Keep Up With Your Checkups
If you have either condition, you’ll need to keep up with your checkups, even if your symptoms start to ease up.
You may also need to get colonoscopies more often and start them at a younger age. A colonoscopy can check for cancer or polyps that need to come out. Experts recommend that you start these tests within 8 to 10 years of developing UC or Crohnâs symptoms, and then typically every 1 to 3 years after that. Your doctor will tell you a schedule that is best for you.
Show Sources
Remission With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
People with inflammatory bowel disease strive to achieve remission statusmeaning there is no more inflammation or agonizing symptoms. Statistically speaking, about 50 percent of Crohn’s patients will be in remission or have mild disease over the course of five years past initial diagnosis.
Comparatively, in a given year, 48 percent of patients with ulcerative colitis are in remission, 30 percent have mild disease activity, and 20 percent have moderate disease activity.
Remission doesn’t mean you should throw your care plan out the window.
“Once remission has been accomplished, patients need ongoing medications to ensure that they stay in remission,” says Dr. Nayak. You’ll still want to avoid triggers and talk to your doctor about how often to get colonoscopies to screen for colon cancer, as the risk is higher with both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
What Are Surgical Treatments For Ulcerative Colitis
After 30+ years of living with ulcerative colitis, about 1 in 3 people need surgery.
A surgeon:
- Removes the colon or the colon and rectum .
- Connects the small intestine and anus.
- Creates an ileal pouch that collects stool, which then exits through the anus.
Rarely, you may need an ileostomy instead of an ileal pouch. An ileostomy bag attaches outside of the belly to collect stool.
A proctocolectomy is curative. Symptoms wont return after surgery to remove the colon and rectum. However, you may have problems with the ileostomy or ileal pouch, such as pouchitis .
Don’t Miss: Skin Graft For Foot Ulcer
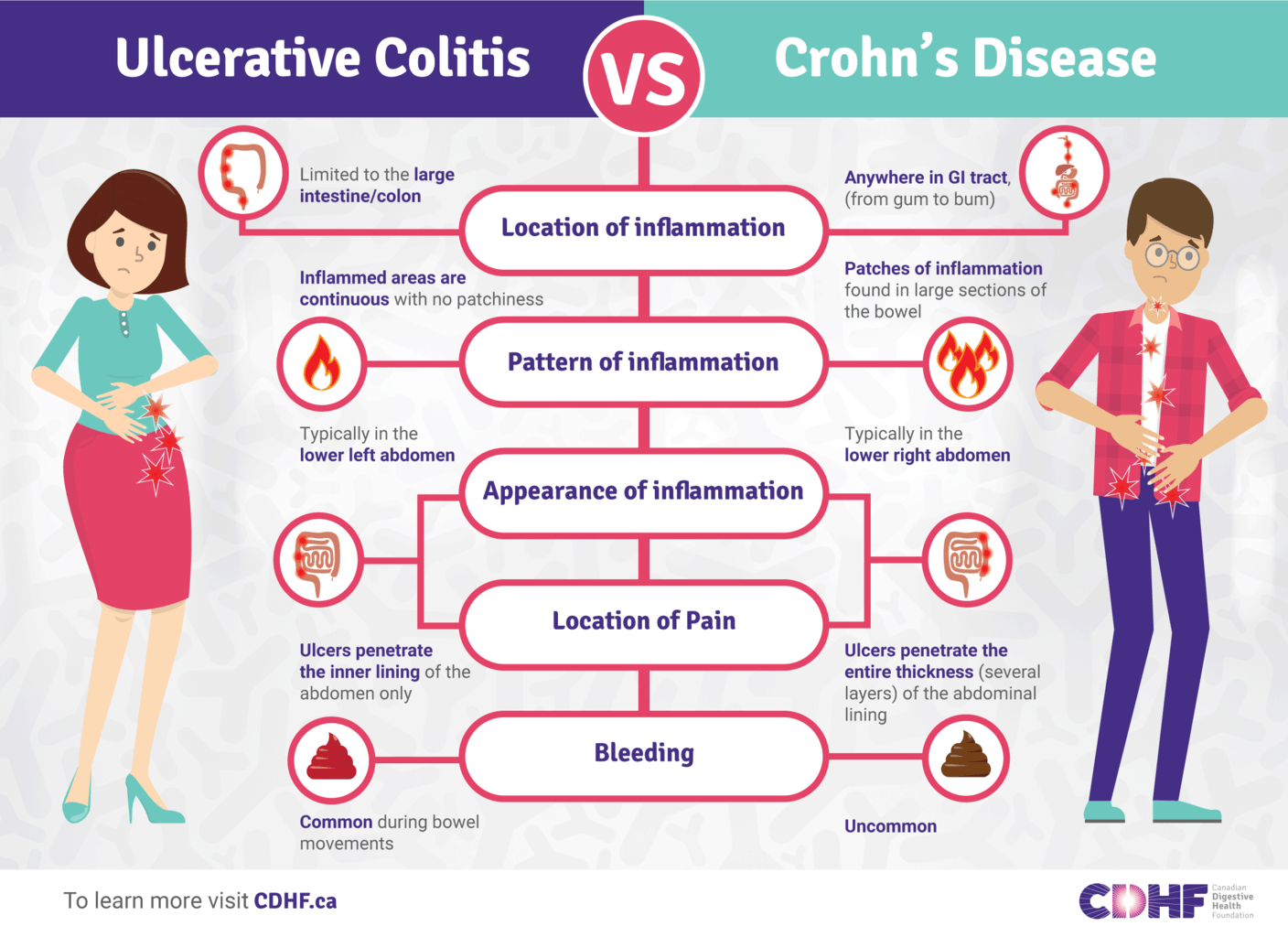
Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohns Disease: How These Bowel Diseases Differ
