After The Solesta Procedure
It is important that you take care of yourself following your Solesta treatment. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics for the chance that you may get an infection, or you may experience some minor bleeding following treatment. It is also possible that you might experience some mild pain or discomfort in the treatment area. As recommended by your doctor, take pain reliever medication if you feel pain or discomfort. By following some simple precautions you may be able to minimize these risks.
Safety Evaluated In > 1000 Adult Patients With Uc10
Serious Adverse Event Rate in Moderate to Severe UC for:8,10
3.5 events per 100 patient-years of HUMIRA exposure
= 1 patient-year
= 1 event of serious infectionac
3407.0 PYs N=1739
Data as of November 20, 2019
Adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population in clinical practice.
PI=prescribing information
aTreatment-emergent AEs were defined as any event with onset or worsening at or after the first dose of HUMIRA and up to 70 days after the last dose of HUMIRA or until the data cutoff date in the study, whichever is the earliest.
bSerious adverse events were defined as fatal or immediately life-threatening required inpatient hospitalization or prolonged existing hospitalization resulted in persistent or significant disability/incapacity congenital anomaly spontaneous or elective abortion or required medical or surgical intervention to prevent a serious outcome.
cData were derived from ULTRA 1 , ULTRA 2 and ULTRA 3 .
Understanding PYs
One event per 100 PYs means that 1 event occurred in a population of 100 clinical trial patients on therapy for1 year.
Safety Considerations1
Reported infections include:
PI=prescribing information
aTreatment-emergent AEs were defined as any event with onset or worsening at or after the first dose of HUMIRA and up to 70 days after the last dose of HUMIRA or until the data cut-off date in the study, whichever is the earliest.
Ulcerative Colitis Surgical Procedures
The standard surgical procedure to treat ulcerative colitis is a proctocolectomy. This surgery removes both your colon and your rectum .
There are two types of proctocolectomy procedures used to treat ulcerative colitis.
-
Proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: Removal of the colon and rectum, and creation of an internal pouch that eliminates the need for a permanent external ostomy.
-
Proctocolectomy with end ileostomy: Removal of the colon, recturm, and anus and creation of an external ostomy.
It can feel overwhelming when you are recommended for one of these surgeries. We can help you understand whats involved with each surgery, and be prepared for life after your proctocolectomy.
You May Like: Foods That Cause Stomach Ulcers
Patient Baseline Characteristics And Treatment Exposure
The overall safety population included 2932 patients who enrolled in the six studies . Of these, 2830 patients were exposed to one or more doses of vedolizumab, contributing a total of 4811 PYs of vedolizumab exposure . The phase 3 safety population was composed of 2884 patients, of whom 504 patients received placebo , contributing a total of 214 PYs of placebo exposure . Placebo-treated patients from GEMINI 1, GEMINI 2 and GEMINI 3 who enrolled in GEMINI LTS received open-label vedolizumab and therefore also contributed to PYs of vedolizumab exposure. Thus, most patients in the phase 3 safety population received one or more doses of vedolizumab . The median vedolizumab exposure in the phase 3 safety population was 378days and 338days for patients with UC and CD, respectively . In the overall safety population, the number of PYs of vedolizumab exposure was > 22 times that for placebo.
Exposure-adjusted incidence rates of GI adverse events in the overall safety population
Who Is Not A Candidate For Solesta
Solesta is only for patients aged 18 and over. People who have an infection or who are currently experiencing bleeding in the rectum or anus should not receive Solesta.
People who have problems in the rectum or anus, such as tumors, abnormal anatomy, large dilated blood vessels or cracks in the tissue , should not receive Solesta.
People who have active inflammation of the bowels should not receive Solesta.
People who have trouble fighting off infection or who take medication to suppress the immune system, such as those used in cancer or organ transplant patients, should not receive Solesta.
If you already have a device or a material placed in your rectum or anus, or if you have had radiation treatments in your pelvic area before, you should not receive Solesta.
You should also not receive Solesta if you have an allergy to any of the materials in the gel.
You should tell your doctor if you have any allergies or if you have had problems with your rectum or anus in the past. Your doctor will determine whether you are a candidate for Solesta.
Also Check: What Should You Not Eat If You Have An Ulcer
Serious Adverse Events Of Interest Across 8 Adult Indications8a
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying and controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population in clinical practice.
Rates displayed as events per 100 PYs as of November 20, 2019
aData derived from global clinical trials of HUMIRA, including randomized controlled, open-label, and long-term extension studies bNon-infectious Intermediate, Posterior, and PanuveitiscExcludes oral candidiasis and tuberculosisdExcludes lymphoma, hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, leukemia, NMSC, and melanoma
AE=adverse event NMSC=non-melanoma skin cancer PYs=patient-years
Patients treated with HUMIRA may be at risk for other serious adverse reactions including:1
Hypersensitivity
Anaphylaxis and angioneurotic edema have been reported. If a serious allergic reaction occurs, stop HUMIRA and begin appropriate therapy.
