Can Celiac Disease Be Confused With Ulcerative Colitis
While celiac disease and ulcerative colitis are both diseases of the digestive system that are associated with abdominal discomfort, they present with symptoms that would differentiate them. The presence of bloody diarrhea points to celiac disease. The presence of symptoms beyond the digestive tract, for example, muscle cramps, joint pains, and tingling in the lower extremities, suggests ulcerative colitis as opposed to celiac disease.
Symptoms Similar In Celiac Gluten Sensitivity And Ibd
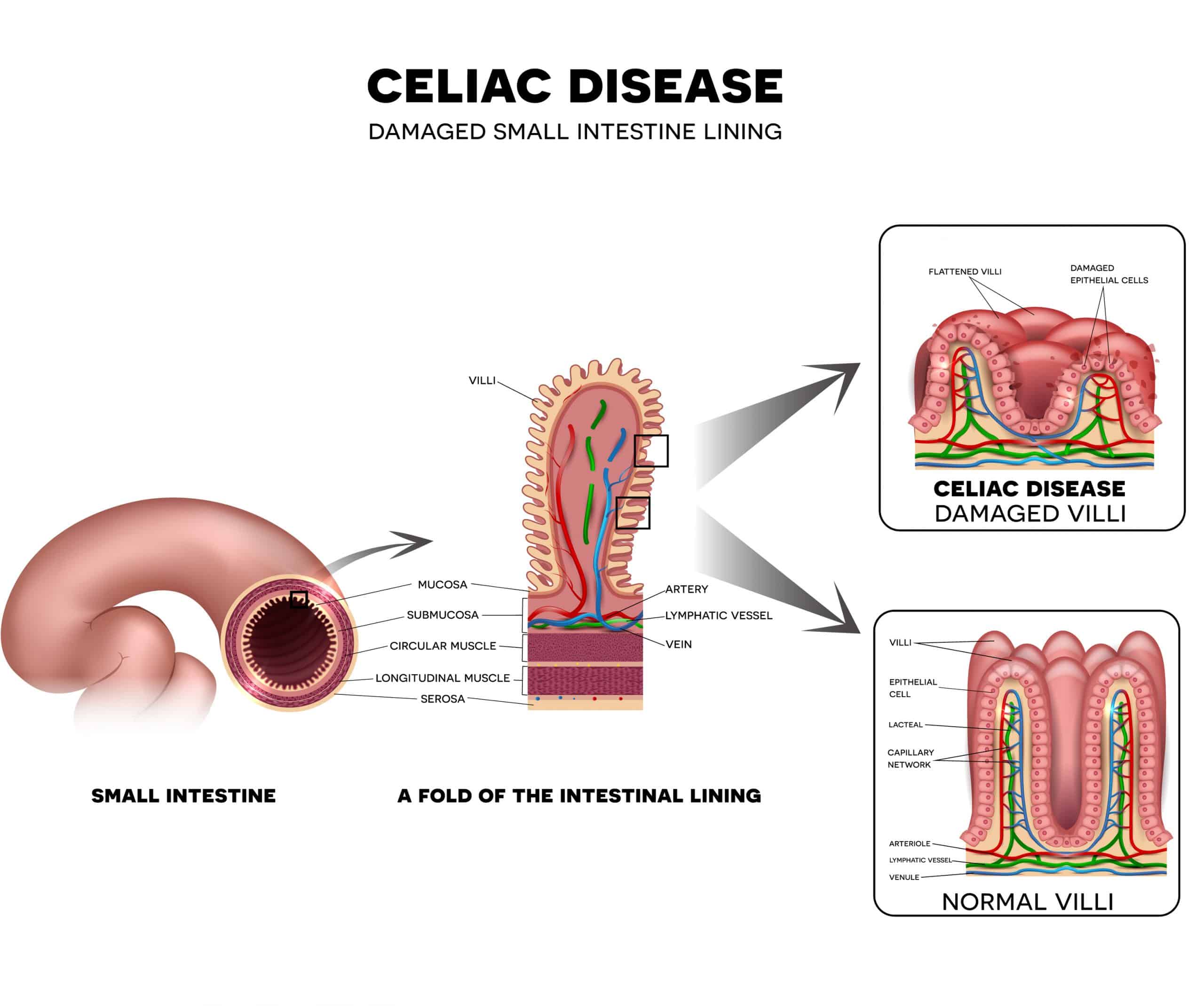
Celiac disease occurs when your body mistakes the gluten protein in wheat, barley, and rye for a foreign invader, triggering your immune system to attack your small intestine. Symptoms of celiac disease can vary widely , but many people with celiac suffer from diarrhea or constipation, stomach pain, fatigue, and anemia.
Symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity can mimic those of celiac diseaseboth conditions include similar types of digestive issues. Those with gluten sensitivity, though, seem to suffer from more headaches and other neurological symptoms , such as nerve damage that causes a feeling of “pins and needles” in the arms and legs, than those with celiac disease.
Finally, symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease differ depending on which specific condition you have . Both Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis can cause abdominal pain, cramping, severe diarrhea, and bloat.
Diseases Of The Digestive Tract With Different Causes
Your digestive tract must maintain a delicate balance. One that allows you to absorb nutrients from the outside world while simultaneously defending you against harmful microbes that sneak in alongside those nutrients.
To balance these two divergent needs, the thin lining that makes up the innermost part of your digestive tract is heavily guarded with lymphoid tissue and immune cells. This is meant to protect you, but in inflammatory bowel conditions, the immune cells and tissue lining your gut become unnecessarily activated creating inflammation without infection.
Pinpointing the exact cause of this inflammation can sometimes be tricky considering that Crohns disease, ulcerative colitis, and celiac disease can all have nearly identical symptoms. Lets explore exactly what these symptoms can be.1
Read Also: Can You Get Ulcers In Your Colon
Center For Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease And Celiac Disease At Stanford Medicine Childrens Health
At Stanford Medicine Childrens Health, we are pleased to provide children and young adults with the very latest solutions for a wide variety of digestive inflammatory diseases. Weve brought together tremendous minds and promising innovations to advance your childs care by providing access to unique programs and active research projects that transform ideas into treatments for excellent outcomes. We understand how worrisome and all-consuming your childs health can be, and we are driven to improve their health so they can live their best life.
To this end, we take a multidisciplinary, whole-child approach that ensures we care for every aspect of your childs health and wellness. Our has physicians who subspecialize in , , , and , along with rarer digestive inflammatory diseases. Our nationally renowned gastroenterologists, pediatric IBD surgeons, and integrative medicine GI doctors are supported by specialized dietitians, psychologists, nurse practitioners, social workers, pharmacists, and clinical researchers to provide your child with well-rounded, informed care.
Telling The Difference Between Conditions
Obviously, there’s considerable overlap between the symptoms of celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and inflammatory bowel disease, and that can make getting an accurate diagnosis somewhat challenging.
Healthcare providers use blood tests to screen for celiac disease , and confirm the diagnosis with an endoscopy and biopsy to look directly at the lining of your small intestine to see if it’s damaged.
To diagnose Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, your healthcare provider likely will perform a colonoscopy and/or an endoscopy to look for specific signs, which are different from those of celiac disease. There’s no one blood test for inflammatory bowel disease, although more general blood testssuch as one to screen for anemiamay provide some information.
Finally, there’s no accepted medical test for non-celiac gluten sensitivity . The only way to know if you have it is to follow the gluten-free diet strictly and see if you feel better. But even that’s not definitive: you may feel better because you’ve reduced or eliminated junk food from your diet along with the gluten, for example, or just the idea that you’re doing something positive for your health may help lessen your symptoms. Still, research shows that some people do, indeed, seem to react to gluten grains with symptoms that are similar to those of celiac disease, even though those people definitely don’t have celiac disease.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Heal An Ulcer
Are You Struggling With Crohns Disease Ulcerative Colitis Or Celiac Disease
Are you or a loved one struggling with an inflammatory bowel condition? If so, the good news is, youre not at the mercy of your diagnosis. While we may not be able to cure these conditions, you have so much power over your own health. I cant overemphasize the importance and influence your diet, supplements, and lifestyle factors can have on your inflammation levels and symptoms.
So if youre ready to take your power and health back from one of these inflammatory bowel conditions, I recommend starting with the steps outlined in this article and seeking out the guidance of an experienced Integrative and Functional Medicine Practitioner. Theyll help you identify the root cause of your condition and come up with a personalized plan of action to begin healing.
And if youre hungry for more practical and research-backed tips on optimizing your health, you can head over to my blog and catch up on hundreds of articles that simplify healthy living.
Diets That May Relieve Ibd Symptoms
Scientists at Kings College London have found that a diet low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols carbohydrates can improve some gut symptoms for people living with IBD.
The low FODMAP diet is helpful for symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea, said Dr. Shannon Chang, assistant professor of medicine and gastroenterologist at NYU Langones Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center.
