Toxic Megacolon And Other Complications Of Severe Uc
Toxic megacolon may be defined as colonic dilatation of more than 5.5 cm along with signs of systemic toxicity. Lifetime incidence of toxic megacolon in patients with UC varies from 1%-2.5% and approximately 5% severe UC patients who are hospitalized may develop toxic megacolon. Risk factors include dyselectrolytemia, full bowel preparation and medications . Earlier identification of this condition, prompt institution of medical therapy and low threshold of surgery in cases of non-response to medical therapy within 48 h will decrease the morbidity and mortality of this condition.
Other complications include perforation which is the most serious complication of severe UC. Risk factors include inappropriate total colonoscopy and delaying treatment of toxic megacolon. Diagnosis of perforation can often be delayed as abdominal signs can be masked when patient is on steroids. Therefore, patients with severe UC should be monitored closely for abdominal signs and on the slightest suspicion abdominal radiographs should be obtained. Other complication includes severe hemorrhage.
Infection Prevention And Control: Isolation Measures For Patients With Cdi
XIII. Should private rooms and/or dedicated toilet facilities be used for isolated patients with CDI?
XIV. Should gloves and gowns be worn while caring for isolated CDI patients?
XV. When should isolation be implemented?
XVI. How long should isolation be continued?
XVII. What is the recommended hand hygiene method when caring for patients in isolation for CDI?
XXI. Should cleaning adequacy be evaluated?
Preoperative Optimisation Of Refractory Moderate
Correction of altered body composition and nutrition imbalances is advised preoperatively, despite limited evidence . There is no evidence to support routine enteral or parenteral nutrition to improve the surgical outcomes of patients with UC . Iron supplementation is recommended when iron-deficiency anaemia is present
Nutritional alterations predict poor postoperative outcomes and mortality and affect QoL., Routine perioperative assessment by a nutritionist should be considered in IBD patients in remission, as part of multidisciplinary management. Even if current evidence is limited, it is advisable to correct undernutrition or overnutrition., No data support routine perioperative administration of enteral or parenteral nutrition. Delaying surgery by 714 days should be considered in patients with malnutrition. High-quality evidence suggests that iron supplementation is recommended when iron deficiency is present, with the goal of normalising haemoglobin levels and iron stores.,
Low-quality studies reported that patients who have received > 20 mg prednisolone for > 6 weeks are at 5-fold increased risk of infectious and short-term pouch-specific complications. Steroids should be weaned before surgery if this is not possible, pouch construction should be postponed. Thiopurines or cyclosporine do not increase the risk of postoperative complications.
Don’t Miss: Does Ulcerative Colitis Cause Weight Loss
Inducing And Maintaining Remission In Uc: Do The Guidelines Agree
Despite the many similarities, there are a number of inconsistencies in the recommendations regarding the management of moderate-to-severe UC between the ACG and AGA guidelines .11,16 Whereas the ACG recommends the use of prednisone or oral budesonide MMX for induction of remission,16 the AGA does not address these therapies given its focus on immunosuppressives, biologics, and small-molecule therapies. However, despite being the drugs that everyone loves to hate, Dr Feagan commented that steroids are excellent induction drugs and good therapies to add on to biologics to get rapid symptomatic remission. He continued, It is imperative to get patients to symptomatic remission, and if you have to use steroids to get thereusing cessation of bleeding as a markeryou should use them.
Assessing Response To Medical Treatment
The FBC, U+Es, albumin, CRP and stool frequency should be checked on a daily basis. The AXR should be repeated daily if there is severe extensive colitis, dilatation on the previous AXR, fever, tachycardia or abdominal tenderness otherwise repeating it every other day will suffice. In patients without evidence of toxic dilatation and impending perforation, a decision to continue with standard therapy, to commence rescue therapy, or to proceed to a colectomy should be made by the consultant gastroenterologist in conjunction with a colorectal surgeon at the end of 72 hours of intravenous hydrocortisone. In patients who respond to standard therapy, intravenous hydrocortisone should be continued for a minimum of five days before switching to prednisolone 40 mg daily, which can be tapered by 5 mg every week provided the patient remains in remission. Furthermore, topical and/or oral 5-ASA therapy can be restarted or commenced once the patient is improving.
