Why Choose Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai has a unique and rich tradition of specialized and individualized treatment and scientific research and discovery in ulcerative colitis. The physicians/scientists in the Mount Sinai Health System are constantly conducting clinical trials and are developing new drug therapies to help patients manage their disease. Learn more about ulcerative colitis.
There are 3 basic tests for colon cancer a stool test , sigmoidoscopy , and colonoscopy . All 3 are effective in catching cancers in the early stages, when treatment is most beneficial.
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
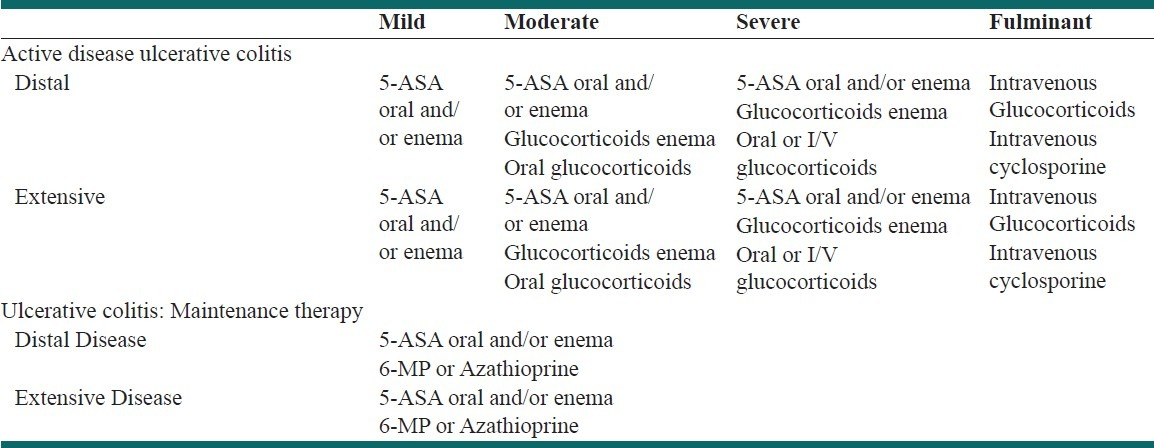
Ulcerative colitis is categorized according to location. Proctitis involves only the rectum. Proctosigmoiditis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon. Left-sided colitis encompasses the entire left side of the large intestine. Pancolitis inflames the entire colon.
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Complementary Treatments And Therapies
You may consider these approaches in addition to what your doctor prescribes. But itâs important to talk to your medical team about any and all of them because some, like supplements, can interfere with treatments from your doctor. Letâs take a look at a few:
Mind-body therapies:Stress and anxiety are well-known triggers for many people with ulcerative colitis, so it is not surprising that mind-body relaxation techniques could help. These techniques help nurture a healthy connection between your mind and body as well as between you and the outside world. In some cases, they encourage behavior changes in your everyday life. They may be worthwhile if only to lessen anxiety and depression linked to UC and improve quality of life. In addition, there is some evidence that yoga, meditation, and gut-centered hypnotherapy could help with some physical symptoms or flare-ups of UC. Some of the techniques, like cognitive behavioral therapy and patient support groups, have been so successful that they have slowly become a part of mainstream treatment for IBD.
Keep in mind that the FDA doesn’t regulate supplements, so claims on packaging may not be accurate. Thatâs yet another reason why itâs important to talk to your doctor before you start taking any supplements for your UC.
Recommended Reading: Best Meds For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis: Diagnosis And Treatment
ROBERT C. LANGAN, MD PATRICIA B. GOTSCH, MD MICHAEL A. KRAFCZYK, MD and DAVID D. SKILLINGE, DO, St. Luke’s Family Medicine Residency, Bethlehem, Pennsylvania
Am Fam Physician. 2007 Nov 1 76:1323-1330.
Patient information: See related handout on ulcerative colitis, written by the authors of this article.
This article exemplifies the AAFP 2007 Annual Clinical Focus on management of chronic illness.
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disease characterized by diffuse mucosal inflammation of the colon. Ulcerative colitis always involves the rectum , and it may extend proximally in a contiguous pattern to involve the sigmoid colon , the descending colon , or the entire colon .1 This article reviews the diagnosis and treatment of ulcerative colitis from a primary care perspective.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Liver disease.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis And Lung Disease
Who Diagnoses Ulcerative Colitis
If you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis, your regular healthcare provider will probably refer you to a specialist. A gastroenterologist a doctor who specializes in the digestive system should oversee the care for adults. For young patients, a pediatric gastroenterologist who specializes in children should manage the care.
What Is The Best Diet For Ulcerative Colitis
Theres no single diet that works best for ulcerative colitis. If the disease damages the lining of the colon, your body might not absorb enough nutrients from food. Your healthcare provider may recommend supplemental nutrition or vitamins. Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan.
Don’t Miss: How Do Doctors Test For Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnostic Tests For Suspected Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The majority of children with ulcerative colitis present with the characteristic features of diarrhoea, blood in stools and abdominal pain, which indicate a colitic process. Blood tests will show abnormalities in around 80% of cases in inflammatory bowel disease , and thus, form part of the initial assessment of suspected cases. Faecal tests such as calprotectin are useful adjuncts to these blood tests in identifying inflammation, but levels can be elevated by causes apart from IBD.
In cases with suspected IBD, following exclusion of an infective cause, both upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy are required. Imaging of the small bowel is also recommended. With the more widespread availability of magnetic resonance enterography this is now the modality of choice, when available, for differentiating UC from Crohn’s disease . It is important to exclude Clostridium difficile infection in the differential diagnosis of IBD initially and exclude C. diff infection as the cause of a disease flare. Despite recommendations to screen for C. diff in these situations, it can often be difficult in practice as this test has not been historically widely performed in children.
Maintenance Of Remission In Mildly
5-ASAs
We recommend the use of oral 5-ASA at a dose2 g/day for maintenance of remission in UC patients
We identified two RCTs involving 306 participants with 4852 weeks of follow-up, which provided evidence relevant to our PICO question. We synthesised these in a meta-analysis .
For clinical remission, there was moderate-quality evidence that oral 5-ASA was statistically significantly superior to placebo for maintaining remission in adult patients with UC . For endoscopic remission there was moderate-quality evidence favouring the use of 5-ASA, but this did not reach significance . Only one RCT contributed evidence for SAEs. Treatment with oral 5-ASA was associated with statistically significantly fewer SAEs .
Although the quality of evidence was judged to be overall very low , we nonetheless felt it appropriate to make a strong recommendation, given the safety and relatively low cost of this intervention. An additional consideration may be the reported potential chemopreventive benefits of maintenance 5-ASA treatment, although this finding has been inconsistently reported in the literature and may reflect selection bias seen in referral centre-based cohorts.
We suggest the use of topical 5-ASA for the maintenance of remission in patients with distal UC
Immunomodulators
We recommend monotherapy with thiopurines for the maintenance of remission in patients with steroid-dependent UC or who are intolerant to 5-ASA
Also Check: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Hair Loss
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Flareups
When youre in remission from ulcerative colitis, youll want to do everything you can to prevent a flareup. Things that may cause a flareup include:
- Emotional stress: Get at least seven hours of sleep a night, exercise regularly and find healthy ways to relieve stress, such as meditation.
- NSAID use: For pain relief or a fever, use acetaminophen instead of NSAIDs like Motrin® and Advil®.
- Antibiotics: Let your healthcare provider know if antibiotics trigger your symptoms.
What Should I Ask My Doctor On Behalf Of My Child Or Teenager
Ask your healthcare provider the following questions in addition to the ones listed above:
- What vitamins should my child take?
- Will my other children have pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child at risk for other conditions?
- Can you recommend a psychiatrist or therapist to help my child with emotional issues related to pediatric ulcerative colitis?
- Is my child growing at a normal rate?
- What can I do to help my child cope at school?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
When you have ulcerative colitis, its essential to work closely with your healthcare team.
Take your medications as prescribed, even when you dont have symptoms. Skipping medications youre supposed to take can lead to flareups and make the disease harder to control. Your best shot at managing ulcerative colitis is to follow your treatment plan and talk to your healthcare provider regularly.
You May Like: What Is Good For Ulcer Pain
Induction Of Remission In Mildly
5-aminosalicylates
We recommend 5-aminosalicylates at a dose of 2 g/day to induce remission in patients with mildly-to-moderately active UC
We performed a meta-analysis of 11 eligible RCTs with a total of 2156 patients evaluated for 412 weeks 5-aminosalicylates had a significantly higher efficacy in achieving clinical remission versus placebo . Similarly, the clinical response in 14 studies evaluated at 210 weeks was significantly better for 5-ASA with response in 59% of patients receiving 5-ASA compared with 35% of those receiving placebo. The efficacy of 5-ASA on endoscopic response as evaluated in four RCTs with 416 patients investigated after 412 weeks was better with 5-ASA 5-ASA was generally very well tolerated. The serious adverse event rate evaluated in 13 studies with 2141 patients for a maximal follow-up of 12 weeks was 6.1% versus 9% in the placebo arms .
The quality of evidence was globally evaluated as low due to significant heterogeneity and possible publication and reporting bias for certain outcomes .
We recommend topical 5-ASA at a dose of1 g/d for the induction of remission in active distal colitis
Overall, the quality of available evidence was classified as low. Despite this, our recommendation is strong considering the extensive clinical experience corroborating efficacy and very few SAEs related to topical 5-ASA administration.
Topical corticosteroids
Colonic-release corticosteroids
Immunomodulators
Ecco Guidelines On Surgical Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis

Opening up the second part of the update on the ECCO Guidelines on the Surgical Treatment of UC, Yves Panis, Professor of Digestive Surgery, Beaujon Hospital, Paris, France, provided key updates to surgery in cases of moderate-to-severe UC. The first statement update outlined that reconstructive ileal pouch-anal anastomosis surgery can be offered to refractory and corticosteroid-dependent patients following evidence that this improves patient quality of life. Panis also touched on the importance of pre-operative optimisation in patients with moderate-to-severe UC. The key update focuses on the use of steroids pre-operatively, which should be markedly avoided or weaned off before restorative surgery. The new guidelines advise that where weaning is not possible, surgery should be postponed. Prophylactic anticoagulation therapy is also advised in adult patients with active UC to reduce the risk of venous thromboembolism, and systemic nutrition is advised despite a lack of evidence.
Variations on total colectomy procedures were also discussed, which can be performed in modified two- or three-stage methods. The updated guidelines state that the modified two-stage procedure may be associated with fewer complications, as patients are subjected to less surgery, but more evidence is needed to confirm this.
You May Like: Is Soy Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Medical Management Of Uc
The treatment recommendations are based on the guidelines produced by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the joint guidelines produced by the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation and European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition . These guidelines provide very useful and comprehensive algorithms, which cover most common clinical eventualities.
Most patients with UC can be treated on an outpatient basis, but with hospitalisation necessary for ASC. The main aim of treatment of UC in children is to achieve maximum possible symptomatic control with minimal side effects, while allowing children to function as normally as possible. The target for treatment increasingly is also looking at intestinal healing beyond simple symptomatic control to try and reduce the risk of long-term complications and surgery. Treatments can be broadly considered as those used to induce remission , such as 5-aminosalicylic acid agents, corticosteroids and biologics, and those used for long-term maintenance of remission such as 5-ASA agents, biologics and thiopurines.
Work With Your Doctor To Understand Uc Severity
It’s important for you and your doctor to understand how severe your symptoms are. Beyond that, tests and procedures may be done to evaluate your disease activity and get an even better understanding of whats really happening inside your bodyand the inflammation thats occurringgetting you to the treatment plan thats right for you.
Also Check: Signs Of Ulcers In Humans
Changes To The Medical Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis
Raine highlighted the key changes, referred to as surprises, in the update of the 2022 ECCO Guidelines on the Medical Treatment of UC. A notable shift from the 2017 guidelines is the recommendation of considering treatment options based on patient disease severity. Previously, guidelines advised treatment according to the site of the disease and its activity, whereas revised guidelines recommend treatment under sections labelled Medical Management of Mildly-to-Moderately Active UC and Medical Management of Moderately-to-Severely Active UC. The decision to change this particular section aims to ensure that patients with limited disease who are displaying active symptoms have access to appropriate treatment options. A statement from the expert ECCO Guidelines Committee explained: We feel that addressing the treatment choice to the clinical activity of a patient is appropriate.
A notable change to the ECCO Guidelines on the Medical Treatment of UC is in regard to new data and treatments. Following the recent MERIT-UC trial conducted by Herfarth et al.,1 which took place in 2018 and concluded that methotrexate was not superior to a placebo in maintaining steroid-free response or remission in UC, the drug has been removed from the guidelines.1 New data for vedolizumab, ustekinumab, and tofacitinib have been included in the updated ECCO Therapeutic Guidelines on UC, which have purposefully been written in a way that allows for new updates to therapeutics to be included.
