Food As Trigger Of Flare
Participants frequently discussed the possibility that certain foods could trigger flares, but had great difficulty in identifying common themes across participants.
I never could figure out what triggers it. When Ive got a flareup going, I mean, its always, I eat, and then half an hour later Im in the bathroom.
I know until I kept a food journal, I had no concept of what would or wouldnt trigger it. I just its hard to isolate.
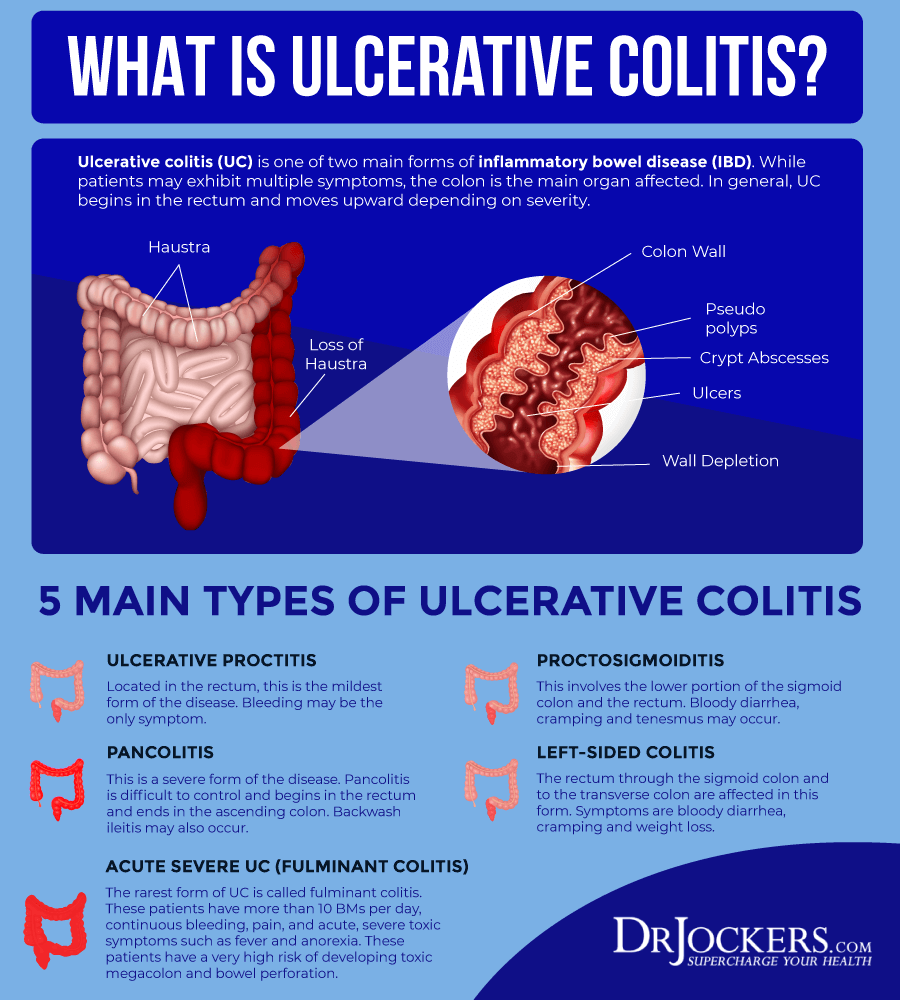
Comparison Of Symptoms Reported In Focus Groups To Symptoms From Pooled Disease Activity Indices
The lists were directly compared to determine which symptoms were present in both the focus group list and in the common indices list which symptoms were only present in the indices and which symptoms were reported by patients to be important, but were not measured by any of the common disease activity indices.
Does Ibs Cause Mucus In Stool
As we explained above, there are many symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome which vary from person to person. Passing mucus in your stool is a symptom that affects many sufferers of irritable bowel syndrome.
Mucus has an important function and is involved in many metabolic processes in the human body such as respiration, digestion, and urination.
It is released by mucous membranes to moisten and protect various linings within the body.
It is normal for mucus to be secreted by the bowel, but for most people the amounts of mucus are so negligible that it cannot be seen.
Irritable bowel syndrome can cause increased amounts of mucus to be secreted, making it visible in the stool.
Mucus can vary greatly in color and texture, but mucus in the stool is often white or clear. It can also take on the colour of the feces.
