Cohen R D Yu A P Wu E Q Xie J Mulani P M And Chao J
Systematic review: the costs of ulcerative colitis in Western countries
2010 â Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics
In-text:
Your Bibliography: COHEN, R., YU, A., WU, E., XIE, J., MULANI, P. and CHAO, J., 2010. Systematic review: the costs of ulcerative colitis in Western countries. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 31, pp.693-707.
The Future What Needs To Be Done
In the future, developments in disease phenotyping and genotyping may help inform earlier intervention. A plethora of new and emerging therapeutic agents and interventions affected through differing mechanisms of action should also help improve future management of IBD. Improving patientphysician communication and supporting patients in their understanding of the evidence base are also important for ensuring patient commitment and involvement in the long-term management of their condition. There is also a desire to create more IBD centres of excellence and to develop IBD networks to ensure a consistent level of care across different settings working alone is no longer acceptable. Finally, improved communication may hold the key to empowering and allowing patients to actively participate in disease management.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis And Lactose Intolerance
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Ulcerative colitis is a systemic disorder with no cure. The disorder has numerous extraintestinal involvement in addition to the colon. Thus, it is best managed by an interprofessional team. All patients with the disorder need lifelong monitoring. Because of the risk of colorectal cancer, surveillance colonoscopy should occur every 1-2 years. Further, since patients are often treated with biological agents, they need to undergo screening for melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer.
The pharmacists should assist the team by educating the patient on the importance of medication compliance to avoid relapse. The nurse should encourage regular vaccinations, hand washing, and cancer screening. A dietary consult should be obtained to educate the patient on foods to eat and what not to eat, especially if they have a stoma. In addition, a stoma nurse should be involved in the teaching of stoma care.
An infectious disease nurse should monitor the patient in the outpatient setting to ensure that they are not immunocompromised. Social workers should be involved to ensure that the patient has ample support and finances so that the treatments are not missed. Patients with risk factors for osteoporosis need screening for bone mineral density periodically. Patients should be encouraged to undergo annual vaccination against influenza and pneumococcus. Finally, many patients with ulcerative colitis develop depression and anxiety and should be referred to a mental health counselor.
Outcomes
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Have An Ulcer
Other Recommendations For Research
Induction of remission for people with moderate ulcerative colitis: prednisolone compared with aminosalicylates
What is the clinical and cost effectiveness of prednisolone compared with aminosalicylates for the induction of remission for people with moderate ulcerative colitis?
Induction of remission for people with moderate ulcerative colitis: prednisolone compared with beclometasone
What is the clinical and cost effectiveness of prednisolone plus an aminosalicylate compared with beclometasone plus an aminosalicylate for induction of remission for people with moderate ulcerative colitis?
Induction of remission for people with subacute ulcerative colitis that is refractory to systemic corticosteroids
What are the benefits, risks and cost effectiveness of methotrexate, ciclosporin, tacrolimus, adalimumab and infliximab compared with each other and with placebo for induction of remission for people with subacute ulcerative colitis that is refractory to systemic corticosteroids?
True Stories: Living With Ulcerative Colitis
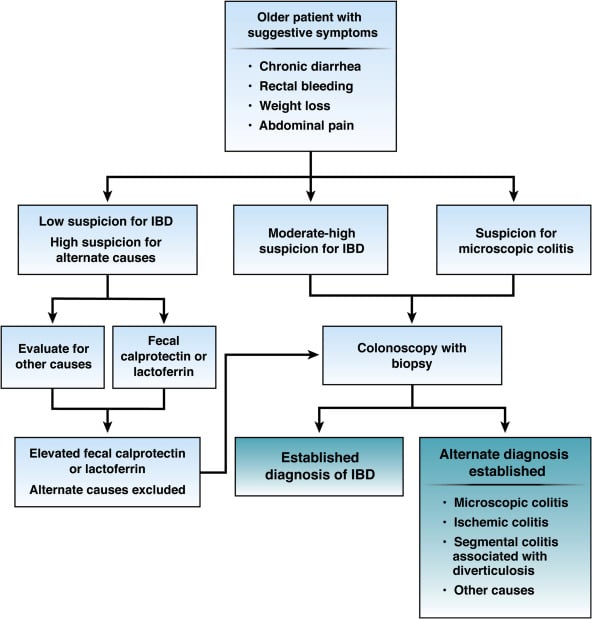
Ulcerative colitis affects about 900,000 people in the United States. In any single year, about 20 percent of these people have moderate disease activity and 1 to 2 percent have severe disease activity, according to the Crohns and Colitis Foundation of America.