Hepatitis B virus reactivation
Risk of reactivation may increase in patients who are chronic carriers. Monitor HBV carriers during and after treatment with HUMIRA. If reactivation occurs, stop HUMIRA and begin appropriate therapy.
Demyelinating disease
Cytopenias, pancytopenia
Consider stopping HUMIRA in patients with significant hematologic abnormalities.
Heart failure
Worsening or new onset congestive heart failure may occur. Exercise caution in patients with CHF and monitor them carefully.
Severe Perineal Crohn Disease
The management of severe perineal CD has evolved toward upfront, combined, aggressive medical and surgical therapy. Following this approach, initial response rates to treatment have increased and recurrence rates have decreased significantly.49 Extensive fistulizing disease and/or severe proctitis, however, increase the likelihood of needing proctectomy.
Fecal diversion is often required to manage severe disease however, less than 20% ultimately have intestinal continuity successfully restored, and the use of biologic therapy has not improved these rates.50 Diversion has been shown to be beneficial to a septic perineum and improve symptoms in majority of the patients.51 This may facilitate surgical intervention by limiting the pelvic inflammation or promote postoperative healing after planned proctectomy.
If a large tissue defect is anticipated, one should consider involvement of a plastics/reconstructive surgeon for use of a myocutaneous flap.52 Alternatives are the use of vacuum-assisted closure device applied to the perineum or a pedicled omental flap to fill the pelvis.17
Also Check: Diet When You Have An Ulcer
Safety Considerations With The Use Of Corticosteroids And Biologic Therapies In Mild
Supplemental digital content is available for this article. Direct URL citations appear in the printed text and are provided in the HTML and PDF versions of this article on the journal’s Web site .
Technical editorial and medical writing support was provided, under the direction of the author, by Mary Beth Moncrief, PhD, and Jillian Gee, PhD, Synchrony Medical Communications, LLC, West Chester, PA. Funding for this support was provided by Salix Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. Salix Pharmaceuticals did not actively contribute to the content of this article but reviewed for scientific accuracy.
R. K. Cross, receives fees for consulting and participation in advisory boards from AbbVie Inc., Janssen, Takeda, and UCB, and receives research funding from AbbVie Inc.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Safety And Tolerability Of Oral Topically Acting Corticosteroids
Unlike conventional oral corticosteroids, GI topical corticosteroids facilitate delivery of active medication directly to the site of inflammation, either through direct application or targeted delivery of active drug . Topical targeting can provide local anti-inflammatory action within the GI tract with potentially reduced systemic levels of corticosteroid. Oral topically acting therapies are second-generation corticosteroids that use various drug delivery technologies to ensure GI targeting, which may potentially reduce the incidence of AEs associated with conventional systemic corticosteroids. However, although several active comparator trials of oral topically acting corticosteroids versus prednisone have been reported, few head-to-head studies with the oral topically acting corticosteroids have been conducted, making it difficult to determine the most favorable benefit-risk profile within this drug class.
Recommended Reading: Vsl 3 And Ulcerative Colitis
Perforation Of The Colon
Chronic inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis can weaken the wall of the colon until a hole, or perforation, develops. Once the colon has been perforated, the contents of the intestine can spill into the abdomen and cause a serious infection called peritonitis.
This is a potentially life-threatening condition that needs immediate medical treatment.