She explained other diets have been tried to manage IBD symptoms, like the:
shown to be more effective than the other.
No diet has reigned supreme in controlling symptoms, and certainly no diet has been shown to be effective in controlling inflammatory bowel disease and the inflammation associated with it, emphasized Chang.
You May Like: Yea Sacc For Horses With Ulcers
Stanford Childrens Health Launches Center For Inflammatory Bowel Disease Celiac Disease
A $70 million donation will enable researchers to offer more treatments to Stanford Children’s Health patients suffering from inflammatory bowel disease or celiac disease.
Michael Rosen, director of the new Stanford Children’s Health Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Celiac Disease, with his lab manager, Yanli Qiao.Stanford Childrens Health
Stanford Childrens Health has launched its new Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Celiac Disease to increase access to care and advance research to improve outcomes for children, thanks to a $70 million gift by an anonymous donor.
Children with IBD and celiac disease require comprehensive and dedicated care to achieve the best outcome and control of their disease. The new center will bring together expert clinicians, researchers, IBD and celiac disease nurses, dietitians, psychologists, and social workers to build a world-class program for state-of-the-art clinical care.
We aim to build the nations destination center for innovation in pediatric IBD and celiac disease care, as well as a major research hub for these conditions, said Michael Rosen, MD, director of the new center. Rosen, a pediatric gastroenterologist at Stanford Childrens Health, is also the Stanford University Endowed Professor for Pediatric IBD and Celiac Disease.
Celiac Disease And Ibd Show Strong Bidirectional Link
New research shows a strong bidirectional relationship between celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease that may hold clues for patient diagnoses and care.
After the first year postdiagnosis, researchers found that patients with celiac disease had an almost 4-fold increased risk of IBD, and patients with IBD had more than a 5-fold increased risk of celiac disease.
The risk of IBD in celiac disease showed a distinct increase even 10 years after the first diagnosis, the authors write. During 20 years of follow-up, 2.5% of celiac disease patients developed incident IBD, and 1.3% of IBD patients developed celiac disease.
The findings were in TheAmerican Journal of Gastroenterology.
Don’t Miss: Foods That Make Ulcerative Colitis Worse
Specialized Diets To Manage Crohns And Ulcerative Colitis
In some cases, following a strict and specific diet protocol can do wonders for managing and reversing the massive inflammation seen in these inflammatory bowel conditions. In particular, two specific diets that have been found to be especially effective components of treatment are:
The Specific Carbohydrate Diet
This diet restricts specific carbohydrates that encourage the overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the gut. These harmful bacteria and their byproducts trigger and amplify inflammation in your gut. The SCD diet eliminates carbohydrates that contain two or more linked sugar molecules such as:
- All grains including wheat, rice, corn, millet, quinoa, etc.
- Any processed meats or meats containing additives
- Processed sugar, artificial sweeteners and sugar alcohols
- All processed foods
Eliminating complex carbs can yield impressive and significant results in many Crohns and ulcerative colitis patients.
The Elemental Diet
This diet allows your digestive tract to take a break without sacrificing your nutritional intake by consuming nutritionally complete liquids that are pre-digested. These premade formulas contain all of the carbs, fat, proteins, and nutrients your body needs in a super digestible form that doesnt require your digestive tract to break them down essentially allowing your gut to focus entirely on healing and repairing inflammation.
Ibd And Gluten Sensitivity May Be More Commonly Related
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity may be more likely than celiac disease in people with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, several studies show.
For example, a group of healthcare providers in Italy and the United Kingdom surveyed their inflammatory bowel disease patients and found that 28% of them believed they had gluten sensitivity , meaning their symptoms seemed to worsen when they ate gluten-containing foods. Only 6% of these people were following the gluten-free diet at the time of the survey, though. The researchers also found that so-called “self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity” was associated with more severe Crohn’s disease, and they called for additional studies to determine whether the gluten-free diet would help in these cases.
In a 2014 report, clinicians in Japan screened 172 people who had inflammatory bowel disease for antibodies to gluten via blood tests and compared those people to 190 control subjects. They found that 13% of those with inflammatory bowel disease also tested positive for anti-gluten antibodies. However, only three of those people carried one of the two main celiac disease genes, and none of them had damage to their small intestines, so none of them actually had celiac disease.
Don’t Miss: Is Kimchi Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Study Design And Cohort
The findings, published in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, are from a retrospective analysis of information in an electronic health record database that reflects experience in more than 72 million patients treated in 26 American health care systems. Of the individuals represented in the database, nearly 144,000 had celiac disease , nearly 200,000 had ulcerative colitis , and nearly 231,000 had Crohn disease .