Its an unpredictable disease. Symptoms tend to come and go, and sometimes they progress over time. Some patients go for years without symptoms, while others experience frequent flare-ups. Symptoms vary depending on the extent of the inflammation, as well. Because of this, its important for people with UC to keep track of how it affects them on an ongoing basis.
Here are the stories of four peoples experiences with UC.
years ago.
How do you manage your symptoms?
My first treatment was with suppositories, which I found extremely uncomfortable, hard to put in, and hard to hold. For the next year and a half or so I was treated with rounds of prednisone and mesalamine . This was awful. I had terrible ups and downs with prednisone, and every time I started to feel better I would feel sick again. I finally switched doctors to Dr. Picha Moolsintong in St. Louis, who actually listened to me and treated my case and not just my disease. I am still on azathioprine and escitalopram , which have been working very well.
What other treatments have worked for you?
What advice would you give to other people with UC?
How long ago were you diagnosed?
How difficult has it been to live with UC?
What helped you?
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Having An Ulcer
Inpatient Severe Disease Considerations
There are several disease scores used to determine the risk of requiring rescue therapy or colectomy in patients with severe colitis. Recent studies have shown a potential advantage of using the UCEIS scoring system, with 1 study showing improved accuracy of the UCEIS score in predicting the need for colectomy compared with the Mayo Score, with score greater than 7 showing a sensitivity of 60.3% with a specificity of 85.5%.98 Another study showed that a UCEIS score of 5 or more was associated with a 50% chance of requiring rescue therapy and 33% rate of colectomy compared with 27% and 9% for those with a score of less than or equal to 4. As mentioned previously, the commonly used Oxford index, developed in 1996, predicted the need for colectomy to be 85% in patients with a CRP level greater than 45 mg/L and 3 to 8 bowel movements a day after 3 days of IVCS treatment.24 Another score, developed in 1998 by Lindgren and colleagues99 using these same variables of bowel movements and CRP on day 3 after IVCS, showed favorable test characteristics for predicting the need for colectomy. The Ho index has also been used to risk stratify patients into low, intermediate, or high risk for colectomy.100 This index was derived from a cohort of patients from 1995 to 2002 and found aggregate scores of 0 to 1, 2 to 3, and greater than or equal to 4 from 3 variables correlated with a risk of progression to colectomy of 11%, 45%, and 85% respectively .
What Can Happen If I Have Diarrhea
Acute diarrhea is uncomfortable but rarely dangerous in healthy adults and children. However, diarrheal stools may contain viruses and bacteria that spread infections. For example, the bacterium Escherichia coli causes about 9% of all foodborne infections in the United States. If there is severe diarrhea with vomiting, dehydration can occur. This occurs when there is excessive water loss from your body due to diarrhea and/or vomiting. Severe dehydration may be life-threatening.
- Avoid eating contaminated food- If food poisoning is suspected to be a cause of your diarrhea, contact a local health department or call your doctor for instructions.
- Maintain hygiene -Keep hands clean by washing with soap and warm water for 20 seconds.
Follow these steps to prevent dehydration:
1. Drink plenty of water and other liquids. Water is important because your body loses water when you have diarrhea. Fluids that contain electrolytes are also helpful.
2. Avoid coffee and tea while you have diarrhea because they may worsen the problem by irritating the bowel wall, causing pain and inflammation, and increasing fluid loss.