It’s understandable if you confuse ulcerative colitis with Crohn’s disease. Both of these chronic conditions are a type of inflammatory bowel disease that targets the digestive system with painful and burdensome symptoms. They both cause stomach pain and cramping, an urgent need to move the bowels, diarrhea, and fatigue. And they both have two phases of activity: flares and remission. On the surface, it can be hard to tell these inflammatory bowel diseases apart.
When it comes to ulcerative colitis vs. Crohn’s disease, the key differences lie where they are located in the body.
What Are The Types Of Ibd
Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are the main types of IBD. Types include:
- Crohns disease causes pain and swelling in the digestive tract. It can affect any part from the mouth to the anus. It most commonly affects the small intestine and upper part of the large intestine.
- Ulcerative colitis causes swelling and sores in the large intestine .
- Microscopic colitis causes intestinal inflammation thats only detectable with a microscope.
Don’t Miss: Natural Supplements For Ulcerative Colitis
The History Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
There is some debate about the earliest description of ulcerative colitis. There are mentions of chronic diarrhea in the writings of Hippocrates , wherein the Ancient Greek physician discussed its causes. In 1793, Scottish doctor Matthew Baillie published Morbid Anatomy of Some of the Most Important Parts of the Human Body, which described fatal cases of what sounds like ulcerative colitis. However, it wasnt until the 1800s that bowel inflammation was studied by medical schools. Doctors François-Joseph-Victor Broussais and John Brown proposed that all diseases stem from inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
The first doctor to use the term ulcerative colitis was Sir Samuel Wilks who, in 1859, published a case report on a condition very similar to what we know today as UC. Fifty years later, a symposium was held by the Royal Society of Medicine in London to discuss over 300 cases of ulcerative colitis. Also in 1859, John Percy Lockhart-Mummery established sigmoidoscopy as a safe and invaluable tool for evaluating the colon and diagnosing UC.
Early treatments for UC included feeding patients raw pork bowel and running an electrical current through the bowel after irrigating it with a zinc solution. At first, surgical treatment of ulcerative colitis was rare and experimental. By 1930, surgical interventions such as ileostomy and colectomy became standard.
