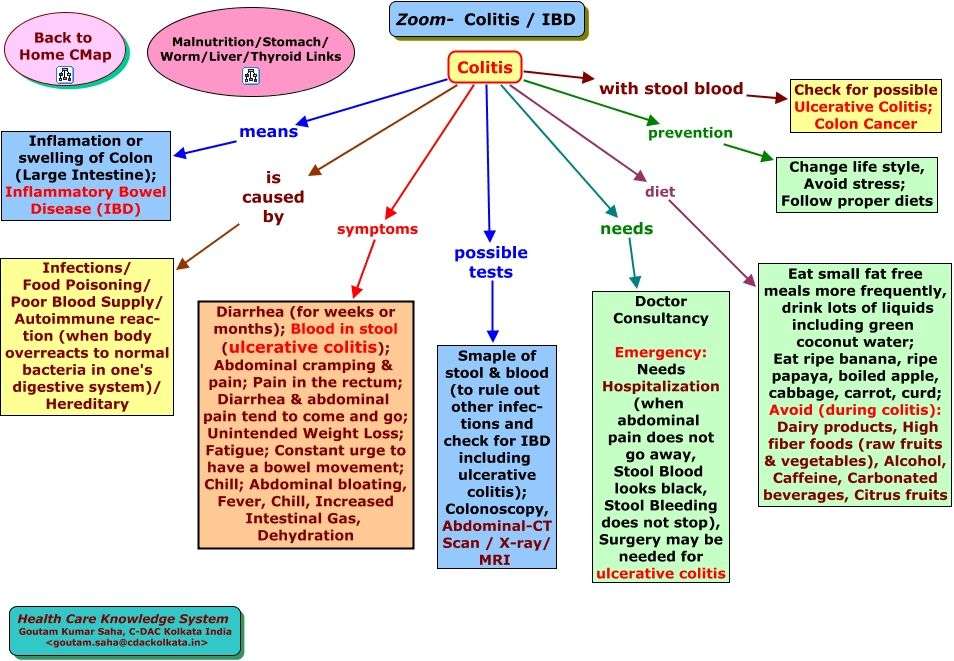
Nursing Interventions For Colostomy
Colostomy irrigation is advised by the dietitian to be done at a frequency of 3 times per day in some cases, 2 times per day in others. Depending on the type of colostomy created, irrigation can be done with either saline or water solution.
The colostomy wound site should be cleaned with antibacterial soap and water prior to each irrigation session. The amount of fluid to be drained depends on the length of time between irrigations or the degree of diarrhea present.
Saline solution is recommended for a return type colostomy rather than tap water for its antibacterial action.
After irrigation, saline solution is used to clean the colostomy opening and surrounding skin surface.
After cleaning, a wafer-like dressing may be applied directly over the top of the wound opening for a permanent colostomy site. If gauze dressing is being used, it should be applied in such a way that an air hole is left open to prevent skin breakdown from continuous pressure.
A collection device may be needed for patients when bowel movements are infrequent or when circumstances such as the need to pass stool from the colon prevents evacuation of stool.
Patient respiration should be checked for 15 seconds after each irrigation session to prevent fluid from entering the lungs.
The patient needs to understand that their dietitian may prescribe 24 ounces of specific fiber supplement twice per day. This will depend on the amount and consistency of stool passed and the time between irrigations comes.