Get the following premium features for free after ordering a custom nursing assignment from us:
You May Like: What Is An Infusion For Ulcerative Colitis
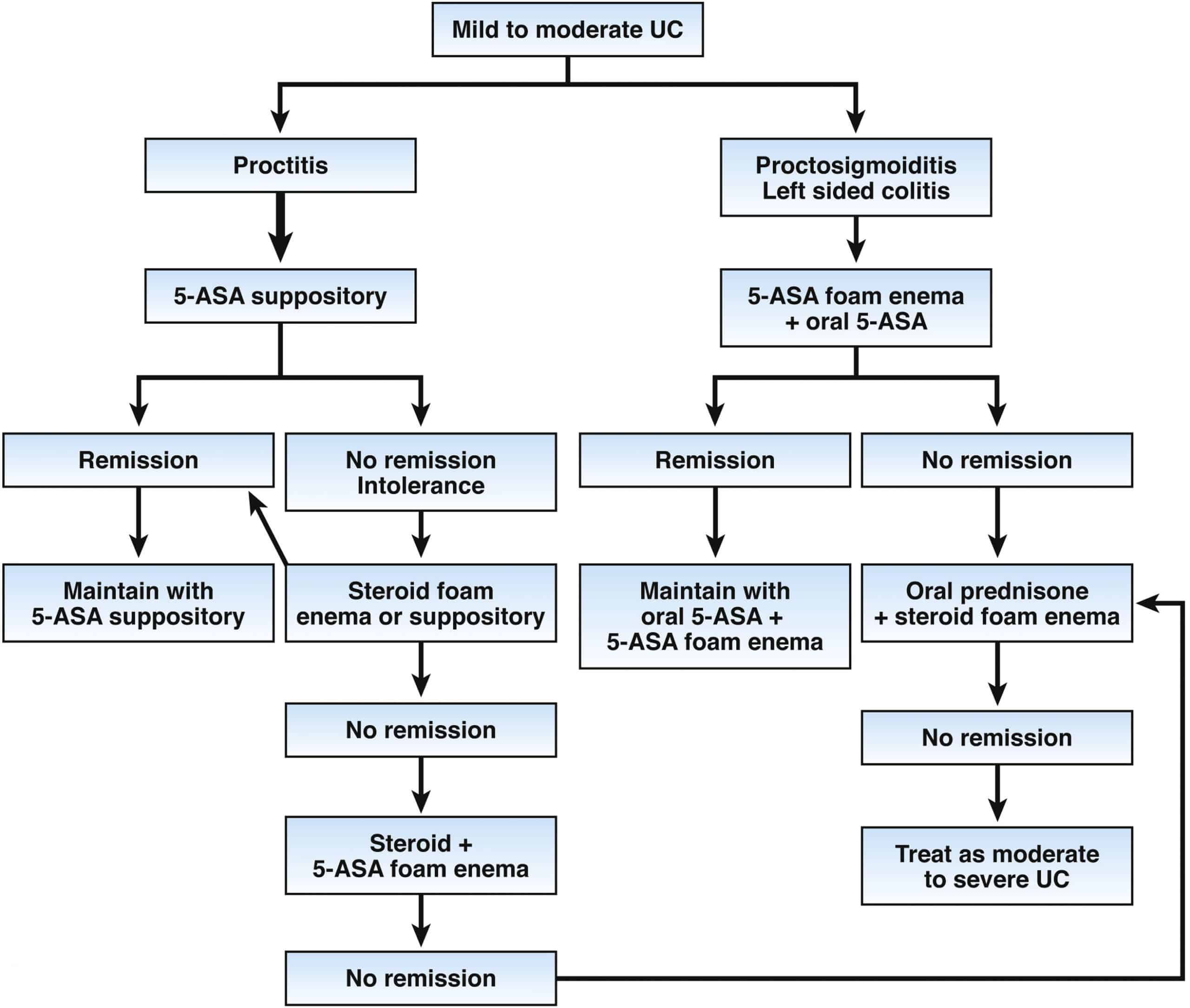
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis:
Let the names help you, so you can understand where the ulcerative colitis is located:
Ulcerative proctitis : affects the rectum and is the most mild form of all types. It tends to have fewer complications due to being located just in the rectum.
Proctosigmoiditis: PROCT: COLON and SIGMOID: SIGMOID COLON and ITIS: inflammationinflammation of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
Pancolitis . It is a very severe form of ulcerative colitis.
Left-sided colitis: LEFT-SIDED: includes the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum and ITIS: inflammation.inflammation of the descending, sigmoid, and rectum.
How Joint Pain Worsens Quality Of Life For Ulcerative Colitis Patients: Study
A recent study found that joint pain can have a significant impact on quality of life for patients with ulcerative colitis, MedPage Today reported Dec. 8.
