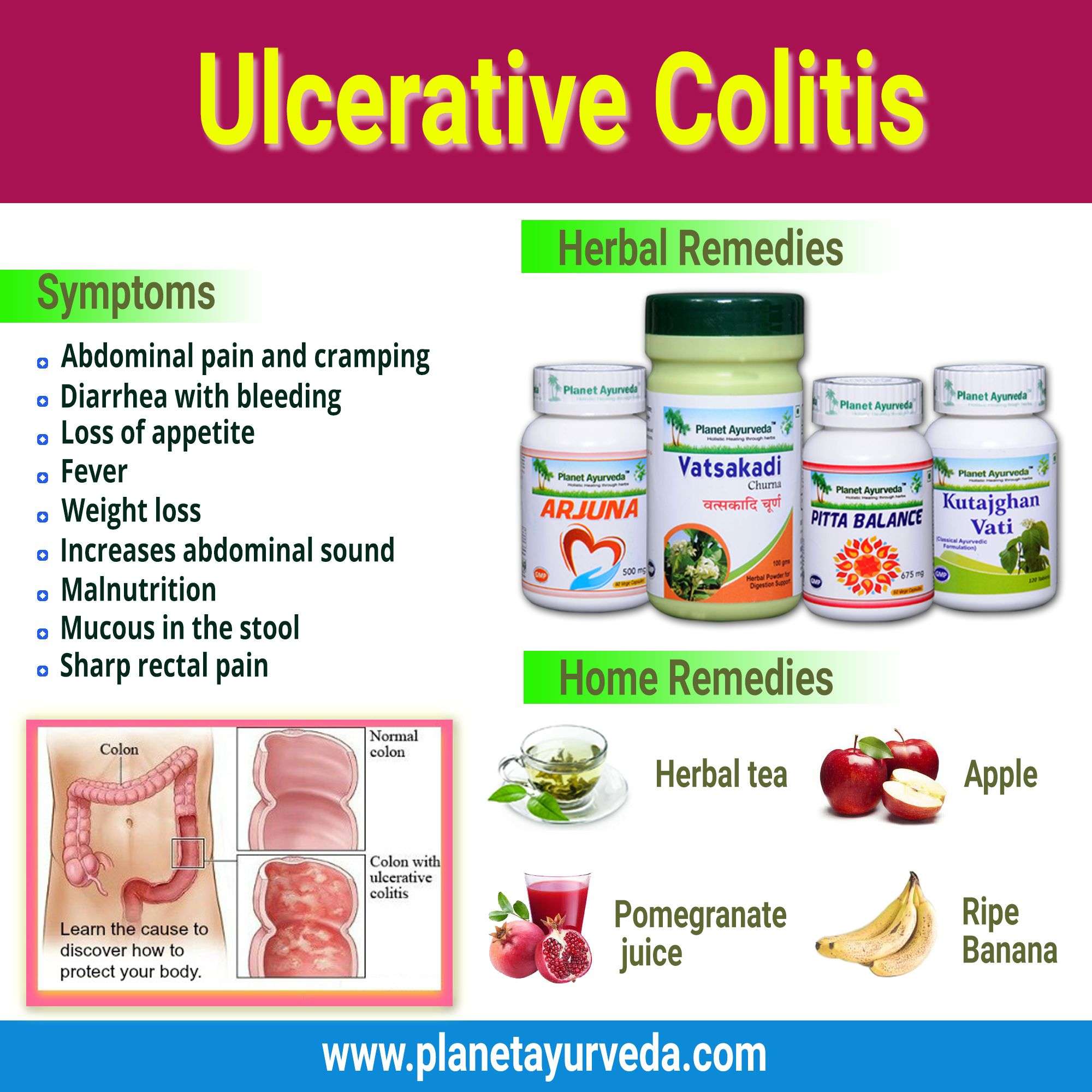
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Ulcerative Colitis

- Liver and bile duct disease
- Kidney problems
Tell a healthcare professional about any persistent changes in bowel habits. If the patient is already under treatment for inflammatory bowel disease or irritable bowel syndrome, contact a doctor if the patient experiences any prolonged changes in the symptoms or passes blood in the stools.
When Should You Call 911 or Go to the Emergency Department?
Seek medical care if any of these conditions are associated with colitis.
- Blood or mucus in your stool
- Diarrhea that lasts more than three days.
Don’t Miss: How To Heal Ulcerative Colitis With Food
Dietary And Lifestyle Modifications
As most nutrients are absorbed higher up in the digestive tract, those with ulcerative colitis generally do not have nutrient deficiencies however, other factors might influence your nutritional state. Disease symptoms may cause food avoidance, leading to food choices that might not provide a balanced diet. If bleeding is excessive, problems such as anemia may occur, and modifications to the diet will be necessary to compensate for this.