For the study, the authors selected a cohort of patients diagnosed with celiac disease and IBD between 1999 and 2020. They used a multivariate model to compare patients with IBD to patients without IBD, and to compare patients with celiac disease to those without celiac disease.
Data about the patients that were extracted from the database included age, sex, and race, plus information on potential confounding factors such as tobacco smoking and use of corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biological agents, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Going Gluten Free With Ibd
If you dont have celiac disease but suspect gluten could be triggering your IBD symptoms, theres no harm in trying a gluten-free diet to see if it helps.
But youll need to take careful steps to make sure youre avoiding gluten completely for a set amount of time to truly understand whether it triggers your symptoms, Singh explains. Itll likely take at least two weeks of eating gluten free to notice any potential benefits, and Many will need a longer period like four to six weeks, he says.
Before cutting out gluten, get the green light from your gastroenterologist and plan to see a dietitian who specializes in IBD, Singh recommends. They can help you identify the sources of gluten in your diet and read food labels to find less obvious sources of gluten, such as packaged sauces and salad dressings. They can also help you fill any nutritional gaps in your diet that might come from cutting out gluten-containing foods, such as wheat-based pasta or bread.
In some cases, those with a mild gluten intolerance are eventually able to reintroduce gluten into their diets in small amounts without a problem. It depends how sensitive you are, Singh says. Oftentimes people might be able to tolerate a little bit of something, but when they cross the threshold of the amount they can take, they get symptomatic.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Ulcers In Your Stomach
Treatment For Celiac Disease
Treatment for celiac disease is far more simple.
Gluten-free diet: This is the centerpiece of treatment for celiac disease. The doctor will tell you to start eating this way before you leave the office. Most people with celiac have to avoid these foods for the rest of their lives:
Once you stop eating gluten, the inflammation in your gut should get better. If your small intestine is severely damaged, you may need steroids.
The Three Types Of Celiac Disease Are Classified According To Their Symptoms:
- Classic celiac disease presents with bouts of diarrhea between constipation, bloating, gas, anemia, a severe blistering skin rash and sores in the mouth, inflammation of the liver, muscle cramps and joint pain, and a tingling sensation in the legs. Long-term health complications include malnutrition, osteoporosis due to problems absorbing calcium and Vitamin D, infertility, and rarely, cancer of the intestine.
- Non-classic celiac disease, which according to the Cleveland Clinic is becoming the most common, presents only with anemia.
- Asymptomatic celiac disease presents with no symptoms at all.
Also Check: Foods To Avoid With An Ulcer Nhs
The Difference Between Celiac Disease And Ulcerative Colitis
Celiac disease and ulcerative colitis are two very different conditions. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the digestive system, while ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Heres a closer look at the key differences between these two conditions:
Celiac disease is caused by an intolerance to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with celiac disease eats gluten, their immune system reacts by damaging the lining of the small intestine. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
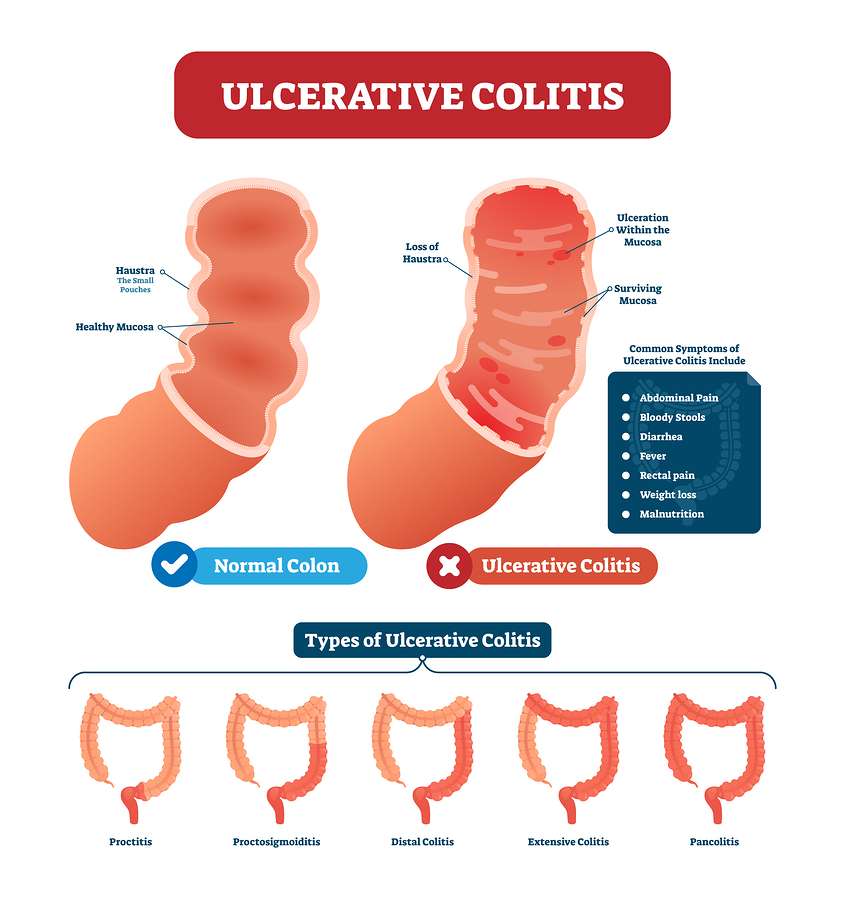
Ulcerative colitis, on the other hand, is a chronic inflammation of the large intestine . The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system. Symptoms of ulcerative colitis include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