Don’t Miss: Besivance Dosage For Corneal Ulcer
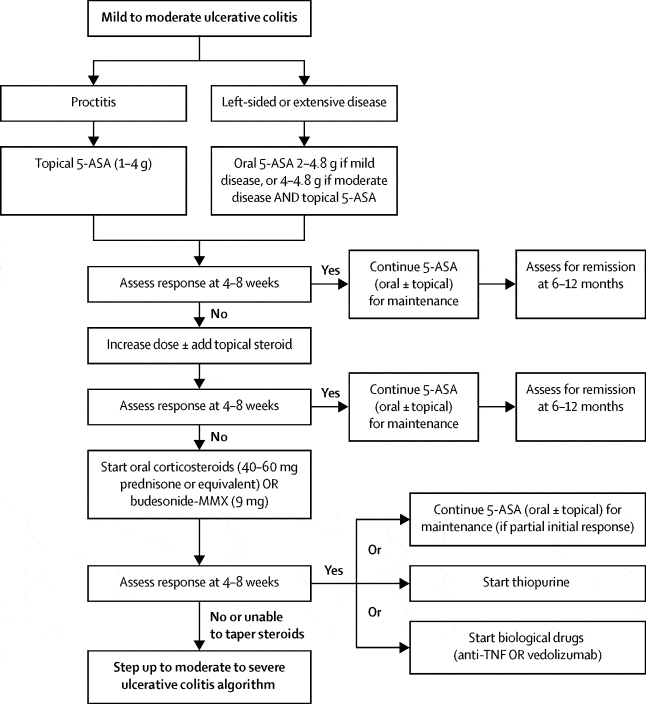
Active Uc Of Any Extent Not Responding To Aminosalicylates
In mild-to-moderate UC of any extent, aminosalicylates such as mesalamine are the preferred initial treatment . In patients with disease activity limited to the rectum, topical therapy alone might suffice, but combination therapy is more effective and is also recommended for left-sided and extensive UC . Table 2 gives an overview on current treatment options.
Table 2.
Medical therapy for UC
Fig. 1.
Active ulcerative colitis of any extent not responding to 5-aminosalicylates . MMX, multimatrix AZA, azathioprine 6-MP, 6-mercaptopurine.
Except in case of isolated proctitis, where topical corticosteroids alone may be considered, treatment with oral corticosteroids should be initiated in patients who do not respond adequately to 5-ASA . In case of isolated proctitis, topical corticosteroids alone might be considered. The introduction of corticosteroids should be a shared decision-making process that includes patients preference of therapy and tolerance to 5-ASA. It is, however, recommended to start corticosteroids in patients with sustained rectal bleeding for 2 weeks, persistent abdominal symptoms after 6 weeks of adequate therapy with 5-ASA or if symptoms deteriorate . In selected cases, a prolonged therapy with up to 16 weeks might still be able to achieve remission.
You May Like: What Is An Ulcer Diet
Medical Versus Surgical Management Of Refractory Moderate
Reconstructive surgery may be offered to refractory and corticosteroid-dependent patients and improves quality of life despite the risk of early and late complications . Proctocolectomy with end-ileostomy is an alternative for some patients and has lower morbidity and comparable quality of life
Five systematic reviews were performed to define the risk of early and late complications after restorative proctocolectomy with IPAA. Early complications occurred in 965% of patients, and late complications occurred in 355% of patients., Systematic reviews indicate that the most frequent complications were pouchitis ,, wound infection ,,, bowel obstruction ,, ileus , sepsis ,, anastomotic leak ,, and fistula . The most common late complications were ileus , faecal incontinence , pouch loss ,, chronic pouchitis ,, Crohns-like disease of the pouch , and fistula . The overall mortality rate after surgery was 0.1%.
The studies that compared ileostomy with IPAA were all retrospective and revealed similar results, using a different QoL score. Occasionally the scores obtained in specific domains of health-related QoL differed significantly between the surgical techniques . Removing the diseased colon offers a good QoL when compared with medical treatment in UC patients, with a morbidity ranging between 20% and 25%.
Don’t Miss: Natural Remedies For Stomach Ulcers In Humans
Early Recognition Close Monitoring And Timely Re
Any patient meeting the criteria for severe disease should be recognized promptly and admitted in the hospital. Stool cultures for enteric pathogens and Clostridium difficile should be taken at the earliest possibility but results should not be awaited before rapid IV corticosteroid therapy. Flexible unprepared sigmoidoscopy with minimal air insufflation should be performed within 24 hours of admission to confirm diagnosis and exclude a superimposed infection with the cytomegalovirus .3,8
Following initiation of corticosteroid therapy patients should be closely monitored with daily blood works, clinical examination and serial abdominal films as clinically indicated. Positive stool cultures should prompt treatment with antibiotics, presence of a significant amount CMV inclusions on colonic biopsy are an indication for ganciclovir treatment. Formal re-assessment is performed between days 3 and 5.3,8 As discussed above, current evidence does not allow for a singular recommendation. Failure of corticosteroid therapy is therefore based on a clinical, biochemical and radiological assessment. Several indices such as stool frequency, CRP and albumin levels and colonic dilatation on plain radiography can be used as described above.