Does Ulcerative Colitis Make You Immunocompromised
Ulcerative colitis doesnt make you immunocompromised. Some of the medicines that treat it may change the way your immune system responds. This change is different for each medication. Some of these changes may increase the risk of certain infections or other issues. A discussion with your health care team before starting a medication is the best way to understand these risks and ways to prevent them.
You May Like: Hand Foot And Mouth Ulcers
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
Surgical Management Of Paediatric Uc
Surgery is an integral part of the management strategy in patients with UC. The most common surgery that is carried out is a subtotal/total colectomy with a temporary stoma. There is evidence to show that laparoscopic surgery is as safe and effective as open surgery, but has the added benefit of reduced hospital stay, improved patient experience and improved cosmetic outcomes. Restorative surgery can be carried out in 13 stage pouch surgery within selected groups of children. Although pouch surgery offers the comfort of not having a stoma for life, there are many concerns that should be discussed to ensure that the child and their parents are aware of the potential risks, which include faecal incontinence, reduced fecundity and erectile dysfunction. Pouchitis is one of the more common problems encountered with antibiotics used as the mainstay of initial treatment.
Recommended Reading: Foods To Eat With Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Medical Management Of Moderately
5.1. Induction of remission in moderately-to-severely active ulcerative colitis
Systemic corticosteroids
We recommend oral prednisolone for induction of remission in non-hospitalised patients with moderately-to-severely active UC
Despite a limited evidence base, the use of systemic corticosteroids for the induction of remission in moderately-to-severely active UC is well established in clinical practice. The limited evidence is due in part to the large effect size and limited alternative options at the time of the original RCTs., A previous meta-analysis included five placebo-controlled RCTs, although only two of them, used standard systemic corticosteroids. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of just these two studies and calculated an RR of 2.83 for the induction of clinical remission. The quality of evidence was rated as very low, due to a serious risk of bias, indirectness, and imprecision .
No information regarding AEs with steroid treatment was available in these two studies. Other studies established the side-effect profile of corticosteroids in both short courses and also longer-term exposure in both UC and Crohns disease., Due to the potential for side effects, some of which are irreversible, corticosteroid-free remission represents a desired outcome for patients.,
Anti-tumour necrosis factor agents
Vedolizumab
Tofacitinib
Ustekinumab
5.2. Maintenance of remission of moderately-to-severely active ulcerative colitis
Anti-TNF agents
Vedolizumab
Tofacitinib
Opportunities For Further Investigation
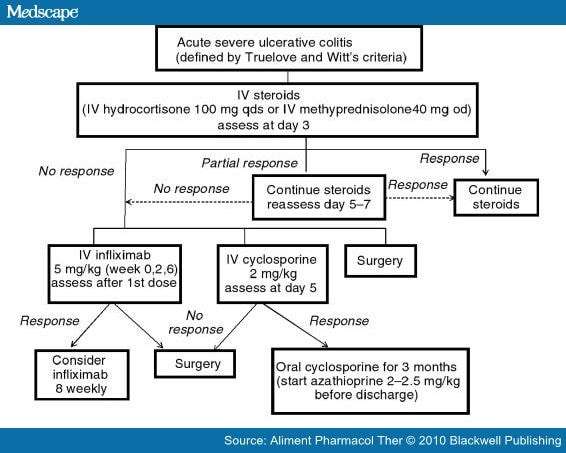
Although there are a number of detailed, evidence-based ASUC guidelines available to guide patient mangement,,, there are many areas where stronger evidence is needed to support definitive consensus recommendations. For instance, it is still not clear whether CMV reactivation drives disease refractoriness or is simply a consequence of severe inflammation and/or immunosuppression. Moreover, the optimal test for detecting CMV in the tissue is now known. Large randomized studies are required to determine if antiviral treatment of colon CMV reactivation improves response to therapy. With regard to thromboembolism prophylaxis, current pediatric guidelines state that there is not sufficient evidence to support the routine use of prophylactic LMWH in pediatric patients as is recommended for adults. Large comparative effectiveness studies will be needed to determine whether the benefit of routine LMWH for reducing thromboembolic complications outweighs any risks in pediatric patients. In the area of anti-TNF salvage therapy, we need more research to determine whether early infliximab pharmacokinetics in ASUC affects outcomes, whether accelerated dosing strategies are more effective, and if so, what dosing strategy is most effective? Future research will also determine how alternative treatments such as antibiotic cocktails and hyperbaric oxygen, and newer therapies including vedolizumab and tofacitinib, may be incorporated into treatment algorithms for ASUC.
Recommended Reading: Probiotics Good For Ulcerative Colitis