While both celiac disease and ulcerative colitis can be serious conditions, they are treated differently. There is no cure for celiac disease, but the condition can be managed by following a gluten-free diet. Ulcerative colitis, on the other
May Have Similar Symptoms
Because all three of these inflammatory bowel diseases involve inflammation of your digestive tract, Crohns disease symptoms, ulcerative colitis symptoms, and celiac disease symptoms have a significant amount of overlap and include:2,3
- Diarrhea and/or constipation
- Canker sores in the mouth
While these inflammatory bowel conditions may be hard to differentiate at first glance, there are actually some important and distinct differences between them.
Read Also: Is Coconut Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Where To Find Help With All 3
Should you find yourself experiencing any of the symptoms laid out above, its imperative that you speak with a gastrointestinal specialist as soon as you can. At the Colorectal Clinic of Tampa Bay, your physician will do a deep dive with you on all of your symptoms, your daily habits, and your overall lifestyle to best understand which condition is truly to blame. We are well versed in treating Ulcerative Colitis, Crohns Disease, and Celiac Disease, having helped many patients throughout the Bay Area find relief. Schedule your first appointment with us now!
Infectious Triggers To Inflammatory Bowel Conditions
There are a few distinct ways that a shift in your gut microbiome can contribute to the widespread inflammation seen in both Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. These include:
- Dysbiosis: This occurs when there is a modification in the composition of microbes that reside in your gut with an imbalance between between beneficial and harmful bacteria
- Excessive bacterial translocation: This is caused by a disruption in the function of your intestinal barrier allowing gut bacteria to mistakenly migrate through the gut wall and inflame surrounding tissues.
- Persistence of a pathogen: Invading bacteria and viruses can adhere to epithelial cells where they survive and proliferate while using your own cells as protection against your immune system. These persistent pathogens induce inflammation and disrupt the function of your intestinal lining that acts as a selective barrier.
Oftentimes, the inflammation seen in Crohns and ulcerative colitis can be caused by a combination of these 3 underlying infectious triggers creating a vicious cycle of inflammation.
Now lets explore our final inflammatory bowel condition celiac disease.
Recommended Reading: Signs A Horse Has Ulcers
Crohns Colitis And Celiac Disease: What Are They Whats The Difference
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two main forms of inflammatory bowel diseases. Celiac disease is a disease in which the small intestine is hypersensitive to gluten, leading to difficulty in digesting food. All of these conditions are characterized by inflammation of the digestive tract. Although they share many similarities, there are key differences between the three diseases. Well review those differences concerning symptoms, causes, treatment and prevalence.Crohns DiseaseCrohns disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that impacts the gastrointestinal tract, and can cause inflammation, ulcers and bleeding. It is one of a group of chronic diseases often called inflammatory bowel disease . What separates Crohns disease from other forms of IBD is that it most commonly affects the end of the small bowel and the beginning of the colon.
The disease causes your immune system to attack healthy cells and produce inflammation. The cause of this is unknown, though doctors are currently looking into both genetic and environmental factors that may signal the body to begin an immune response, without a clear stop signal.
Crohns disease is commonly treated with dietary restrictions such as avoiding dairy products, seasoning and high-fiber foods medication designed to suppress the immune system and surgery. The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation notes that 70 percent of people with the disease eventually require surgery.Common Symptoms of Crohns Disease: