Whats The Difference Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Irritable Bowel Syndrome
IBD is a disease IBS is a syndrome, or group of symptoms. The causes and treatments are different.
IBS is a type of functional gastrointestinal disease. It affects how the bowels function, causing them to contract more often than usual. IBS is also known as spastic colon or nervous stomach.
IBS doesnt inflame or damage the intestines like IBD, so imaging scans cant detect it and it doesnt increase the risk of colon cancer. People with IBS rarely need hospitalization or surgery.
Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease Comparison Essay
Ulcerative colitis or regional enteritis manifests through inflammation that can be either acute or chronic. The inflammation penetrates thus preceding across the layers, estimated from the bowel wall to intestinal mucosa. On the other hand, ulcerative colitis manifests by affecting the mucous membrane of the colon. Crohns disease is characterized by disappearance, reduction, or exacerbation of inflammation of the colon. Colitis is recognized by having many ulcerations, the colon epitheliums ability to shed . As a result of edema, the condition exacerbates, leading to the tissues of the colon getting inflamed.
Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis And Diet
Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD, and long-term special diets are not effective in treating IBD. However, adjusting your diet can help manage some of your symptoms, and can help IBD medications work better. A person with IBD has to pay close attention to their diet, since they may have malnutrition.
Don’t Miss: How To Heal Mouth Ulcers Fast
Specialty Clinics For Crohns And Colitis
Many patients are diagnosed with IBD in their late teens. Our Pediatric to Adult Transition Clinic and College Clinic, which have gained national attention and recognition, are two important ways to help this segment of our patients get needed information, adjust more easily to adulthood and possibly college, and ensure their healthcare remains a priority as they make room for other important times of their lives.
Sporadic Crohn’s Disease Crohn’s Disease In Genetically Unrelated Individuals Is The Same Disease As Familial Crohn’s Disease Crohn’s Disease In Genetically Related Individuals
We have thus far determined that Crohn’s disease, whether in related or unrelated individuals, is an infectious disease, meaning that people develop Crohn’s disease because they have been infected with the causative microorganism. But is sporadic Crohn’s disease the same kind of disease as familial Crohn’s disease? Is the infectious microorganism that causes unrelated people to develop Crohn’s disease the same microorganism that causes families to develop Crohn’s disease? Studies of families with Crohn’s disease have concluded that there is no essential difference between the pathology of Crohn’s disease in families with the disease and in unrelated individuals with the disease. Since there are no essential differences in the pathology of sporadic versus familial Crohn’s disease , the organism that causes them must also be the same.
Recommended Reading: What To Avoid With An Ulcer
Ibd And Changing Your Diet
Some dietary changes that may help a person with IBD include:
- Low-fibre diet when IBD is active, most people find a bland , low-fibre diet helps to ease diarrhoea and abdominal cramping. People with Crohns disease who have a narrowed small intestine may need to eat a low-fibre diet most of the time.
- Low-fat diet people with Crohns disease who experience steatorrhoea may benefit from a low-fat diet.
- Low-lactose diet the milk sugar lactose is broken down by the enzyme lactase, commonly found in the lining of the small intestine. Some people with Crohns disease lack this enzyme, so should avoid milk and other dairy products. Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed with a simple test ask your doctor.
- Liquid diet a person with severe Crohns disease may need a nutritionally balanced liquid diet.
- Plenty of water people with IBD need to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
Crohn’s Disease In Families In Genetically Related Individuals Is Also An Infectious Disease
Genetically related individuals, families who have several members with Crohn’s disease, also develop Crohn’s disease because they are infected with the causative microorganism. In 1993, Van Kruiningen and colleagues published a “Study of Crohn’s disease in Two French Families.” In the first family, the father developed Crohn’s disease in 1970. In 1974, within several months of each other, 2 of their 4 children developed Crohn’s disease. In 1982 and 1983, the other two children developed Crohn’s disease. Finally, in 1988, the mother developed Crohn’s disease. In the second family, 7 of the 11 children developed Crohn’s disease, again in a pattern that led the authors of this study to conclude that “an enteric pathogen” caused these families to develop Crohn’s disease:
The uniformity of ileal and cecal disease in family 1 is akin to that which might be expected had a uniform dose of an enteric pathogen been given to a genetically uniform group of experimental subjects, e.g., a litter of mice or piglets .