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
The differences between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are:
- Ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere between the mouth and the anus
- In Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed in between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is continuous inflammation of the colon
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the inner most lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls
You May Like: How Do You Get Rid Of Stomach Ulcers
Can You Drink Alcohol With Crohn’s Disease
- Drinking alcohol is not recommended for most people with Crohn’s disease.
- Alcohol may irritate the lining of the intestinal wall, causing or worsening symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
- It also may contribute to malabsorption, further complicating nutritional deficiencies.
- Alcohol interacts with many medications, causing side effects that may be serious.
- Alcohol disrupts sleep cycles and can leave you feeling tired, and irritable the next day. However, if alcohol is well tolerated and not causing any complications, it can be consumed in moderation.
- Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration very easily.
- Dehydration makes you feel weak, tired, light-headed, or just “blah.”
- Alcohol can cause headaches, abdominal pain, and other symptoms. It also can place dangerous strain on your kidneys.
- Dehydration can be avoided by making a special effort to take in plenty of nonalcoholic fluids.
- You should take at least 8 full glasses of fluid every day.
- Try to stick to water, diluted fruit juice, sports drinks, decaffeinated beverages, and fruit and vegetable drinks.
- Avoid caffeinated beverages and sodas.
Symptoms Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The recurring bouts of diarrhea and belly pain that sent people to the doctor are hallmark signs of both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Despite their similarities, the two inflammatory bowel diseases can differ in how symptoms present.”I have found that patients with ulcerative colitis tend to have more diarrhea, which can be bloody at times,” says Rahul Nayak, MD, a gastroenterologist with Kaiser Permanente in Atlanta. “Crohn’s typically presents with more abdominal pain but can also include diarrhea as well.”
Mouth sores and fistulas are unique to Crohn’s disease. A fistula is an abnormal connection between two parts of the body, such as between the bowel and the skin, bladder, and other parts of the bowel.The symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease can be embarrassing, painful, and unbearable at times, but Dr. Nayak says that early and aggressive treatment can reduce or eliminate the possible symptoms and complications.
Treatment depends on the location of the inflammation in the body. That’s why it’s essential to know the different types of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease and the specific symptoms they present.
You May Like: What To Avoid With An Ulcer
About Harvard Medical School Guides
Harvard Medical School Guides delivers compact, practical information on important health concerns. These publications are smaller in scope than our Special Health Reports, but they are written in the same clear, easy-to-understand language, and they provide the authoritative health advice you expect from Harvard Health Publishing.
- What is IBD?
- Causes and risk factors of IBD
- Complications of IBD
Whats The Difference Ulcerative Colitis Vs Crohn’s Disease
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two main forms of inflammatory bowel diseases , both characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Although they share many similarities, there are key differences between the two diseases, according to the Crohns and Colitis Foundation.
Both conditions can cause significant health challenges and be difficult to manage without an expert doctor to help properly diagnose and treat which specific disease you have.
Also Check: Wound Treatment For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Actions For This Page
- Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are collectively known as inflammatory bowel disease .
- Crohns disease can appear in any part of a persons digestive tract from mouth to anus.
- Ulcerative colitis is located only in a persons large bowel .
- Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD.
- Medications help manage the symptoms of IBD.
- People with IBD can lead useful and productive lives.
- Some dietary changes can help you manage symptoms of IBD and allow medications to work better.
- Always talk with your doctor, healthcare specialist or dietitian before changing your diet. Arrange an emergency plan of action with your doctor, including after-hours phone numbers.
What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is an umbrella term used to describe both Crohns and colitis. IBD differs from irritable bowel syndrome , although there is often overlap in causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Inflammatory bowel diseases are diagnosable through imaging, and irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by a group of symptoms that do not show any definitive disease in testing.
Also Check: Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Plan
Distinguishing Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis Signs And Symptoms
In either disease, symptoms can range from mild to severe and can even occur as flare-ups if not well managed. Although primary symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis affect the gastrointestinal tract, other symptoms may also occur, affecting other parts of the body.
Both conditions often share the following symptoms:
- Belly cramps and pain
- Fatigue
- Night Sweats
- Problems with your period. You might skip them, or their timing might be harder to predict.
However, each has its own unique characteristics as well. Crohns disease, for example, can affect nearly any tissue found in the digestive tract, going from the mouth all the way to the anus. Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, only affects the large colon. Inflammation is a common feature of both, but ulcerative colitis tends to have more uniform and uninterrupted lesions as opposed to Crohns disease, which can have healthy areas in between inflamed spots. Additionally, ulcerative colitis is more often associated with rectal bleeding and blood in the stool.
Complications Caused By Nutritional Deficiencies
Some of the complications of malnutrition include:
- Dehydration diarrhoea causes your body to lose fluid, which can lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia reduced iron in the diet combined with losing blood from the bowel can lead to anaemia .
- Weight loss reduced appetite and poor absorption of food nutrients can cause weight loss.
- Reduced growth inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can impair a childs growth and physical development.
Read Also: Aloe Vera Gel For Horses Ulcers
Crohns Disease Vs Ulcerative Colitis: Us Prevalence And Incidence Rate
The CDC estimated that one to 1.3 million Americans is affected by IBD. Generally, ulcerative colitis is found to be more common in males where Crohns disease is more common in females. Prevalence of Crohns disease in the U.S. is 26 to 199 per 100,000 persons,and ulcerative colitis is 37 to 246 per 100,000 persons.
Incidence rate of Crohns disease is 3.1 to 14.6 cases per 100,000 person years, and for ulcerative colitis it is 2.2 to 14.3 cases per 100,000 person years.
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative proctitis
The inflammation is restricted to less than six inches of the rectum. Symptoms include urgent bowel movements, rectal pain, and bleeding from the rectum.
Left-sided colitis
Inflammation expands from the rectum up to the splenic flexure, a part of the colon near the spleen in the upper left abdomen. Proctosigmoiditis, which affects the rectum and lower section of the colon, is a form of left-sided colitis as well. Pain is felt on the left side of the abdomen, with symptoms like diarrhea, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
Extensive Colitis
Inflammation affects the entire colon. Symptoms include belly pain, bloody diarrhea, lack of appetite, and weight loss.
Don’t Miss: How To Heal Ulcerative Colitis With Food
Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis And Diet
Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD, and long-term special diets are not effective in treating IBD. However, adjusting your diet can help manage some of your symptoms, and can help IBD medications work better. A person with IBD has to pay close attention to their diet, since they may have malnutrition.
Risk Factors For Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease
An estimated 3 million adults have ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. Both conditions affect men, women, and children, and can occur at any age.Ulcerative colitis is most often diagnosed in people in their mid-30s. Crohn’s disease is usually diagnosed between ages 20 and 30.
You might think that the conditions are related to food intolerances , but that’s not the case.Research is ongoing, but for now experts know there are a few factors that increase the risk of developing either disease.
First, there’s the immune system. Normally, the immune system is on our side, attacking and killing viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms we don’t want in our bodies. But in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, the immune system doesn’t retreat. Instead, it stays in the “attack and kill” mode, which results in excessive inflammation.
Second, family history is a risk factor. People who have inherited inflammatory bowel disease genes are more susceptible to it. The genetic risk is greater in Crohn’s disease about 15 percent of people with Crohn’s have a first-degree relative with the disease.
Third, unknown environmental factors may trigger the overzealous immune response.
Read Also: Foam Dressings For Leg Ulcers
Ibd And Changing Your Diet
Some dietary changes that may help a person with IBD include:
- Low-fibre diet when IBD is active, most people find a bland , low-fibre diet helps to ease diarrhoea and abdominal cramping. People with Crohns disease who have a narrowed small intestine may need to eat a low-fibre diet most of the time.
- Low-fat diet people with Crohns disease who experience steatorrhoea may benefit from a low-fat diet.