Generally, better overall nutrition provides the body with the means to heal itself, but research and clinical experience show that diet changes alone cannot manage this disease. Depending on the extent and location of inflammation, you may have to follow a special diet, including supplementation. It is important to follow Canadas Food Guide, but this is not always easy for individuals with ulcerative colitis. We encourage you to consult a registered dietitian, who can help set up an effective, personalized nutrition plan by addressing disease-specific deficiencies and your sensitive digestive tract. Some foods may irritate the bowel and increase symptoms even though they do not worsen the disease.
In more severe cases, it might be necessary to allow the bowel time to rest and heal. Specialized diets, easy to digest meal substitutes , and fasting with intravenous feeding can achieve incremental degrees of bowel rest.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
Read Also: Evidence Based Practice Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Vitamin And Mineral Supplements
People with IBD often have vitamin or mineral deficiencies because digestive dysfunction prevents the body from absorbing important nutrients. These include iron, folate, vitamin D, and vitamin B12. As part of treatment at NYU Langone’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, nutritionists may recommend dietary changes. They may also advise supplementing your diet with vitamins and minerals to boost your digestive health.
Keeping A Food Journal
Everyones body is different, so its possible for two people who have UC to have different trigger foods.
Logging what you eat throughout the day and when digestive issues occur can help you and your doctor narrow down your personal food triggers.
A food journal can be especially helpful if youre trying a new diet.
Read Also: What To Eat With An Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
The diagnosis of ulcerative colitis is made from the clinical symptoms, an endoscopic examination of the rectum and colon, and a biopsy of colon tissues. A stool test will be used to rule out infection. Lab testing may be done to corroborate the diagnosis and check for anemia. Diagnosis may begin with a general practitioner, but endoscopic examination and treatment of the condition usually fall to a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in digestive diseases.
People usually seek medical help first during an active flare-up, showing symptoms of ulcerative colitis such as:
- Bloody diarrhea
- Urgency to defecate
- Inability to defecate even when the need is urgent
Severe disease will also include symptoms such as involuntary weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and fever. A small number of patients will have other symptoms not involving the gut. These include swollen or painful eye tissues, joint pain or swelling, and red lumps or sores/rashes on the skin.
In taking a history, a doctor will be interested in how quickly symptoms appeared, how often theyve been experienced, the length of remissions, and risk factors such as age and family history of inflammatory bowel disease.
A definitive diagnosis is made with an endoscopic examination of the rectum and the colon . The gastroenterologist is not only looking for signs of ulcerative colitis but also needs to determine how much of the colon is affected. Biopsies with multiple colon tissue samples will help to confirm the diagnosis.
How To Use Suppositories
Your doctor or pharmacist will tell you how many suppositories to use each day. Some types you use once a day before you go to bed, and others you use several times a day with the last dose before you go to bed. Use them after you do a poo.
Try not to do a poo for at least an hour after using a suppository. This gives the medicine time to work.
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis Cured After 30 Years
How Can I Look After My Mental Health
Living with a condition like ulcerative colitis, especially if your symptoms are severe and unpredictable, can be a frustrating and isolating experience. Remember that ulcerative colitis does not have to dominate your life.
- Talking to others with the condition can provide support and comfort. Crohn’s and Colitis NZ provides information on where you can find help and support.
- Remember to take a sick day when you need to.
- If you have unpredictable bowel movements in the morning and worry about getting to work on time, speak to your employer to see if you can change your working hours or work from home.
- Plan your trip so you know where the nearest bathroom is.
- This “I Can’t Wait!” toilet card from Crohn’s and Colitis NZ may help you gain access to a toilet quickly.
- Connect with others who have ulcerative colitis. Even though everyone’s experience will be different, it may help to share ideas.
More Drugs That Work On Your Immune System

Other types of medicines for ulcerative colitis target your immune system, too. Your doctor may call these immunomodulators. They may be good options if 5-ASAs and corticosteroids havenât worked well for you.
The most common ones are azathioprine , mercaptopurine , and cyclosporine . Due to the risk of side effects, doctors usually save cyclosporine for people who donât have success with other meds. They may also try methotrexate paired with folic acid.
Ozanimod is an oral medication and is the first sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator approved for patients with moderately to severely active UC.
The goal is to lower inflammation in your colon.
These drugs can have side effects. They can damage your liver and make you more likely to get skin cancers, lymphoma, and infections. If you take them, your doctor will test your blood and check you for skin cancer regularly.
Cyclosporine is especially strong, but it works fast. Your doctor might prescribe it to get a severe flare under control, and then give you 6-MP or azathioprine afterward. The drug may cause kidney problems, gout, infections, and high blood pressure.
It can take several months for some of these drugs to work. So your doctor may give you a faster-acting medicine, like a low dose of a corticosteroid, to help in the meantime.
Also Check: Ways To Prevent Decubitus Ulcers