It is not clear exactly why irritable bowel syndrome can cause mucus to appear in the stool.
Some researchers believe it is linked to inflammation of the bowel, but more work needs to be done to determine the exact cause.
One study found that men are twice as likely as women to report experiencing mucus in their stool as a symptom of irritable bowel syndrome.
Another study found that around half of irritable bowel syndrome sufferers reported mucus in stool as a symptom.
The good news is that if you suffer with irritable bowel syndrome and you notice mucus in your stool, this is not a cause for concern.
You May Like: Ulcerative Colitis Is It Deadly
Can I Get Surgery For My Ulcerative Colitis
Surgery is an option if medications arent working or you have complications, such as bleeding or abnormal growths. You might develop precancerous lesions, or growths that can turn into colorectal cancer. A doctor can remove these lesions with surgery or during a colonoscopy.
Research shows that about 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery sometime during their life. About 20% of children with ulcerative colitis will need surgery during their childhood years.
There are two kinds of surgery for ulcerative colitis:
Proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch
The proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch is the most common procedure for ulcerative colitis. This procedure typically requires more than one surgery, and there are several ways to do it. First, your surgeon does a proctocolectomy a procedure that removes your colon and rectum. Then the surgeon forms an ileoanal pouch to create a new rectum. While your body and newly made pouch is healing, your surgeon may perform a temporary ileostomy at the same time. This creates an opening in your lower belly. Your small intestines attach to the stoma, which looks like a small piece of pink skin on your belly.
After you heal, waste from your small intestines comes out through the stoma and into an attached bag called an ostomy bag. The small bag lies flat on the outside of your body, below your beltline. Youll need to wear the bag at all times to collect waste. Youll have to change the bag frequently throughout the day.
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medicine, such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. But more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital.
If medicines are not effective at controlling your symptoms or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
Don’t Miss: Will A Stomach Ulcer Cause Bloating
Different Types Of Mucus Discharge That Can Be Seen In The Stool
Mucus is natural and plays a very important role in the functioning and protection of the body’s organs. Tissues produce mucus that lines and protects the mouth, nose, sinuses, throat, lungs, and intestines. Most of the time, the mucus is clear and thin. However, factors related to illness, diet or the environment can sometimes increase the consistency of mucus and even change its color.
- People usually have more mucus when they have a sinus infection and may notice that the mucus is greenish in color.
- White mucus, yellow, green, or brown impurities in the feces appear in adults due to food allergies or lactose intolerance. These discharges occur in dull life, accompanied by poor digestion of food. This indicates that there is no liquid medium that promotes the movement of feces.
- In the case of mucus in the stool, men and women of all ages may also see signs of dysfunction in their digestive system and the colon in particular, depending on the content of mucus in the stool.
- A large amount of obvious mucus is evidence of cystic fibrosis, which occurs on the background of increased mucus production by the glands. This condition indicates an inflammatory process in the respiratory tract or intestines. Food allergies are also accompanied by a clear blood clot discharge.
The increase in mucus can be interpreted as how the body tries to warn us that something is wrong.
Abdominal And Rectal Pain
People with ulcerative colitis often experience rectal or abdominal pain. Having a large amount of abdominal pain may be a sign that youre having a flare-up or that your condition is getting worse. Pain can range from mild to severe and may also affect your rectum.
Pain may be accompanied by persistent muscle spasms and cramping.
Recommended Reading: Best Dressing For Venous Stasis Ulcer
How Is Colitis Treated
The specific cause of colitis will dictate the appropriate treatment. Non-specific treatment includes fasting for 24 to 48 hours, feeding a low residue or hypoallergenic diet, increasing dietary fiber content, and adding fermentable fiber such as psyllium, beet pulp, or fructooligosaccharides to the food. Some dogs with colitis will do better on low-fiber diets. See the handout “Nutrition for Dogs with Colitis” for more information on the role of diet and nutrition for dogs diagnosed with colitis.
Antimicrobial drugs may be indicated, depending on your dog’s diagnosis. Anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive drugs may be used in cases of inflammatory or immune-mediated colitis. Drugs that modify the colon’s motility may also provide symptomatic relief.
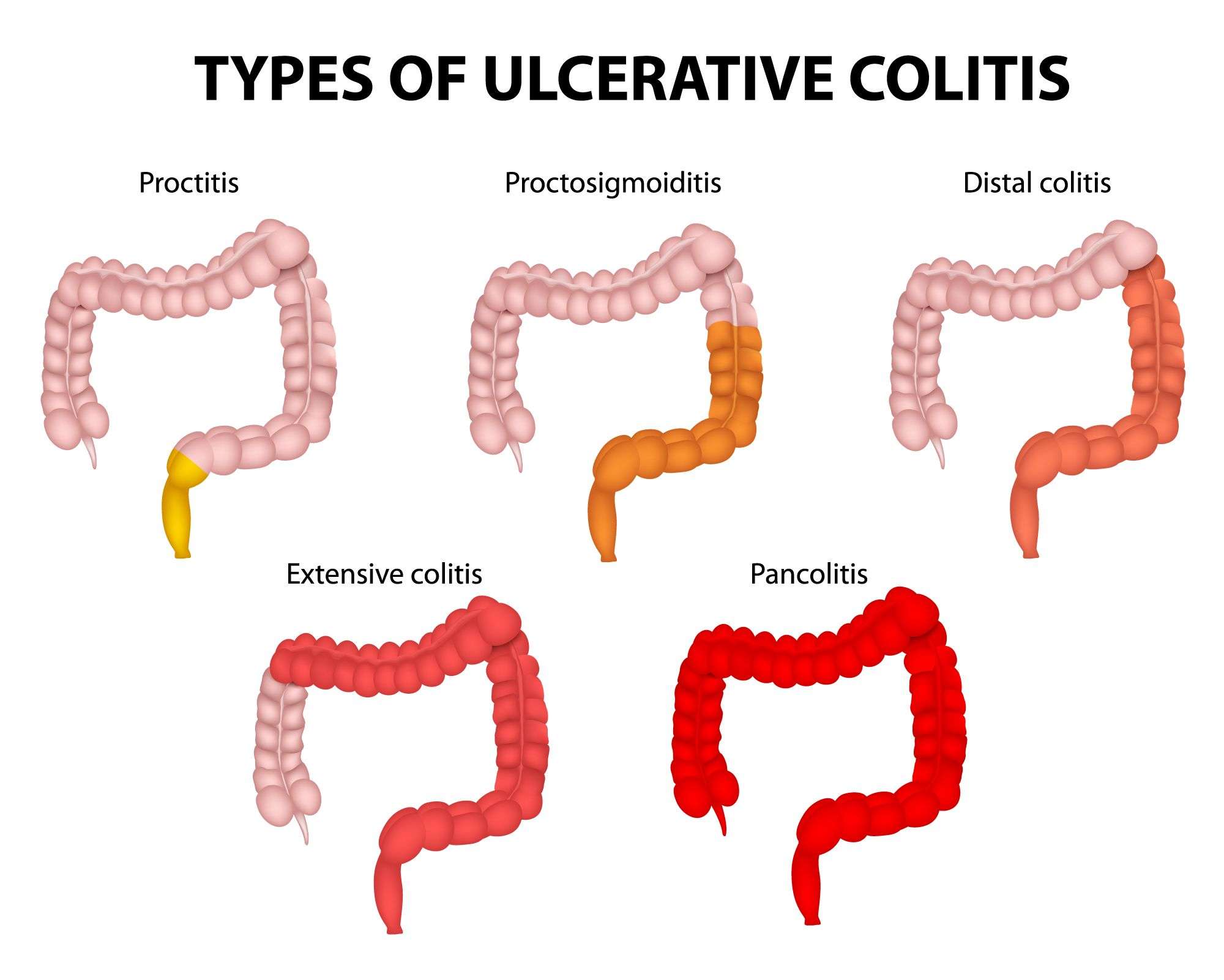
Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
The main symptoms of ulcerative colitis are:
- recurring diarrhoea, which may contain blood, mucus or pus
- needing to empty your bowels frequently
You may also experience extreme tiredness , loss of appetite and weight loss.
The severity of the symptoms varies, depending on how much of the rectum and colon is inflamed and how severe the inflammation is.
For some people, the condition has a significant impact on their everyday lives.
You May Like: What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Flare Ups
Dietary And Lifestyle Modifications
As most nutrients are absorbed higher up in the digestive tract, those with ulcerative colitis generally do not have nutrient deficiencies however, other factors might influence your nutritional state. Disease symptoms may cause food avoidance, leading to food choices that might not provide a balanced diet. If bleeding is excessive, problems such as anemia may occur, and modifications to the diet will be necessary to compensate for this.