The conclusions that can be drawn from these two studies are that genetically unrelated people develop Crohn’s disease because they have been infected with the causative microorganism, and genetically related people also develop Crohn’s disease because they have been infected with the causative microorganism.
You May Like: What Does Asacol Do For Ulcerative Colitis
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease Different
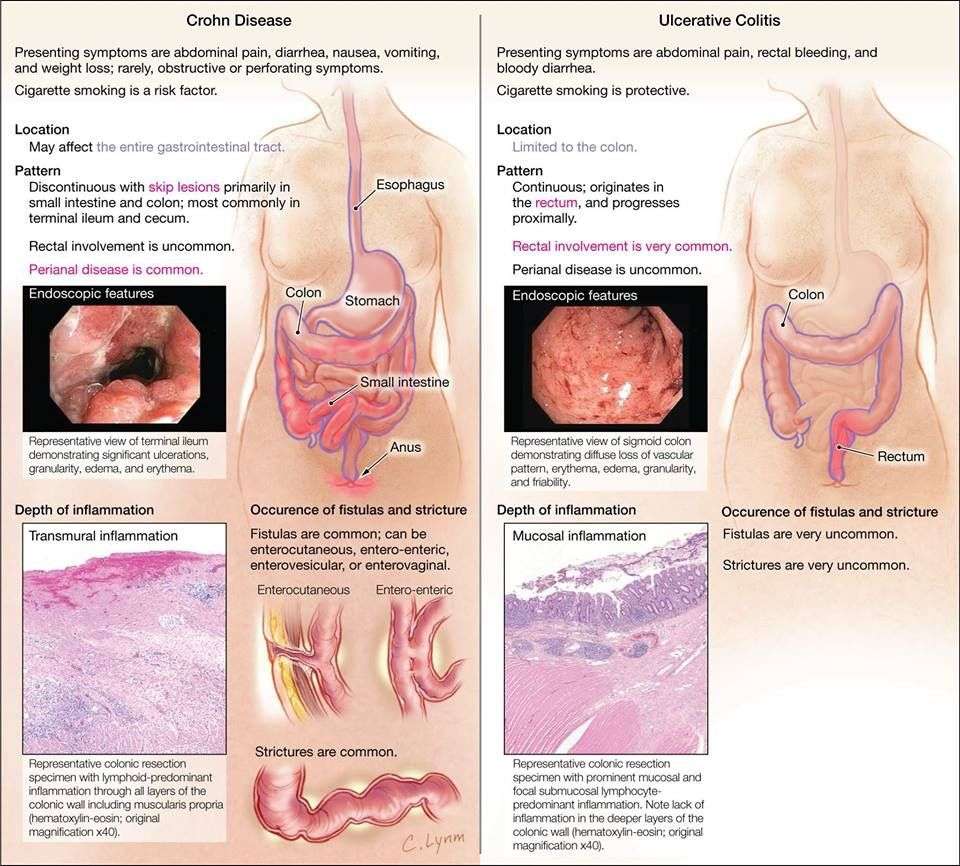
Crohns disease causes chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract . It can affect any part of the GI tract, as well as areas from the mouth to the anus. But it most commonly affects the end of the small intestine where it links to the beginning of the colon.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms reside in the large intestine only and often vary from person to person, depending largely on the part of the colon thats affected and the severity of the inflammation. It affects everyone differently, and symptoms range in severity. UC is a progressive disease and will change over time in your body.
Ongoing inflammation of the GI tract happens with both Crohns and UC, but there are a few key distinctions, such as:
- Ulcerative colitis is limited to the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere between the mouth and the anus.
- With Crohn’s disease, there are healthy parts of the intestine mixed between inflamed areas. Ulcerative colitis includes continuous inflammation of the colon.
- Ulcerative colitis only affects the innermost lining of the colon while Crohn’s disease can occur in all the layers of the bowel walls.
In approximately 10% of cases, an inflammatory bowel disease will exhibit features of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. We typically refer to these as indeterminate colitis.
In My Shoes: 24 Hours With Crohns Or Colitis App
In My Shoes is an immersive experience that allows anyone to find out first-hand what its like to have Colitis.