The study, led by Marlana Radcliffe, MD, of the University of North Carolina School of Medicine Chapel Hill, analyzed patient surveys from 631 individuals with gastrointestinal symptoms linked to ulcerative colitis and found that 36 percent reported joint pain. Dr. Radcliffe presented the results in a poster presentation at the Advances in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases annual meeting, according to the publication.
Dr. Radcliffe also noted that joint pain was related to increased risks of depression, anxiety and social impairment.
“We have to be aware that patients have other things happening other than just with their gastrointestinal discomfort that also needs to be addressed,” Dr. Radcliffe told MedPage Today. “Our findings support further research and clinical attention on addressing the extraintestinal manifestations of arthritis in ulcerative colitis patients.”
“Joint pain is very common among our patients,” Svein-Oskar Frigstad, MD, PhD, of Vestre Viken Bærum Hospital and the University of Oslo in Norway, told MedPage Today. “Inflammatory bowel disease involves inflammation, and of course, pain in the joints is often caused by inflammation as well. We also see increases in bowel symptoms among patients who also have joint pain.”
Don’t Miss: Does Ulcerative Colitis Cause Hair Loss
What Do Ibd Nurse Specialists Do
Within the multidisciplinary team operates a small team of IBD Nurse Specialists. They have extensive training and experience in gastroenterology and are especially interested in treating and supporting patients with IBD.
IBD Nurse Specialists can conduct both face-to-face and telephone clinics, provide advice on how to manage the condition and refer patients to other relevant specialists within the team.
Benefits Of An Ibd Nurse
The Advanced IBD Nurse provides a pivotal and important role in the care of patients with IBD, within the IBD MDT and to health-care providers. Nurse-led services, including telephone ALs and out-patient clinics, have been demonstrated to be cost-effective and beneficial to patients and health-care providers .
Although generally accepted as beneficial to patients and services, a key challenge for the Advanced IBD Nursing role since its inception has been to demonstrate this benefit. This specialist nursing role was the first to be reviewed for the Cochrane database393 however, reviewed studies were assessed as having low methodical quality, resulting in benefits being difficult to quantify. ECCO, N-ECCO and the N-ECCO Research Forum continue to work to improve the quality and transferability of research into the Advanced IBD Nurse role.
You May Like: What Causes Ulcers In Your Stomach
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis: Care Plan 2 Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Related To Altered Absorption Of Nutrients Secondary To Ulcerative Colitis
Evidenced by:
- Loss of appetite
Desired Outcome
The patient will be able to achieve weight within his/her normal BMI range, demonstrating healthy eating patterns and choices.
| Intervention | Rationale |
| Explore the patients daily nutritional intake and food habits | To create a baseline of the patients nutritional status and preferences. |
| Create a daily weight chart and a food and fluid chart. Discuss the short-term and long-term nutrition and weight goals related to Ulcerative colitis with the patient. | To effectively monitor the patients daily nutritional intake and progress in weight goals. |
| Help the patient to select appropriate dietary choices to reduce the intake of milk products, caffeinated drinks, alcohol, and high fiber, high-fat foods. | To relieve abdominal pain and cramping, alleviate diarrhea, and healthy food habits. Caffeine is a stimulant of gastric acid production, which can worsen the condition. |
| Refer the patient to the dietitian. | To provide more specialized care for the patient in terms of nutrition and diet in relation to newly diagnosed Ulcerative colitis. |
| Start the patient on a nothing by mouth status and gradually progress to clear liquids, followed by a bland and low residue diet. The patient can then have a low-fat, low-fiber diet on a long-term basis. | Nothing by mouth status can help rest the bowel by decreasing peristalsis. Gradual progression from NBM up to low fat and low fiber diet can help manage the symptoms of Ulcerative colitis. |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Conditions Require Long
Both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are conditions that fall under the umbrella term of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and both require management, and sometimes treatment, for a lifetime. However, with proper care from a facility that specializes in these diseases, you can expect to have a good quality of life. The University of Michigan Inflammatory Bowel Disease program is dedicated to the comprehensive medical and surgical treatment of adult patients with Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Our dedicated inflammatory bowel disease specialists exclusively treat IBD.
What you should know about Crohns and ulcerative colitis:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease is an umbrella term that Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis fall under.