Generally, better overall nutrition provides the body with the means to heal itself, but research and clinical experience show that diet changes alone cannot manage this disease. Depending on the extent and location of inflammation, you may have to follow a special diet, including supplementation. It is important to follow Canadas Food Guide, but this is not always easy for individuals with ulcerative colitis. We encourage you to consult a registered dietitian, who can help set up an effective, personalized nutrition plan by addressing disease-specific deficiencies and your sensitive digestive tract. Some foods may irritate the bowel and increase symptoms even though they do not worsen the disease.
In more severe cases, it might be necessary to allow the bowel time to rest and heal. Specialized diets, easy to digest meal substitutes , and fasting with intravenous feeding can achieve incremental degrees of bowel rest.
Digestive Changes In Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition, meaning it comes on slowly over a long period of time. Currently, there is no known cure for UC.
With UC, inflammation and ulcers develop on the lining of the large intestine . Sometimes the rectum is affected, as well.
This inflammation can cause changes in bowel habits, including urgency, diarrhea, blood or mucus in the stool, and abdominal pain. When your large intestine is inflamed, it contracts and empties often, which is why you may have urgent bowel movements and diarrhea.
When chronic inflammation damages the lining of your colon, ulcers can develop. The ulcers can bleed, leading to blood in your stool. If you regularly lose a lot of blood in your stool, you might develop anemia .
Though diarrhea is more common, some people with UC experience constipation. Inflammation limited to the rectum, known as ulcerative proctitis, may result in constipation.
Other symptoms of UC include painful bowel movements, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, unintentional weight loss, and fever.
Read Also: Calcium Alginate For Pressure Ulcers
What Are The Clinical Signs Of Colitis
Most dog owners report seeing frequent, small volumes of semi-formed to liquid feces. Many dogs will exhibit straining during and after defecation, and small amounts of bright red blood will often be passed near the end of defecation. Mucus or fat is seen in many cases of chronic colitis. Most dogs with colitis will exhibit a sense of urgency and need to defecate frequently. Vomiting occurs in less than a third of the cases of colitis or large bowel diarrhea. Weight loss is rare.
Anxiety And Control Over Activities

Participants acknowledged a large amount of anxiety resulting from a pattern of their symptoms controlling their lives and the resulting effects of their disease on their quality of life.
Ive got a full-blown flareup, and uh, I try and schedule things around when Ive got to go to the bathroom in a half hour, so lets not start this meeting or lets get this meeting over, um, excuse me, Ive gotta go.
if I dont go in the morning, then its in the back of my head, Ok, whens it going to hit? But if I go in the morning, right after I get up, I have no worries the rest of the day.
You end up planning your whole life around what your gut is doing.
I mean, you plan your life around it .
When it started, I just had to stay home because so often I couldnt handle it and it had absolutely no control, and when you teach, you cannot have that in the classroom.
Read Also: How To Cure Mouth Ulcer Permanently
When Is The Mucus In The Stool Normal
As pointed out above, mucus is a slippery, natural substance that lines many cavities in the body. Often the mucus is not visible to the naked eye, but it is found in many body fluids.
- The mucus found in the stool is produced by cells in the lining of the digestive system. It is also found in other organs that need their uppermost cell layer to be kept moist. The mucus also serves as a layer of defense to prevent harmful germs from entering the body like those in the sinuses.
- The mucus also acts as a lubricant to these orifices, preventing them from drying out and cracking, which would make them vulnerable to attack.
- The mucus in the digestive tract helps stool pass easily through the intestine.
Note that having mucus in the body is an absolute necessity, but overproduction could indicate that there is a problem with the body.
Thus a packet of mucus in the stool, which is easily seen with the naked eye, can only be a sign of digestive problems due to the proliferation of bacteria or problems related to digestive enzymes. While this sign of increased mucus is not inherently harmful, it can serve as a clue for a more accurate diagnosis.
When To Get Medical Advice
You should see a GP as soon as possible if you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis and you have not been diagnosed with the condition.
They can arrange blood or stool sample tests to help determine what may be causing your symptoms.
If necessary, they can refer you to hospital for further tests.
If you have been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis and think you may be having a severe flare-up, contact a GP or your care team for advice.
You may need to be admitted to hospital.
If you cannot contact your GP or care team, call NHS 111 or contact your local out-of-hours service.
