Determining What Treatment Is Right For You
Diagnosis provides the basis for choosing a suitable treatment method. However, its worth noting that both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis arent completely curable. Your GI specialist or physician can only work with you to manage the symptoms. The treatment majorly involves reducing inflammation, which helps suppress the symptoms, allows your body to repair damaged tissue, and eventually slows the diseases progression.
Some treatment methods include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids and oral 5-aminosalicylates.
- Immune system suppressors.
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Colitis
Colitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. Colitis causes symptoms such as abdominal pain and cramping, bloating, and diarrhea.
An inflamed colon can be caused by several conditions. UC is one possible cause. Other possible causes of colitis include:
- Crohns disease
- an allergic reaction
To diagnose the cause of colitis, a doctor will order a series of tests. These tests will help them understand what other symptoms youre experience and rule out conditions based on what youre not experiencing.
Treatment for colitis will depend on the underlying cause and other symptoms you have.
Who Diagnoses Ulcerative Colitis
If you have symptoms of ulcerative colitis, your regular healthcare provider will probably refer you to a specialist. A gastroenterologist a doctor who specializes in the digestive system should oversee the care for adults. For young patients, a pediatric gastroenterologist who specializes in children should manage the care.
Don’t Miss: Best Treatment For Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
What Symptoms Do Colitis And Ulcerative Colitis Share
Colitis can cause similar belly and bowel issues no matter the cause. Some symptoms are mild while others are more serious.
General signs of colitis and UC include:
- Stomach cramps that come and go
- Constant belly pain
- Mucus or blood in your poop
- Weight loss without trying
- An urgent need to poop
- A feeling like you didnât get all your poop out
If you have periods, you may have:
- Worsening diarrhea during your period
How Often Do I Need A Colonoscopy
Especially when you have symptoms or are just starting or changing medications, your doctor may want to periodically look at the inside of the rectum and colon to make sure the treatments are working and the lining is healing. How often this is needed is different for each person.
Ulcerative colitis also increases your chance of developing colon cancer. To look for early cancer signs, your healthcare provider may have you come in for a colonoscopy every one to three years.
You May Like: Ulcerative Colitis Rectal Pain Relief
In My Shoes: 24 Hours With Crohns Or Colitis App
In My Shoes is an immersive experience that allows anyone to find out first-hand what its like to have Colitis.
From low energy levels to managing pain, from rushing to the toilet to juggling work and a social life, the app will allow friends, family and anyone you want, to see first-hand how the condition can affect every part of your body, and every aspect of your life.
We have information for friends and family, employers, and colleagues. Find all our information online.
We have around 50 Local Networks across the UK that bring local people affected by Crohns and Colitis together. They are run by volunteers and host a range of events, from educational talks to socials. Check our website or call our Helpline to find your nearest Local Network.
How Common Is Back Pain If You Have Ulcerative Colitis
According to results presented at the 2019 American College of Rheumatology Annual Meeting, chronic axial back pain is seen in almost 25% of UC cases. Axial pain was more likely to occur in older people and after sleep or rest.
The researchers estimated that about 10% of IBD patients had axial spondyloarthritis but noted that they needed a larger sample size to be more accurate.
A hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis is sacroiliitis. In one study , 16.9% of the UC patients were found to have sacroiliitis, which was significantly more than the control group but similar to those with Crohns disease, another IBD condition.
More research with larger sample sizes is still needed to learn more about the connection between UC and conditions like axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
The treatment of back pain thats caused by UC may depend on several factors, such as your age, level of pain, and severity of spinal inflammation.