- Crohnâs disease and colitis are easily confused because both have similar symptoms and treatments, but also distinct differences. With a series of tests, your doctor can usually tell ulcerative colitis from Crohns disease however, in some cases the two diseases cant be distinguished from each other.
- The diseases affect men and women about equally.
- While the diseases can occur at any age, they often start between the ages of 15 and 25 and last a lifetime.
- Crohns disease is more common in people with a family history of the disease.
- Ulcerative colitis affects about 600,000 people in the U.S, while Crohns disease affects about 700,000 people.
You May Like: How To Remove Ulcers In Stomach
More Than 200 Genes Identified
While no single underlying cause for IBD has been identified, genetics certainly play a role.
Jeffrey C. Barrett, Ph.D. who is a senior group leader from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in Cambridge in the United Kingdom explains in an article published in the Journal of Autoimmunity that identical twins had nearly 10 times the rate of Crohns disease and nearly four times the rate of ulcerative colitis as non-identical twins.
This support the importance of genetics in IBD risk, he says. But it is not straightforward.
More than variations in the DNA code have now been linked to IBD, and this number is continuing to rise as molecular biology technology is becoming ever more sophisticated.
What are all these genetic data telling us about IBD?
Certain biological processes or pathways keep on cropping up. These include genes involved in the innate immune response including some genes responsible for keeping the lining of our gut intact as well as those involved in the activation and regulation of the adaptive immune response.
Perhaps these findings come as no surprise the classic hallmark of IBD is a dysregulated immune response. However, without detailed knowledge of how these pathways are disrupted, treatments will mostly focus on symptoms, rather than the underlying causes of the condition.
Yet genetics can only explain a proportion of the risk associated with developing IBD.
article in The Lancet thathighlights how IBD rates have evolved across the globe.
Nursing Care Plans For Ulcerative Colitis: Care Plan 1 Diagnosis: Diarrhea Related To Inflammation Of The Bowel
Evidenced by:
- Loose, watery stools, abdominal cramping, and pain
- Increased urgency to defecate
The patient will be able to return to more normal stool consistency and frequency.
Nursing Care Plans for Ulcerative Colitis
As you continue reading remember that our top and qualified writers are here to help with any of your assignment. All you need to do is place an order with us.
Also Check: What R The Symptoms Of A Stomach Ulcer
Communicating With The Patient With Ibd
Nurses need to develop an empathetic and active listening role, and be able to provide essential IBD-related information and holistic support . Nurses have a role in facilitating communication between the MDT and the patient, enabling shared decision-making .
Verbal and non-verbal communication is vital in nursing it helps meet patients needs, and enables provision of support, advice, compassion, caring and empathy that is highly valued by patients.46,71,72 Virtual contact with IBD Nurses via telephone and email clinics is recommended, enabling a more flexible and patient-focused approach to management.73 Age-appropriate support should be offered by those who are best placed to meet the needs of patients and their family members or carers.74
In any chronic illness in which the individual will have an ongoing relationship with health-care professionals, communication facilitates rapport and trust.75 The resulting therapeutic nursepatient relationship can encourage the patient to have an active rather than passive role in their care, and to recognize their expertise about their own illness.7678
How Is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed
There is no single test to diagnose ulcerative colitis, so your childs doctor will first rule out other likely causes of symptoms. In addition to a standard physical exam and discussion of symptoms and family history, a combination of tests and procedures will be used to confirm a diagnosis. Those may include laboratory tests of blood and stool .
Other procedures include:
- Colonoscopy:Thedoctor uses a small camera mounted to the end of a lighted tube to examine the interior of the colon. This is done when your child is asleep under general anesthesia.
- Sigmoidoscopy: This is similar to a colonoscopy, but the physician only examines the rectum and the lower colon.
- Capsule endoscopy: The patient swallows a capsule that has a camera in it. The capsule travels through the small intestine, taking pictures that are transmitted to a receiver belt. The camera is expelled through a bowel movement and does not need to be retrieved.
- Imaging: The patient drinks a contrast dye and has an X-ray, Computed Tomography Enterography , or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Enterography.
Recommended Reading: How To Reverse Ulcerative Colitis
Also Check: Natural Remedies For Mouth Ulcers