- Low-lactose diet the milk sugar lactose is broken down by the enzyme lactase, commonly found in the lining of the small intestine. Some people with Crohns disease lack this enzyme, so should avoid milk and other dairy products. Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed with a simple test ask your doctor.
- Liquid diet a person with severe Crohns disease may need a nutritionally balanced liquid diet.
- Plenty of water people with IBD need to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
There are multiple contributing risk factors that can lead to ulcerative colitis and Crohns. Evidence does suggest that both are associated with an inappropriate immune response, which can arise from many different environmental factors, gut microbiome imbalance, as well as genetics .
The body creates temporary inflammation as part of a normal immune system response to threats and foreigners that may cause harm. An inappropriate immune response occurs when the immune system attacks something that is probably not harmful or overreacts to a possible pathogen. This creates unnecessary or excessive inflammation that can become chronic inflammation.
For example, in addition to toxins and infections, the immune system may attack food particles, beneficial gut bacteria, and, in the case of ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease, the lining of the digestive tract [1
What might be causing the inflammation of the digestive tract and an inappropriate immune response?
Some of the contributing factors in IBD are:
Read Also: Is Soy Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Difference Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis Causes
As with many autoimmune diseases, the exact cause of either Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis is unknown. Some theorized causes of Crohns disease include the immune system being triggered by a virus or bacteria, and heredity as many patients with Crohns disease will also have a relative with the condition.