From low energy levels to managing pain, from rushing to the toilet to juggling work and a social life, the app will allow friends, family and anyone you want, to see first-hand how the condition can affect every part of your body, and every aspect of your life.
We have information for friends and family, employers, and colleagues. Find all our information online.
We have around 50 Local Networks across the UK that bring local people affected by Crohns and Colitis together. They are run by volunteers and host a range of events, from educational talks to socials. Check our website or call our Helpline to find your nearest Local Network.
You May Like: Skin Graft For Foot Ulcer
How Can I Prevent Inflammatory Bowel Disease
While there isnt anything you can do to prevent IBD, certain dietary and lifestyle changes may control the symptoms. You can:
- Eat smaller meals every two to four hours.
- Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, movement like tai chi, listening to music or going for a walk.
- Get plenty of sleep and stay physically active.
- Keep a food diary to identify foods that trigger IBD flares. You may find you have a food intolerance, such as lactose intolerance. If so, your body has a harder time digesting certain foods, which causes stomach upset.
- Reduce foods that irritate the intestines, such as those that are fibrous, spicy, greasy or made with milk. During flares, choose soft, bland foods that are less inflammatory.
- Cut back on caffeinated, carbonated and alcoholic beverages. Drink more water to prevent dehydration.
Can You Drink Alcohol With Crohn’s Disease
- Drinking alcohol is not recommended for most people with Crohn’s disease.
- Alcohol may irritate the lining of the intestinal wall, causing or worsening symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
- It also may contribute to malabsorption, further complicating nutritional deficiencies.
- Alcohol interacts with many medications, causing side effects that may be serious.
- Alcohol disrupts sleep cycles and can leave you feeling tired, and irritable the next day. However, if alcohol is well tolerated and not causing any complications, it can be consumed in moderation.
- Chronic diarrhea can lead to dehydration very easily.
- Dehydration makes you feel weak, tired, light-headed, or just “blah.”
- Alcohol can cause headaches, abdominal pain, and other symptoms. It also can place dangerous strain on your kidneys.
- Dehydration can be avoided by making a special effort to take in plenty of nonalcoholic fluids.
- You should take at least 8 full glasses of fluid every day.
- Try to stick to water, diluted fruit juice, sports drinks, decaffeinated beverages, and fruit and vegetable drinks.
- Avoid caffeinated beverages and sodas.
Also Check: Natural Supplements For Ulcerative Colitis
Integrating The Metabolic Model Into The Community Model