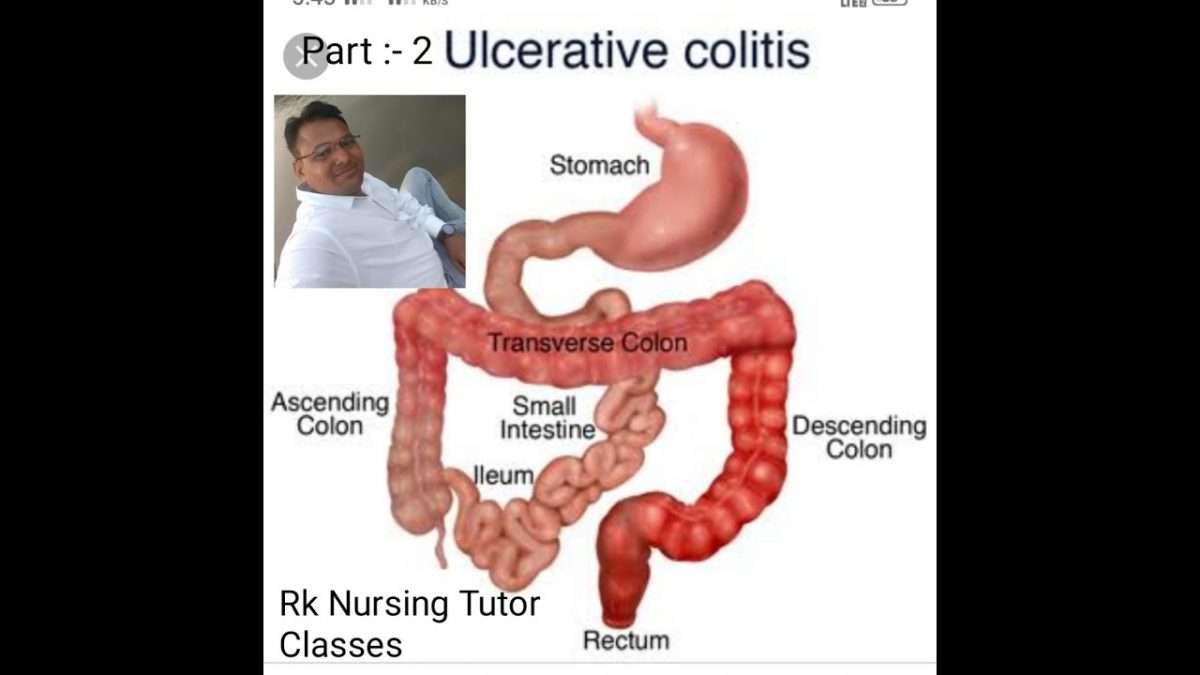
What Is Happening To The Large Intestine With Ulcerative Colitis
There is massive inflammation in the large intestine . The inflammation causes the cells of the lining to die which causes ulcers to form and they bleed and produce pus.
Due to the massive amount of inflammation, the large intestine cannot function normally. Therefore, it cant absorb water. Normally, when GI contents enter into the large intestine from the small intestine the contents is watery. The large intestine will absorb that water as it travels through the different areas of the colon. The stool will then start to have a solid form. However, due to the inflammation with ulcerative colitis it cant, so the patient has diarrhea. The diarrhea will be bloody because as the contents passes over the ulcers it will mix with the blood/pus/mucous.
Furthermore, the patient will have frequent bowel movements because of the inflammation causing the rectum to want to empty.
Patients will have bouts of flare-ups and remission . The ulcerative sites will heal but the lining will be damaged. So, from the continuous cycle of healing and ulcer formation, polyps will form along with scar tissue which leads to bowel narrowing and shortening.
Overtime, due to severe cases, the large intestine will start to lose its unique form. It wont have those small pouches present. The haustra help with food churning throughout the large intestine. Instead, the large intestine will start to appear smooth.like a lead pipe which is called the lead pipe sign and is seen on a barium enema.
Read Also: Symptoms Of A Bleeding Ulcer In Your Stomach
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Care Plans
Inflammatory bowel disease is an idiopathic disease caused by a dysregulated immune response to host intestinal microflora. It results from a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Similarities involve chronic inflammation of the alimentary tract and periods of remission interspersed with episodes of acute inflammation. There is a genetic predisposition for IBD, and patients with this condition are more prone to the development of malignancy.
The two major types of inflammatory bowel disease are ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease .
Ulcerative colitis : A chronic condition of unknown cause usually starting in the rectum and distal portions of the colon and possibly spreading upward to involve the sigmoid and descending colon or the entire colon. It is usually intermittent , but some individuals have continuous symptoms. Cure is effected only by total removal of colon and rectum/rectal mucosa.
Regional enteritis : May be found in portions of the alimentary tract from the mouth to the anus but is most commonly found in the small intestine . It is a slowly progressive chronic disease of unknown cause with intermittent acute episodes and no known cure. UC and regional enteritis share common symptoms but differ in the segment and layer of intestine involved and the degree of severity and complications. Therefore, separate databases are provided.
Safety And Tolerability End Points And Analyses

Safety and tolerability were evaluated in all patients in the safety population according to their exposure to study drug. Exposure was calculated using the number of days the patient received study drug, based on first and last dose dates. For patients not enrolled in the ongoing GEMINI LTS study at the data cut-off date, 16weeks were added to the date of the last dose to account for the known duration of detectable vedolizumab serum concentrations. In phase 2 studies, a dose was defined as any amount of infusion, and in phase 3 studies, as 75% of the infusion by volume. Total vedolizumab exposure for a patient was calculated as the sum of exposures in all applicable studies. For patients who received only placebo, exposure to vedolizumab was calculated as 0days.
Infusion-related reactions were defined as AEs occurring on the day of or one calendar day after the infusion that were assessed by the investigator as infusion-related. In addition, blood samples for antivedolizumab antibody assessment were collected within 30min before dosing in the phase 3 studies and within 2h in the phase 2 studies. Immunogenicity was determined as described elsewhere.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Oral Ulcers
Controlling Your Ibd With Medications During Pregnancy
If you’ve been diagnosed with IBD and are considering pregnancy, or are currently pregnant or breastfeeding, you might be thinking about the safety of your medications for your baby. Rest assured, we’re here to help you understand how IBD drugs may impact your pregnancy so you can have the information you need as you prepare for the future.