Assessment Of Bowel Function
- Stool frequency, consistency, and presence of blood or mucus
- Patients with UC predominantly appear with symptoms of diarrhea mixed with blood and mucus, rectal bleeding, and frequent stools
- Pain associated with passing stools
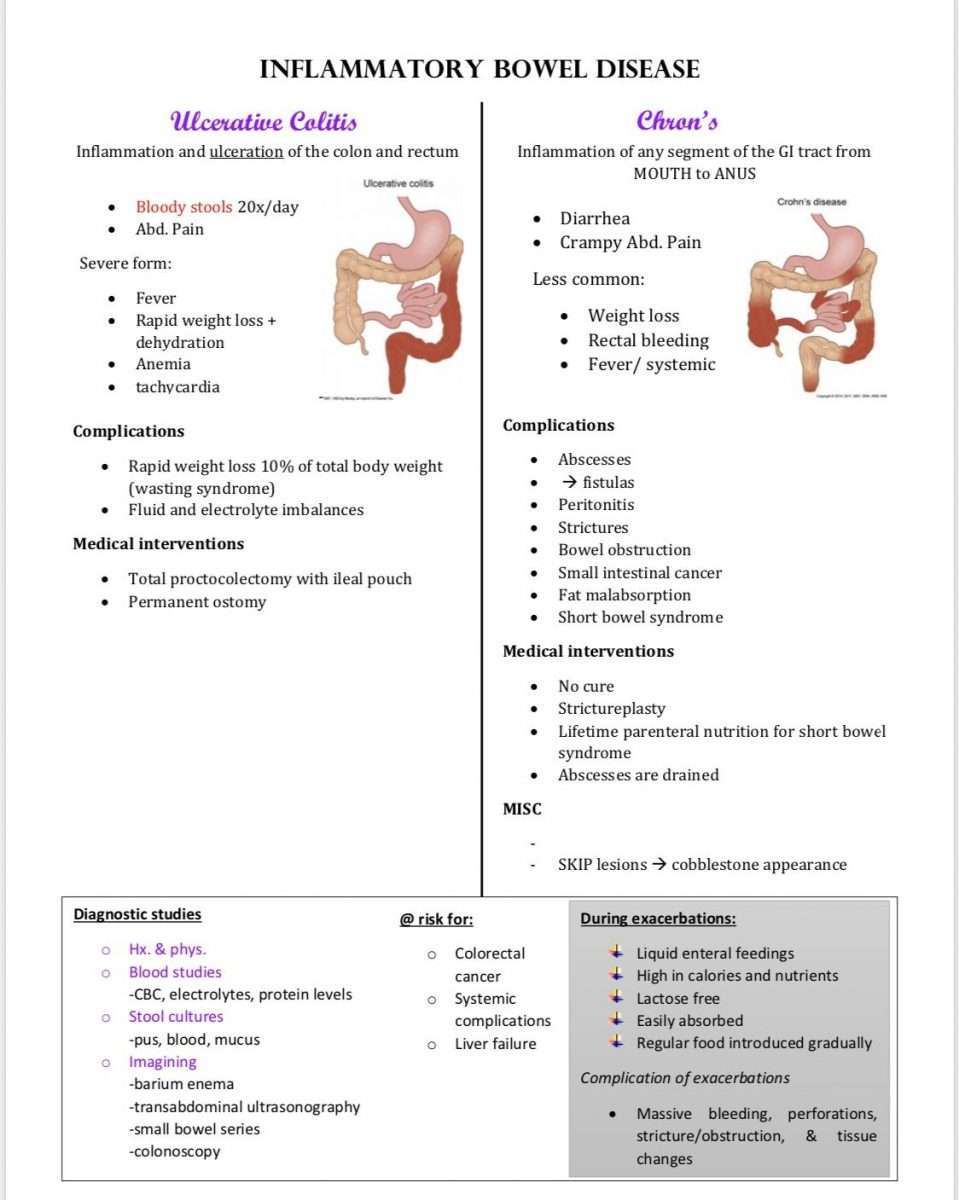
Peritonitis Nursing Care Plans
Peritonitis is the acute or chronic inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the visceral organs. Inflammation may extend throughout the peritoneum or may be localized as an abscess. Peritonitis commonly decreases intestinal motility and causes intestinal distention with gas. mortality is 10% with death usually a result of bowel obstruction.
The peritoneum is sterile, despite the GI tract normally contains bacteria. When bacteria invade the peritoneum due to an inflammation or perforation of the GI tract peritonitis usually occurs. Bacterial invasion usually results from appendicitis, diverticulitis, peptic ulcer, ulcerative colitis, volvulus, abdominal neoplasms, or a stab wound. It may also be associated with peritoneal dialysis.
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis Rectal Pain Relief
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis Risk Factors Of Ulcerative Colitis
Things that can affect ones risk of getting ulcerative colitis include:
Its most likely to get ulcerative colitis if one is between 15 and 30 years old or older than 60.
Ethnicity
The risk is highest in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
Family history
A persons risk could be up to 30% higher if they have a close relative with the condition.
Food and stress dont cause it, but they can trigger a flare of symptoms.
What Ulcerative Colitis Surgery Involves
A surgeon usually removes your colon and rectum. Next they’ll attach the lowest part of your small intestine to a hole they make in your torso to let waste leave your body and empty into an external bag. Another procedure creates an internal waste pouch that allows stool to be passed through the anus.
Don’t Miss: Natural Ways To Heal Stomach Ulcers
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis:
Let the names help you, so you can understand where the ulcerative colitis is located:
Ulcerative proctitis : affects the rectum and is the most mild form of all types. It tends to have fewer complications due to being located just in the rectum.
Proctosigmoiditis: PROCT: COLON and SIGMOID: SIGMOID COLON and ITIS: inflammationinflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Pancolitis . It is a very severe form of ulcerative colitis.
Left-sided colitis: LEFT-SIDED: includes the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum and ITIS: inflammation.inflammation of the descending, sigmoid, and rectum.
Ibd In Population Genetics
Detection of natural selection in the human genome is also possible via detected IBD segments. Selection will usually tend to increase the number of IBD segments among individuals in a population. By scanning for regions with excess IBD sharing, regions in the human genome that have been under strong, very recent selection can be identified.
In addition to that, IBD segments can be useful for measuring and identifying other influences on population structure. Gusev et al. showed that IBD segments can be used with additional modeling to estimate demographic history including bottlenecks and admixture. Using similar models Palamara et al. and Carmi et al. reconstructed the demographic history of Ashkenazi Jewish and Kenyan Maasai individuals. Botigué et al. investigated differences in African ancestry among European populations. Ralph and Coop used IBD detection to quantify the common ancestry of different European populations and Gravel et al. similarly tried to draw conclusions of the genetic history of populations in the Americas. Ringbauer et al. utilized geographic structure of IBD segments to estimate dispersal within Eastern Europe during the last centuries. Using the 1000 Genomes data Hochreiter found differences in IBD sharing between African, Asian and European populations as well as IBD segments that are shared with ancient genomes like the Neanderthal or Denisova.
Read Also: What To Avoid Eating If You Have An Ulcer
Caring For An Ostomy Bag
If you need this bag after your surgery you’ll get advice from your medical team about how to care for it and the stoma. You can empty or throw out the bags when you need to. Irrigating the stoma can help you control the timing of bag changes. To prevent leaks, the pouch system that connects the stoma to the bag needs to be changed every 4 to 7 days. Call your doctor if you notice a change in color, bleeding, or swelling.
Scheduled And Emergency Uc Surgery
Most UC surgery can be arranged at time that’s convenient for you. Try scheduling it while your symptoms are calm to cut the chances of complications.
The risks are higher when you have emergency surgery. You may need it if you get toxic megacolon — a life-threatening condition when your colon rapidly swells and gas and bacteria build up inside. Get medical help right away if you have fever, belly pain, constipation, or swelling.
Recommended Reading: Best Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up
Procedure For Permanent Colostomy
This procedure is done when the damaged bowel cannot be restored after surgery, as in the case of colon cancer. In this procedure, the surgeon will create a stoma at the level of the damaged section of the colon and rectum and then staple or suture the remaining ends together. The stoma will be sealed from about 4-12 inches below the exit site. The goal is to divert stool away from the damaged area and prevent the accumulation of stool at the opening from the intestine to the skin surface.
Potential complications for permanent colostomy are infection at the site of an open wound, skin breakdown, stomal stenosis and fecal accumulation at the opening from the intestine to the skin surface.
This is a specific technique of undertaking a colostomy. The aim is to prevent fecal matter from leaking out of the stoma. This technique helps reduce pain, swelling and other complications after surgery.
Bowel technique procedure has a low risk of complications.
Treatment Of Ulcerative Colitis
There is a wide array of treatment options for patients with ulcerative colitis.
Treatments usually involve pharmacologic therapy and surgical procedures. Alternative treatments are also widely available.
Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs. These are the first line of treatment for people with ulcerative colitis.
5-Aminosalicylates can be given by mouth or as suppository depending on the affected part of the colon.
On the other hand, corticosteroids are commonly prescribed if other treatments cause no response.
Immune system suppressors. These drugs work by prohibiting inflammatory response through suppressing the immune system.
They usually work better in combination with other drugs.
They usually require regular checking of the liver and pancreatic functions. Cyclosporines, like corticosteroids, are not indicated for long term use due to their side effects.
However, it is also the choice of drug when other treatments fail to work.
Biologics. Also called monoclonal antibodies, these drugs are usually prescribed to people with ulcerative colitis who cannot tolerate other treatments.
They work by stopping proteins in the body from causing inflammation.
Other medications can be used to treat symptoms related to ulcerative colitis. Examples are anti-diarrheal drugs, pain relievers, antispasmodics, and iron supplements.
Surgery
A more sophisticated procedure called ileoanal anastomosis can be done to prevent the patient from needing an external pouch to collect stool.
Read Also: Mouth Ulcer On Tongue Remedies
Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis
Further problems could develop if ulcerative colitis is left untreated.
These complications can range from a simple dehydration to a more life-threatening condition as thrombosis and toxic megacolon.
The most common and possible complications related to ulcerative colitis are as follows:
Strengths And Limitations Of This Study
-
Design strengths included comparing hospitalisations 1year before and 1year after the introduction of an inflammatory bowel disease nurse position.
-
The extraction of patients with IBD with two information systems allowed exhaustiveness.
-
The major limitation was that costs were only attributed to the reduction of hospitalisation.
Read Also: Bland Diet Recipes For Ulcers
What Is It And Who Gets It
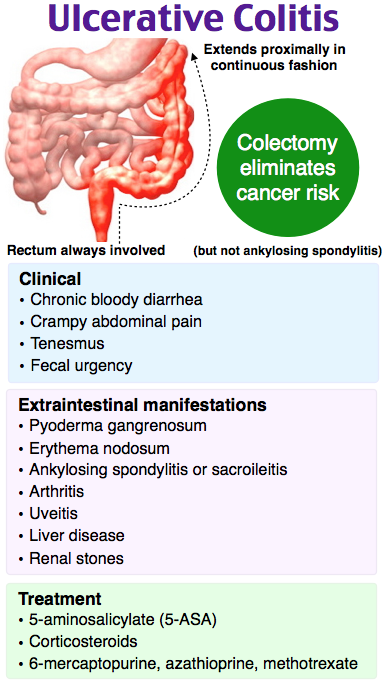
Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease characterised by diffuse inflammation of the colonic mucosa. It affects the rectum and extends proximally along a variable length of the colon. The disease can be categorised as left sided colitis or extensive colitis . These categories are useful when formulating treatment options and planning the timing of surveillance colonoscopy, which is used to detect and prevent colorectal carcinoma. Colitis affects about one in 1000 people in the Western world.
Ulcerative Colitis Surgery Risks Complications
If you have any of these symptoms, get medical help right away:
- Infection or pouch inflammation . Signs: Diarrhea, frequent bowel movements, stomach cramps and pain, fever, joint pain. Treatment: Antibiotics.
- Blockage or bowel obstruction. Signs: Cramping, nausea, vomiting. Treatment: IV fluids and fasting, sometimes surgery.
- Pouch failure. Signs: Fever, swelling, pain. Treatment: Surgery and permanent ileostomy.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis And Lactose Intolerance
Stool Bulking Agents Or Laxatives
Colonic motility is affected by inflammation and rapid transit occurs through the inflamed colon. In left sided disease, distal transit is rapid but proximal transit is slowed, which can result in proximal constipation. Relief of proximal constipation by stool bulking agents or laxatives may help induce remission in proctitis.
Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel Disease 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to abdominal muscle spasms secondary to Inflammatory bowel disease as evidenced by a pain score of 10 out of 10, verbalization of abdominal pain and cramping, guarding sign on the abdomen
Desired Outcome: The patient will demonstrate relief of pain as evidenced by a pain score of 0 out of 10, stable vital signs, and absence of restlessness.
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Interventions | Rationale |
| AnalgesicsVitamins and supplements | |
| Assess the patients vital signs and characteristics of pain at least 30 minutes after administration of medication. | To monitor effectiveness of medical treatment for the relief of heartburn and stomach pain. The time of monitoring of vital signs may depend on the peak time of the drug administered. |
| Teach the patient on how to perform non-pharmacological pain relief methods such as deep breathing, massage, acupressure, biofeedback, distraction, music therapy, and guided imagery. | To reduce stress levels, thereby relieving the symptoms of Inflammatory bowel disease, especially stomach pain and heartburn. |
| Help the patient to select appropriate dietary choices to reduce the intake of milk products, caffeinated drinks, alcohol and high fiber, high fat foods. | To relieve abdominal pain and cramping, alleviate diarrhea, and healthy food habits. |
Other possible nursing diagnoses:
Also Check: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
Treatment Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The treatment goal for IBD is to reduce inflammation and control the symptoms. Treatment includes medication use and surgery.
Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Inflammatory Bowel Disease Nursing Care Plan : Nursing Interventions & Rationale
| Nursing Interventions | Rationale |
| Monitor I& O. Note number, character, and amount of stools estimate insensible fluid losses, e.g., diaphoresis. Measure urine specific gravity observe for oliguria. | Provides information about overall fluid balance, renal function, and bowel disease control, as well as guidelines for fluid replacement. |
| Assess vital signs . | Hypotension , tachycardia, fever can indicate response to and/or effect of fluid loss. |
| Observe for excessively dry skin and mucous membranes, decreased skin turgor, slowed capillary refill. | Indicates excessive fluid loss/resultant dehydration. |
| Weigh daily. |
Inflammatory bowel disease results froma complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Similarities involve chronic inflammation of the alimentary tract and periods of remission interspersed with episodes of acute inflammation.
Ulcerative colitis : A chronic condition of unknown cause usually starting in the rectum and distal portions of the colon and possibly spreading upward to involve the sigmoid and descending colon or the entire colon. It is usually intermittent , but some individuals have continuous symptoms. Cure is effected only by total removal of colon and rectum/rectal mucosa.
Here are 7 Nursing Care Plan for inflammatory bowel disease
Medications
They usually work better in combination with other drugs.
Surgery
Read Also: Signs You May Have Stomach Ulcers
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis: Care Plan 1 Diagnosis: Diarrhea Related To Inflammation Of The Bowel
Evidenced by:
- Loose, watery stools, abdominal cramping, and pain
- Increased urgency to defecate
The patient will be able to return to more normal stool consistency and frequency.
Nursing Care Plans for Ulcerative Colitis
As you continue reading remember that our top and qualified writers are here to help with any of your assignment. All you need to do is place an order with us.
How Do We Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis
The Digestive Health Center at Stanford Health Care delivers expert diagnosis for all forms of inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis. Part of what makes Stanford different is our expertise in measuring the degree of intestinal injury for each patient. This helps us understand the severity of your condition and how best to treat it.
Don’t Miss: Natural Ways To Heal Ulcerative Colitis
Active Left Sided Disease And Extensive Disease
Doses of oral mesalazine > 3 g a day are associated with greater clinical improvement than lower doses. Combined topical and oral treatment can help induce remission in left sided colitis and extensive colitis., Oral corticosteroids are indicated in mild disease that fails to respond to topical treatment and in moderate disease .
Delays in treatment may increase the risk of colectomy. Patients should be treated promptly with an optimal dose of corticosteroids .
Nursing Interventions For Ulcerative Colitis
- Monitor VS, patients bowel movements , keep patient hydrated, monitor daily weights , focus on GI assessment
- Signs and symptoms of toxic megacolon: abdominal distention, fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dehydration, tachycardia, hypoactive or absent bowel sounds
- Signs and Symptoms of peritonitis: distention or abnormal bloating, increased heart rate, tachypnea, pain
- May be NPO with IV hydrationadvance diet per MD order as symptoms subsidewill typically start with clear, fulls, and then solids
- Diet Education:
- Watch foods that can cause a flare-up or should be avoidedduring a flare-up:
- High-fiber foods
- Food hard to digest like: nuts, raw vegetables or fruits
- Allergen type foods: dairy or certain foods that the person may be intolerant too like wheat, fish
- Avoid spicy, high-fat foods, gluten, gas causing foods like onions, beans etc.
Administering Medications per MD order:
Goal: control flare-ups and maintain remission
- Medications prescribed depend on the severity of the disease .
- Combination of medications are used if patient has moderate to severe case.
Anti-inflammatory: decrease the inflammation in the bowel
Immunosuppressors: Azathioprine/Imuran risk for infection and cancer, no live vaccines
Surgery:
Don’t Miss: What To Take For Mouth Ulcers
Diagnosis Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
The diagnosis of IBD comes after studying the results of imaging studies and endoscopic procedures. Also, physicians may perform stool sampling to rule out other possible causes like infections.
- Endoscopic Procedures
- Colonoscopy This is a procedure to examine the entire colon. It involves the insertion of a thin, flexible camera through the anus into the colon. It can also be used to obtain tissue samples for biopsy. It is the study of choice for the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy this procedure is similar to colonoscopy. However, instead of studying the entire colon, only the sigmoid, or the last part of the colon, is assessed. This may be favored over full colonoscopy in cases where the colon is severely inflamed.
- Upper endoscopy This test also uses a thin, flexible camera that is inserted in the mouth to assess the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the intestines called duodenum.
- Capsule endoscopy this test is mostly used to diagnose Crohns disease. IT involves swallowing a small capsule containing a camera. Images are then transmitted to a recorder that can be worn on the belt.
- Balloon-assisted enteroscopy this procedure is performed when the results of capsule endoscopy come back inconclusive. It is similar to a simple endoscopy however, this procedure uses additional equipment called overtube. This piece of equipment allows doctors to reach further down the intestines.
Read Also: Pressure Ulcer Interventions And Rationales