The immune system is also suspected to play a role in ulcerative colitis along with genetics and environmental factors. There seems to be some genes involved in the development of ulcerative colitis, and having more than four family members with ulcerative colitis increases your risk of developing it. Environmental factors include place of residence, especially because there appear to be higher rates of ulcerative colitis in urban areas, North America, and Western Europe. Air pollution, medications, and consuming certain diets have also been found to be associated with a higher risk of ulcerative colitis.
What Is Crohns Disease
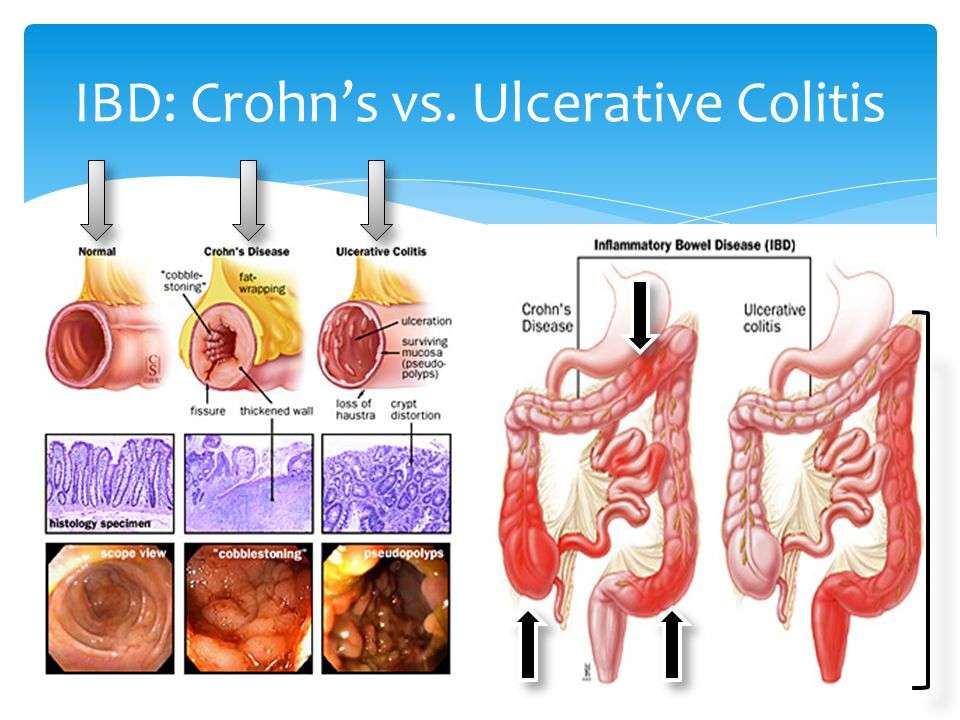
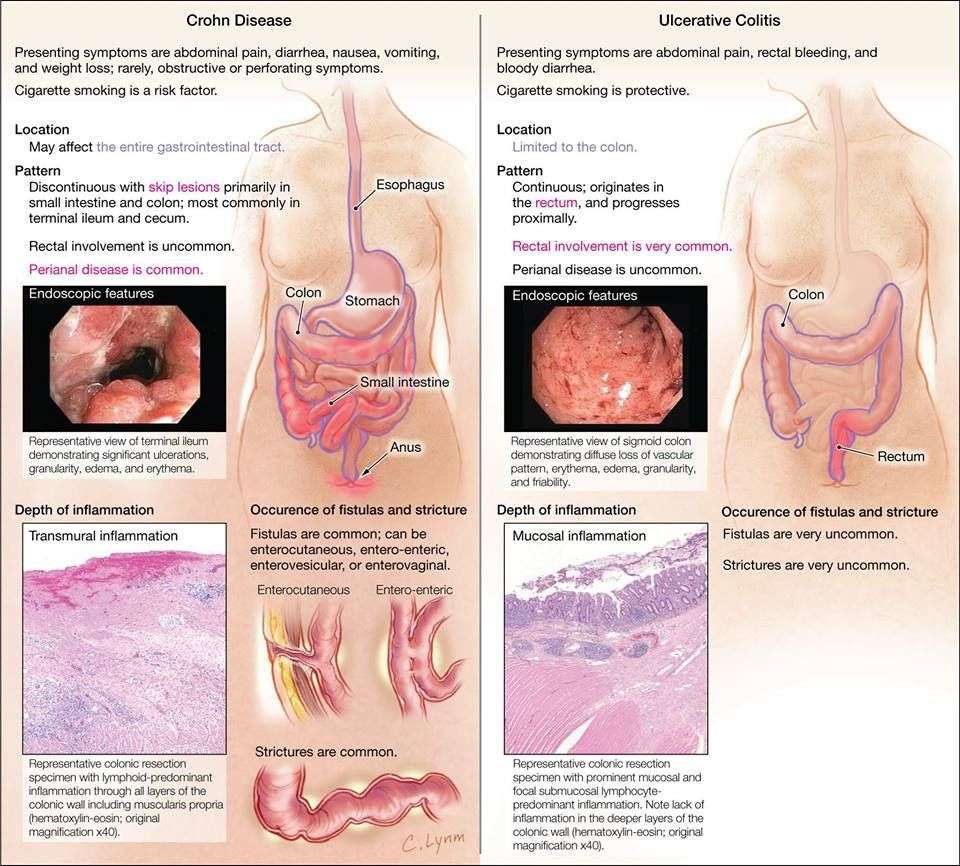
Crohns disease can attack any part of the gastrointestinal system between the mouth and the anus. Crohns is most often found at the end of the small intestine and upper part of the large intestine, or colon. Crohns disease can appear anywhere in the GI tract, in patches between healthy sections of the intestine. Damage and inflammation from Crohns can penetrate deep into all layers of the bowel wall. Disease can recur even if the affected portion of the bowel is surgically removed. There are multiple types of Crohns.
Also Check: Diet Plan For Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease Different
Crohns disease causes chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract . It can affect any part of the GI tract, as well as areas from the mouth to the anus. But it most commonly affects the end of the small intestine where it links to the beginning of the colon.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms reside in the large intestine only and often vary from person to person, depending largely on the part of the colon thats affected and the severity of the inflammation. It affects everyone differently, and symptoms range in severity. UC is a progressive disease and will change over time in your body.
Ongoing inflammation of the GI tract happens with both Crohns and UC, but there are a few key distinctions, such as:
- Ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere between the mouth and the anus.
- With Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis includes continuous inflammation of the colon.
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the innermost lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls.
In approximately 10% of cases, an inflammatory bowel disease will exhibit features of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. We typically refer to these as indeterminate colitis.