Metabolic models were constructed for all three groups , where each group contained four group-specific microbes. We then used the KBase tool Merge Metabolic Model into Community Model v.1.7.6 to construct three community models, where similar reactions among the four microbes within each group were merged by a mixed-bag model. After building three community models, we performed the flux balance analysis in KBase using Run Flux Balance Analysis v.1.7.6, with the default media and Biomass reaction to predict metabolic fluxes in a metabolic model. Then, we identified the reactions with flux values that are involved in pathways.
Symptomatic Differences Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
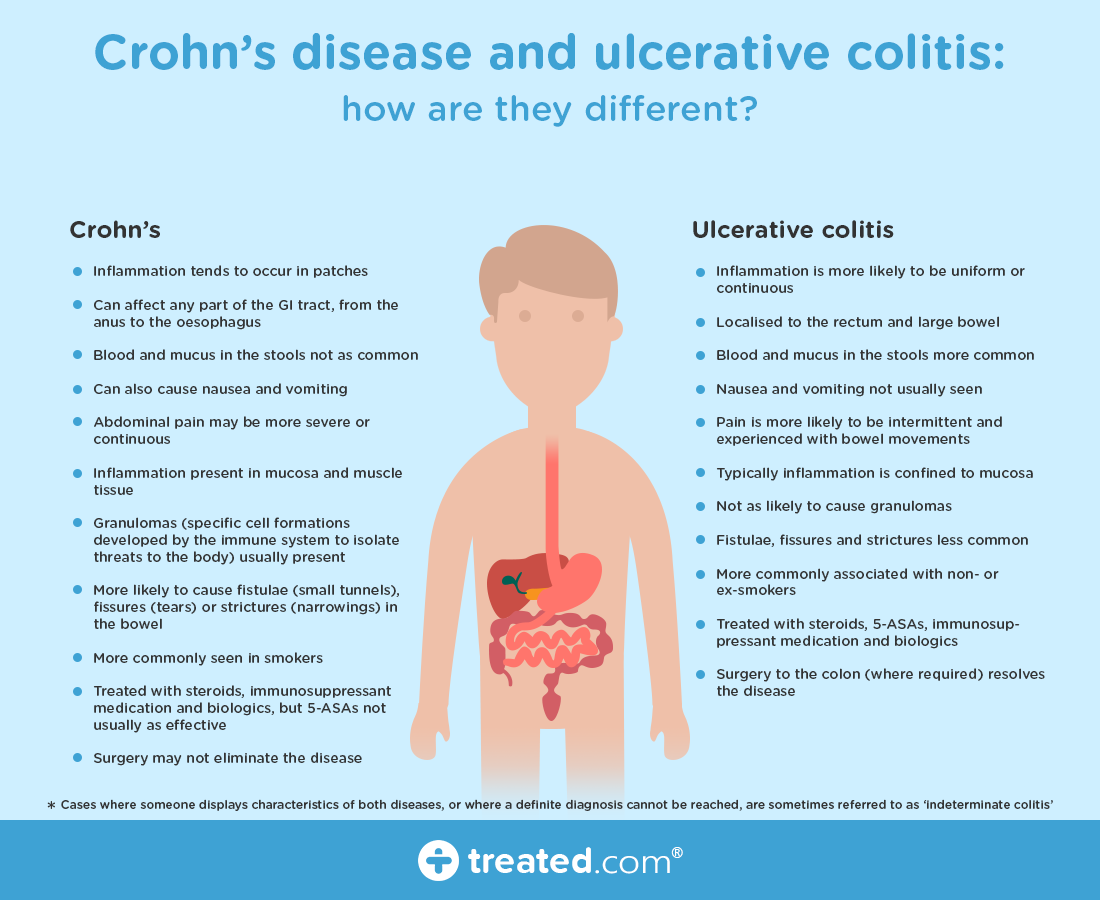
There are some subtle differences in symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. In Crohns disease rectal bleeding is less common, whereas in ulcerative colitis, bleeding from the rectum is much more common. In Crohns disease, continuous abdominal pain is more common and perianal problems such as fistulas, anal sores and skin tags, can occur. In contrast, people living with ulcerative colitis usually have intermittent pain coinciding with bowel movements. Perianal issues are uncommon in ulcerative colitis.
Clinical Trials Updates
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Surgery J Pouch
Crohn’s Disease And Ulcerative Colitis Are Not Genetic Diseases But Genetic Polymorphisms Related To The Processing Of Intracellular Bacteria And Specifically Mycobacteria Increase The Risk Of Developing Crohn’s Disease Rather Than Ulcerative Colitis When Infected With Map
Previous authors have suggested that ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease have the same etiology, with Crohn’s disease patients having more of the predisposing genes than ulcerative colitis patients:
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis may be the same disease with similar causes and with a quantitatively related genetic basis. Crohn’s disease would be the result in people with a large concentration of genes, while fewer of the relevant genes would result in ulcerative colitis .
Individuals with these genetic polymorphisms do not, however, develop Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis in any significant numbers. Infection with MAP causes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis independently of having these polymorphisms. “In other words, regardless of whether you carry the mutant allele or not, M. avium paratuberculosis infection has the same tendency to produce CD” . Depending on the country and region, these genetic polymorphisms are not associated with Crohn’s disease .
If You Think You May Be Suffering From Ulcerative Colitis Or Crohns Disease Contact Alabama Colon & Rectal Institute Today For Diagnosis And Treatment
Alabama Colon & Rectal Institute specializes in treating diseases of the colon, rectum, and anus. We are experts in performing colonoscopies, anorectal surgery, and minimally invasive colon surgery. Our three doctors are known regionally for their expertise in these areas. Visit our website for more information, give us a call to make an appointment at 205-458-5000, or email us at .