Remember, talking with a doctor who specializes in the treatment of IBD during pregnancy is the best way to find out what’s right for you.
Aga Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Management Of Moderate To Severe Ulcerative Colitis
- Joseph D. FeuersteinAffiliations
- Kim L. IsaacsAffiliations
- Division of Gastroenterology, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OhioDepartment of Veterans Affairs Northeast Ohio Healthcare System, Cleveland, Ohio
- AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines CommitteeAuthors List
Abbreviations used in this paper:
Gastroenterology.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
- Colombel J.F.
- et al.
Am J Gastroenterol.
- Colombel J.F.
- et al.
Am J Gastroenterol.
N Engl J Med.Br Med J.
Br Med J.
| Variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal no. of daily bowel movements | 0 | ||
| 12 more bowel movements than normal | 1 | ||
| 34 more bowel movements than normal | 2 | ||
| 5 or more bowel movements than normal | 3 | Ulcerations, severe friability, spontaneous bleeding | 3 |
| Most severe rectal bleeding of the day | None | ||
| Blood streaks seen in the stool less than half of the time | 1 |
Gastroenterology.Gastroenterology.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.Gastroenterology.
Recommended Reading: Align Probiotic For Ulcerative Colitis
Metabolic And Hematologic Complications
Most biologic medications have been associated with at least 1 metabolic or hematologic side effect or derangement. Liver enzyme abnormalities with anti-TNFs have been described. These are typically asymptomatic and discovered incidentally, though anti-TNFs have also been associated with autoimmune hepatitis.48,49 Excluding autoimmune hepatitis, liver enzyme abnormalities with anti-TNFs are usually self-limited.50 Neutropenia is the most commonly reported anti-TNF hematologic complication, with 0.6%5.7% of patients treated with anti-TNF ever developing neutropenia and more commonly reported in rheumatologic diseases than IBD.51 Classically mild and transient, anti-TNF-induced neutropenia rarely requires discontinuation.51,52
Hepatobiliary events were observed more frequently in vedolizumab-treated participants compared with placebo in the clinical trials, with hepatic steatosis the most common hepatobiliary event .19 There was no difference in isolated abnormal liver enzymes in vedolizumab compared with placebo , and isolated liver enzyme abnormalities did not lead to vedolizumab discontinuation. No hematologic abnormalities were observed in the clinical trials of vedolizumab.53,54
No significant liver enzyme abnormalities have been observed in ustekinumab- or tofacitinib-treated patients. In the OCTAVE trials of tofacitinib, 2 tofacitinib-treated subjects with baseline low neutrophil counts developed absolute lymphopenia.22
Understanding Humira Safety Through 5 Years Of Data
Rates of treatmentemergent adverse events a of interest in 3 controlled and uncontrolled moderate to severe adult UC studies for:11,12,b
Risk of Serious Infection1
Patients treated with HUMIRA are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death. Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
Carefully consider the risks and benefits of treatment with HUMIRA prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. Monitor patients closely for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with HUMIRA.
- Do not start HUMIRA in patients with an active infection, including localized infections.
- Patients older than 65 years, patients with comorbid conditions, and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants may be at greater risk of infection.
The use of HUMIRA in UC beyond 1 year has not been evaluated in controlled clinical studies.1
- OLE populations generally consist of treatment responders, as patients who are unable to tolerate the drug or who do not respond to the drug drop out.
OLE=open-label extension PYs=patient-years TNF=tumor necrosis factor
Risk of Tuberculosis1
The use of HUMIRA in UC beyond 1 year has not been evaluated in controlled clinical studies.1
OLE=open-label extension PYs=patient-years TNF=tumor necrosis factor
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis And Bloody Stool
Predictors Of Serious Infections
A Cox proportional hazards model with time-dependent covariates was used to determine the relative contribution of different factors to the occurrence of serious infections in the phase 3 safety population, which included patients in both treatment arms. Predictors were analysed in the UC and CD populations alone and combined. Factors assessed were age, sex, disease duration, baseline disease activity, prior history of tumour necrosis factor antagonist failure, baseline use of immunosuppressives, on-study use of narcotic analgesics or on-study use of corticosteroids. Patients were considered corticosteroid users in this model if they received corticosteroids within 30days before the infection date. When patients with UC and CD were combined, a common disease activity index was created to measure the contribution of baseline disease activity . Vedolizumab treatment was not included as a covariate because nearly all patients analysed were exposed to vedolizumab at one point , invariably resulting in significantly lower HRs for serious infection.