Some treatment options may include:
- anti-inflammatory medications or injections
Don’t Miss: Natural Supplements For Ulcerative Colitis
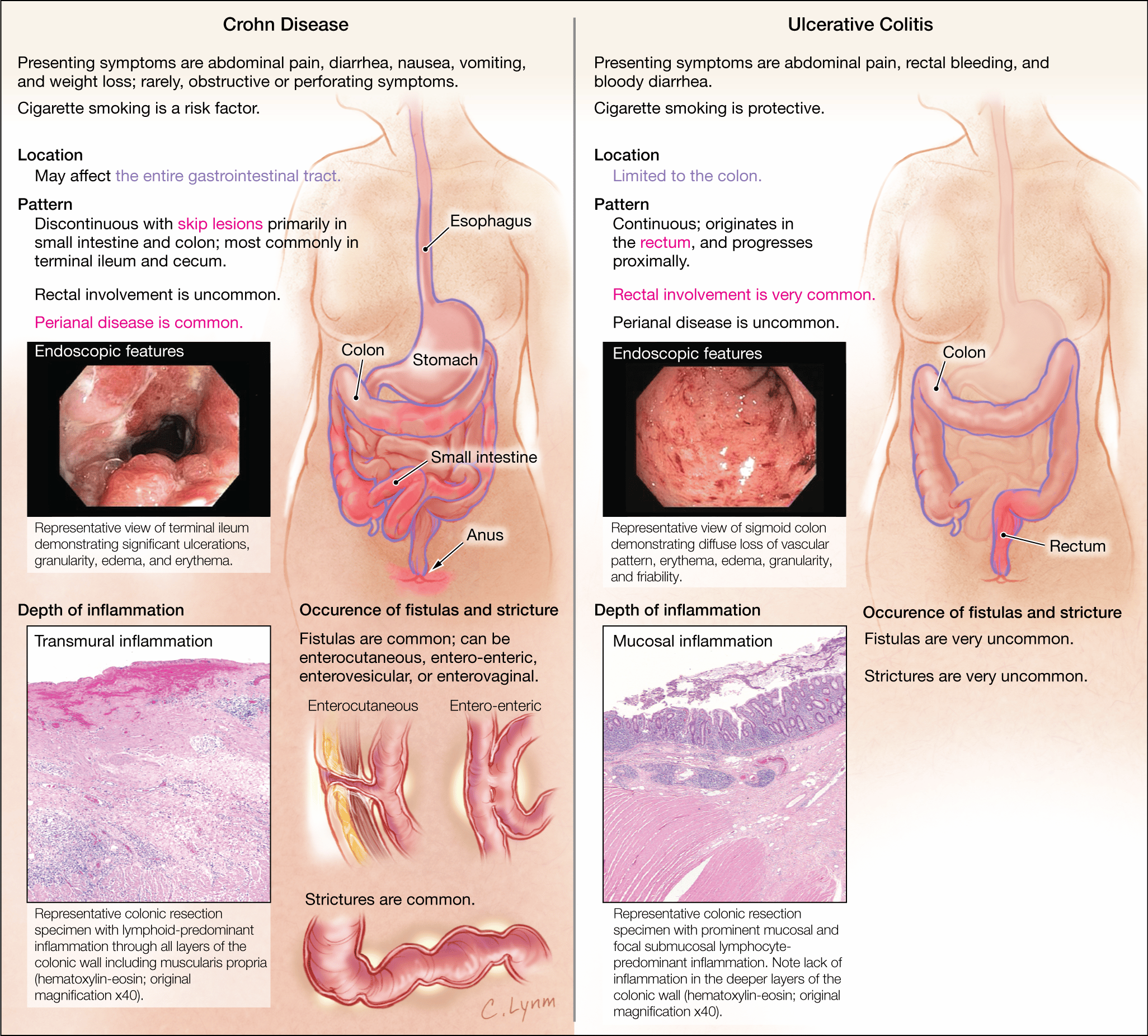
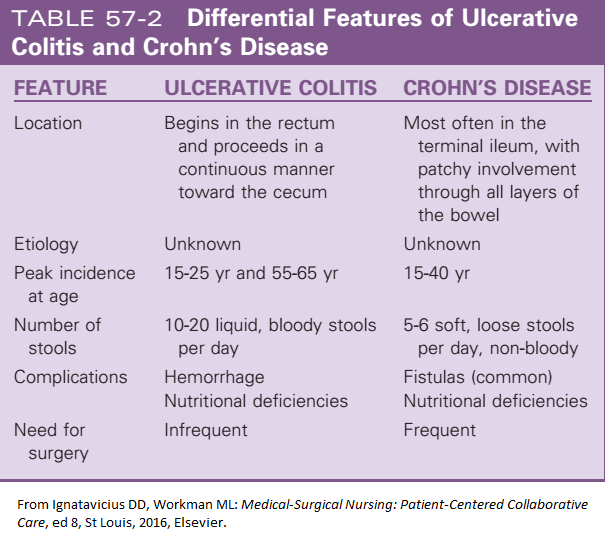
What Is The Difference Between Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are inflammatory bowel diseases , however, there are distinct differences between these diseases. This video developed by the GI Society with Dr. Mike Evans, illustrates the differences between Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis, the impact of these diseases, possible causes and prevalence.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease video courtesy of GI Society
How Are Ulcerative Colitis And Crohn’s Disease Similar
- Both diseases often develop in teenagers and young adults although the disease can occur at any age
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease affect men and women equally
- The symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are very similar
-
The causes of both UC and Crohn’s disease are not known and both diseases have similar types of contributing factors such as environmental, genetic and an inappropriate response by the body’s immune system
Recommended Reading: What Does A Mouth Ulcer Look Like
Whats The Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
UC and Crohns disease are the most common forms of IBD. Both conditions are thought to be the result of an overactive immune system.
They also share many symptoms, including:
However, UC and Crohns disease do have distinct differences. Understanding the key differences between them can help you obtain a proper diagnosis.
Location
These two conditions affect different portions of the GI tract.
Response to treatment
Similar medications are prescribed to treat both conditions. Surgery is also a treatment option. Its a last resort for both conditions, but it can be a cure for UC, whereas its only a temporary therapy for Crohns.
Crohns & Colitis Uk Local Networks
Our Local Networks of volunteers across the UK organise events and provide opportunities to get to know other people in an informal setting, as well as to get involved with educational, awareness-raising and fundraising activities. You may find just being with other people and realising that you are not alone can be reassuring. Families and relatives may also find it useful to meet other people with Crohn’s or Colitis. All events are open to members of Crohns & Colitis UK
Also Check: Entyvio Infusion For Ulcerative Colitis
Can I Get Surgery For My Ulcerative Colitis
Surgery is an option if medications arent working or you have complications, such as bleeding or abnormal growths. You might develop precancerous lesions, or growths that can turn into colorectal cancer. A doctor can remove these lesions with surgery or during a colonoscopy.
Research shows that about 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery sometime during their life. About 20% of children with ulcerative colitis will need surgery during their childhood years.
There are two kinds of surgery for ulcerative colitis:
Proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch
The proctocolectomy and ileoanal pouch is the most common procedure for ulcerative colitis. This procedure typically requires more than one surgery, and there are several ways to do it. First, your surgeon does a proctocolectomy a procedure that removes your colon and rectum. Then the surgeon forms an ileoanal pouch to create a new rectum. While your body and newly made pouch is healing, your surgeon may perform a temporary ileostomy at the same time. This creates an opening in your lower belly. Your small intestines attach to the stoma, which looks like a small piece of pink skin on your belly.
After you heal, waste from your small intestines comes out through the stoma and into an attached bag called an ostomy bag. The small bag lies flat on the outside of your body, below your beltline. Youll need to wear the bag at all times to collect waste. Youll have to change the bag frequently throughout the day.
What Role Does Diet And Nutrition Play In Ulcerative Colitis
Diet does not cause the development of ulcerative colitis nor can any special diet cure the disease. However, the foods you or your child eat may play a role in managing symptoms and lengthening the time between flareups.
Some foods may make symptoms worse and should be avoided, especially during flareups. Foods that trigger symptoms are different from person to person. To narrow down what foods affect you, keep track of what you eat each day and how you feel afterward .
Problem foods often include:
- High sugar foods and drinks.
- Carbonated beverages.
- High-fiber foods.
In addition to the problem foods listed above, infants, children and teenagers can also experience issues with:
- Dairy products.
Keep a careful eye on your childs diet and nutrition. Their appetite may decrease during a flareup and they might not eat enough to stay healthy, and grow. Also, the inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis may keep their digestive tract from absorbing enough nutrients. This can also affect your childs health. For these reasons, you may have to increase the amount of calories your child consumes.
Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan if you or your child has ulcerative colitis.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Is Characterized By
Causes Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is the result of several factors that are not yet well understood. Abnormal immune response, genetics, microbiome, and environmental factors all contribute to ulcerative colitis.
Research suggests that ulcerative colitis could be triggered by an interaction between a virus or bacterial infection in the colon and the bodys immune response.
-
Typically, the cells and proteins that make up your immune system protect you from infection.
-
A normal immune response would cause temporary inflammation to combat an illness or infection. The inflammation would then go away once you are healthy and free of the illness.
-
In ulcerative colitis patients, the inflammation persists long after the immune system should have finished its job. The body continues to send white blood cells into the lining of the intestines, where they produce chronic inflammation and ulcers.
Is It Important To Treat A Flare Early Or Is It Ok To Wait A Bit
Inflammation typically does not resolve without treatment and early intervention has a better outcome than waiting to treat. At an early stage of a flare, a more optimal baseline treatment is often enough to get the inflammation under control. If you wait, there is a greater risk that you might need drugs with greater side effects, such as oral steroids. By waiting, you will have to manage longer with your symptoms before getting relief. Living with constant or longer periods of inflammation might increase your risk for future complications, as inflammation might cause damage to the gut wall that accumulates in severity with each flare.
If you are experiencing worsening symptoms, you have probably already had the flare for some time without symptoms. Evidence shows that a stool test for inflammation in the colon, called fecal calprotectin, is often elevated for two to three months before any symptoms appear. Your colon might also start to show visual evidence of inflammation before you have symptoms, or at least indicate an increased risk for a flare.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Frequent Mouth Ulcers
Complications Caused By Nutritional Deficiencies
Some of the complications of malnutrition include:
- Dehydration diarrhoea causes your body to lose fluid, which can lead to dehydration. Severe dehydration can damage your kidneys.
- Anaemia reduced iron in the diet combined with losing blood from the bowel can lead to anaemia .
- Weight loss reduced appetite and poor absorption of food nutrients can cause weight loss.
- Reduced growth inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can impair a childs growth and physical development.
Keep Up With Your Checkups
If you have either condition, you’ll need to keep up with your checkups, even if your symptoms start to ease up.
You may also need to get colonoscopies more often and start them at a younger age. A colonoscopy can check for cancer or polyps that need to come out. Experts recommend that you start these tests within 8 to 10 years of developing UC or Crohnâs symptoms, and then typically every 1 to 3 years after that. Your doctor will tell you a schedule that is best for you.
Show Sources
Read Also: Is Smoking Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Getting The Right Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about the type and timing of your symptoms. Theyâll probably feel your belly to see if itâs tender. Let them know about any medications that you take and if anyone in your family has ever had IBD or other digestive issues.
Everything you tell your doctor gives them clues about other tests you might need, such as:
Stool samples and bloodwork. Your poop and blood can reveal signs of infection or inflammation. Blood tests can also show low levels of iron. Thatâs called anemia. It can happen when colitis causes a lot of bleeding in your colon.
Imaging. Your doctor may take pictures inside your colon or rectum. They might use a special liquid called barium for some tests. Thatâs a substance thatâll coat your colon to help it show up better on X-rays.
You may also need:
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans
- Computed tomography scans
Endoscopic tests. An endoscope is a camera attached to a thin, bendy tube. Your doctor can use it to look at your lower colon and rectum or entire colon .
Tissue biopsy. Your doctor may remove some tissue during a colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. A lab technician will use a microscope to check for signs of inflammation or other abnormal cells.
Is Ulcerative Colitis Curable
Currently, theres no nonsurgical cure for UC. Treatments for the inflammatory disease aim to extend periods of remission and make flare-ups less severe.
For people with severe UC, curative surgery is a treatment option. Removing the entire large intestine will end the symptoms of UC.
This procedure requires your doctor to create a pouch on the outside of your body where waste can empty. This pouch can become inflamed and cause side effects.
For that reason, some people choose to have only a partial colectomy. In this surgery, your doctor only removes the parts of the colon that are affected by UC.
While these surgeries can help ease or end symptoms of UC, they can have adverse effects and possible long-term complications. Read more about these issues to determine if surgery is an option for you.
You May Like: What To Eat To Cure Ulcer
Ulcerative Colitis And Diverticulitis: Similarities And Differences
UC and diverticulitis both start out in the large intestine and share symptoms like belly pain and bloody poop. Both conditions are more likely the older you get, and both can range from mild to severe and vary for each person. But they differ in terms of what causes them and how your doctor might treat them.
UC is a lifelong condition that can lead to life-threatening problems. About a million Americans are affected by it. It can affect people at any age, including those in their 20s and 30s. If you have UC, you also might have weight loss or arthritis.
Diverticulitis, not a lifelong condition, is a complication of âdiverticulosis.â Itâs the term doctors use when one or more of the small bulging sacs grow on your colon wall. It usually starts in middle age and itâs common in older people. Diverticulitis can happen to you once and never happen again, or it might come and go. About 50% of those over the age of 60 have it, and almost everyone above 80 has it, too. Most are mild cases that donât cause any symptoms and arenât reasons to worry. Up to 30% of the people with diverticulosis go on to have diverticulitis. And among them, anywhere between 5%-15% will have symptoms like bloody poop.
Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis

UC increases your risk of developing colon cancer. The longer you have the disease, the higher your risk of this cancer.
Because of this increased risk, your doctor will perform a colonoscopy and check for cancer when you receive your diagnosis.
Repeat screenings are recommended thereafter, according to the American Cancer Society. Regular screenings help lower your risk of colon cancer. Follow-up screenings can detect precancerous cells early.
Other complications of UC include:
- thickening of the intestinal wall
- intestinal bleeding
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Corneal Ulcer
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis
Researchers think the cause of ulcerative colitis is complex and involves many factors. They think its probably the result of an overactive immune response. The immune systems job is to protect the body from germs and other dangerous substances. But, sometimes your immune system mistakenly attacks your body, which causes inflammation and tissue damage.
How Is Treatment Of Crohns Disease Different From Ulcerative Colitis
Although the medications may seem similar, there are differences in how Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are treated. Many medication classes treat both conditions, so there is a lot of overlap. However, there are enough differences that getting the right diagnosis is important. For example, people with ulcerative colitis usually take aminosalicylates, while only a limited number of people with Crohns disease will benefit from these medications. When it comes to more advanced therapies like biologic agents, some can only be used for ulcerative colitis and some can only be used for Crohns disease.
Getting the correct diagnosis can be tricky. Sometimes it might look like you have ulcerative colitis at first, but later your providers will find out that its actually Crohns disease. Work closely with them to be sure you get the right treatment.
Also Check: How Do They Test For Ulcers