You May Like: Causes Of Bleeding Ulcers In Stomach
When Infected With Map Why Do Some Individuals Develop Ulcerative Colitis Rather Than Crohn’s Disease The Usual Influences Of Dose Route Age Sex And Genes On The Clinical Expression Of An Infection
Like any other pathogenic microorganism, a variety of factors influences the phenotype, the clinical expression of MAP infection whether an individual develops one disease caused by MAP or another. Not everyone infected by a pathogenic microorganism develops a disease caused by that organism. “Infection” means the “multiplication of the organism in or on the host.” In contrast, “disease represents a clinically apparent response of the host to infection.” A review of the literature suggests that five factors influence whether an individual develops ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease when infected with MAP:
The dose of the MAP organism, or how many organisms infect an individual. For a given age, a small dose of MAP causes ulcerative colitis, while a large dose of MAP causes Crohn’s disease.
The route of infection. The literature suggests that routes of infection that increase the concentration of MAP increase the risk of developing Crohn’s disease rather than ulcerative colitis. The two routes of infection that potentially concentrate MAP are aerosolized water from rivers and other bodies of water contaminated with MAP, and MAP present in hyperosmolar milk rather than hypoosmolar water.
The age at which an individual is infected. It takes a smaller dose of MAP to cause either ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease in a child as compared to an adult.
What You Should Know About The Normal Digestive Tract
The digestive tract or canal begins in the mouth. Here, the food is chewed and mixed with saliva, lubricating and partially digesting it. Once swallowed, the food passes into the esophagus, a muscular tube, whose walls move in wave-like patterns propelling the food downward into the stomach. In the stomach, the food is mixed with gastric juices, which consist of acid, mucus and various enzymes, which begin the breakdown of proteins. In the duodenum, the food is further mixed with secretions from the pancreas, which contain other digestive enzymes, and with bile. Bile is produced in the liver and contains bile acids, which also help in digestion. These functions are rarely compromised in ulcerative colitis, and, when they are, it is usually due to an associated disorder of the biliary tract. They are sometimes be affected in Crohns disease.
The upper segment of the small bowel, also known as the jejunum, is where fats, fat-soluble vitamins , protein breakdown products, sugars and some trace elements are absorbed. Vitamin B12 and bile acids, however, are absorbed in the ileum, the lower part of the small bowel. This latter function is often compromised in patients with Crohns disease, though disturbances of the upper small bowel are less frequent.
The insufficient absorption and resulting loss of bile acids in the ileum, however, may adversely affect the digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins in the upper small bowel.
You May Like: How To Ease Mouth Ulcer Pain
What Are The Types Of Ibd
Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are the main types of IBD. Types include:
- Crohns disease causes pain and swelling in the digestive tract. It can affect any part from the mouth to the anus. It most commonly affects the small intestine and upper part of the large intestine.
- Ulcerative colitis causes swelling and sores in the large intestine .
- Microscopic colitis causes intestinal inflammation thats only detectable with a microscope.
Treating Crohns And Colitis
Its important to know that neither Crohns nor ulcerative colitis can be cured, though doctors will work with patients to manage symptoms. The two illnesses are generally treated with the same types of medication, although each patient may respond differently to the same drug. The goal of treatment is to reduce the inflammation, which in turn reduces symptoms, allows your body to repair damaged tissue, and helps slow the progression of the disease.
Today, many patients get a relatively new class of drugs, called biologics, which are live antibodies that are given to patients to help their immune cells fight the inflammation. Other classes of drugs include immunomodulators, which help tamp down the immune systems inflammatory response, and aminosalicylates, the oldest class of drugs, which are used to help keep the disease in remission. According to the Crohns and Colitis Foundation, immunomodulators can take up to six months to become fully effective, so doctors usually prescribe them along with fast-acting steroids that patients will ideally go off of once the immunomodulators reach their full potential. I absolutely think that with these new drugs, its a new era in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, says Dr. Cohen.
You May Like: Do Stomach Ulcers Cause Gas
Where Inflammation Occurs
Both illnesses are caused by inflammation in the GI tract, but where the inflammation occurs can lead a doctor to the correct diagnosis. The most basic difference is that Crohns disease can involve the entire GI tract, from the mouth all the way down to the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis is restricted to the colon, says Louis Cohen, MD, assistant professor of gastroenterology at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City.
According to the UCLA Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Crohn’s disease usually results in healthy stretches of the intestine between inflamed areas. People who suffer from colitis experience continuous inflammation of the colon.