Read Also: What Helps With Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Saddles With Mucus Coating
- In this case, the jelly-like discharge has formed a transparent coating on the stool. It does not appear to be mixed in the stool.
- This mucus does not appear to be related to the parasite because it is clear.
- If microbes were present in the mucus, it would be opaque, yellow, or green, just like the infected respiratory mucus that is released during sputum.
- The stools appear hard, small and compact, which is usually indicative of constipation.
- The likely cause of this mucus is irritation of the sigmoid colon which could result from constipation.
- The irritation causes copious amounts of mucus to secrete, which then coats the stool, to protect the walls of the intestine.
Treatment For Mucus In Stool
Treatment will depend on the results of diagnostic tests.
If mucus in the stool is related to diet, a doctor might recommend drinking more water, increasing fiber intake, or taking probiotics.
Treatment might include prescription medication and lifestyle changes for long-term conditions such as Crohns, UC, and IBS.
If doctors diagnose cancer, they will refer a person to an oncologist, a specialist cancer doctor, who will devise a treatment plan specifically for them.
You May Like: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Fever
When To Get Treatment
An increase in inflammation causes a flare, and the nature of inflammation means that you should treat it as quickly as you can. Inflammation grows exponentially, because inflammation itself causes an increase in inflammation. The longer you leave it untreated, the worse it will get. In addition, untreated inflammation not only leads to the symptoms associated with ulcerative colitis, it can also increase your risk of developing complications such as colorectal cancer down the line. Pay attention to your symptoms, and visit your physician if you notice that they change or increase even a small amount.
What Your Poop Should Look Like
First, lets talk about how poop is categorized. GI doctors usually refer to the Bristol Stool Chart to determine if someones poop appears normal, says Simon Hong, M.D., gastroenterologist and assistant professor of medicine at the IBD Center at NYU Langone Health in New York City. The chart breaks down how poop might look into seven different types according to size, texture, and consistency. Those descriptions include:
-
Type 1: Separate hard lumps, like nuts
-
Type 2: Sausage-shaped but lumpy
-
Type 3: Like a sausage but with cracks on the surface
-
Type 4: Like a sausage or snake, smooth and soft
-
Type 5: Soft blobs with clear-cut edges
-
Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges
-
Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces, entirely liquid
So, how do you know if your poop passes the sniff test? Generally between 3 and 5 is what would be considered the normal form, whereas 6 and 7 are more on the loose or diarrhea side, and 1 and 2 are more on the hard or constipated side, Dr. Hong explains.
Healthy poops are poops that are reasonably well-formed without being hard, adds Peter Higgins, M.D., professor of gastroenterology and internal medicine at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
Read Also: Generic Drugs For Ulcerative Colitis
Reducing Blood In Stools
prebiotic supplement may help reduce bloody stools and other symptoms of UC.
Participants taking the prebiotics supplement experienced significantly decreased abdominal pain and cramping. They also reported reduced nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and blood in stools, although these effects were not statistically significant.
The study was small, so more research is needed to determine the best way to reduce blood in stools.
If a person frequently has bloody stools, a doctor may prescribe iron supplements to help prevent anemia.
Why Is There Mucus In My Stools Ulcerative Colitis
Posted: December 12, 2016 at 3:43 am
This post was added by Dr Simmons
Mucus In My Stools:
What can be more annoying than looking into the toilet when you are in the middle of ulcerative colitis symptoms and seeing something that is unfamiliar?
mucus on a stool in the toilet bowl
How often should people be examining their stools or poops if you want to call them that anyways?
It seems that for everyone with ulcerative colitis, what ends up in the toilet bowl is almost the most exciting or sometimes depressing part of the day. How strange is that.
Yet again, I threw myself back into denial, and just avoided thinking about what this strange slimmy mucus stuff was. I had no idea why it was attached to almost every crap that landed in the toilet bowel, and I really was worried that something was wrong inside of me.
Mucus is simply a secretion that comes from many different parts of the body. It is not limited to the intestines, but rather it can be found on the inner lining walls of the stomach as well as other organs of the body. It is not something to be worried about most of the time. The job of mucus is to protect and lubricate the areas that it attaches to. Due to its composition, it is not absorbed by the intestines. There are bacteria in the intestines that can actually break it down further and the mucus can sometimes become a food source for certain bacteria within the gut. Wow, that is some pretty crazy mucus information.
Read more from the original source:
Don’t Miss: Holistic Treatment For Ulcerative Colitis