Medical Management Of Asuc
Intravenous corticosteroids as the initial standard treatment for adult patients with ASUC are recommended, as this treatment induces clinical remission and reduces mortality
The only randomised controlled trial including placebo in the setting of ASUC is the paramount work by Truelove and Witts, who observed that steroids induced clinical remission and decreased mortality without increasing serious adverse events., Risk of bias led to downgrading of the evidence level from 2 to 3. No conclusions could be drawn about the need for surgery, as the authors included derivative ostomies and colectomies without distinguishing the type of surgery in the report. Since the results of this pivotal study, placebo-controlled trials to clarify these and other aspects would be unethical.
Either infliximab or cyclosporine should be used in adult patients with steroid-refractory ASUC. When choosing between these strategies, centre experience and a plan for maintenance therapy after cyclosporine should be considered
There is currently insufficient evidence to determine the optimal regimen of infliximab rescue therapy in patients with ASUC refractory to corticosteroid therapy
A retrospective cohort study did not reveal differences in short-term or long-term colectomy rates between ASUC patients treated with accelerated- or standard-dose infliximab.
Recommended Reading: Is Black Tea Good For Ulcerative Colitis
How Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Treated
ASUC is a challenging condition to treat. Once you’re admitted to the emergency room, you’ll get a series of tests, including blood tests, stool tests, and an exam of your bowel called a sigmoidoscopy. You’ll also get intravenous fluids to boost hydration.
The average hospital stay for ASUC treatment ranges from 4.6 to 12.5 days. During this time, your health care providers may include a gastroenterologist, colorectal surgeon, dietitian, pharmacist, and stomal therapist. The goal of hospitalizing you is to end the flare, get your symptoms under control, and put the disease into remission. Your doctors will want to make sure that rectal bleeding and diarrhea have stopped and normal bowel movements have returned. Rehospitalization is common.
Intravenous steroid medications are the most common treatment for ASUC. For 30% to 40% of ASUC patients, steroid treatments donât work â and taking steroid medications for more than 10 days increases your risk of complications.
If the steroids donât help within 3 to 5 days, your health care team will start âmedical rescue therapyâ with immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or infliximab.
You might get an operation to remove part of your colon, called a colectomy, if your ASUC doesnât respond to steroids, immunosuppressants, or other medical treatments.
Sequential Therapy In Asuc
Sequential therapy is defined as the use of a calcineurin inhibitor as rescue therapy in patients not responding to infliximab and vice versa. Sequential therapy is not recommended by current guidelines as it has been associated with serious side effects and infections because of cumulative immunosuppression . According to ECCO guidelines, only one attempt at rescue therapy should be considered before referral for colectomy and third-line medical therapy should only be considered in specialist referral centres and highly selected cases .
You May Like: What Helps With Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Is Combination Therapy For A Lifetime
The optimal duration of combination therapy is an important area of uncertainty, as there are currently very limited prospective data to guide decision-making.54–56 However, Dr Feagan noted that there is a large randomized controlled trial fully recruited in Europe that should help answer this question. Although he speculates that combination therapy will prove to be superior over time, he added that given the risks of thiopurines, his practice is to discontinue azathioprine in his patients who are older than 60 years. Dr Sandborn agreed that his practice is to discontinue thiopurines and switch to monotherapy in patients after they reach 60 to 65 years of age.
American Gastroenterological Association Guidelines
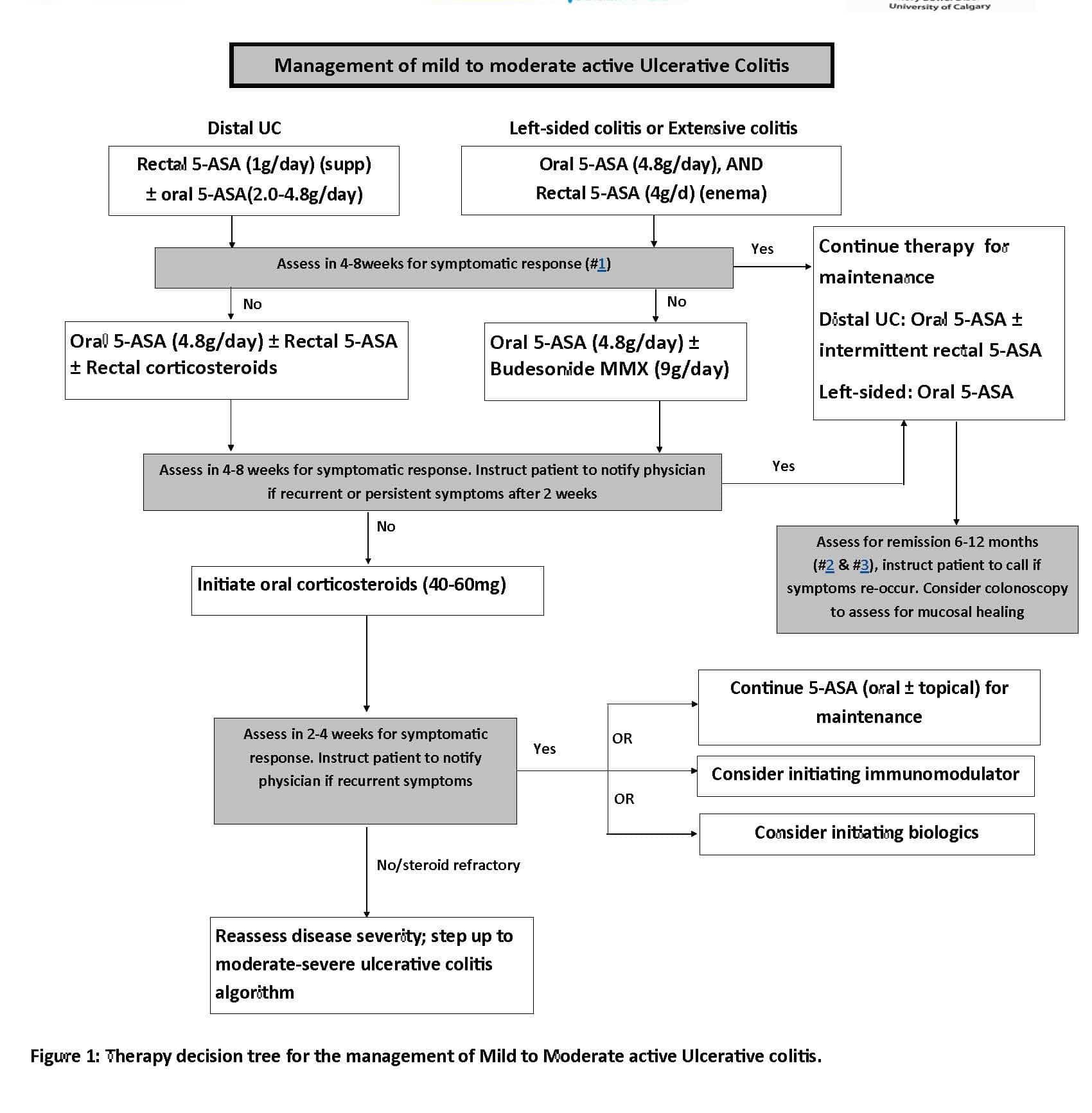
The AGA released new guidelines on the management of mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis in February 2019, with a focus on the use of oral and topical 5-aminosalicylates agents, rectal corticosteroids, and PO budesonide.
Strong recommendations
Patients with extensive mild-moderate UC: The AGA recommends using either standard-dose mesalamine or diazo-bonded 5-ASA rather than low-dose mesalamine, sulfasalazine, or no treatment.
Patients with mild-moderate ulcerative proctitis who choose rectal therapy over oral therapy: The AGA recommends using mesalamine suppositories.
Conditional recommendations
Patients with extensive or left-sided mild-moderate UC: The AGA suggests adding rectal mesalamine to oral 5-ASA.
Patients with mild-moderate UC with a suboptimal response to standard-dose mesalamine or diazo-bonded 5-ASA or with moderate disease activity: The AGA suggests using high-dose mesalamine with rectal mesalamine.
Patients with mild-moderate UC being treated with oral mesalamine: The AGA suggests using once-daily dosing rather than multiple times per day dosing.
Patients with mild-moderate UC: The AGA suggests using standard-dose oral mesalamine or diazo-bonded 5-ASA, rather than budesonide MMX or controlled ileal release budesonide for induction of remission.
Patients with left-sided mild-moderate ulcerative proctosigmoiditis or proctitis: The AGA suggests using mesalamine enemas rather than oral mesalamine.
No recommendations
Read Also: Do I Have An Ulcer
New Molecules Might Change The Approach To Asuc In The Future
In the last decade, many new options for treating IBD have become available. As some of these molecules can induce a rapid remission, they might be useful in the management of ASUC although data are still limited.64
Tofacitinib is a small molecule that inhibits the Janus kinases 1.2 and 3 which is a central molecule in pro-inflammatory cytokine production and response. In the OCTAVE trials tofacitinib was shown to induce remission more often than placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis that failed initial anti-TNF therapy.65 Post-hoc analysis of the trials moreover shows that induction of remission is particularly fast with these JAK inhibitors and occurs over a three-day period, making it a viable solution for treating ASUC.66 Data with tofacitinib in ASUC management are still limited, however. In a case series of 4 patients with ASUC, 3 out of 4 patients achieved clinical remission and colectomy was avoided in 50%.67 In another case series of again only 4 patients all patients achieved remission, and no one had to undergo colectomy.68 In a recent case series of 5 ASUC patients who had failed anti-TNF therapy, 3 improved under tofacitinib therapy while 2 eventually had to undergo a colectomy.69 Further prospective studies are needed.
Predictors Of Response To Steroids
Response to steroids is indicated by improvement in patients symptoms and improved laboratory parameters .
At day 3 of admission, response to steroids should be measured by assessing stool frequency and CRP levels .1). In the landmark study by Travis et al, which included patients with 51 episodes of severe UC, presence of more than 8 stools/d or 3-8 stools/d plus a CRP > 45 mg/L at day 3 predicted a colectomy rate of 85%. In another prospective study by Lindgren et al which included 97 episodes of severe UC, the following mathematical model was devised to predict colectomy: number of stoolsd + 0.14 × CRP 8 predicted a colectomy rate of 72%.
Algorithm for treatment decisions for patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis on intensive steroid therapy. AZA: Azathioprine.
Therefore regular assessment of response to steroids is of paramount importance in treating patients with acute severe UC. In a group of 80 patients who underwent emergency colectomy for severe UC between 1994 and 2000 in Oxford, patients with signicantly longer duration of preoperative medical therapy were more likely to have major post-operative complications.
Read Also: Is Okra Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Incorporating Combination Therapy Into Practice
The TNF- antagonists are relatively immunogenic, and combination therapy is essential, if tolerated, to prevent immunogenicity and loss of efficacy. Analyses of data from large pivotal trials have demonstrated reduced antibody formation, higher serum concentrations of TNF- antagonists, and greater clinical benefit when immunosuppressive therapies are combined with these agents.48–50 Most notably, the landmark prospective UC-SUCCESS trial clearly demonstrated the superiority of combination infliximab/ thiopurine therapy compared with either agent as monotherapy.31 Accordingly, the ACG and AGA guidelines agree that TNF- antagonists should be combined with immunosuppressives during induction.11,16
Outcome with combination therapy compared with monotherapy for vedolizumab and ustekinumab in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.53
Combination therapy is essential with anti-TNF therapies, but in my opinion, there is not enough evidence to suggest that combination therapy is necessary to optimize efficacy with ustekinumab or vedolizumab.
William J. Sandborn, MD
Technical Aspects Of Surgical Approaches For Refractory Moderate
IPAA may be constructed using either a stapled or a handsewn technique, with comparable functional outcomes. Thus, the type of anastomosis should be left to the surgeons discretion
Overall, stapled and handsewn IPAAs seem to result in comparable complication rates, functional outcomes, and QoL. In a meta-analysis of four randomised controlled trials including 184 patients , no significant differences were observed in terms of functional outcomes, sphincter resting pressure, or squeeze pressures. Based on low-quality evidence, the stapled technique may be more likely to achieve perfect continence compared with the handsewn approach. Despite slightly better functional outcomes after stapled anastomosis, overall QoL appears equivalent between the two groups.,
Due to a paucity of high-quality data, no recommendations can be made with regards to sexual function, strictures, and septic complications between stapled and handsewn techniques, although stapled IPAA is likely associated with a higher rate of cuffitis.,
Laparoscopic surgery is the preferred approach to patients with medically refractory UC, as it is associated with lower intra- and postoperative morbidity, faster recovery, fewer adhesions and incisional hernias, shorter hospital length of stay, improved female fecundity, and better cosmesis
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetic Foot Ulcer